当前位置:网站首页>Complex, complicated and numerous: illustration of seven types of code coupling
Complex, complicated and numerous: illustration of seven types of code coupling
2022-07-05 01:13:00 【Java geek Technology】
1 complex 、 multifarious 、 Miscellaneous
In the development work, we often hear : This business is very complicated , The system is very complicated , This logic is very complicated , As long as it is dealing with difficult situations , It seems that the word complex can be used to describe .
But I think the reason why difficulties are difficult , The reasons are different , The word complexity cannot be generalized , It is necessary to distinguish . In general, I think it can be divided into complex 、 multifarious 、 There are three types of miscellaneous .
Both complexity and complexity contain the meaning of more branches and more logic , But the difference is , Complex scenes can be sorted out , If you design it right , It is possible to design a very elegant system . But it is difficult to figure out the complicated scenes , In order to be compatible, you can only make various patches , Finally, the accumulated difficulties can only be reconstructed .
There is another type that can be called miscellaneous , When the quantity reaches a certain scale , Complexity and complexity can evolve into complexity . Although it is also complex , But there are also differences between complexity and complexity . This article only needs to discuss clearly the complexity and complexity , As long as the quantitative dimension is added, it is complex .
We can write complex code in development , Try to avoid complicated code , Code coupling is a typical complex scenario , The highly coupled code between modules makes it ultimately impossible to maintain , In this article, we discuss seven types of code coupling .
2 Code coupling type
The seven types of code coupling are sorted from high to low according to the degree of coupling : Content coupling 、 Public coupling 、 External coupling 、 Control coupling 、 Tag coupling 、 Data coupling and indirect coupling .
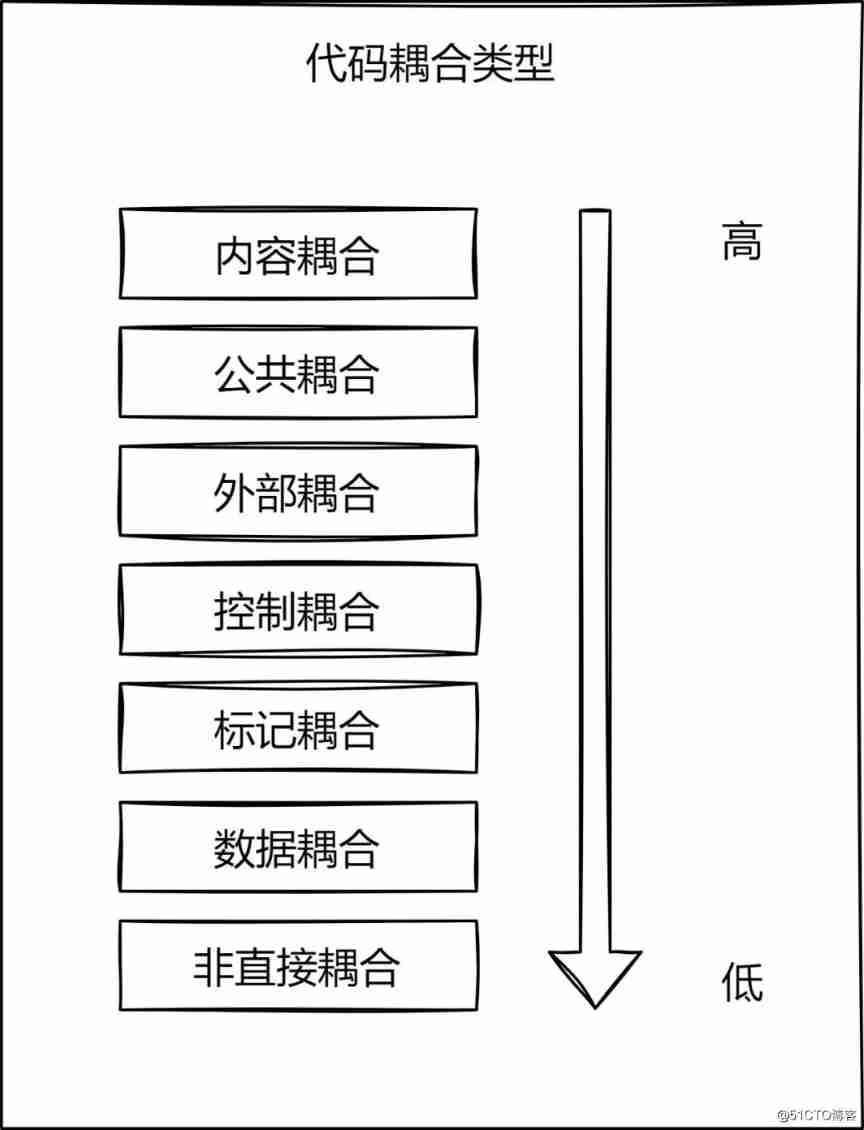
2.1 Content coupling
One module can directly access the internal data of another module, which is called content coupling , This is the most coupling type , This is what we need to avoid as much as possible .
