当前位置:网站首页>[quick start of Digital IC Verification] 18. Basic grammar of SystemVerilog learning 5 (concurrent threads... Including practical exercises)
[quick start of Digital IC Verification] 18. Basic grammar of SystemVerilog learning 5 (concurrent threads... Including practical exercises)
2022-07-07 15:34:00 【luoganttcc】
Reading guide : The author has the honor to be a pioneer in the field of electronic information in China “ University of electronic technology ” During postgraduate study , Touch the cutting edge Numbers IC Verification knowledge , I heard something like Huawei Hisilicon 、 Tsinghua purple light 、 MediaTek technology And other top IC related enterprises in the industry , Pairs of numbers IC Verify some knowledge accumulation and learning experience . Want to get started for help IC Verified friends , After one or two thoughts , This column is specially opened , In order to spend the shortest time , Take the least detours , Most learned IC Verify technical knowledge .
List of articles
One 、 Description of content
- Concurrent operation characteristics of logic simulation tools
- Threads :
fork...join | join_any | join_none wait forkdisable fork
Two 、 Logic simulation tool Concurrent Handling characteristics
2.1、 Concurrency means
- For all concurrent threads , Within the current simulation time of the simulation tool , The scheduled events will be completed before the simulation step to the next simulation time
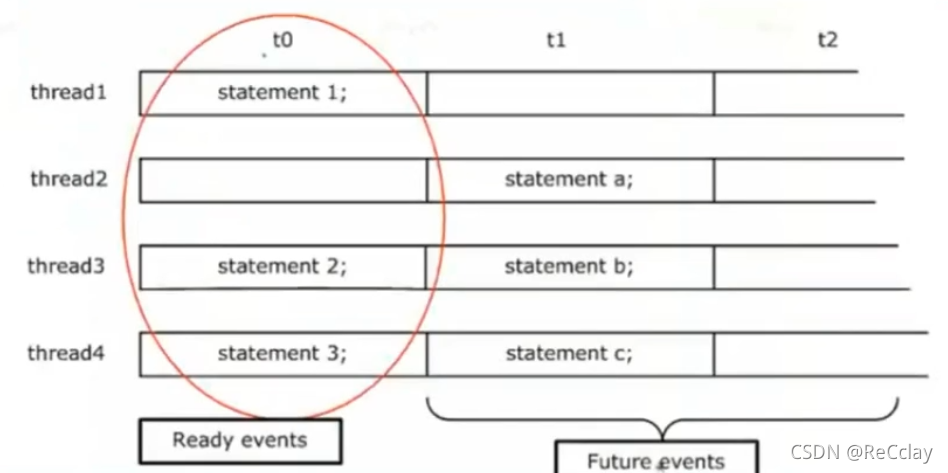
2.2、 Concurrent thread execution
- When a thread executes , Only meet
waitStatement will stop- There are sub threads generated by the executing thread Execute by queue
- When the executing thread encounters Wait statement when , In the queue
readyThreads in state can execute - When all threads enter
waitIn the state of , Simulation time update - Examples of waiting statements :
@(router.cb);
wait(var_a == 1);
##1 router.cb.din <= 4’hf;
join_any;
join
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
2.3、 Concurrent thread execution mode
When a thread executes , All other threads enter the queue and wait
READY- Represents the thread executing within the current simulation timeWAIT- Indicates that the statement is blocked ( Thread cannot execute ), When a waiting condition is encountered, you can continue to execute
When the executing thread enters
WAITIn the state of , Thread intoWAITSequence , nextREADYThe thread in state continues to executeWhen all threads enter
WAITIn the state of , The simulation time steps to the next simulation cycle
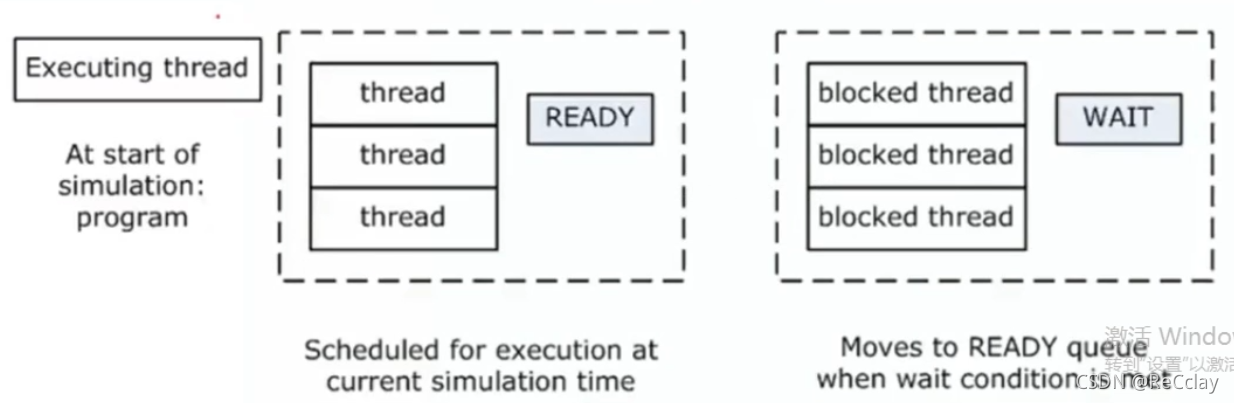
3、 ... and 、 Concurrent thread thread
3.1、 Statement set
VeilogThere is a typical set of concurrent statementsinitialsentence : Only once in the entire simulation time ,initial Statements are concurrentalwayssentence : It can model combinational circuits and sequential circuits ,always Statements are concurrentassignsentence : It can model the combinational circuit ,assign Statements are concurrentbegin...end: Sentence from top to bottom , Sequential executionfork...join: sentence Parallel execution , Independent of statement order
fork...joinfork...joinStatement blocks can create processes that execute in parallel ; Twofork...joinstayinitialinbegin..endBetween , Twofork...joinIs a serial relationship , If twofork...joinThe two outer edges arefork...join, Well, the two one.fork...joinIt's parallel .
