当前位置:网站首页>Reading notes of "micro service design" (Part 2)
Reading notes of "micro service design" (Part 2)
2022-07-03 15:30:00 【Nie Bingyu】
Chapter vii. : test
1. Test type
- Business oriented
- Technology oriented
- Evaluate the product
- Support team

trend : Give up large-scale manual testing , Using automation as much as possible is a trend in the industry in recent years .
2. Test range
“ Test pyramids ” Model : Divide automated tests into unit tests 、 There are three layers of service testing and user interface testing .
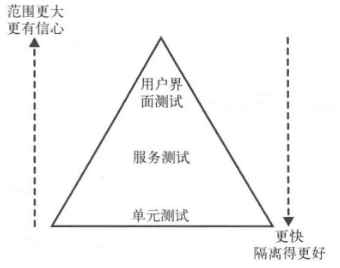
2.1 unit testing
Unit tests usually test only one function and method call .
TDD: Test-driven development
adopt TDD (Test-Driven Design, Test-driven development ) Written tests fall into this category , Tests produced by attribute based testing techniques also fall into this category . In unit test , We will not start the service , And the use of external files and network connections is also very limited . Usually you need a lot of unit tests . If done reasonably , They will run very, very fast , Run thousands of such tests on modern hardware environments , Maybe not even a minute .Unit test purpose :
Can quickly give feedback on whether the function is normal . Unit testing is very important for code refactoring , If you make a mistake carelessly , These small-scale tests can quickly make a reminder , In this way, we can safely adjust the code at any time .
2.2 Service Testing
Service testing bypasses the user interface 、 Testing directly for services .
Service test scope :
In stand-alone applications , Service testing may only test some classes that provide services for the user interface . For systems with multiple services , A service test only tests the function of one of the individual services .
Service test purpose :
Testing only a single service can improve the isolation of testing , In this way, we can locate and solve problems faster .
2.3 End to end testing
End to end testing will cover the entire system .
The test method :
Such tests usually require opening a browser to operate the graphical user interface (GUI), It is also easy to imitate user interaction such as uploading files .
2.4 Balance
Pyramid model , Test features near the top of the pyramid :
- The larger the test coverage , The more confident we are about the function after being tested
- The feedback cycle will be longer ;
- It is difficult to locate the cause of failure ;
Pyramid model , Test features near the bottom of the pyramid :
- The test is fast , The test cycle is short ;
- Easy to locate the cause of failure ;
- The build time of continuous integration is short ;
- Passing the test does not mean that the whole service can run normally ;
2.5 The proportion
A good rule of thumb is , Down the pyramid , The number of tests on the lower layer is one order of magnitude more than that on the upper layer . If the current trade-off does cause problems for you , Then try to adjust the proportion of different types of automated tests .
3. Implement service testing
Unit testing is relatively simple , The implementation of service testing and end-to-end testing is much more complex .
Service testing only wants to test the function of a single service , In order to isolate other related services , Need a way to pile all external partners .
For every downstream partner , We all need a piling service , Then start them when running service tests ( Or make sure they work properly ). We also need to configure the tested service , Connect these piling services during the test . next , In order to mimic the real service , We need to configure the piling service to send back the response to the request of the tested service .
4. Disadvantages of end-to-end testing
4.1 Fragile testing
With the expansion of the test scope , The more services under test , The probability of failure of the test process itself increases , The more fragile the test will be , The greater the uncertainty .
4.2 Who will write the test
4.2.1 Method 1 : All team members can add tests at will without any understanding of the quality of the test suite .
The problem is :
- Test case explosion ;
- Because the test has no real owner , So their results will be ignored ;
- Everyone doesn't care whether the test passes ;
4.2.2 Method 2 : A dedicated team to write these tests .
The problem is :
- Software developers are moving away from testing code , The feedback cycle time will be longer ;
- The team that wrote the test , It is difficult to understand the details of system operation ;
4.2.3 resolvent
- Share the code rights of the end-to-end test suite , But at the same time, he is jointly responsible for the test suite .
- The team can submit tests to this suite at will , But the team that implements the service must all be responsible for maintaining the health of the suite .
4.3 How long is the test
The scale of test cases is large , Slow operation and vulnerability , The test time is prolonged .