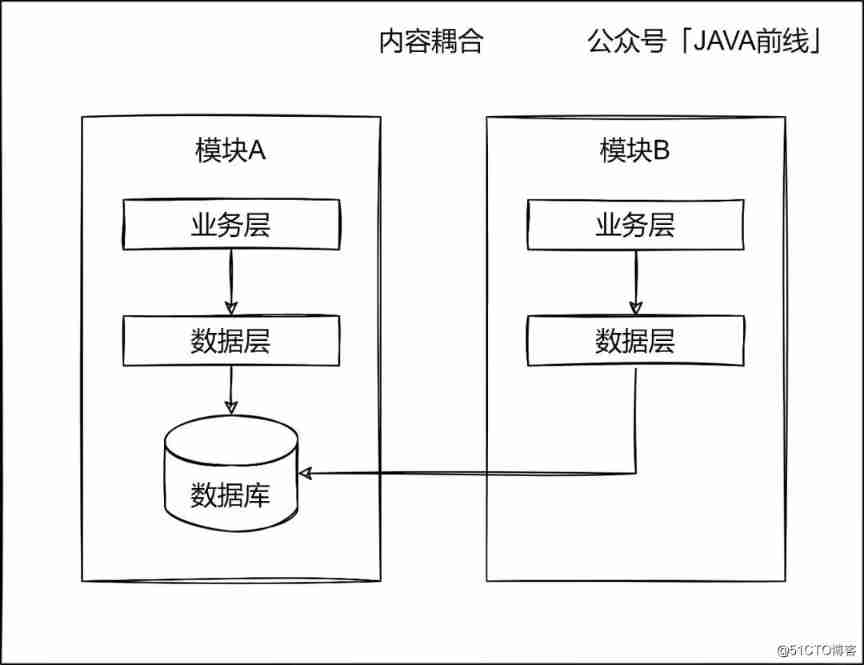
Hypothesis module A It's the order module , modular B It's the payment module , If the payment module can directly access the order data table , Then it will at least bring the following problems .
The first problem is the existence of duplicate data access layer code , Both payment and order modules should write order data access code . The second problem is if the order business changes , Order data fields need to be changed , If the payment module does not follow in time change , Then it may cause business errors .
The third problem is if the order business changes , You need to split data by database and table , If the payment module is not changed in time , For example, not using shardingKey Query or stop writing the old database table , Then it may cause serious errors in the payment module .
The fourth problem is that the business entry does not converge , Access entrances are scattered everywhere , If you want to make business changes, you need to make several modifications , Very difficult to maintain .
2.2 Public coupling
Multiple modules accessing the same common data environment is called common coupling , Public data environments such as global data structures 、 Shared communication area and memory common coverage area .
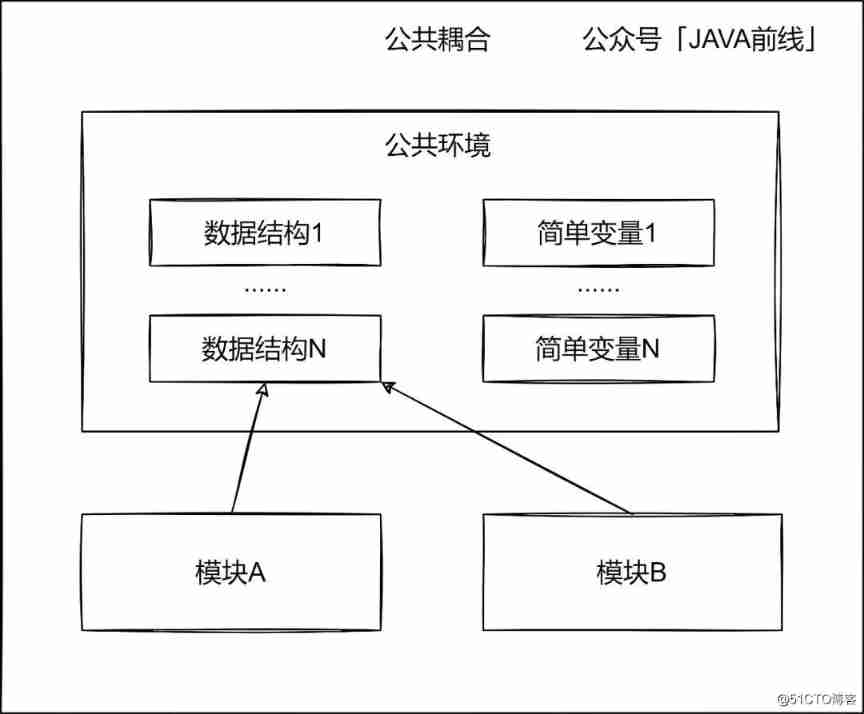
For example, use... In a project Apollo Dynamic configuration , Configuration item A The content is a paragraph JSON, Both the order module and the payment module read and parse this data structure for business processing .