3.2、fork-join Create concurrent threads
- Use
fork-joinStatement to create a concurrent thread
int a, b, c;
fork
statement0; // Threads 1
begin // Threads 2
statement1;// Threads 2.1
statement2;// Threads 2.2
end
join | join_any | join_none
statement
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
fork-joinThread in 1 And thread 2 Is executed in parallelfork-joinStatements are encapsulated inbegin-endStatements in form a single child thread ( Threads2.1And thread2.2), And in the order of statements , From top to bottom- Concurrent thread There is no fixed sequence of execution
- All child threads share the variables of the parent thread
3.3、join Options
notes : The parent thread here refers to
for...joinOutside the statement block, below The thread of
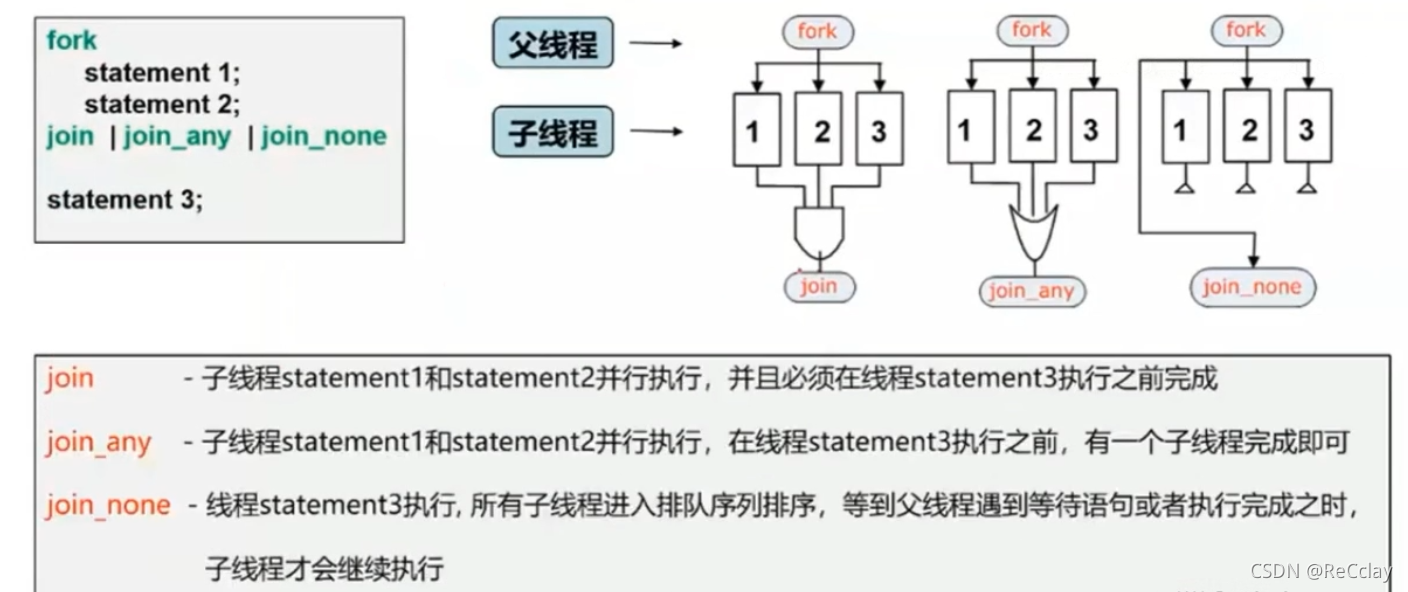
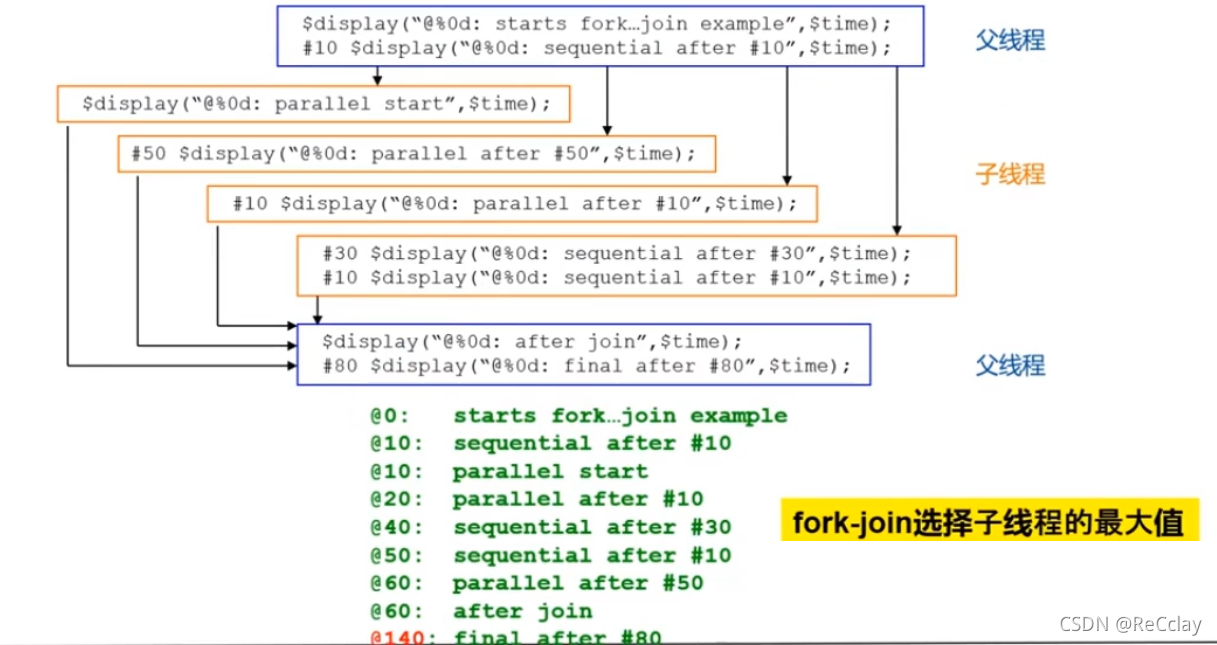
fork...join( And The relationship between )- When all the sub threads are finished , The parent thread will continue to execute
- stay
fork...joinIn the block , have access tobegin...endThe statement block encapsulates a separate thread , All statements in this thread are executed sequentially
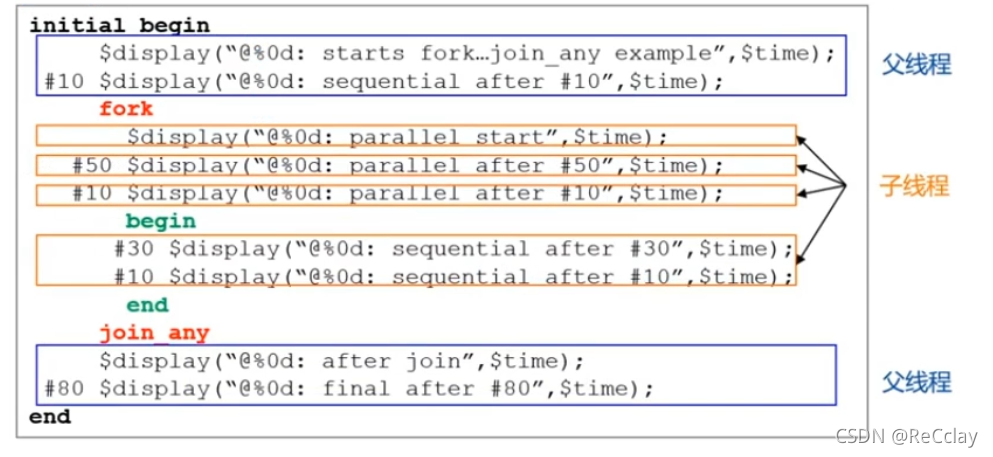
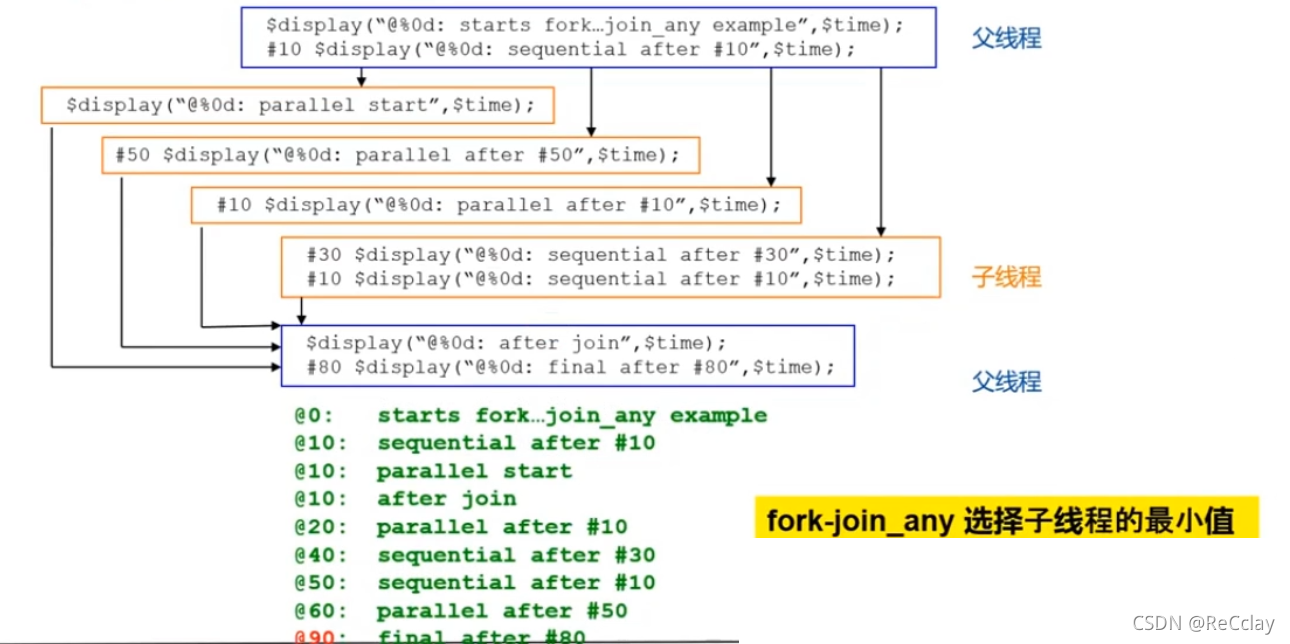
fork...join_any( or The relationship between )- When
fork...join_anyAfter any child thread in the statement block completes , The parent thread continues to execute
- When

fork...join_noe- Parent thread and for The sub threads in the statement block are executed in parallel
- When the parent thread executes a blocking statement , The child thread starts to execute ( The parent thread executes first )