Running tests in parallel can improve the slow problem , But it can't replace to really understand what needs to be tested , And what unnecessary tests can be deleted .
Delete the test , Risks are hard to understand .
The phenomenon : It's rare to see someone who can deal with a wide range of problems in detail 、 High burden of testing for management and maintenance .
5. Submit stack
The feedback cycle of end-to-end testing is too long , The failure repair cycle will also become longer , Reduce the number of end-to-end test passes , This leads to a large number of submissions piling up .
One way to solve this problem is : It is forbidden to submit code after the end-to-end test fails , But considering the long running time of the test suite , This requirement is usually unrealistic .
The more changes you deploy , The higher the risk of release , The more likely we are to destroy some functions . The key to ensuring the frequent release of software is based on such an idea : Publish small-scale changes as often as possible .
6. Scenario test
As services increase , The test suite will become very cheap , The test scenario may even have a Cartesian explosion .
The best way to solve this problem is , Put the focus of testing the whole system on a few core scenarios .
By focusing on a small number of tests , We can alleviate the shortcomings of end-to-end testing , But it can't avoid all the shortcomings .
7. Consumer driven testing
Use the end-to-end testing mentioned earlier , What is the key problem we are trying to solve ? It is trying to ensure that new services are deployed to the production environment , Change will not destroy consumers of new services . There is a way to achieve the same goal without using real consumers , It is CDC (Consumer-Driven Contract, Consumer driven contracts ).
characteristic :
- Defining services ( Or producers ) The expectations of consumers , These expectations will eventually become test code for the producer .
- Use it properly , these CDC Should be a producer CI Part of the assembly line ;
- If these contracts are broken , Producers cannot deploy ;
- Test faster , And more reliable .
The testing of consumer contracts is integrated into the testing pyramid :
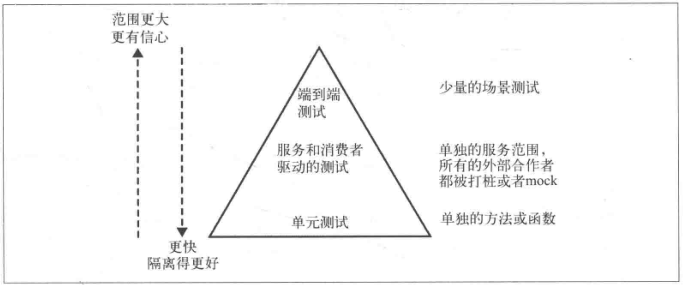
7.1 Testing tools Pact
- Consumer use Ruby DSL To define the expectations of producers ;
- Start a local mock The server , And expect it to run to generate Pact Specification documents ;
8. Test after deployment
You need to test the reason after deployment : Rely only on tests conducted before deployment , The defect rate cannot be reduced to zero .
8.1 Release of canary
Canary release refers to : Divert part of the production flow to the newly deployed system , To verify whether the system performs as expected .
9. Cross functional testing
Nonfunctional requirements , It is a general term for some features of the system , These features cannot be implemented as easily as ordinary features .
10. Performance testing
10.1 Why performance testing is needed :
- Trace the source of delay , After the system is split into smaller microservices , The number of calls across network boundaries has increased significantly , These calls may slow down the speed of system operation ;
- When synchronizing the call chain , Any part of the chain becomes slow , The whole chain will be affected , It will eventually have a significant impact on the overall speed ;
10.2 alert :
Usually, the reason why the performance test is postponed is , At first, there were not enough system resources for testing . I understand this reason , But usually the performance test will be delayed , If it doesn't happen until it goes online , It usually only happens before going online ! Don't fall into the trap of procrastination .
10.3 The test method
- Simulated customers are gradually increasing , Then run together in the given customer scenario ;
- How the invocation delay changes as the load increases , This means that the performance test needs to be run for a period of time ;
- Need a data volume similar to production , And more machines are needed to match the infrastructure ;
- Run a subset every day , Run a larger collection every week . Make sure to run as often as possible ;
- The performance test needs to be carried out simultaneously with the monitoring of system performance , Ideally , You should use the same visualization tools in the performance test environment as in the production environment , In this way, it is easier for us to compare the two .