public class ApolloConfig {
@Value("${apollo.json.config}")
private String jsonConfig;
}
public class JsonConfig {
public int type;
public boolean switchOpen;
}
public class OrderServiceImpl {
public void createOrder() {
String jsonConfig = apolloConfig.getJsonConfig();
JsonConfig config = JSONUtils.toBean(jsonConfig, JsonConfig.class);
if(config.getType() == TypeEnum.ORDER.getCode() & & config.isSwitchOpen()) {
createBizOrder();
}
}
}
public class PayServiceImpl {
public void createPayOrder() {
String jsonConfig = apolloConfig.getJsonConfig();
JsonConfig config = JSONUtils.toBean(jsonConfig, JsonConfig.class);
if(config.getType() == TypeEnum.PAY.getCode() & & config.isSwitchOpen()) {
createBizPayOrder();
}
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
2.3 External coupling
Multiple modules access the same global simple variable ( Non global data structure ) And the global variable information is not transmitted through the parameter table, which is called external coupling .
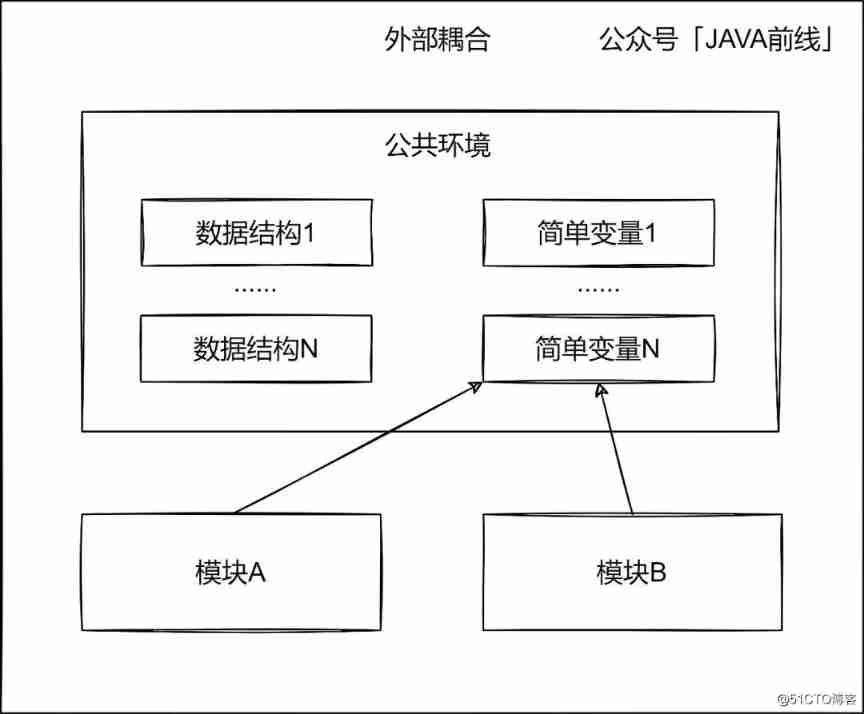
For example, use... In a project Apollo Dynamic configuration , Configuration item A Content is a simple variable , Both the order module and the payment module read this simple variable for business processing .
public class ApolloConfig {
@Value("${apollo.type.config}")
private int typeConfig;
}
public class OrderServiceImpl {
public void createOrder() {
if(apolloConfig.getTypeConfig() == TypeEnum.ORDER.getCode()) {
createBizOrder();
}
}
}
public class PayServiceImpl {
public void createPayOrder() {
if(apolloConfig.getTypeConfig() == TypeEnum.PAY.getCode()) {
createBizPayOrder();
}
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
2.4 Control coupling
The information transferred between modules includes the information used to control the interior of the module, which is called control coupling . Control coupling may cause the control logic between modules to be intertwined , Logic interacts with each other , It is very detrimental to code maintenance .