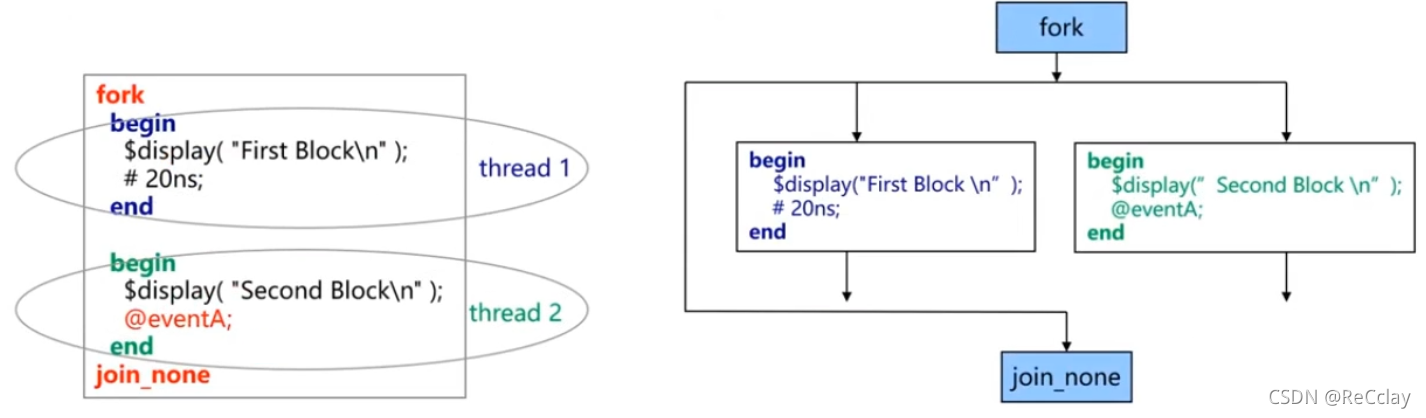
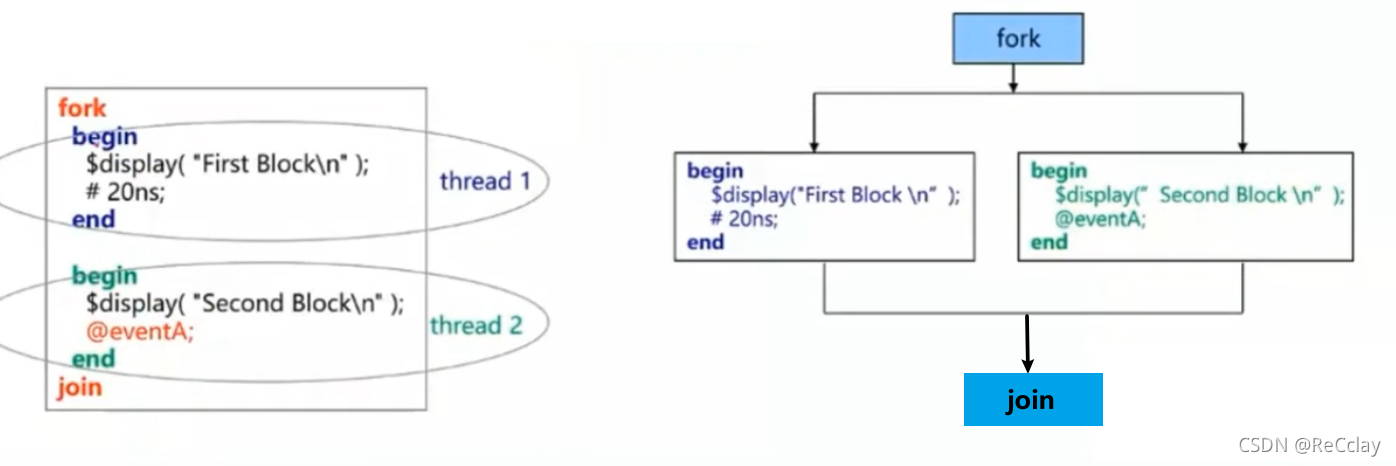
fork...joinandbegin...endExample

fork...join_anyandbegin...endExample
fork...join_noneandbegin...endExample

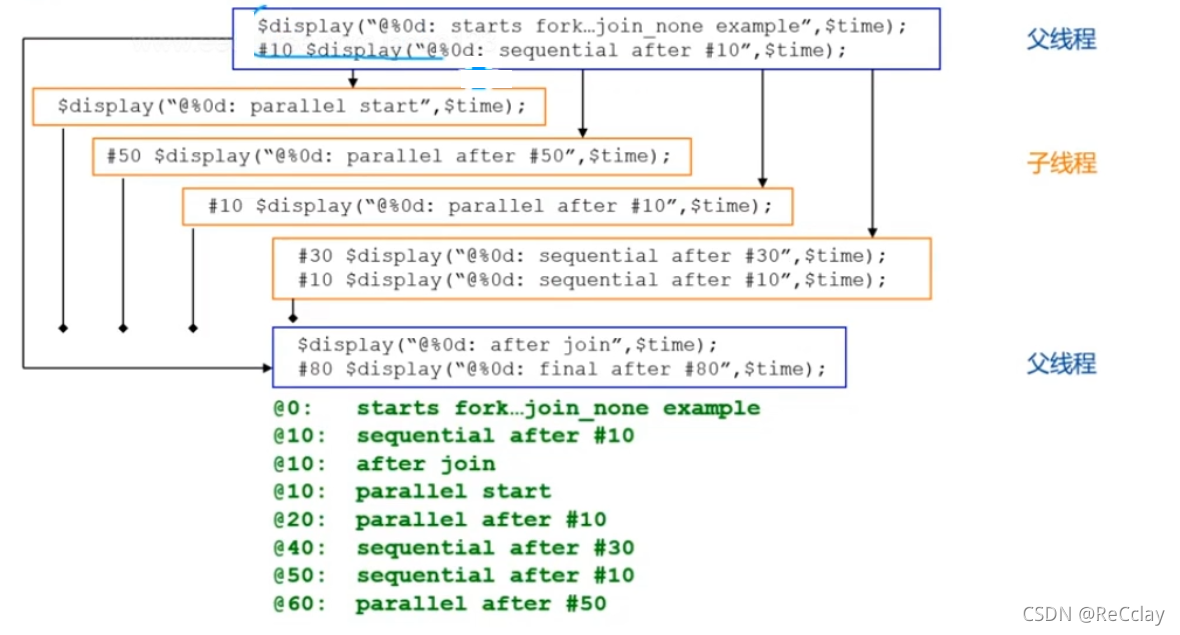
Q: The above statements are preceded by time units , If there is no time unit in front of some sentences ,fork How to execute the statement ?
- A: There is no time unit , The sequence of execution of these statements can be determined at the compilation stage , After the compilation phase is determined, it is executed in sequence at the actual run time .【 The actual project must have a time unit !】
3.4、 Concurrent thread control
wait fork- Wait for all
