当前位置:网站首页>FAQs and answers to the imitation Niuke technology blog project (II)
FAQs and answers to the imitation Niuke technology blog project (II)
2022-07-06 13:37:00 【Li bohuan】
Take the book back : FAQs and answers of the imitation Niuke technology blog project ( One )_ Li bohuan's blog -CSDN Blog
8. Which part of the project is used aop 了
When processing logs uniformly in the project , Yes AOP.

If we record logs in every business component , Then there will be a lot of duplicate code . If we adopt OOP Thought , Encapsulate the function of logging into a bean To call , Then there will be problems of high coupling . Because logging itself is not a business requirement , It belongs to system requirements , So we should not couple business requirements with system requirements , At this time, we need to use AOP To deal with it .
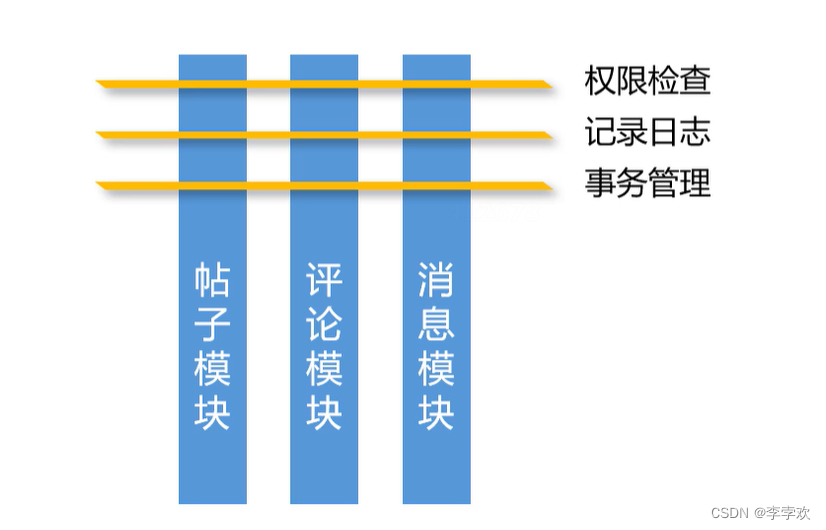

Target It is one by one of the business logic we have developed bean, We call it the target , There are many places on the target object that can be woven into code , Places that can be woven into code are collectively referred to as join points joinpoint.AOP The way to solve the unified processing system requirements is to define the code into an additional bean, It's called section component Aspect, This component needs to be woven into some connection points by the framework before the program runs . Section component pointcut Declare where to weave , notice Advice Method declaration aspect to deal with what kind of logic .

Specific use :
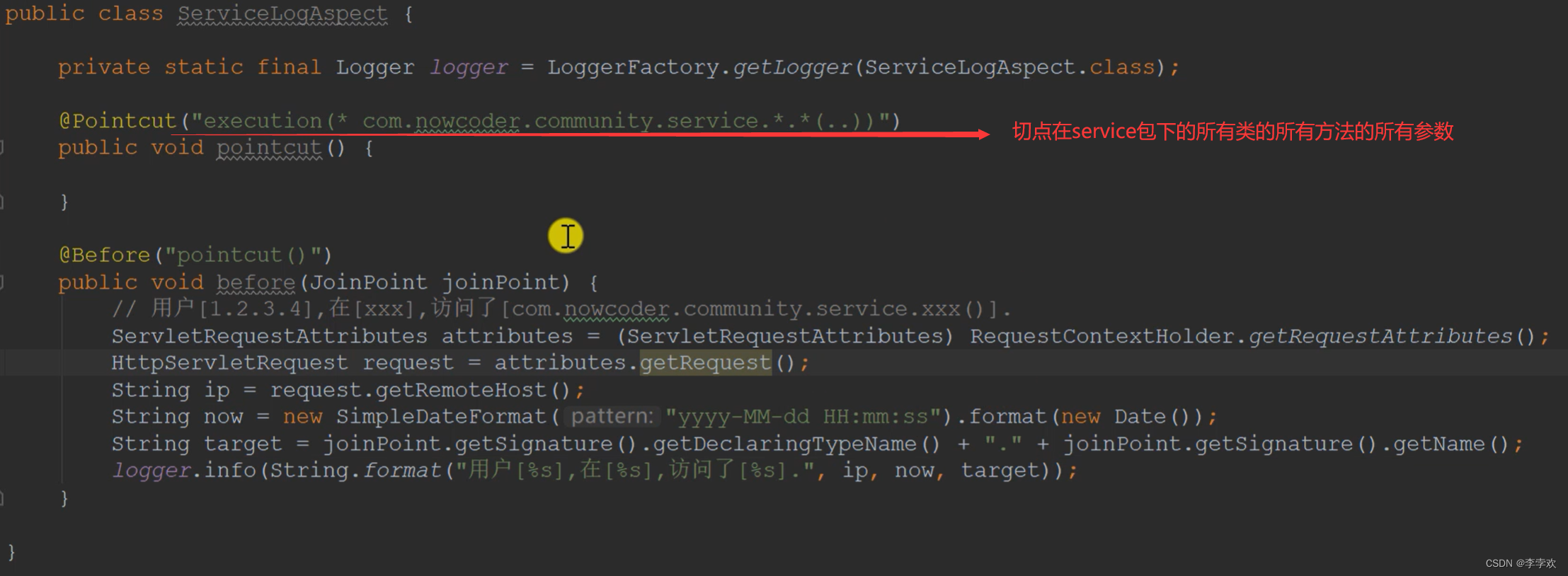
before Code pre notification , Weave the program at the beginning .
