当前位置:网站首页>Classes and objects (I) detailed explanation of this pointer
Classes and objects (I) detailed explanation of this pointer
2022-07-06 05:41:00 【Less debug every day】
Indexes
The definition of a class
stay C In language , A structure can only define variables , But in C++ The middle structure can not only define variables , You can also define functions , At this point, we call the structure class and use the keyword class Express .
class className
{
// The class body : It consists of member functions and member variables
};
The general composition is shown above
eg
class STu
{
void Print()
{
cout << "printf" << endl;
}
int a;
int b;
int c;
};
At the same time, the class name can be directly typed STu a; STu b;
notes : If the definitions of function declarations are all in the class , Then this function will be regarded by the compiler as Inline function Handle , Therefore, it is generally recommended to separate statements and definitions .
Access qualifier
Access qualifier , seeing the name of a thing one thinks of its function , It is to limit whether the variables or functions in the class can be directly accessed outside the class , Here are three access qualifiers and their functions .
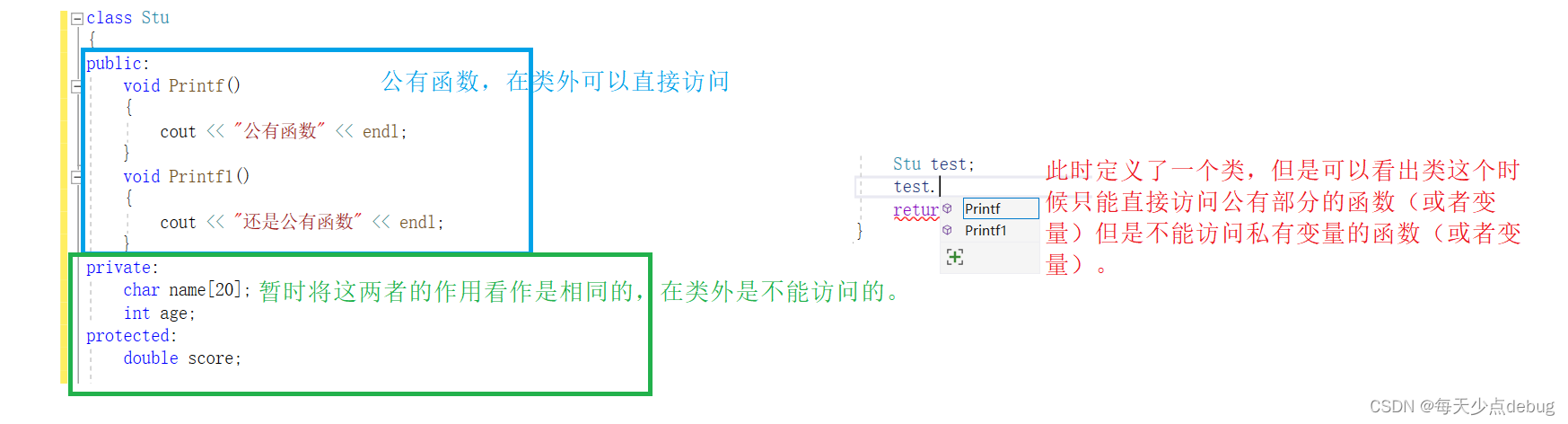
Be careful : Access qualifiers are only useful at compile time , When the data is mapped to memory , There is no difference in access qualifiers
Be careful public The default access is private ,struct The default access permission is public ( because struct To be compatible with C)
Class encapsulation
encapsulation : Organically combine data and methods of operating data , Hide object properties and implementation details , Only expose interfaces to interact with objects .
