当前位置:网站首页>Mongdb learning notes
Mongdb learning notes
2022-07-05 14:38:00 【JavaSupeMan】
1.NoSQL Characteristics
It's a non relational database , Storage in document form
characteristic : The document database stores data in the form of documents ,BSON Format , similar JSON, It's a collection of data items . Each data item has a name and a corresponding value , Values can be simple data types , Such as a string / Numbers / Date, etc. . It can also be a complex type .
== advantage :== Data structure requirements are not strict , Variable table structure , You don't need to predefine the table structure like a relational database
== shortcoming :== Poor query performance , Lack of uniform query syntax
Application scenarios : journal ,web Application etc. 
Start command :
--dbpath: Specify the directory where the data file is stored
--logpath: Specify log files , Note that the specified file is not a directory
--logappend: Log by appending
--port: Designated port , The default is 27017
--bind_ip: Binding services IP, If bound 127.0.0.1, Can only be accessed locally , Default to local address
mongod --dbpath D:\MongDB\data\db

3. Safety certification
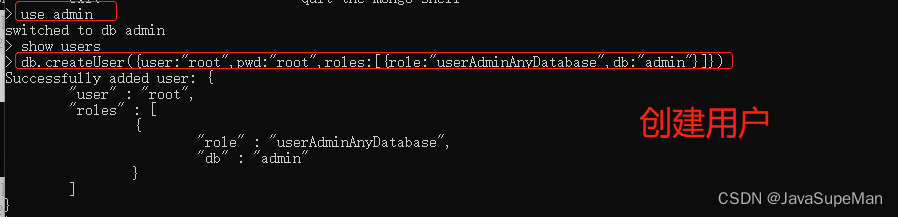
Create administrator account
# To set the administrator user name and password, you need to switch to admin library
use admin
# Create administrator
db.createUser({
user:"fox",pwd:"fox",roles:["root"]})
# View all user information
show users
# Delete user
db.dropUser("fox")
# Log in with the user , Default to admin library
mongo -ufox -pfox --authenticationDatabase=admin
4.MongoDB The document operation
1. Inserted into the document
2. Query the document
db.collection.find(query,projection)
db.collection.findOne(query,projection)
*query: Optional , Use the query operator to specify the query criteria
*projection: Optional , Use the projection operator to specify the returned key
Query cross reference table 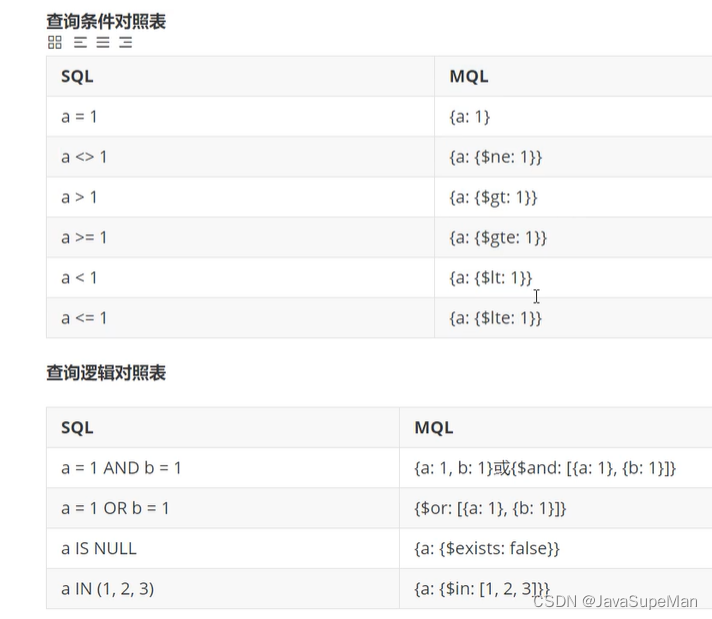