9. In the project redis How to use the
Cache praise and attention :
1、Redis Cache user likes String type , To the user ID by key, When you like , Self increasing , Cancel like , Self reduction ;
Cache entity likes ,set type , Add to the list when users like entities , When you cancel the like, remove , Last use size Statistics ;
2、 Cache fan list , Use zset, Deposited into fans id And the timestamp of interest , Use zCard Number of fans obtained . utilize reverseRange Timestamp reverse sort , Load the fan list according to the following time .
Optimize login :
1、 Use Redis Cache user information . take user The cache to Redis in , obtain user when , First from Redis obtain . I can't get it , Query from the database , Cache to Redis in . Because many interfaces are used user Information , Concurrent , Frequent access to databases , It will cause the database to crash . When changing the database , Update the database first , Then empty the cache ;
2、 Use Redis Cache verification code . Originally added to session in , Reduce server pressure . Save verification code to Redis in , Convenient for inquiry and inspection ;
- Captcha needs frequent access and refresh , High performance requirements ;
- The verification code does not need to be permanently stored , It usually fails in a very short time ;
- Distributed deployment , There is session Sharing issues ;
3、 Login credentials : Originally added to MySQL in , To reduce the pressure of querying the database every time you log in , The login credentials ticket cached Redis in , Prevent the database from being queried every time , Improve concurrency . When logging out , The login credentials in the database were originally to be modified , Now you just need to modify Redis that will do .
10.redis Of key How to design ?
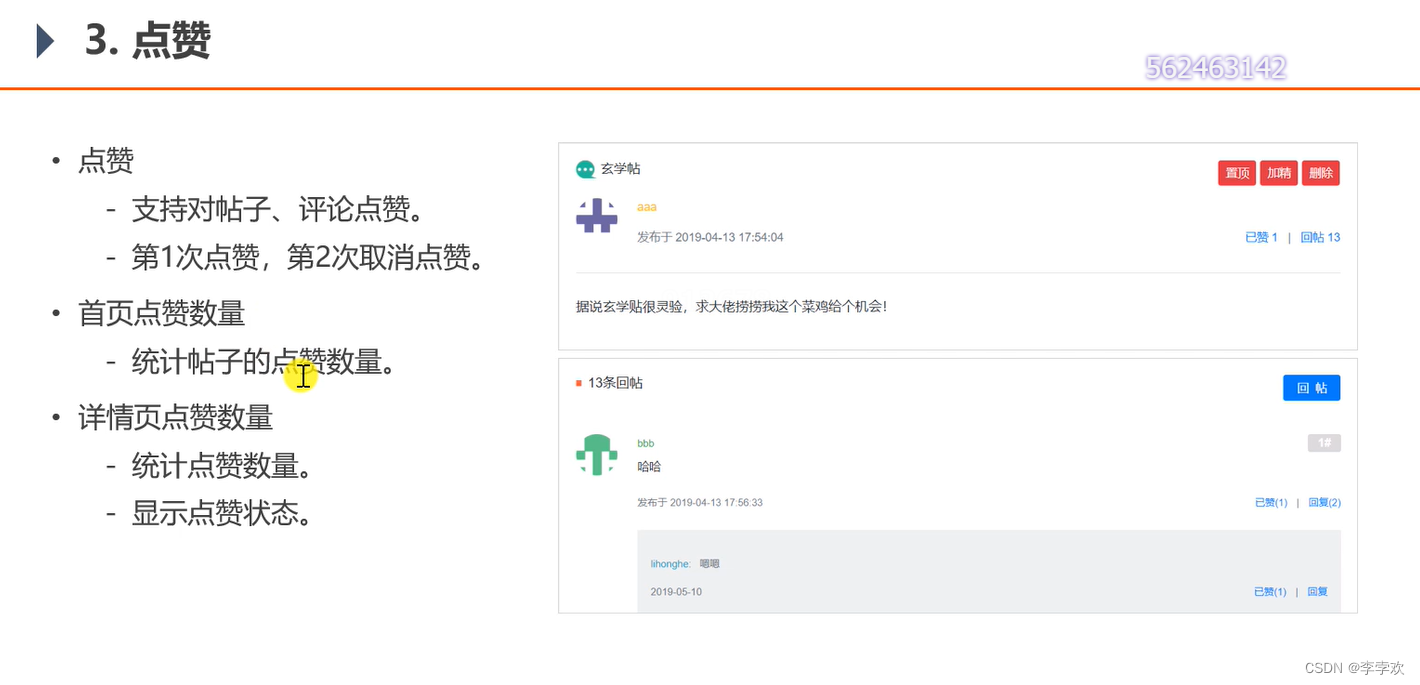
redis Of key yes String Type of , Write a tool class to generate redis Of key.key It is composed of several words , The middle is separated by colons , Some words are fixed , Some words are dynamic , The design method is as follows :
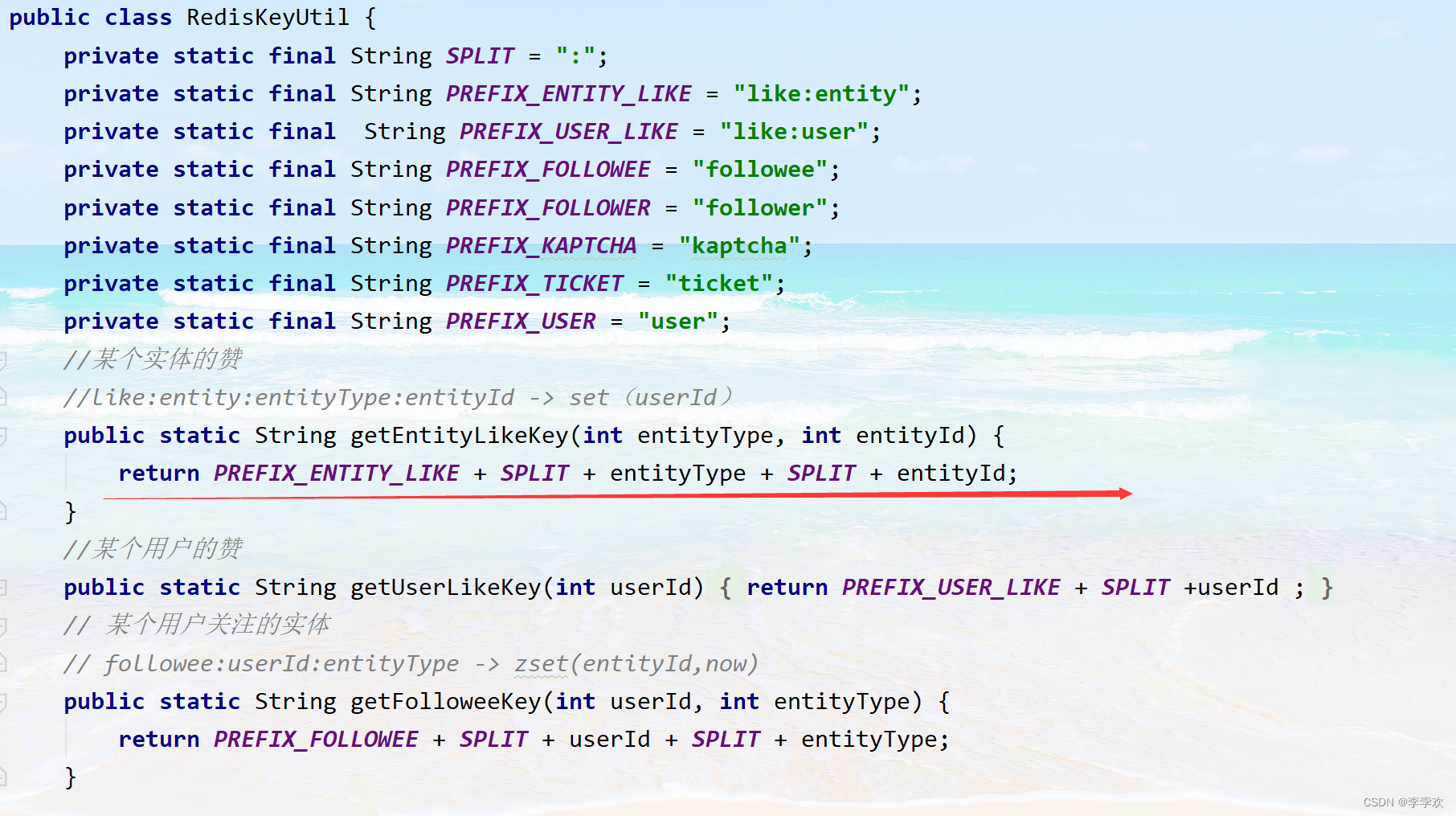
Here, for example, the favor of an entity adopts set To deposit , Deposit is userId, In this way, you can get everyone who likes you , And quantity .
Here users like int save , It is equal to the user entity ( post + Comment on ) The total number of likes received .

Both the entities concerned and the fans owned by the entities use zset save .set Save followers and follow for score
Cache user data usage Value type ,key For use userID Got key,value by user object ( Set expiration time , And the cache needs to be cleared when data is modified )
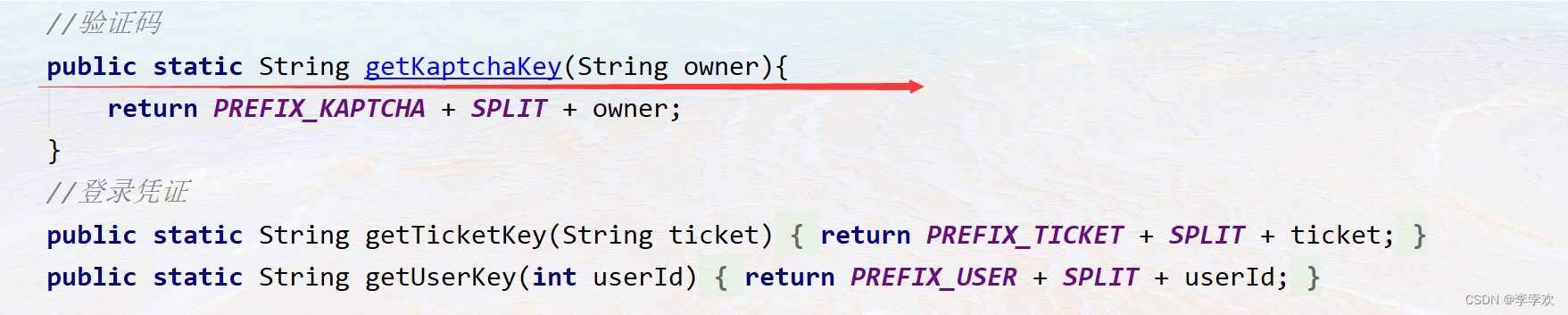 The verification code is with user dependent , But here we can't directly transmit userId, Because I haven't logged in , We don't know who the user is . Here comes a string owner, This is when the user visits the login page , Send him a voucher ( Random string ), Deposit in cookie in , As shown in the figure below .
