当前位置:网站首页>[the Nine Yang Manual] 2016 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2016 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
2022-07-06 13:30:00 【Elder martial brother statistics】
Catalog
The real part
One 、(15 branch ) Three people decipher the code independently at the same time , And the probability that three people can decipher the password is 1/5, 1/3 and 1/4, Find the probability that this password can be decoded .
Two 、(15 branch ) from (0,1) Take two numbers randomly in , Find that the product is not less than 3/16 And its sum is not greater than 1 Probability .
3、 ... and 、(15 branch ) X ∼ N ( 0 , 1 ) , X \sim N(0,1), X∼N(0,1), seek Y = X 2 Y=X^{2} Y=X2 Density function of .
Four 、(30 branch ) remember (0,1),(1,0),(0,0) The area enclosed by three points is D , ( X , Y ) D,(X, Y) D,(X,Y) obey D D D Even distribution on , seek
(1)(15 branch ) E ( X + Y ) , Var ( X + Y ) E(X+Y), \operatorname{Var}(X+Y) E(X+Y),Var(X+Y);
(2)(15 branch ) X , Y X, Y X,Y The correlation coefficient of .
5、 ... and 、(15 branch ) For two random variables with only two values X , Y , X, Y, X,Y, Try to prove X , Y X, Y X,Y Independent if and only if X , Y X, Y X,Y Unrelated .
6、 ... and 、(15 branch ) Set from the overall X ∼ N ( μ , σ 2 ) X \sim N\left(\mu, \sigma^{2}\right) X∼N(μ,σ2) Of 2 n 2 n 2n Random sample , Try to expect
E ( ∑ i = 1 n ( X i + X n + i − 2 X ˉ ) 2 ) . E\left(\sum_{i=1}^{n}\left(X_{i}+X_{n+i}-2 \bar{X}\right)^{2}\right). E(i=1∑n(Xi+Xn+i−2Xˉ)2).
7、 ... and 、(15 branch ) X 1 , X 2 , X 3 X_{1}, X_{2}, X_{3} X1,X2,X3 yes i.i.d. To obey U ( 0 , 1 ) U(0,1) U(0,1) Random variable of , Find order statistics X ( 1 ) X_{(1)} X(1) Distribution function and expectation of .
8、 ... and 、(30 branch ) From X ∼ f ( x ) = { θ , 0 ≤ x < 1 1 − θ , 1 ≤ x < 2 , 0 , otherwise X \sim f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cl}\theta, & 0 \leq x<1 \\ 1-\theta, & 1 \leq x<2, \\ 0, & \text { otherwise }\end{array}\right. X∼f(x)=⎩⎨⎧θ,1−θ,0,0≤x<11≤x<2, otherwise Of n n n A simple random sample , seek
(1)(15 branch ) θ \theta θ The moment estimate of ;
(2)(15 branch ) θ \theta θ Maximum likelihood estimation of , It is known that m = ∑ i = 1 n I [ X i < 1 ] m=\sum_{i=1}^{n} I\left[X_{i}<1\right] m=∑i=1nI[Xi<1].
The analysis part
One 、(15 branch ) Three people decipher the code independently at the same time , And the probability that three people can decipher the password is 1/5, 1/3 and 1/4, Find the probability that this password can be decoded .
Solution: According to de Morgan formula , P { At least one person decoded } = 1 − P { No one decoded } = 1 − 4 5 × 2 3 × 3 4 = 0.6. \begin{aligned} P\{\text { At least one person decoded }\} &=1-P\{\text { No one decoded }\} \\ &=1-\frac{4}{5} \times \frac{2}{3} \times \frac{3}{4}=0.6 . \end{aligned} P{ At least one person decoded }=1−P{ No one decoded }=1−54×32×43=0.6.
Two 、(15 branch ) from (0,1) Take two numbers randomly in , Find that the product is not less than 3/16 And its sum is not greater than 1 Probability .
Solution: Let the two numbers obtained be X , Y ∼ U ( 0 , 1 ) X, Y \sim U(0,1) X,Y∼U(0,1), Its product is not less than 3 16 \frac{3}{16} 163 signify X Y ≥ 3 16 X Y \geq \frac{3}{16} XY≥163, Its sum is not greater than 1 signify X + Y ≤ 1 X+Y \leq 1 X+Y≤1.