example :
example :
Check stock out users All data in
db.users.find()
Conditions of the query , Inquire about user The value is root Of
db.users.find({user:“root”})
Query a value greater than a certain number
db.users.find({age:{$gt:60}})
Find the first
db.users.findOne()
Sort & Pagination
stay MongoDB Use in sort() Method to sort the data
# Specify by collection (favCount) Return in descending order -1 Representation of descending order Expressing ascending order
favCount type All field names
db.books.find({
type:"travel"}).sort({
favCount:-1})
Paging query : adopt skip and limit To achieve ,skip Indicates the specified number of skipped records ,limit It means to limit the number of returned results
example :
db.books.find().skip().limit(5)
3. Update the document
It can be used update Command to update the specified data , The command format is as follows :
db.collection.update(query,update,options)
db.collection.updateOne(query,update,options) // Update individual documents amount to multi The attribute is true
db.collection.updateMany(query,update,options) // Update multiple documents
db.collection.replaceOne(query,update,options) // Replace a single document
# Attribute interpretation :
# query : Describe the updated query criteria
# update: Describe the updated actions and new content
# options: Describe the options for updating
# - upsert: Optional , If it doesn't exist update The record of , Whether to insert a new record . Default false, Do not insert
- multi: Optional , Whether to update all the multiple records queried by criteria . Default false, Update only the first record found
- writeConcern: Optional , Determine how many nodes a write operation falls on before it is considered successful ( Similar to transaction operation )
update The operators are as follows :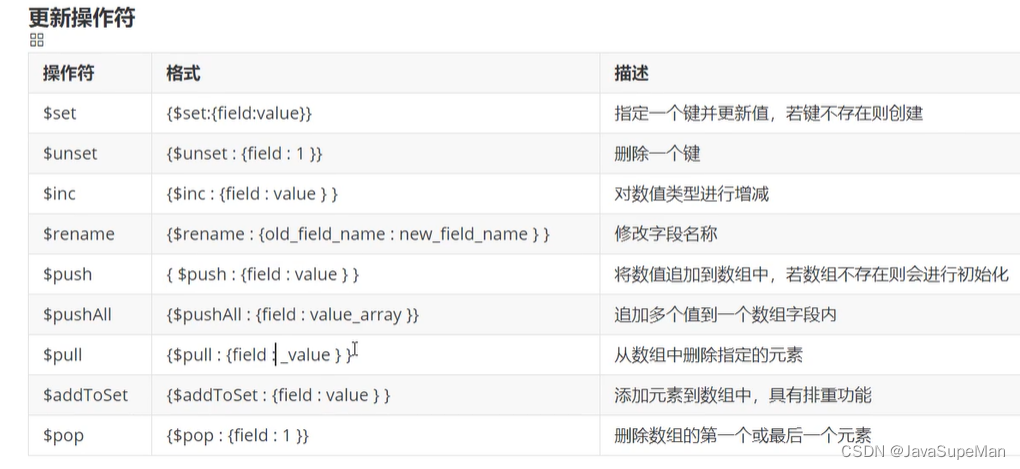
example :
db.books.update({
type:"novel"},{
$Set:{
publishedDate:new Date()}},{
"multi":true})
Be careful : If udate The update description in the command does not contain any operators , that MongoDB It will realize the of documents replace semantics
example :
db.books.update({
type:"novel"},{
age:"1"})
Will find type by novel The data of , Then its contents are completely replaced , Only age:1
findAndModify command :
Find and update , Only single documents can be operated , Cannot operate on multiple documents
Format :
example : increase new :true, The updated value will be returned ,false Return the value before update
db.books.findAndModify({
query:{
},update:{
}},new :true)
findOneAndUpdate: Update a single document and return to the pre update ( Or after update ) Documents
findOneAndReplace: Replace a single document and return to the previous ( Or after replacement ) Documents
4. Delete the document
remove command
example :
example :
db.books.remove({
age:28}) // Delete age be equal to 28 The record of
db.books.remove({
age:{
$lt:25}}) // Delete age Less than 25 The record of
db.books.remove({
}) // Delete all records
If there are more than one qualified , But only delete the first , You need to make justOne Parameters of , The format is as follows
example :
example :
db.books.remove({
age:28},true)
delete command :
Official recommendation deleteOne() and deleteMany() Method delete stable , The syntax is as follows :
example :
db.books.deleteMany({
}) // Delete all documents under the collection
db.books.deleteMany({
type:"novel"}) // Delete all data with specified conditions
db.books.deleteOne({
type:"novel"}) // Specify the data of the condition , Delete only the first
If you need to return the deleted document
command :findOneAndDelete
example :
db.books.findOneAndDelete({
type:"novel"}) // Delete all documents under the collection
MongoDB Integrate SpringBoot
1 Introduce dependencies
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.yml File configuration
spring:
data:
mongodb:
uri: mongodb://fox:[email protected]:27017/user?authSource=admin
#uri Equivalent to the following configuration
# database: user
# host: 127.0.0.1
# port: 27017
# username: fox
# password: fox
# authentication-database: admin
3. Inject bean
@Autowired
MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
4. Use
1. Add, delete and change the set
// Operations on collections
@RequestMapping("/test1")
public void ok(){
// Determine whether a set exists
boolean flag = mongoTemplate.collectionExists("emp");
if(flag){
// Delete the collection
mongoTemplate.dropCollection("emp");
}
// Create set
MongoCollection<Document> emp1 = mongoTemplate.createCollection("emp");
}
// Querying documents
@RequestMapping("/test2")
public void test2(){
//============= Common query ====================
// Find all documents
List<User> list = mongoTemplate.findAll(User.class);
// according to ID Inquire about
User us = mongoTemplate.findById(1, User.class);
// The query result is multiple , Return to the first one
User u = mongoTemplate.findOne(new Query(), User.class);
//============= Conditions of the query =====================
// Build query criteria
Query query1 = new Query(Criteria.where("salary").gte(8000));
Query query2 = new Query(Criteria.where("salary").gte(8000).lt(10000));
Query query3 = new Query(Criteria.where("name").regex(" Zhang ")); // Fuzzy matching
//============== Multiconditional query ===================
Criteria criteria1 = new Criteria();
Criteria criteria2 = new Criteria();
//and Conditions
criteria1.andOperator(Criteria.where("age").gt(25),Criteria.where("salary").gt(8000));
//or Conditions
criteria1.orOperator(Criteria.where("age").gt(25),Criteria.where("salary").gt(8000));
Query query = new Query(criteria1);
//sort Sort
query.with(Sort.by(Sort.Order.desc("salary")));
// Pagination
query.skip(1).limit(10);
// Find all documents , The third parameter is the set name
List<User> list = mongoTemplate.findAll(query, TestUser.class, "test2");
}
// Document update operation
@RequestMapping("/test3")
public void test3(){
// First, find out what you want to modify
Query query = new Query(Criteria.where("salary").gte(8000));
User u = mongoTemplate.findOne(query, User.class);
Update update = new Update();
update.set("name"," Zhang San ");
//UpdateResult()
//UpdateFirst() Update the first record that meets the condition
//UpdateMulti() Update all records that meet the conditions
//upsert() If there are no qualified records, insert data
UpdateResult updateResult = mongoTemplate.upsert(query, update, User.class);
// Return the number of modified records
System.out.println(updateResult.getModifiedCount());
}
2. Inquire about
Use bson Query as query criteria
//1. Construct query conditions
Bson filters = Filters.and(
Filters.eq("deviceId", warningEvent.getDeviceId()),
Filters.gte("date", strTime.getTime()),
Filters.lte("date", endTime.getTime()),
Filters.eq("lastUpdateTime", DateUtil.format(updateDate, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm"))
);
//2. Specify field sort , Ascending or descending
Bson sort = Sorts.ascending("name");
// Bson sort = Sorts.descending("name");
//3. Specify the return field
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("name");
list.add("age");
// Inclusion Contains the specified fields and ( implicit )_id Field
// Exclusion Contains the specified fields and ( implicit )_id Field
Bson fields = Projections.fields(Projections.include(list));
//4. To query in the specified set
MongoCursor<Document> mongoCursor = mongoTemplate.getCollection("weatherall").find(filters).projection(fields).sort(sort).iterator();
while (mongoCursor.hasNext()) {
Document document = mongoCursor.next();
//3. Get data according to the field name
wdspList.add(document.getDouble("name"));
wdirList.add(document.getDouble("age"));
//document.getInteger()
lstDate.add(DateUtil.format(new Date(document.getLong("date")), "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm"));
}
边栏推荐
- Mysql database installation tutorial under Linux
- 分享 12 个最常用的正则表达式,能解决你大部分问题
- 长列表优化虚拟滚动
- 01. Solr7.3.1 deployment and configuration of jetty under win10 platform
- APR protocol and defense
- [detailed explanation of Huawei machine test] happy weekend
- Topology visual drawing engine
- 03_ Dataimport of Solr
- leetcode:881. lifeboat
- 【NVMe2.0b 14-9】NVMe SR-IOV
猜你喜欢
Online electronic component purchasing Mall: break the problem of information asymmetry in the purchasing process, and enable enterprises to effectively coordinate management
How to protect user privacy without password authentication?