The verification code is with user dependent , But here we can't directly transmit userId, Because I haven't logged in , We don't know who the user is . Here comes a string owner, This is when the user visits the login page , Send him a voucher ( Random string ), Deposit in cookie in , As shown in the figure below .

Use it from cookie Inside this owner out , Get in rediskey, Then get the verification code , Compare with the entered verification code .
11. How to cache likes
Post and comment likes are saved together , Collectively referred to as entity likes . You also need to count users' likes ( The sum of likes received by users' posts and comments ) As shown in the figure below . Because it's too troublesome to count the likes of all users' posts and comments and get the likes of users , So here is the user ID use rediskey The tool splicing is key Record the number of likes ( This will involve transaction operations . The number of likes of users' posts or comments increases, and the likes of corresponding users should increase )

Concrete realization : Use redis To store likes , First, we need to construct redis Of key, As shown in the following figure
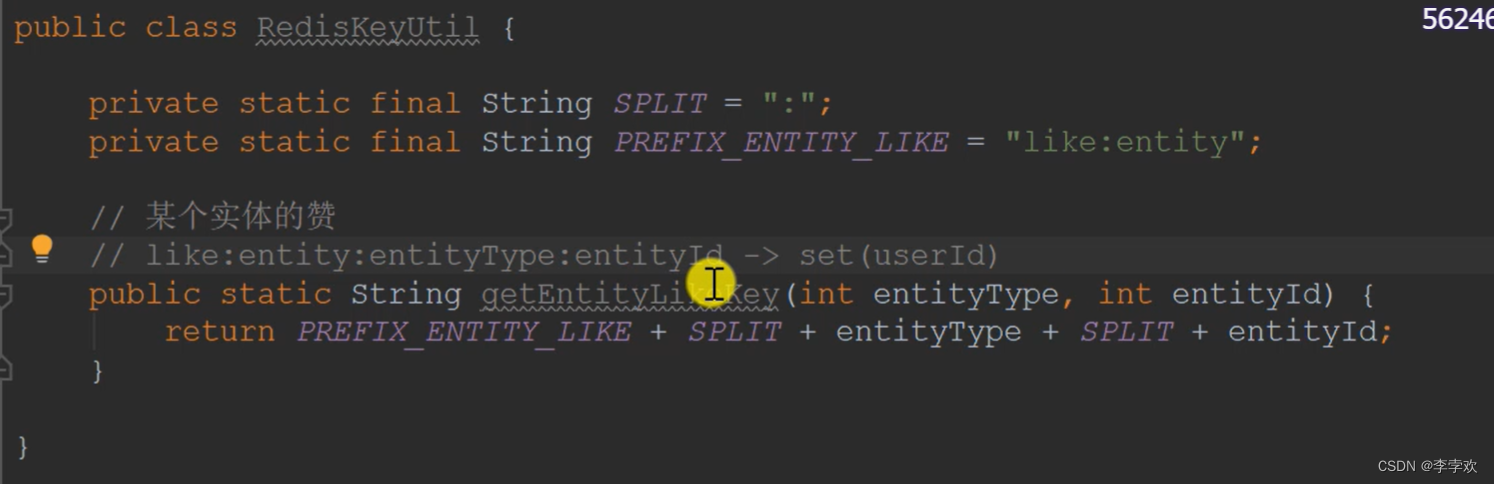