forkConcurrent process execution completed - Before executing the parent thread , Ensure that all
forkParallel sub thread execution is completed - Wait for all
forkSend all the sub threads to complete the execution
- Wait for all
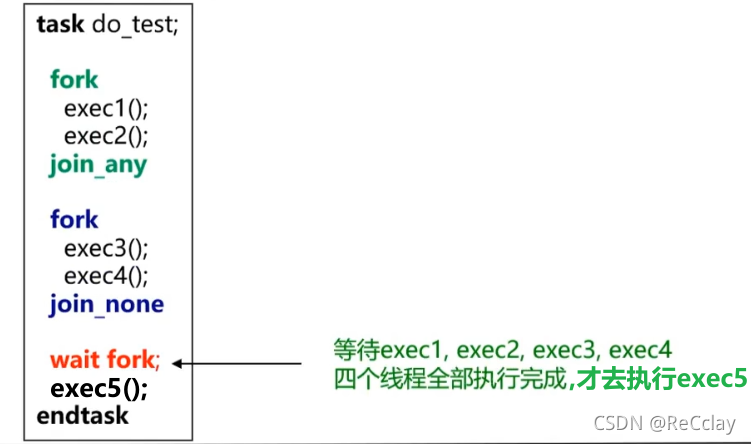
without
wait fork,exec5(); Need to wait untilfork...join_anyAfter any one of them is executed , andfork...join_noneNeed to wait untilexec5()Only after the execution is completed .disable fork- Stop the execution of all parallel sub threads

3.5、 Test questions
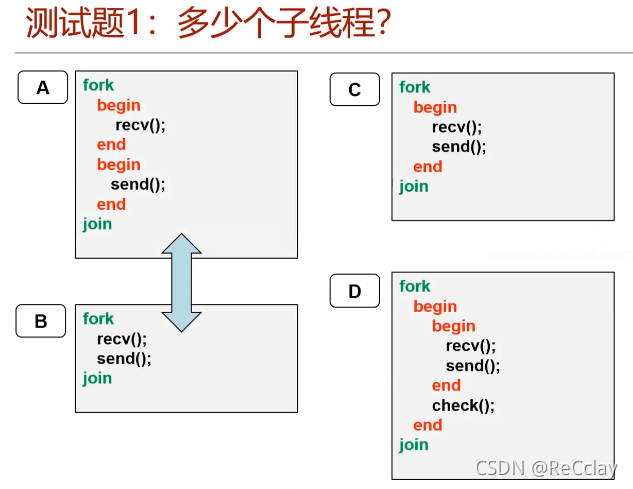
- A: 2 individual ;B:2 individual ;C:1 individual ;D:1 individual


- Cannot simulate normally : Threads 1 The clock is simulating 0 Act at all times , Threads 2 Is in 5 In time units , hold a become 5, Threads will not emulate to the 5 Time units !