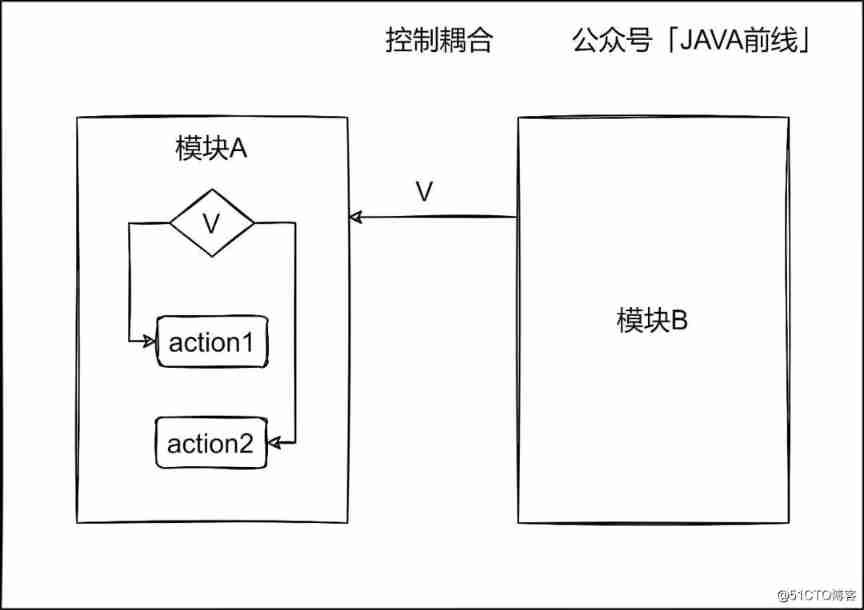
An example of control coupling code is as follows , We can see the module B Code logic heavily depends on modules A type , hypothesis A Changes in type are likely to affect B Logic :
public class ModuleA {
private int type;
}
public class A {
private B b = new B();
public void methondA(int type) {
ModuleA moduleA = new ModuleA(type);
b.methondB(moduleA);
}
}
public class B {
public void methondB(ModuleA moduleA) {
if(moduleA.getType() == 1) {
action1();
} else if(moduleA.getType() == 2) {
action2();
}
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
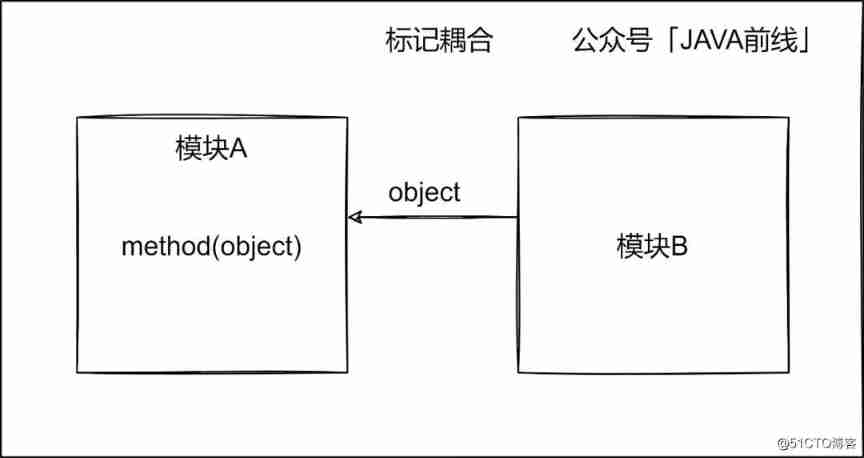
2.5 Tag coupling
Multiple modules transfer data structure information through parameter tables, which is called tag coupling , By analogy JAVA Language reference passing .
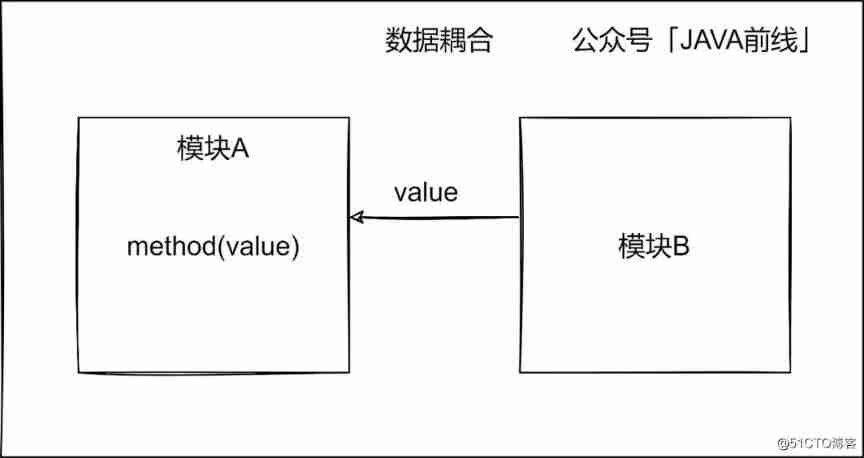
2.6 Data coupling
Multiple modules transmit simple data information through parameter tables, which is called tag coupling , By analogy JAVA Language value passing .