Why package ?
stay C Language time , When we simulate the implementation of stack area ,
struct Stack
{
int* a;
int top;
int capacity;
};
struct Stack q;
When we need the elements at the top of the stack , Sometimes we just write q.a[top] perhaps q.a[top-1], It depends on how the writer initializes top Initialize to -1 still 0, In this case, it is very inconvenient for users , And once there are more functions , Each has its own implementation and representation , therefore C Language is very free , Because its data and method are separated , It mainly depends on the quality of programmers , To avoid that ,C++ Combine data and methods directly , Public interface , The function you want users to use is set to public, Functions or variables that you don't want users to see are set to private .
eg:( Stack )
class Stack
{
public:
void Push(){
}// Insert pop-up we want users to use this function of the stack, so we set it to public , Users can access directly outside the class
void Pop(){
}
int Top(){
}
private:
void Check_capacity() {
};// Check whether it needs to be expanded. We don't want users to use , So set it as private
int* a;// If we don't want users to use member variables, we also set them to private
int _top;
int _capacity;
};
So encapsulation is essentially a kind of Management , We directly set up a public interface for users to use , Settings that you don't want users to use are private , Make the user use the unique interface .
Scope of class
Class defines a new scope , All members of a class are in the scope of the class . Define members outside the class , Need to use :: The scope resolver indicates which class domain the member belongs to 
The above mentioned , Function in class , It is generally recommended to separate declarations from definitions , When defining, we need to add in front of it which class domain this function belongs to .
eg
void Stu::Print()
{
}
Class instantiation
The process of creating objects with class types , Called class instantiation
- Class is just a model thing , Defines which members of the class , Defining a class does not allocate the actual memory space to store it
- A class can instantiate multiple objects , Instantiated object Take up actual physical space , Store class member variables
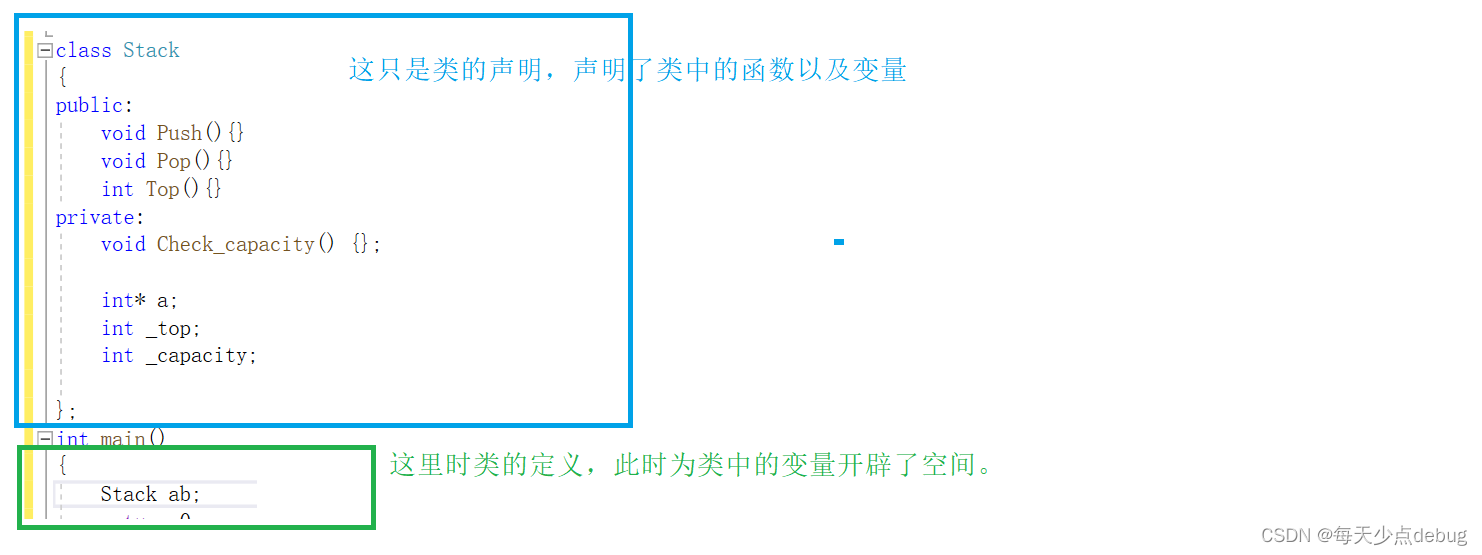
understand The difference between declaration and definition opens up space .