World Environment Day | Chow Tai Fook serves wholeheartedly to promote carbon reduction and environmental protection
CYCA少儿形体礼仪 宁波市培训成果考核圆满落幕
日化用品行业智能供应链协同系统解决方案:数智化SCM供应链,为企业转型“加速度”

Differences between IPv6 and IPv4 three departments including the office of network information technology promote IPv6 scale deployment
FR练习题目---综合题
![[learning notes] stage test 1](/img/22/ad16375d8d1510c2ec75c56403a8bf.png)
[learning notes] stage test 1

用 Go 跑的更快:使用 Golang 为机器学习服务
Thymeleaf th:with局部变量的使用
随机推荐
Microframe technology won the "cloud tripod Award" at the global Cloud Computing Conference!
Handwriting promise and async await
CyCa children's physical etiquette Ningbo training results assessment came to a successful conclusion
Differences between IPv6 and IPv4 three departments including the office of network information technology promote IPv6 scale deployment
FR练习题目---简单题
CPU设计实战-第四章实践任务二用阻塞技术解决相关引发的冲突
How can non-technical departments participate in Devops?
做自媒體視頻二次剪輯,怎樣剪輯不算侵權
Shanghai under layoffs
启牛学堂班主任给的证券账户安全吗?能开户吗?
浅谈Dataset和Dataloader在加载数据时如何调用到__getitem__()函数
Mysql database installation tutorial under Linux
Long list optimized virtual scrolling
2022年国内正规的期货公司平台有哪些啊?方正中期怎么样?安全可靠吗?
Thymeleaf 常用函数
Structure - C language
SSL证书错误怎么办?浏览器常见SSL证书报错解决办法
LeetCode_ 69 (square root of x)
Google eventbus usage details
通过npm 或者 yarn安装依赖时 报错 出现乱码解决方式