2.7 Indirect coupling
There is no direct connection between multiple modules , The connection through the control and call of the main module is called indirect coupling , This is also an ideal coupling mode .
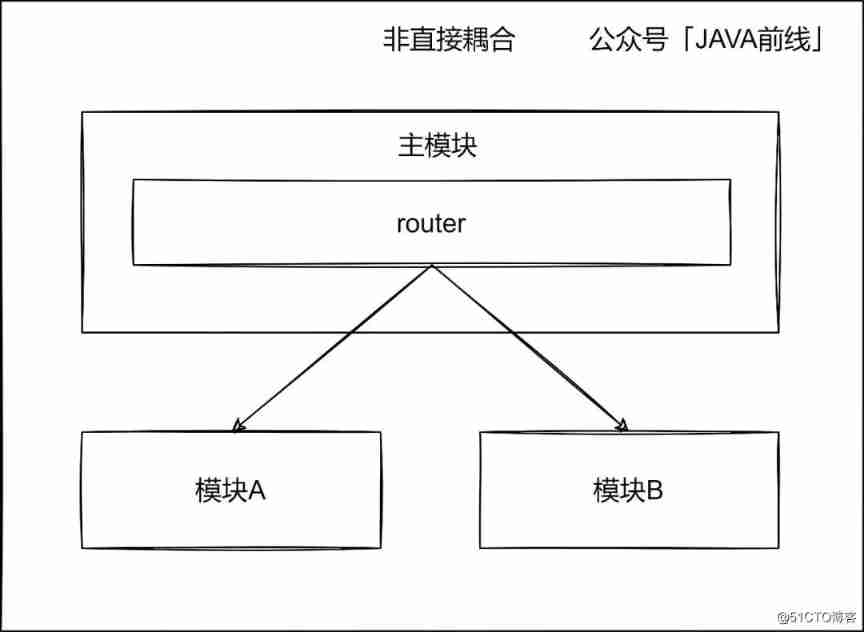
Let's focus on indirect coupling . Complex business is complex , An important reason is that there are many roles or types involved , It is difficult to design plainly . If you have to do tile design , There will inevitably be a large number of if else Code block .
Let's first analyze an order placing scenario . The current is ABC Three order types :A Order price 9 fold , The maximum weight of logistics cannot exceed 9 kg , Refund not supported .B Order price 8 fold , The maximum weight of logistics cannot exceed 8 kg , Support refund .C Order price 7 fold , The maximum weight of logistics cannot exceed 7 kg , Support refund . It's not difficult to write code plainly according to the literal meaning of the requirements :
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Resource
private OrderMapper orderMapper;
@Override
public void createOrder(OrderBO orderBO) {
if (null == orderBO) {
throw new RuntimeException(" Parameter exception ");
}
if (OrderTypeEnum.isNotValid(orderBO.getType())) {
throw new RuntimeException(" Parameter exception ");
}
// A Type order
if (OrderTypeEnum.A_TYPE.getCode().equals(orderBO.getType())) {
orderBO.setPrice(orderBO.getPrice() * 0.9);
if (orderBO.getWeight() > 9) {
throw new RuntimeException(" Exceeding the maximum weight of logistics ");
}
orderBO.setRefundSupport(Boolean.FALSE);
}
// B Type order
else if (OrderTypeEnum.B_TYPE.getCode().equals(orderBO.getType())) {
orderBO.setPrice(orderBO.getPrice() * 0.8);
if (orderBO.getWeight() > 8) {
throw new RuntimeException(" Exceeding the maximum weight of logistics ");
}
orderBO.setRefundSupport(Boolean.TRUE);
}
// C Type order
else if (OrderTypeEnum.C_TYPE.getCode().equals(orderBO.getType())) {
orderBO.setPrice(orderBO.getPrice() * 0.7);
if (orderBO.getWeight() > 7) {
throw new RuntimeException(" Exceeding the maximum weight of logistics ");
}
orderBO.setRefundSupport(Boolean.TRUE);
}
// Save the data
OrderDO orderDO = new OrderDO();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(orderBO, orderDO);
orderMapper.insert(orderDO);
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
The above code can fully realize the business requirements from the function , But programmers should not only meet the function , We also need to think about the maintainability of the code . If you add an order type , Or add an order attribute processing logic , Then we need to add code to the above logic , If handled carelessly, the original logic will be affected .
In order to avoid touching the whole body with one hair , The opening and closing principle in the design pattern requires us to face the new opening , Close for modification , I think this is the most important principle in design patterns .