Chapter viii. : monitor
Microservices will split the system into smaller 、 Fine grained microservices can bring many benefits . However , It also increases the monitoring complexity of the production system . Fine grained system brings new challenges to system monitoring and positioning . resolvent : Monitor small services , Then aggregate to see the whole .
1. Single service , Single server
A host runs a service , Just need yourself , Data to be monitored :CPU、 Memory 、 Server log . Single machine service monitoring is relatively simple . Over time , Load increase , The system needs to be expanded .
2. Single service , Multiple servers
When CPU When the occupancy rate is high , If this problem occurs on all hosts , Then it may be the problem of service ;
But if it only happens on one host , Then it may be the problem of the host itself ;
Except to view the data of all hosts , Also check the data of a single host .
3. Multiple services , Multiple servers
Multiple services cooperate to provide functions for our users , These services run on multiple physical or virtual hosts .
How to work on multiple hosts 、 Reasons for positioning errors in thousands of lines of logs ?
How to determine whether it is a server exception , It is still a systematic problem ?
How to track a wrong call chain among multiple hosts , Find out the cause of this error ?
The answer is , From logs to application metrics , Collect and aggregate as much data as possible into our hands .
4. Indicator tracking of multiple services
Required functionality :
- It is easy to collect indicators from new hosts ;
- You can see the aggregated indicators of the whole system ;
- It can obtain the indicators of a given service instance after aggregation .
5. Service indicators
Indicators can reflect the behavior of the system . Understand the users' use of our services through indicators , Then rely on the index system to deal with them .
6. Association marks
The association ID is used to track the calls triggered in the system .
Suggest : Consider using it as early as possible .
7. cascade
Cascading failures are particularly dangerous , It will make the related services unable to interact , Cause network connection paralysis .
The integration point between monitoring systems is very critical . Every instance of a service should track and display the health status of its downstream Services , From databases to other cooperative services .
This information should be summarized , To get an integrated picture . So as to understand the response time of downstream service invocation , And check for errors .
Chapter nine : Security
1. Authentication and Authorization
Through the authorization mechanism , You can map the subject to the operations he can perform . When a subject passes authentication , Will get information about him , This information can help us decide what we can do .
1.1 Common single sign on implementations
SSO (Single Sign-On, Single sign on ): A common authentication and authorization ;
SAML and OpenID Connect: Occupy a dominant position in the enterprise level field , It also provides authentication and authorization functions ;
1.2 Single sign on gateway
Function of gateway :
- Use the gateway between the service and the external world as a proxy ;
- Centrally handle the behavior of redirected users , And only perform handshake in one place ;
The problem is :
- Locating problems in microservices in isolation becomes more difficult .
- It brings a false sense of security . The concept of defense in depth is from the network boundary , To subnet , To firewall , To host , To the operating system , Then to the bottom hardware , We need the ability to implement security measures in all these areas , Instead of relying on the gateway to handle every step of the security measures .
2. Authentication and authorization between services
2.1 Allow everything within the boundary
Any call to the service within the boundary is trusted by default . Risks of implicit trust model , There is basically no defense against the typical middleman .
2.2 HTTP(S) Basic Authentication
HTTP Basic Authentication , Allow clients to HTTP Send user name and password in the header . The server can verify this information , And confirm whether the client has access to the service .
advantage :
- This is a very easy to understand and widely supported protocol ;
shortcoming :
- HTTP There is a high risk , User name and password are not sent in a secure way .HTTP Basic authentication should usually pass HTTPS communicate ;
- SSL The traffic above cannot be used by the reverse proxy server ( such as Varnish or Squid) The cache ;
- If you use off the shelf SSO programme , Need to bear the risk of repeated behavior .
2.3 Use SAML or OpenID Connect
If you are already using SAML or OpenID Connect As an authentication and authorization scheme , You can also use them in the interaction between services . If you are using a gateway , You can use the same gateway to route all intranet traffic , But if each service handles integration by itself , Then the system should work naturally .
The benefits of doing this :
- You can use the existing infrastructure , And centralize the access control of all services in the central directory server . If you want to avoid middleman attacks , We still need to pass HTTPS To route communications .
shortcoming :
- Need to store credentials securely ( Account name and password );
- To do authentication, you need to write quite tedious code .