Mainly considering this entityType( Post or comment ) and entityId( Goals under this type ) Determine the entity type and id
and redis Value usage of set Type instead of a simple integer , This is mainly for possible demand changes , For example, I want to see who likes me . In the collection userid. The value of users' likes is value
Like to use set Type storage ,key For likes ,set Save likes in ID
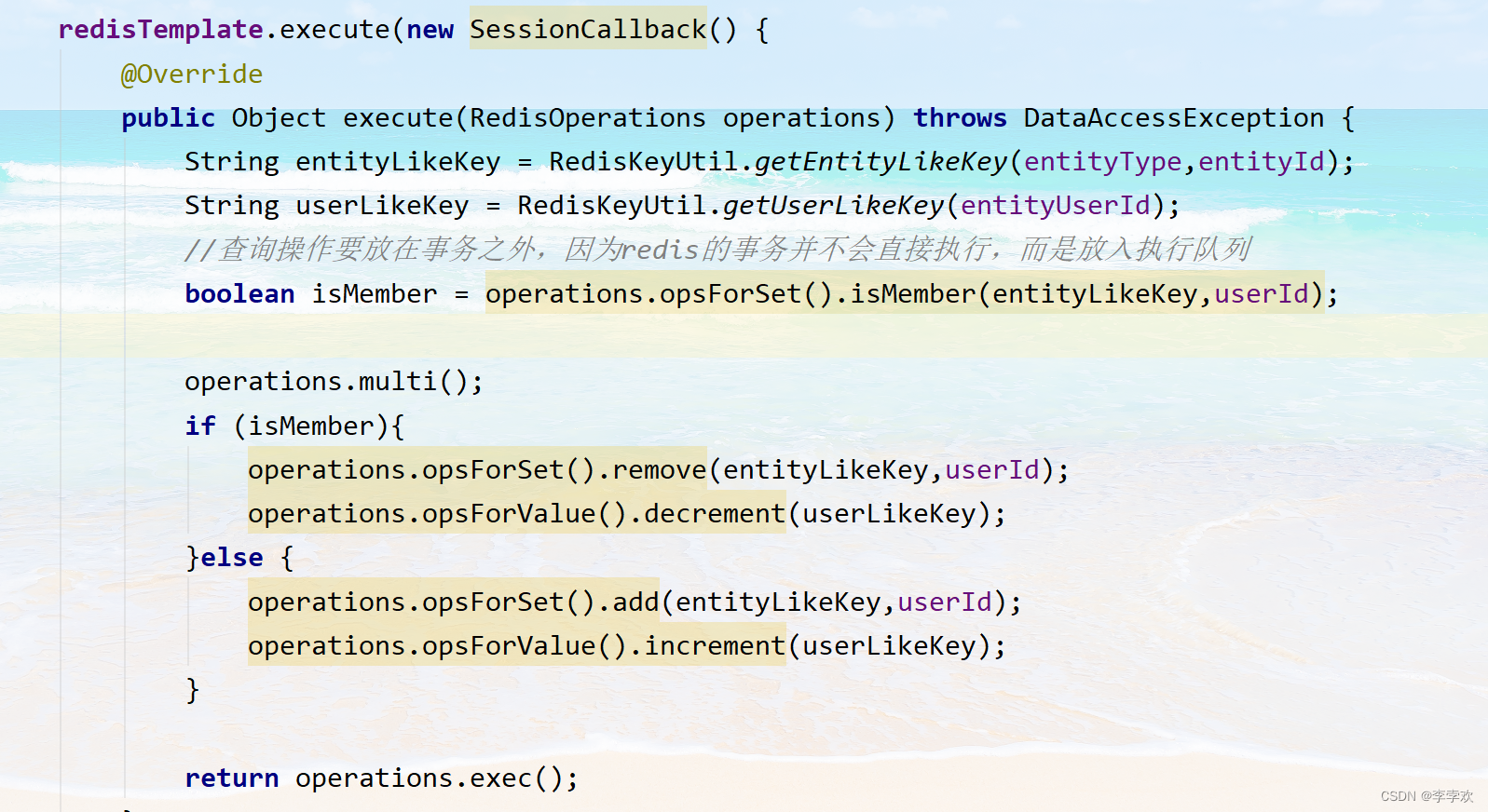
When you like, you need to judge whether the user has liked : adopt redistemplate.opsforSet().ismember Method If you have already liked, delete the likes record Otherwise add data . Transaction operations are used here Rewrote execute Method
You also need to query the number and status of likes of an entity :
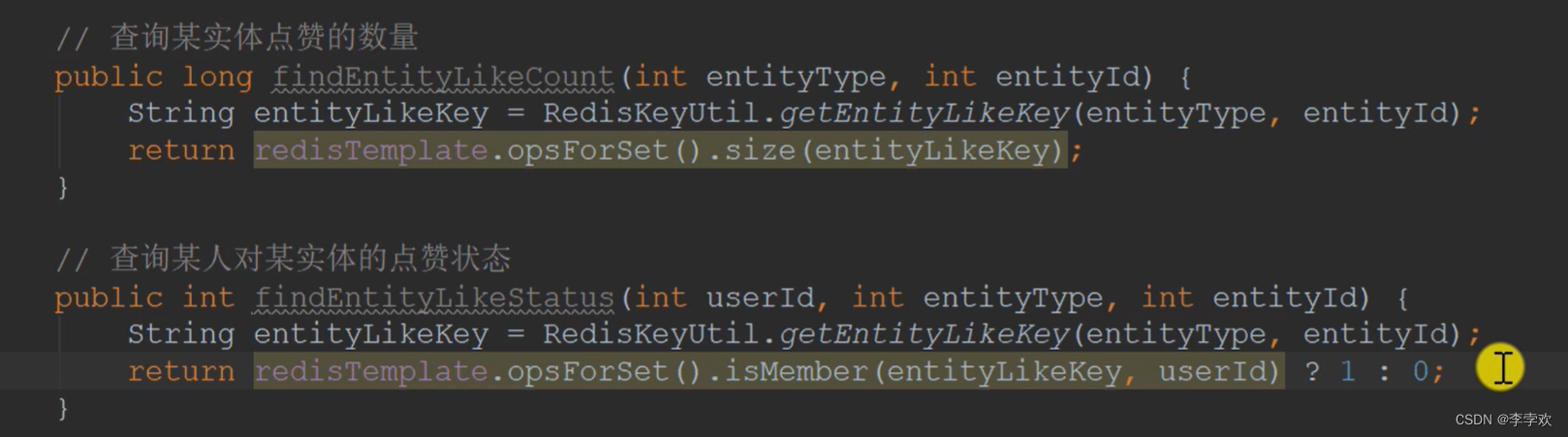
There is no Boolean value for the like status here in order to develop new functions later , For example, it can be used by stepping -1;
12 How to ensure redis And database consistency ?
There are only redis This problem only occurs when you save user information !! because redis For likes 、 Focus on 、 For functions such as user credentials and authentication codes, they are used as database To use , So there is no such problem .