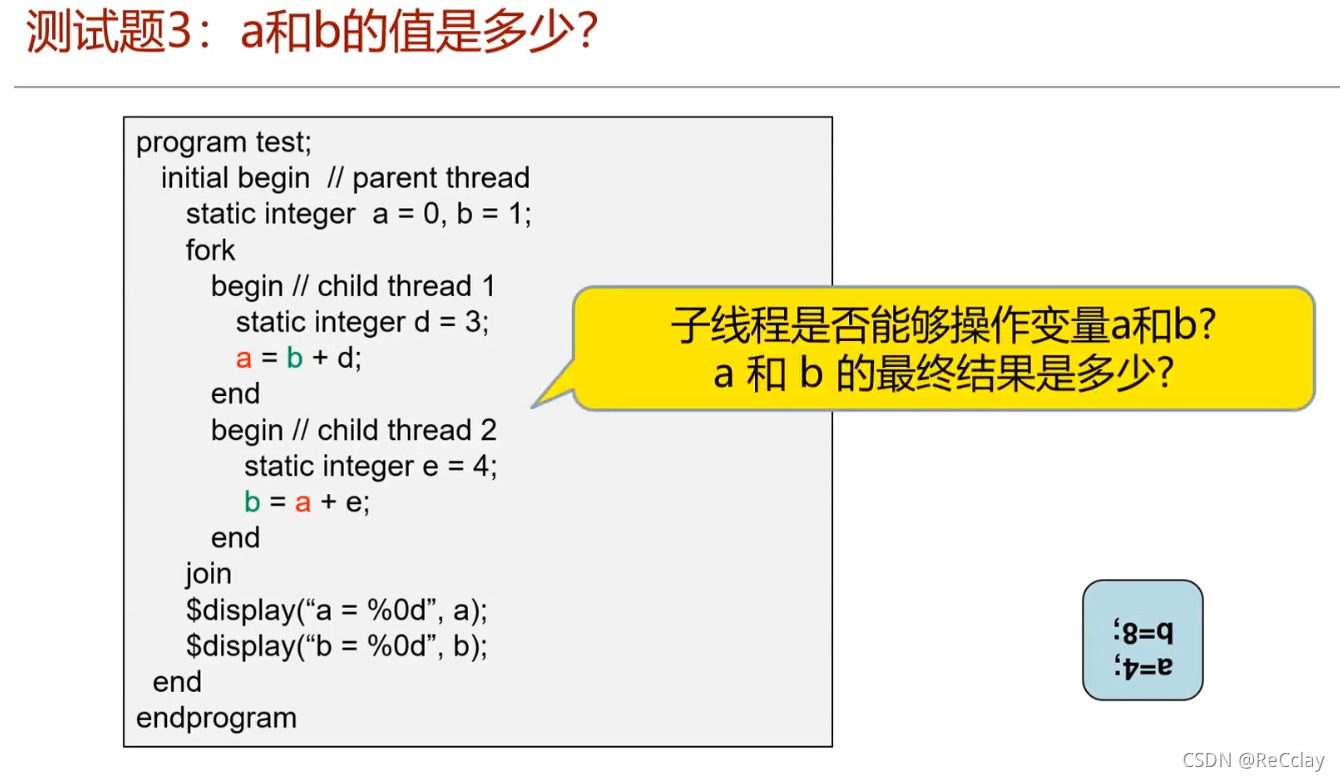
- a = 4;b = 8;
- Although the print results are parallel , But the simulator can't be fully parallel , The following can still use the above value !( There are tiny