2.4 Client certificate
Another way to verify the identity of the client is , Use TLS (Transport Layer Security, Secure transport layer protocol ),TLS yes SSL Successor in client certificate . ad locum , Each client has one installed X.509 certificate , It is used to establish a communication link between the client and the server . The server can verify the authenticity of the client certificate , Provide a strong guarantee for the effectiveness of the client .
characteristic :
- The work of certificate management is more onerous than using only server-side certificates ;
- Problems are not easy to diagnose ;
- The difficulty of revoking and reissuing certificates ;
Suggest :
- Pay special attention to the sensitivity of the data sent , Or unable to control the network used to send data , Before considering using this technology ;
2.5 API secret key
API The key allows the service to identify who is calling , Then limit what they can do . Restrictions are usually not limited to access to specific resources , It can also be extended to a speed limit similar to that for a specific caller , To protect the quality of others' service calls .
3. Security of static data
Among many famous security vulnerabilities , The static data is obtained by the attacker , And the content is readable to the attacker . This is either because the data is stored in an unencrypted form , Or because the mechanism of protecting data has fundamental defects .
####3.1 Use the well-known encryption algorithm
Encryption of static data , Unless you have a good reason to choose another , Otherwise, choose your development platform AES-128 or AES-256 A well-known implementation of .
About passwords , You can use a technique called salt password hashing .
3.2 Everything is about passwords
Key storage method :
- One solution : Use a separate security device to encrypt and decrypt data .
- Another option is : Use a separate keystore , When your service needs a key, you can access it .
3.3 Decrypt on demand
Decrypt only when needed , And ensure that the decrypted data is not stored anywhere .
3.4 Encrypted backup
It is necessary to ensure that the backup is also encrypted .
4. Defense in depth
4.1 A firewall
Restrict specific communication types only on specific ports .
4.2 journal
Good logging practice , In particular, the ability to aggregate logs from multiple systems , Although it can't play a preventive role , But it can help detect bad things , For later recovery .
The log allows you to see if something bad has happened after the event . But we need to pay attention , The information stored in the log ! Sensitive information needs to be eliminated .
4.3 Intrusion detection ( And prevention ) System
IDS (Intrusion Detection Systems, Intrusion detection system ) It can monitor the network or host , Report problems when suspicious behavior is found .IPS (Intrusion Prevention Systems, Intrusion prevention system ), It will also monitor suspicious behavior , And further prevent it from happening .
Different from the firewall, it mainly prevents bad things from coming in ,IDS and IPS It is to actively look for suspicious behaviors within the scope of credibility .
4.4 Network isolation
In microservice system , You can put services into different network segments , Control the communication between services .
4.5 operating system
Give users of the operating system as few permissions as possible , At first, you may only be able to run services , To ensure that even if this account is stolen , The damage caused is also minimal .
5. The golden rule
Don't implement your own encryption algorithm . Don't invent your own security protocols
6. Built in security
It is critical to help develop the security awareness of developers , Raise everyone's general awareness of safety issues , Help reduce these problems from the beginning .
7. External validation
- Simulate the intention of the real world through experiments such as penetration tests carried out by external parties ;
- If the company has a special information security team, they can help you ;
- If the company does not have a dedicated information security team , You can find an external party ;
- Contact the security team early , Understand how they work , And learn from them what they need to pay attention to when doing a security test .
Chapter 11 : Large scale services
1. Faults are everywhere
- We can try our best to limit the factors that cause the failure , But after reaching a certain scale , Failure is unavoidable .
- We need a mindset that can embrace failure , In order to better manage the system .
- Spend less time trying to prevent inevitable failures , And spend more time dealing with it gracefully .
2. Function degradation
Build an elastic system , Especially when the functions are scattered in many different 、 On microservices that may be down , It is important to be able to safely downgrade functions .
What we need to do is to understand the impact of each failure , And figure out how to downgrade the function properly . If the shopping cart service is not available , We may have a lot of trouble , But you can still display the list page . Maybe you can just hide the shopping cart , Replace it with a new icon “ get back right away !
3. Architectural security measures
There are some patterns , Together, they are called architectural security measures , They can ensure that if something really goes wrong , No serious cascading effects . These are the key points you need to understand , I strongly recommend standardizing them in your system , To ensure that the whole system will not collapse due to a service problem .
4. Anti fragile organizations
By rehearsing the potential or extreme conditions in the production environment , Whether the system can work normally .