As long as we use Redis cache , It is bound to face the problem of consistency assurance between cache and database , This is also a Redis Caching applications “ Will answer ” 了 . most important of all , If the data is inconsistent , Then the data read by the business application from the cache is not the latest data , This can lead to serious errors . for instance , We cache the inventory information of e-commerce products in Redis in , If the inventory information is incorrect , Then the order placing operation of the business layer may be wrong , This is certainly unacceptable .
How does data inconsistency between cache and database happen ? First , We need to know “ Data consistency ” What exactly does it mean . Actually , there “ Uniformity ” There are two cases :
- 1. Data in cache , that , The cached data value needs to be the same as the value in the database ;
- 2. There is no data in the cache itself , that , The value in the database must be the latest value .
- Not in both cases , It belongs to the problem of inconsistent data between the cache and the database . however , When the read and write modes of the cache are different , The occurrence of cache data inconsistency is different , Our response will be different , therefore , Let's first follow the cache read-write mode , To understand cache inconsistencies in different modes .
about Read write buffer Come on , If you want to add, delete or modify the data , You need to do it in the cache , At the same time, according to the writeback strategy , Decide whether to write back to the database synchronously .
- 1. Synchronous write through strategy : Write cache , Also write to the database synchronously , The cache is consistent with the data in the database ;
- 2. Asynchronous writeback policy : Write to the database is not synchronized when writing to the cache , Wait until the data is eliminated from the cache , Write back to the database . When using this strategy , If the data has not been written back to the database , The cache fails , that , here , There is no latest data in the database .
therefore , For read-write caching , To ensure the consistency between the cache and the data in the database , We're going to use Synchronous write through strategy . however , It should be noted that , If you use this strategy , You need to update the cache and database at the same time . therefore , We want to use transaction mechanism in business applications , To ensure that the cache and database updates are atomic , in other words , The two are not updated together , Or don't update , Return error message , retry . otherwise , We can't achieve synchronous write through . Of course , In some cases , Our requirements for data consistency may not be so high , For example, it caches the non key attributes of e-commerce products or the creation or modification time of short videos , that , We can use an asynchronous writeback policy .
Now let's talk about read-only cache . For a read-only cache , If there is new data , Will be written directly to the database ; When there is data deletion and modification , You need to mark the data in the read-only cache as invalid . thus , When the application accesses these added, deleted and modified data later , Because there is no corresponding data in the cache , A cache miss occurs . here , The application then reads the data from the database into the cache , So when you access the data later , You can read directly from the cache .
In the project redis When storing user information , It's read-only mode , Look at the code :
 First take... From the cache , Direct return if any , If not, initialize ( Get from the database and store it in the cache ), Then return .
First take... From the cache , Direct return if any , If not, initialize ( Get from the database and store it in the cache ), Then return .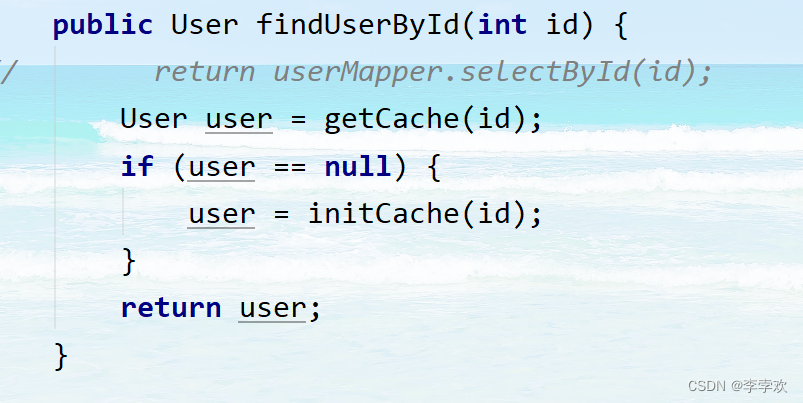
Then in the case of read-only , Will there be data inconsistency in this process ? Considering the difference between adding data and deleting data , So let's look at it separately .
If it is new data , The data will be written directly to the database , You don't have to do anything with the cache , here , There is no new data in the cache itself , And the database is the latest value , here , The cache and database data are consistent .