Demand changes through expansion , Instead of modifying existing code , This ensures code stability . Expansion is not arbitrary , Because the algorithm is defined in advance , The extension is also based on the algorithm , Building framework with abstraction , Extend details with implementation . In the final analysis, the 23 design patterns in the standard sense are all following the open and close principle .
How to change the straightforward way of thinking ? We need to add analysis dimension . One of the most common is to add horizontal and vertical dimensions , In general, the horizontal expansion is the breadth of thinking , The vertical expansion is the depth of thinking , Corresponding to the system design, it can be summarized as : Isolate vertically , Arrange horizontally .
At this time, we can add vertical and horizontal dimensions to the problem analysis , Choose to use the analytical matrix method , Among them, the vertical represents the strategy , Horizontal represents the scene :
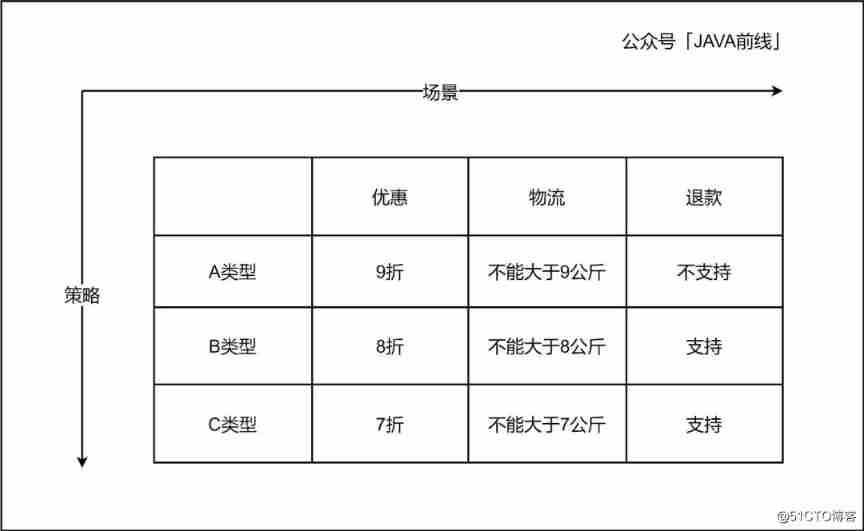
2.7.1 Isolate vertically
The vertical dimension represents the strategy , Different strategies should be isolated in logic and business , This example includes preferential policies 、 Logistics strategy and refund strategy , Strategies as abstractions , Different order types extend this abstraction , The strategy mode is very suitable for this scenario . This paper analyzes the preferential policies in detail , Logistics strategy and refund strategy are the same .
// Preferential policies
public interface DiscountStrategy {
public void discount(OrderBO orderBO);
}
// A Type preferential policy
@Component
public class TypeADiscountStrategy implements DiscountStrategy {
@Override
public void discount(OrderBO orderBO) {
orderBO.setPrice(orderBO.getPrice() * 0.9);
}
}
// B Type preferential policy
@Component
public class TypeBDiscountStrategy implements DiscountStrategy {
@Override
public void discount(OrderBO orderBO) {
orderBO.setPrice(orderBO.getPrice() * 0.8);
}
}
// C Type preferential policy
@Component
public class TypeCDiscountStrategy implements DiscountStrategy {
@Override
public void discount(OrderBO orderBO) {
orderBO.setPrice(orderBO.getPrice() * 0.7);
}
}
// Preferential strategy factory
@Component
public class DiscountStrategyFactory implements InitializingBean {
private Map < String, DiscountStrategy > strategyMap = new HashMap < >();
@Resource
private TypeADiscountStrategy typeADiscountStrategy;
@Resource
private TypeBDiscountStrategy typeBDiscountStrategy;
@Resource
private TypeCDiscountStrategy typeCDiscountStrategy;
public DiscountStrategy getStrategy(String type) {
return strategyMap.get(type);
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
strategyMap.put(OrderTypeEnum.A_TYPE.getCode(), typeADiscountStrategy);
strategyMap.put(OrderTypeEnum.B_TYPE.getCode(), typeBDiscountStrategy);
strategyMap.put(OrderTypeEnum.C_TYPE.getCode(), typeCDiscountStrategy);
}
}
// Preferential strategy implementation
@Component
public class DiscountStrategyExecutor {
private DiscountStrategyFactory discountStrategyFactory;
public void discount(OrderBO orderBO) {
DiscountStrategy discountStrategy = discountStrategyFactory.getStrategy(orderBO.getType());
if (null == discountStrategy) {
throw new RuntimeException(" No preferential strategy ");
}
discountStrategy.discount(orderBO);
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
2.7.2 Arrange horizontally
The horizontal dimension represents the scene , In a broad sense, an order type can be regarded as a business scenario , Concatenate independent strategies in the scenario , The template method design pattern is suitable for this scenario .