The above mentioned opens up space for variables , What about functions ? See the following how to calculate the size of a class
Class size calculation

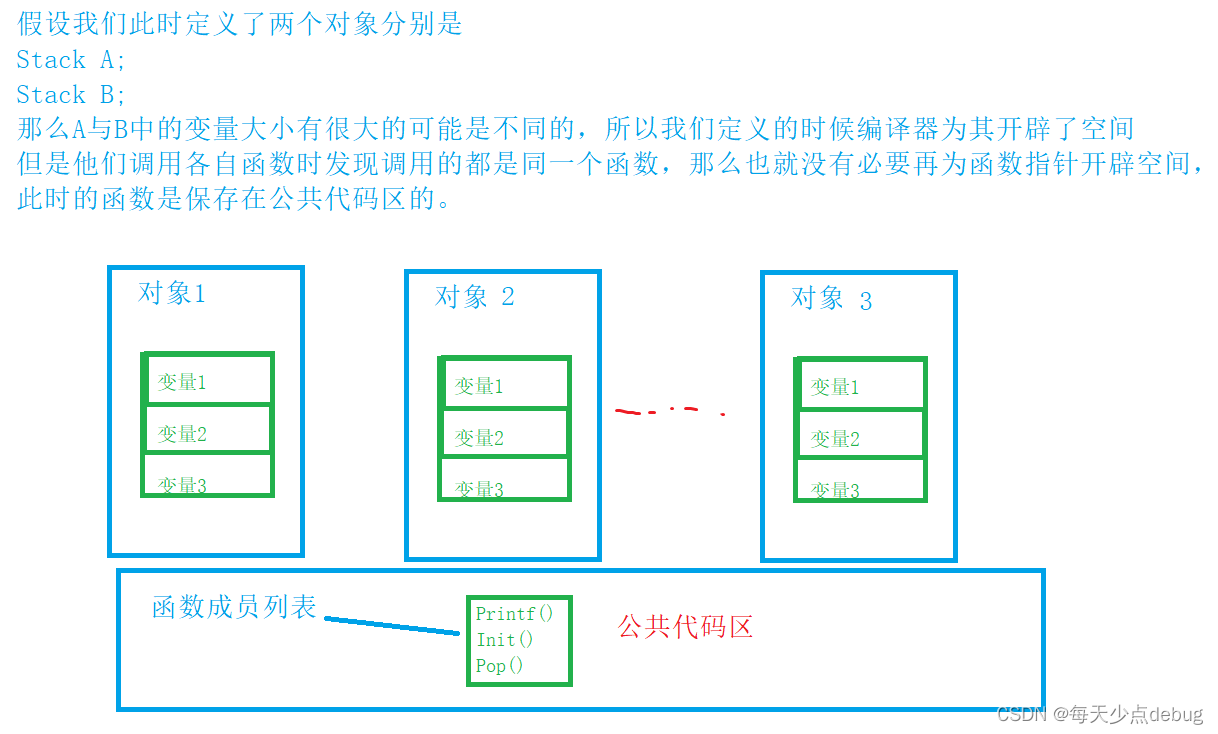
put questions to
Suppose the class is like this :class A3{};
At this time, the class has no member variables , At this point, the compiler will give the class a byte placeholder , Indicates that it existed .
This The pointer
1,This Introduction of pointer
First define a date class
class Date
{
public:
void Init(int year, int month, int day)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Date A;
Date B;
A.Init(2022, 7, 5);
A.Print();
B.Init(2022, 7, 4);
B.Print();
return 0;
}
As mentioned above , The functions called by different classes of objects are the same function , But the member variables in class objects are different , How does the function know A The member variable used when calling the function is at this time A The variable of ?