4.1 Overtime
Set timeout for all cross process calls , And select a default timeout . When the timeout occurs , Record it in the log to see what happened , And adjust them accordingly .
4.2 Circuit breaker
When using a circuit breaker , When a certain number of requests for downstream resources fail , The circuit breaker will open . Next , All requests are made with the circuit breaker open , Will fail quickly . After a while , The client sends some requests to check whether the downstream service has been restored , If it gets a normal response , The circuit breaker will be reset .
4.3 bulkhead
By separating functions into independent microservices , It reduces the possibility of affecting another function due to the downtime of one function .
4.4 Isolation
The more a service depends on another , The health of another service will affect its ability to work properly . If the integration technology we use allows downstream servers to go offline , Upstream services are less likely to be affected by planned or unplanned macros .
5. Curtain, etc
For burst operations , The impact of its repeated implementation , All have the same impact as one execution .
If the operation is curtain and so on , We can call it repeatedly , Don't worry about the adverse effects . When we are not sure whether the operation is performed , Want to reprocess messages , So as to recover from the error , The curtain will be very useful .
6. Expand
There are two reasons to expand the system .
- To help handle failures . If we are worried that something will fail , So many of these things will help ;
- Expand for performance , Whether dealing with more loads 、 Reduce latency or both .
6.1 More powerful host
One has a faster CPU And better I/O Machine , Latency and throughput can usually be improved , Allow you to handle more work in less time . This form of expansion is often referred to as vertical expansion .
Vertical expansion features :
- It can quickly and effectively improve the system performance ;
- It's very expensive ;
- We need to make full use of its performance to play its value ;
- This form of expansion cannot improve the elasticity of our server .
6.2 Split the load
Because to expand, you need to split the existing microservices into several parts , To better handle the load
6.3 Risk diversification
- Don't put multiple services on one host , Because the startup opportunity of the host affects multiple services .
- Don't let all services run on the same rack in the same data center , It is distributed in multiple data centers .
6.4 Load balancing
To make the service elastic , To avoid a single point of failure . The easiest way to achieve this is , After a load balancer , Place multiple hosts to run your microservice instance .
The function of load balancer is , Remove instances when they are no longer healthy , And add them when they are healthy .
7. Extended database
Extending stateless microservices is relatively simple . But if we store data in a database , We also need to know how to expand the database . Different types of databases provide different forms of extensions , Understand which form is most suitable for your use scenario , It will ensure that you choose the right database technology from the beginning .
7.1 Service availability and data persistence
Data written to the database : I can store a copy in an elastic file system . If the database fails , Data will not be lost , Because there is a copy , But the database itself is not available , This will make our microservices unavailable .
The primary database has failed : Data is secure , But if there is no mechanism for the master database to recover or promote the replica to the master database , Even if the data is secure , The database is still unavailable .
8. cache
Caching is a common method of performance optimization , By storing the results of previous operations , So that subsequent requests can use this stored value , Instead of spending time and resources recalculating this value . Usually , Caching can eliminate unnecessary round-trip communication to databases or other services , Make the result return faster . If used properly , It can bring huge performance benefits .
9. Automatic telescopic
Basic conditions for automatic scaling : You need to be able to fully automate the creation of virtual hosts and the deployment of your microservice instances .
advantage :
- Can save money ;
- Load adjustment can be carried out responsibly .
10. CAP theory
- C: Uniformity (consistency), When accessing multiple nodes, you can get the same value ;
- A: Usability (availability), Every request can get a response ;
- P: Zone tolerance (partition tolerance), Some nodes in the cluster cannot be contacted , The ability of the cluster as a whole to continue to serve .
This theorem tells us that we can only guarantee two out of three .
10.1 Sacrifice consistency
AP System : The system abandons the practice of consistency to ensure partition tolerance and availability , It is called final consistency ; in other words , We hope that sometime in the future , All nodes can see the updated data , But it won't happen immediately , So we must be clear about the possibility that users will see invalid data .
10.2 Sacrifice availability
CP System : Sacrifice availability , The system is consistent and partition tolerant .
10.3 Sacrifice partition tolerance
non-existent . If the system has no partition tolerance , You can't run across the network . let me put it another way , You need to run a separate process locally . therefore ,CA Systems do not exist in distributed systems at all .