Template method pattern generally uses abstract classes to define algorithm skeleton , At the same time, define some abstract methods , These abstract methods are deferred to subclass implementation , Such subclasses not only abide by the algorithm skeleton convention , Also implemented its own algorithm . It guarantees both the statute and flexibility , This is to build a framework with abstraction , Extend details with implementation .
// Create order service
public interface CreateOrderService {
public void createOrder(OrderBO orderBO);
}
// Abstract create order process
public abstract class AbstractCreateOrderFlow {
@Resource
private OrderMapper orderMapper;
public void createOrder(OrderBO orderBO) {
// Parameter checking
if (null == orderBO) {
throw new RuntimeException(" Parameter exception ");
}
if (OrderTypeEnum.isNotValid(orderBO.getType())) {
throw new RuntimeException(" Parameter exception ");
}
// Calculate the discount
discount(orderBO);
// Calculated weight
weighing(orderBO);
// Refund support
supportRefund(orderBO);
// Save the data
OrderDO orderDO = new OrderDO();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(orderBO, orderDO);
orderMapper.insert(orderDO);
}
public abstract void discount(OrderBO orderBO);
public abstract void weighing(OrderBO orderBO);
public abstract void supportRefund(OrderBO orderBO);
}
// Realize the order creation process
@Service
public class CreateOrderFlow extends AbstractCreateOrderFlow {
@Resource
private DiscountStrategyExecutor discountStrategyExecutor;
@Resource
private ExpressStrategyExecutor expressStrategyExecutor;
@Resource
private RefundStrategyExecutor refundStrategyExecutor;
@Override
public void discount(OrderBO orderBO) {
discountStrategyExecutor.discount(orderBO);
}
@Override
public void weighing(OrderBO orderBO) {
expressStrategyExecutor.weighing(orderBO);
}
@Override
public void supportRefund(OrderBO orderBO) {
refundStrategyExecutor.supportRefund(orderBO);
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
2.7.3 Vertical and horizontal thinking
The above example business and code are not complicated , In fact, complex business scenarios are just a superposition of simple scenarios 、 Combination and interweaving , Nothing more than isolation through vertical 、 Make horizontal arrangements to seek answers .
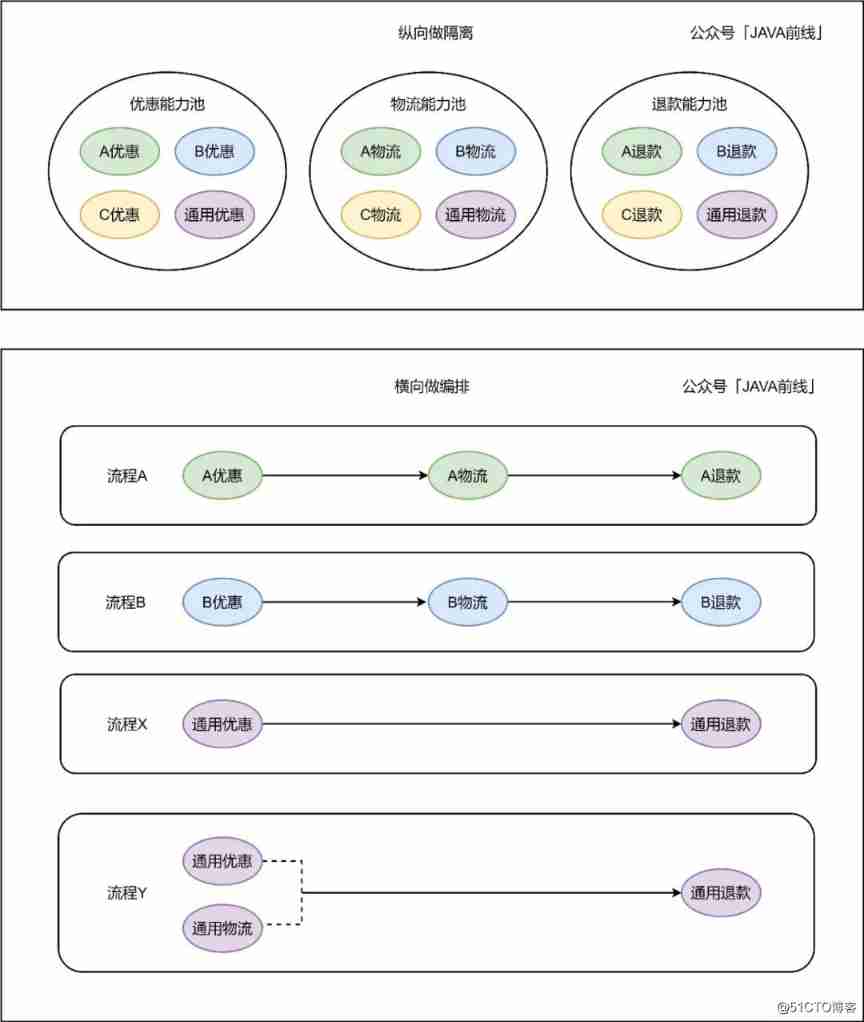
The vertical dimension abstracts the concept of capability pool , The capability pool contains many capabilities , Different capabilities are aggregated according to different business dimensions , For example, preferential capacity pool , Logistics capacity pool , Refund capability pool . We can see two levels of isolation , Capacity pools are isolated from each other , Capabilities are also isolated from each other .