C++ Introduced in This Pointers solve this problem .
namely
C++ The compiler gives each “ Non static member functions “ Added a hidden pointer parameter
Count , Let the pointer point to the current object ( The object that the function calls at run time ), Operation of all member variables in the function body , All through the
Pointer to access . But all operations are transparent to users , That is, the user does not need to deliver , Compiler autocompletes .
eg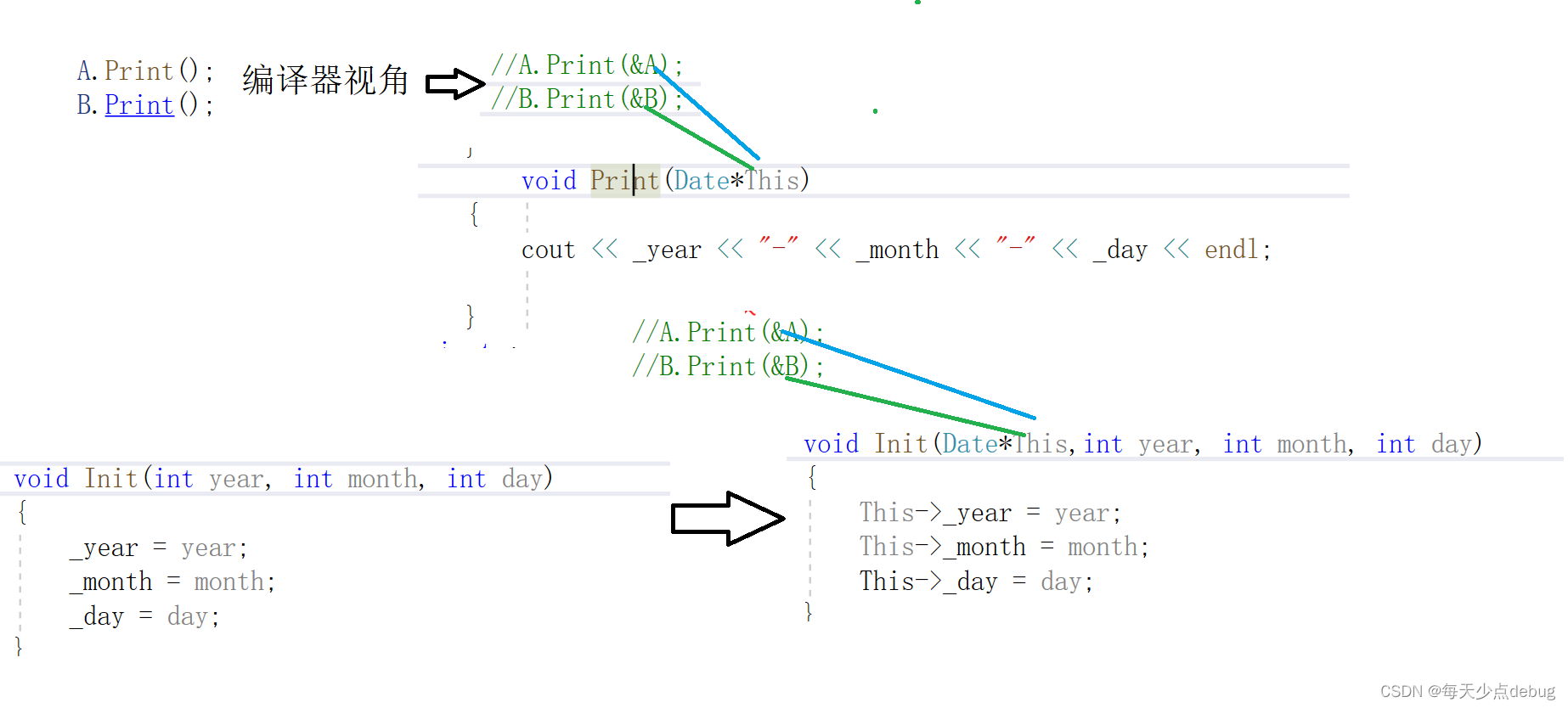
That is, the compiler will automatically pass the address of the object itself to the function as an implicit parameter , Even if we
You didn't write This Pointer compiler also adds this Of , It is an implicit parameter of a non static member function , Visits to members were made through this Conduct .