δTime difference )

- a = 7; b = 4;



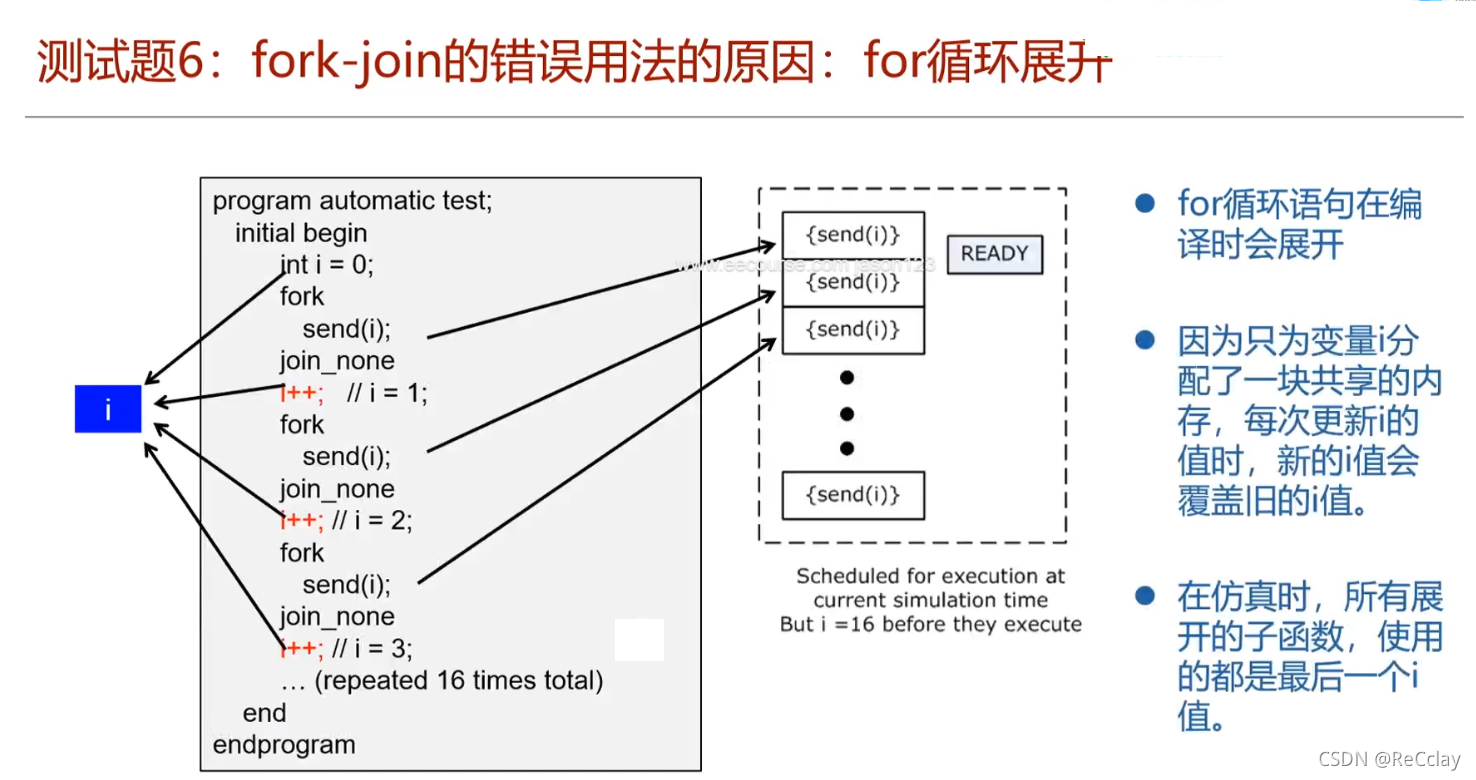

- Generally, we will not be in for Use in circulation
fork...join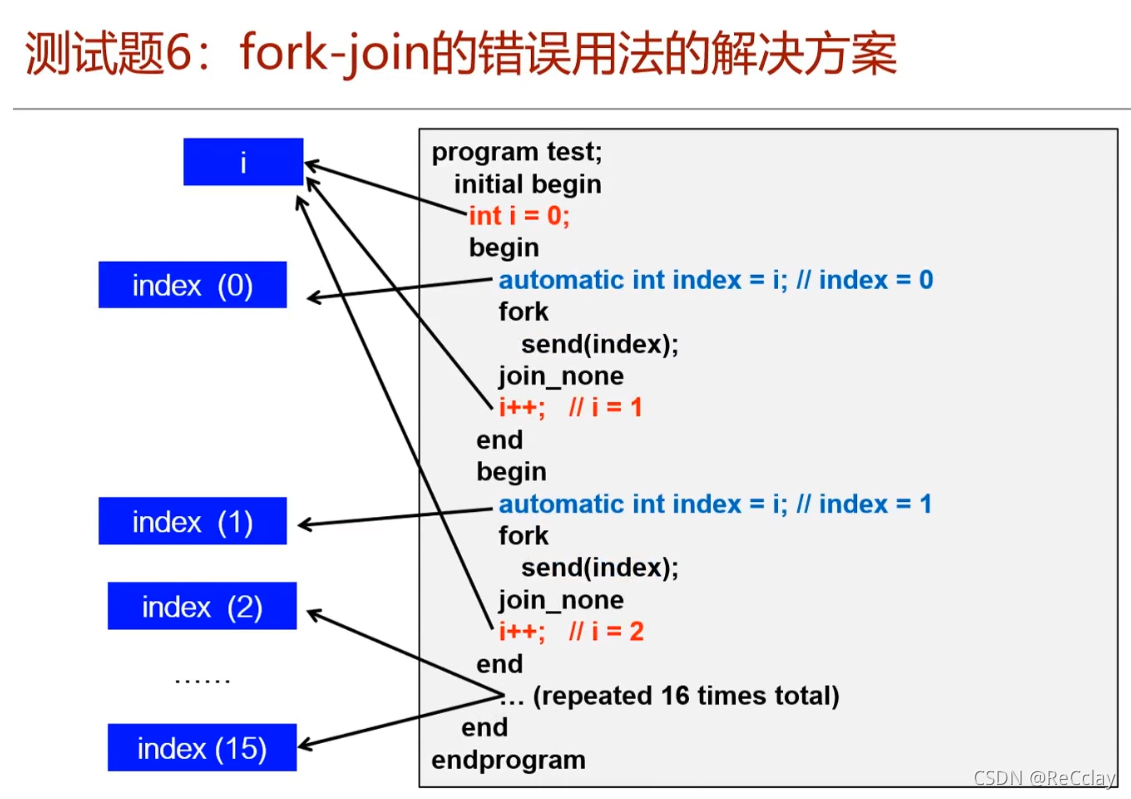
- Just understand this mistake !