If deletion occurs , The application needs to update the database , Also delete data from the cache . There are two problems ( Under the premise of the previous element achievement )

We use the second case in the project , That is, update the database value first , Then delete the cache , Pictured :
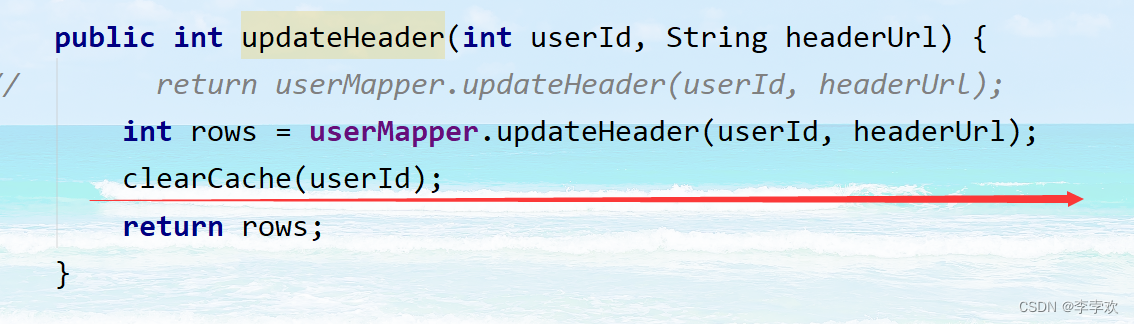 The main reason why you don't choose to delete the cache first is that it may cause requests to access the database due to missing cache , Put pressure on the database
The main reason why you don't choose to delete the cache first is that it may cause requests to access the database due to missing cache , Put pressure on the database
How to solve the problem of data inconsistency ?
Data inconsistency between cache and database is generally caused by two reasons , Provides the corresponding solution .
- Data inconsistency caused by failure to delete cache value or update database , You can use the retry mechanism to ensure that the delete or update operation is successful .
- Delete cache value 、 In these two steps of updating the database , Yes Concurrent read operations of other threads , Cause other threads to read the old value , The solution is to delay double deletion .
Retry mechanism : say concretely , The cache value to be deleted or the database value to be updated can be temporarily stored in the message queue . When the application fails to successfully delete the cache value or update the database value , These values can be re read from the message queue , then Delete or update again . If you can successfully delete or update , We need to remove these values from the message queue , So as not to repeat the operation , here , We can also ensure that the database and cached data are consistent . Otherwise , We need to try again . If you retry more than a certain number of times , Still no success , We need to send an error message to the business layer .
Delay double delete : Generally used in So let's delete the cache , Update the multithreaded concurrent access of the database . This is because , Update the database values first , Then delete the cached value , If the thread A Deleted the value in the database , But I haven't had time to delete the cache value , Threads B Start reading data , So at this time , Threads B When querying the cache , Find cache hits , It will be read directly from the cache The old value . however , under these circumstances , If there are few concurrent requests from other threads to read the cache , that , There won't be many requests to read old values . and , Threads A Generally, the cache value will be deleted soon , thus , When another thread reads again , A cache miss occurs , Then read the latest value from the database . therefore , This situation has little impact on the business .
And suppose threads A After deleting the cached value , I haven't had time to update the database yet ( For example, there are network delays ), Threads B Start reading data , So at this point , Threads B You will find that the cache is missing , You can only read from the database . This brings two questions :
- Threads B Old value read ;
- Threads B Is the database read when the cache is missing , therefore , It also writes old values to the cache , This may cause other threads to read old values from the cache .
Wait until the thread B Finished reading data from the database 、 After updating the cache , Threads A Just started updating the database , here , The data in the cache is old , And in the database is the latest value , The two are inconsistent .
In this case, we use delayed double deletion to solve it : In a thread A After updating the database values , We can let it first sleep For a short time , Do another cache delete operation . Why add sleep During this period of time , Just to make the thread B Be able to read data from the database first , Then write the missing data to the cache , then , Threads A Then delete , In this way, there is another thread to read , There won't be what we said above , Threads A Updated database , But I found that the cache value is inconsistent with the database .