2,This Characteristics
1.this The type of pointer : type const
namely Date*const this namely this The pointer itself cannot be changed , But the object it points to can be changed
2, Only in “ Member functions ” Internal use of
Global function 、 Static functions cannot be used this. In fact, the first parameter of the member function in the class is (Dateconst this) We can also see from the above example
3,this Pointer is essentially a parameter of a member function , When an object calls a member function , Pass the object address as an argument to this Shape parameter . So objects don't store this The pointer is thus visible ,this Construct... Before the start of the member function , Clear after the end of the member function . however this Pointers themselves are somewhat different from static functions , Compilers usually do this Pointer to do some optimization , Generally, the compiler passes through ecx Register auto transfer , No need for users
Pass therefore ,this Pointer transfer efficiency is relatively high
Interview questions :
1,this Where the pointer is stored
The above story ,this A pointer is actually a formal parameter of a member function , that this Pointers may be stored in the stack ,
2, Some compilers use register optimization , all this Pointers may also be stored in registers
Is there any mistake in the following procedure ?
class A
{
public:
void PrintA()
{
cout << _a << endl;
}
void Show()
{
cout << "Show()" << endl;
}
private:
int _a;
};
int main()
{
A* p = nullptr;
p->PrintA();
p->Show();
}
The above program can work normally , because show Functions are placed in the public code area , Is not a variable in a class object , although p Is a null pointer , And the message is p, then Show Function this Pointer acceptance , You can still call functions , There is no dereference of null pointers , So there's no mistake , It's going to work
But if you say main If you change the content in the function, an error will be reported 