X、 Practice
X.1、fork...join/join_any/join_none Demo
module thread(); initial begin fork // Thread 1 begin #6; $display("******@%0t, fork join sub thread 1 begin", $time); end // Thread 2 begin #5; $display("******@%0t, fork join sub thread 2 begin", $time); end join $display("******@%0t, fork join father thread begin", $time); #20; fork // Thread 1 begin #6; $display("******@%0t, fork join_any sub thread 1 begin", $time); end // Thread 2 begin #5; $display("******@%0t, fork join_any sub thread 2 begin", $time); end join_any $display("******@%0t, fork join_any father thread begin", $time); #20; fork // Thread 1 begin #6; $display("******@%0t, fork join_none sub thread 1 begin", $time); end // Thread 2 begin #5; $display("******@%0t, fork join_none sub thread 2 begin", $time); end join_none $display("******@%0t, fork join_none father thread begin", $time); end endmodule******@5000, fork join sub thread 2 begin ******@6000, fork join sub thread 1 begin ******@6000, fork join father thread begin ******@31000, fork join_any sub thread 2 begin ******@31000, fork join_any father thread begin ******@32000, fork join_any sub thread 1 begin ******@51000, fork join_none father thread begin ******@56000, fork join_none sub thread 2 begin ******@57000, fork join_none sub thread 1 begin
边栏推荐
- [understanding of opportunity -40]: direction, rules, choice, effort, fairness, cognition, ability, action, read the five layers of perception of 3GPP 6G white paper
- [data mining] visual pattern mining: hog feature + cosine similarity /k-means clustering
- Novel Slot Detection: A Benchmark for Discovering Unknown Slot Types in the Dialogue System
- 【数字IC验证快速入门】20、SystemVerilog学习之基本语法7(覆盖率驱动...内含实践练习)
- Used by Jetson AgX Orin canfd
- 如何在opensea批量发布NFT(Rinkeby测试网)
- Connecting FTP server tutorial
- Apache multiple component vulnerability disclosure (cve-2022-32533/cve-2022-33980/cve-2021-37839)
- How to release NFT in batches in opensea (rinkeby test network)
- What is data leakage
猜你喜欢
【数字IC验证快速入门】20、SystemVerilog学习之基本语法7(覆盖率驱动...内含实践练习)
![[server data recovery] a case of RAID data recovery of a brand StorageWorks server](/img/aa/6d820d97e82df1d908dc7aa78fc8bf.png)
[server data recovery] a case of RAID data recovery of a brand StorageWorks server
Ctfshow, information collection: web14

微信小程序 01
【數據挖掘】視覺模式挖掘:Hog特征+餘弦相似度/k-means聚類
Unity之ASE实现卡通火焰
![[server data recovery] data recovery case of raid failure of a Dell server](/img/5d/03bc8dcc6e554273b34a78c49a9eaf.jpg)
[server data recovery] data recovery case of raid failure of a Dell server

【數字IC驗證快速入門】20、SystemVerilog學習之基本語法7(覆蓋率驅動...內含實踐練習)
CTFshow,信息搜集:web7
从 1.5 开始搭建一个微服务框架链路追踪 traceId
随机推荐
CTFshow,信息搜集:web5
8大模块、40个思维模型,打破思维桎梏,满足你工作不同阶段、场景的思维需求,赶紧收藏慢慢学
使用cpolar建立一个商业网站(2)
STM32F103C8T6 PWM驱动舵机(SG90)
一个需求温习到的所有知识,h5的表单被键盘遮挡,事件代理,事件委托
[data mining] visual pattern mining: hog feature + cosine similarity /k-means clustering
Novel Slot Detection: A Benchmark for Discovering Unknown Slot Types in the Dialogue System
Use cpolar to build a business website (2)
从 1.5 开始搭建一个微服务框架链路追踪 traceId
Niuke real problem programming - day20
Guangzhou Development Zone enables geographical indication products to help rural revitalization
写一篇万字长文《CAS自旋锁》送杰伦的新专辑登顶热榜
CTFshow,信息搜集:web3
2. Basic knowledge of golang
Oracle control file loss recovery archive mode method
有一头母牛,它每年年初生一头小母牛。每头小母牛从第四个年头开始,每年年初也生一头小母牛。请编程实现在第n年的时候,共有多少头母牛?
知否|两大风控最重要指标与客群好坏的关系分析
如何在opensea批量发布NFT(Rinkeby测试网)
什么是数据泄露
Wechat applet 01