The summary is shown in the figure :
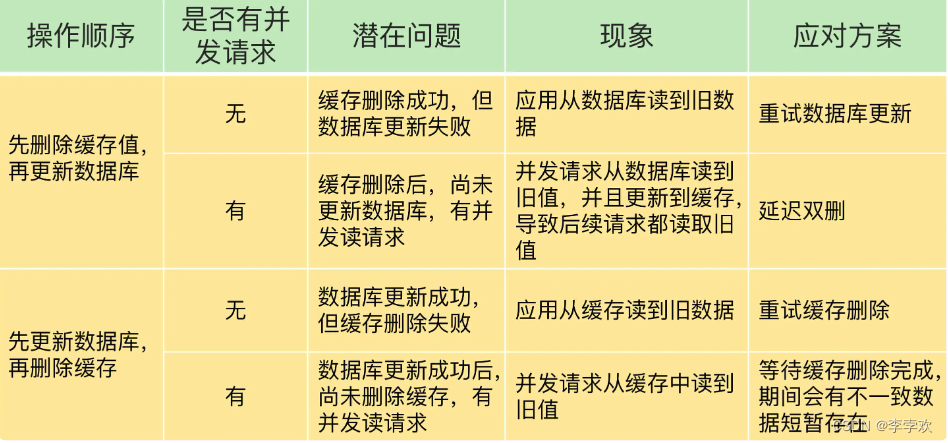
Reference material : Geek time Geek time - Easy to learn , Efficient learning - Geek state (geekbang.org) redis Core technology and actual combat
边栏推荐
- 自定义RPC项目——常见问题及详解(注册中心)
- [modern Chinese history] Chapter V test
- 【九阳神功】2020复旦大学应用统计真题+解析
- string
- Alibaba cloud microservices (IV) service mesh overview and instance istio
- E-R graph to relational model of the 2022 database of tyut Taiyuan University of Technology
- View UI plus released version 1.2.0 and added image, skeleton and typography components
- Set container
- 西安电子科技大学22学年上学期《基础实验》试题及答案
- ABA问题遇到过吗,详细说以下,如何避免ABA问题
猜你喜欢
(ultra detailed onenet TCP protocol access) arduino+esp8266-01s access to the Internet of things platform, upload real-time data collection /tcp transparent transmission (and how to obtain and write L
Arduino+ds18b20 temperature sensor (buzzer alarm) +lcd1602 display (IIC drive)
C语言入门指南

8. C language - bit operator and displacement operator

西安电子科技大学22学年上学期《基础实验》试题及答案
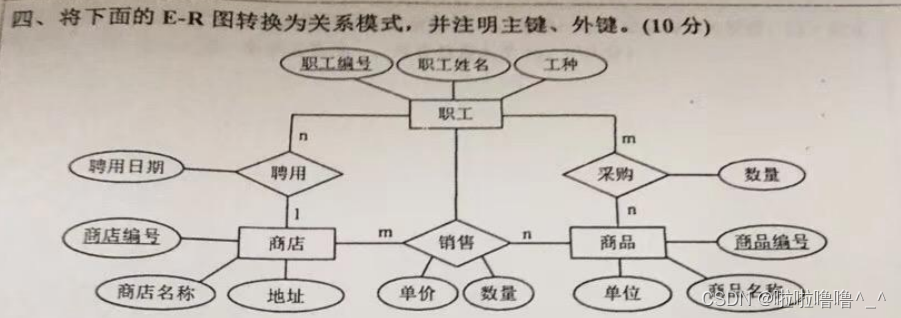
E-R graph to relational model of the 2022 database of tyut Taiyuan University of Technology
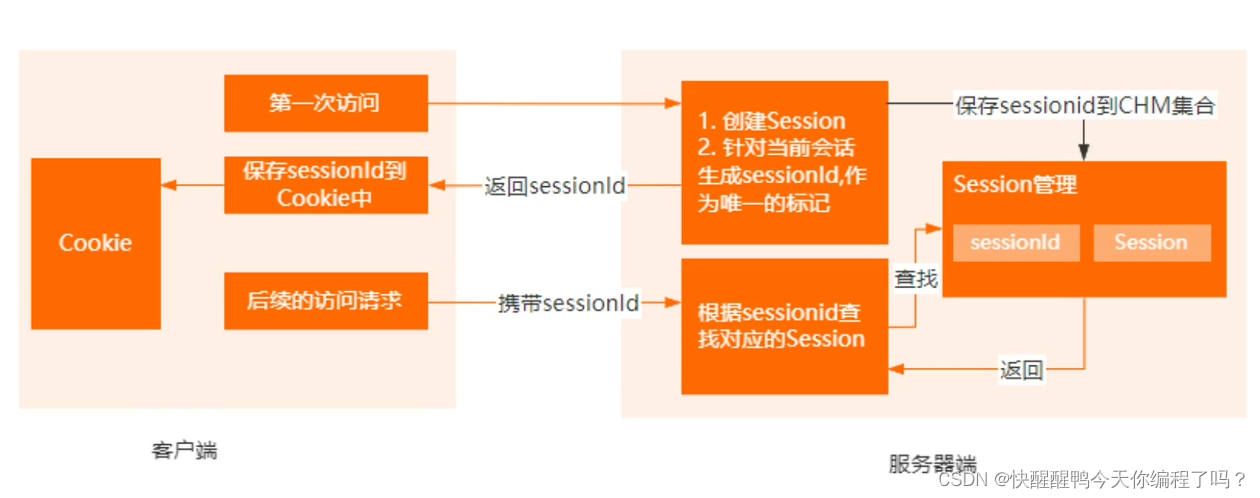
Cookie和Session的区别
Conceptual model design of the 2022 database of tyut Taiyuan University of Technology
Pit avoidance Guide: Thirteen characteristics of garbage NFT project
关于双亲委派机制和类加载的过程
随机推荐
2.C语言矩阵乘法
Smart classroom solution and mobile teaching concept description
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2018 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
魏牌:产品叫好声一片,但为何销量还是受挫
2.初识C语言(2)
Redis实现分布式锁原理详解
Pit avoidance Guide: Thirteen characteristics of garbage NFT project
3.猜数字游戏
【九阳神功】2022复旦大学应用统计真题+解析
1.初识C语言(1)
Conceptual model design of the 2022 database of tyut Taiyuan University of Technology
fianl、finally、finalize三者的区别
更改VS主题及设置背景图片
Set container
string
ABA问题遇到过吗,详细说以下,如何避免ABA问题
View UI plus released version 1.3.1 to enhance the experience of typescript
View UI plus released version 1.3.0, adding space and $imagepreview components
【九阳神功】2020复旦大学应用统计真题+解析
编写程序,模拟现实生活中的交通信号灯。