The horizontal dimension selects capabilities from the capability pool , In line with business needs , Form different business processes . Because abilities can be combined arbitrarily , So it reflects a strong flexibility . besides , Different capabilities can be executed serially , If there is no dependency between different abilities , It can also be like a process Y Same parallel execution , Improve execution efficiency .
3 Article summary
First, this paper distinguishes between complex 、 multifarious 、 The complex group of concepts , Complex and complicated, although they are relatively difficult to deal with , But complexity can be sorted out , And the complexity will eventually accumulate . We should try to avoid complicated code . Complexity and complexity, coupled with the quantitative dimension, become complex .
Second, this paper introduces seven types of code coupling , According to the degree of coupling, the order is : Content coupling 、 Public coupling 、 External coupling 、 Control coupling 、 Tag coupling 、 Data coupling and indirect coupling . We should try to write code with low coupling .
Thirdly, this paper starts with an example of a complex order scenario , The indirect coupling type is mainly introduced , You can see even complex scenes , It can also be achieved gracefully through reasonable design , I hope this article can help you .
Out of order ! Out of order !
Java There are many excellent partners in Geek technology wechat group discussing Technology , Occasionally, there are irregular information sharing and red envelope distribution ! If you want to improve yourself , And want to make progress with excellent people , Interested friends , You can reply in the background of the official account below : Add group .
边栏推荐
- 【大型电商项目开发】性能压测-性能监控-堆内存与垃圾回收-39
- Discrete mathematics: propositional symbolization of predicate logic
- Research Report on the overall scale, major producers, major regions, products and application segmentation of agricultural automatic steering system in the global market in 2022
- POAP:NFT的采用入口?
- 揭露测试外包公司,关于外包,你或许听到过这样的声音
- dotnet-exec 0.6.0 released
- node工程中package.json文件作用是什么?里面的^尖括号和~波浪号是什么意思?
- Apifox (postman + swagger + mock + JMeter), an artifact of full stack development and efficiency improvement
- 107. Some details of SAP ui5 overflow toolbar container control and resize event processing
- 实战模拟│JWT 登录认证
猜你喜欢
Take you ten days to easily complete the go micro service series (IX. link tracking)
JS implementation determines whether the point is within the polygon range

测试部新来了个00后卷王,上了年纪的我真的干不过了,已经...
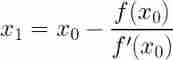
Visual explanation of Newton iteration method
Playwright recording
Roads and routes -- dfs+topsort+dijkstra+ mapping
资深测试/开发程序员写下无bug?资历(枷锁)不要惧怕错误......
各大主流编程语言性能PK,结果出乎意料

Arbitrum: two-dimensional cost

Chia Tai International Futures: what is the master account and how to open it?
随机推荐
107. SAP UI5 OverflowToolbar 容器控件以及 resize 事件处理的一些细节介绍
微信小程序:微群人脉微信小程序源码下载全新社群系统优化版支持代理会员系统功能超高收益
FEG founder rox:smartdefi will be the benchmark of the entire decentralized financial market
Daily question brushing record (13)
What you learned in the eleventh week
大专学历,33岁宝妈又怎样?我照样销售转测试,月入13k+
Talking about JVM 4: class loading mechanism
创新引领方向 华为智慧生活全场景新品齐发
抓包整理外篇——————状态栏[ 四]
[FPGA tutorial case 9] design and implementation of clock manager based on vivado core
Innovation leads the direction. Huawei Smart Life launches new products in the whole scene
Playwright之录制
pycharm专业版下载安装教程
微信小程序:全新独立后台月老办事处一元交友盲盒
Package What is the function of JSON file? What do the inside ^ angle brackets and ~ tilde mean?
资深测试/开发程序员写下无bug?资历(枷锁)不要惧怕错误......
POAP:NFT的采用入口?
[Yocto RM]10 - Images
Redis(1)之Redis简介
微信小程序:星宿UI V1.5 wordpress系统资讯资源博客下载小程序微信QQ双端源码支持wordpress二级分类 加载动画优化