It's not easy to create , I hope you can give me more support , Crab



边栏推荐
- 【torch】|torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_
- First acquaintance with CDN
- Node 之 nvm 下载、安装、使用,以及node 、nrm 的相关使用
- Easy to understand IIC protocol explanation
- [SQL Server Express Way] - authentification et création et gestion de comptes utilisateurs
- 自建DNS服务器,客户端打开网页慢,解决办法
- 03. Login of development blog project
- 注释、接续、转义等符号
- Installation de la Bibliothèque de processus PDK - csmc
- 02. 开发博客项目之数据存储
猜你喜欢
Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2) Editorial(A-B)

巨杉数据库再次亮相金交会,共建数字经济新时代
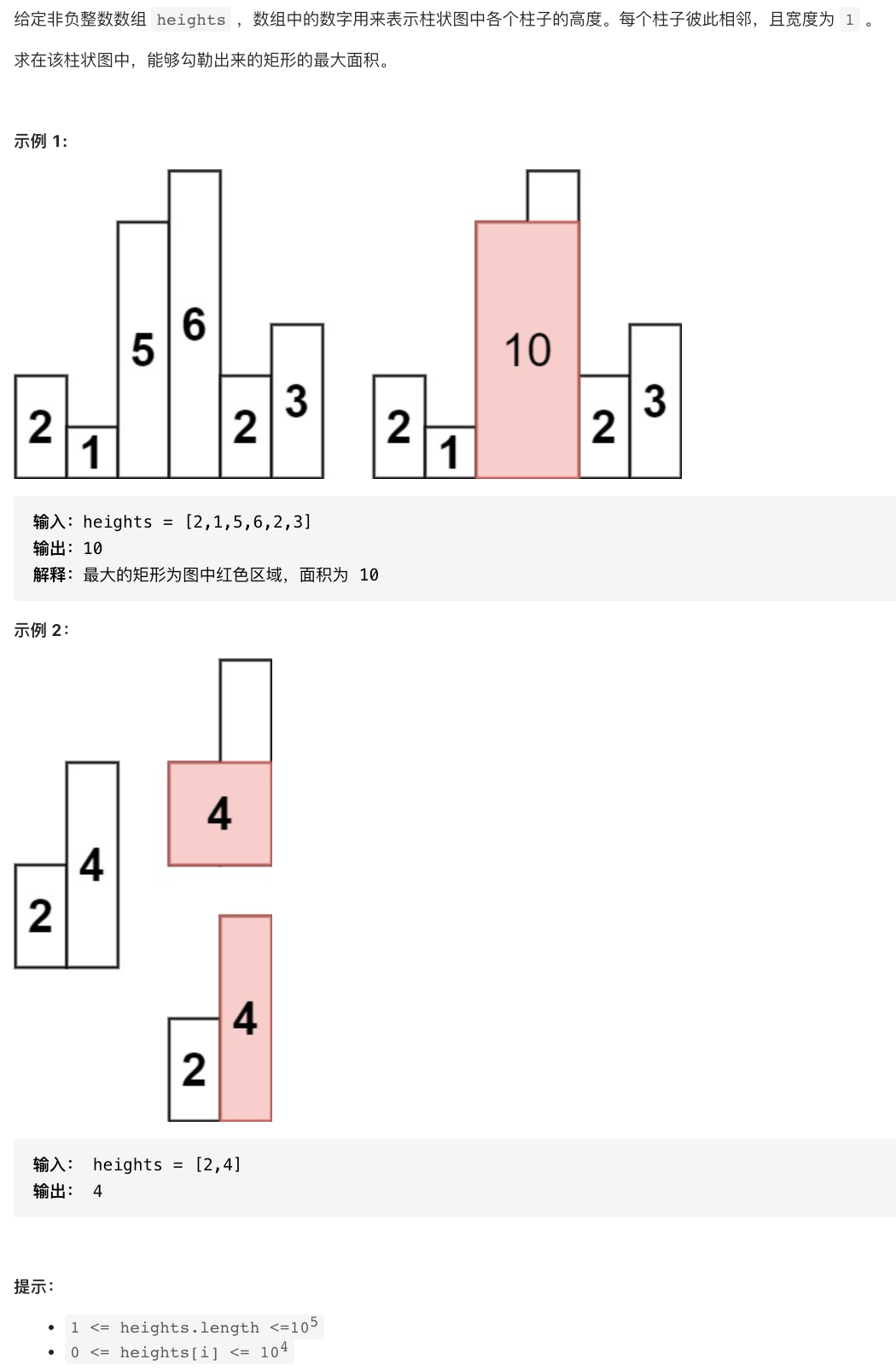
剑指 Offer II 039. 直方图最大矩形面积

26file filter anonymous inner class and lambda optimization
B站刘二大人-数据集及数据加载 Lecture 8
自建DNS服务器,客户端打开网页慢,解决办法
Summary of deep learning tuning tricks

What is independent IP and how about independent IP host?

28io stream, byte output stream writes multiple bytes
![[Tang Laoshi] C -- encapsulation: classes and objects](/img/4e/30d2d4652ea2d4cd5fa7cbbb795863.jpg)
[Tang Laoshi] C -- encapsulation: classes and objects
随机推荐
应用安全系列之三十七:日志注入
Summary of deep learning tuning tricks
Jushan database appears again in the gold fair to jointly build a new era of digital economy
Vulhub vulnerability recurrence 67_ Supervisor
YYGH-11-定时统计
28io stream, byte output stream writes multiple bytes
Application Security Series 37: log injection
B站刘二大人-线性回归及梯度下降
[string] palindrome string of codeup
Zoom and pan image in Photoshop 2022
Pytorch代码注意的细节,容易敲错的地方
The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
Redis message queue
ArcGIS application foundation 4 thematic map making
Vulhub vulnerability recurrence 73_ Webmin
Pix2pix: image to image conversion using conditional countermeasure networks
29io stream, byte output stream continue write line feed
Promise summary
【经验】UltralSO制作启动盘时报错:磁盘/映像容量太小
Graduation design game mall