11. Service discovery
Service discovery is divided into two parts :
- Provides some mechanisms , Let an instance register and tell all services its basic information ;
- Once the service is registered, you can find it .
12. Dynamic service registration
12.1 Zookeeper
Zookeeper Used in many usage scenarios , Including configuration management 、 Data synchronization between services ,leader Election message queuing and naming services .
Zookeeper The core of is to provide a hierarchical namespace for storing information . Clients can be in this hierarchy , Insert a new node , Change or query them .
Zookeeper The features provided by itself are quite general , This is why it applies to so many scenarios . You can think of it as just a copy of the information tree , Remind you when it changes . It means , You usually build some functions on it , To suit your particular situation .
12.2 Consul
and Zookeeper equally , Consul It also supports configuration management and service discovery . But it is better than Zookeeper Further more , Provide more support for these key usage scenarios .
Consul From the registration service 、 Query key / The value is stored in the plug-in health check , They all use RESTful HTTP Interface , This makes it very easy to integrate different technology stacks . Another thing I like very much is ,Consul The team behind split the underlying cluster management .Consul At the bottom Serf It can handle node monitoring in the cluster 、 Fault management and alarm . then Consul Service discovery and configuration management are added to it .
13. Document services
By decomposing the system into finer grained microservices , We hope to API The form exposes many seams . adopt API The document tells users to correctly perform service discovery .
Documents tend to be outdated . Ideally , We will ensure that documents are always up to date with the latest microservices API Sync , And when you need to know where the service is , You can easily see this document . Two different technologies ,Swagger and HAL, Try to make this a reality .
边栏推荐
- Vs2017 is driven by IP debugging (dual machine debugging)
- Popular understanding of linear regression (II)
- Enable multi-threaded download of chrome and edge browsers
- Popular understanding of linear regression (I)
- Didi off the shelf! Data security is national security
- 视觉上位系统设计开发(halcon-winform)-1.流程节点设计
- 软件逆向破解入门系列(1)—xdbg32/64的常见配置及功能窗口
- 《微服务设计》读书笔记(下)
- 开启 Chrome 和 Edge 浏览器多线程下载
- Redis single thread problem forced sorting layman literacy
猜你喜欢

需要知道的字符串函数
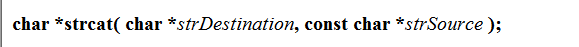
Detailed explanation of string function and string function with unlimited length
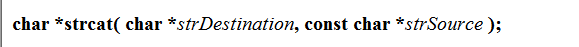
求字符串函数和长度不受限制的字符串函数的详解

视觉上位系统设计开发(halcon-winform)-3.图像控件
Redis主从、哨兵、集群模式介绍

详解指针进阶2

Basic SQL tutorial

Jvm-08-garbage collector
Concurrency-01-create thread, sleep, yield, wait, join, interrupt, thread state, synchronized, park, reentrantlock

Kubernetes帶你從頭到尾捋一遍
随机推荐
从 flask 服务端代码自动生成客户端代码 -- flask-native-stubs 库介绍
Redis lock Optimization Practice issued by gaobingfa
[combinatorics] combinatorial identities (recursive combinatorial identities | sum of variable terms | simple combinatorial identities and | sum of variable terms | staggered sums of combinatorial ide
[combinatorial mathematics] binomial theorem and combinatorial identity (binomial theorem | three combinatorial identities | recursive formula 1 | recursive formula 2 | recursive formula 3 Pascal / Ya
The wonderful use of do{}while()
视觉上位系统设计开发(halcon-winform)-4.通信管理
秒殺系統3-商品列錶和商品詳情
Jvm-02-class loading subsystem
QT use qzxing to generate QR code
【云原生训练营】模块八 Kubernetes 生命周期管理和服务发现
The method of parameter estimation of user-defined function in MATLAB
Using notepad++ to build an arbitrary language development environment
Detailed pointer advanced 1
Redis cache penetration, cache breakdown, cache avalanche solution
Redis主从、哨兵、集群模式介绍
Tensorflow realizes verification code recognition (I)
Puppet automatic operation and maintenance troubleshooting cases
Jvm-08-garbage collector
Use of Tex editor
互斥对象与临界区的区别