Make D = { ( x , y ) : x y ≥ 3 16 , x + y ≤ 1 } ∩ ( 0 , 1 ) 2 D=\left\{(x, y): x y \geq \frac{3}{16}, x+y \leq 1\right\} \cap(0,1)^{2} D={ (x,y):xy≥163,x+y≤1}∩(0,1)2, The probability is ∫ D f ( x , y ) d x d y = 1 8 − ∫ 1 4 3 4 ∫ 1 4 3 16 x d y d x = 1 8 − ∫ 1 4 3 4 ( 3 16 x − 1 4 ) d x = 1 4 − 3 ln 3 16 \int_{D} f(x, y) d x d y=\frac{1}{8}-\int_{\frac{1}{4}}^{\frac{3}{4}} \int_{\frac{1}{4}}^{\frac{3}{16 x}} d y d x=\frac{1}{8}-\int_{\frac{1}{4}}^{\frac{3}{4}}\left(\frac{3}{16 x}-\frac{1}{4}\right) d x=\frac{1}{4}-\frac{3 \ln 3}{16} ∫Df(x,y)dxdy=81−∫4143∫4116x3dydx=81−∫4143(16x3−41)dx=41−163ln3
3、 ... and 、(15 branch ) X ∼ N ( 0 , 1 ) , X \sim N(0,1), X∼N(0,1), seek Y = X 2 Y=X^{2} Y=X2 Density function of .
Solution: When y ≥ 0 y \geq 0 y≥0 when ,
F ( y ) = P { Y ≤ y } = P { X 2 ≤ > y } = P { − y ≤ X ≤ y } = 2 Φ ( y ) − 1 F(y)=P\{Y \leq y\}=P\left\{X^{2} \leq>y\right\}=P\{-\sqrt{y} \leq X \leq \sqrt{y}\}=2 \Phi(\sqrt{y})-1 F(y)=P{ Y≤y}=P{ X2≤>y}=P{ −y≤X≤y}=2Φ(y)−1, so
f Y ( y ) = F ′ ( y ) = 2 φ ( y ) ⋅ 1 2 y = 1 2 π y e − y 2 , y ≥ 0 f_{Y}(y)=F^{\prime}(y)=2 \varphi(\sqrt{y}) \cdot \frac{1}{2 \sqrt{y}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi y}} e^{-\frac{y}{2}}, y \geq 0 fY(y)=F′(y)=2φ(y)⋅2y1=2πy1e−2y,y≥0
Four 、(30 branch ) remember (0,1),(1,0),(0,0) The area enclosed by three points is D , ( X , Y ) D,(X, Y) D,(X,Y) obey D D D Even distribution on , seek
(1)(15 branch ) E ( X + Y ) , Var ( X + Y ) E(X+Y), \operatorname{Var}(X+Y) E(X+Y),Var(X+Y);
(2)(15 branch ) X , Y X, Y X,Y The correlation coefficient of .
Solution: (1) E ( X + Y ) = 2 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 − y ( x + y ) d x d y = ∫ 0 1 ( 1 − y 2 ) d y = 1 − 1 3 = 2 3 E(X+Y)=2 \int_{0}^{1} \int_{0}^{1-y}(x+y) d x d y=\int_{0}^{1}\left(1-y^{2}\right) d y=1-\frac{1}{3}=\frac{2}{3} E(X+Y)=2∫01∫01−y(x+y)dxdy=∫01(1−y2)dy=1−31=32, E ( X + Y ) 2 = 2 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 − y ( x + y ) 2 d x d y = 2 3 ∫ 0 1 ( 1 − y 3 ) d y = 2 3 ( 1 − 1 4 ) = 1 2 , E(X+Y)^{2}=2 \int_{0}^{1} \int_{0}^{1-y}(x+y)^{2} d x d y=\frac{2}{3} \int_{0}^{1}\left(1-y^{3}\right) d y=\frac{2}{3}\left(1-\frac{1}{4}\right)=\frac{1}{2}, E(X+Y)2=2∫01∫01−y(x+y)2dxdy=32∫01(1−y3)dy=32(1−41)=21, therefore
Var ( X + Y ) = 1 2 − 4 9 = 1 18 . \operatorname{Var}(X+Y)=\frac{1}{2}-\frac{4}{9}=\frac{1}{18}. Var(X+Y)=21−94=181.(2) E X Y = 2 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 − y x y d x d y = ∫ 0 1 ( y 3 − 2 y 2 + y ) d y = 1 4 − 2 3 + 1 2 = 1 12 E X Y=2 \int_{0}^{1} \int_{0}^{1-y} x y d x d y=\int_{0}^{1}\left(y^{3}-2 y^{2}+y\right) d y=\frac{1}{4}-\frac{2}{3}+\frac{1}{2}=\frac{1}{12} EXY=2∫01∫01−yxydxdy=∫01(y3−2y2+y)dy=41−32+21=121, E X = E Y = 2 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 − y x d x d y = ∫ 0 1 ( y 2 − 2 y + 1 ) d y = 1 3 − 1 + 1 = 1 3 , E X=E Y=2 \int_{0}^{1} \int_{0}^{1-y} x d x d y=\int_{0}^{1}\left(y^{2}-2 y+1\right) d y=\frac{1}{3}-1+1=\frac{1}{3}, EX=EY=2∫01∫01−yxdxdy=∫01(y2−2y+1)dy=31−1+1=31, so
Cov ( X , Y ) = 1 12 − 1 9 = − 1 36 . \operatorname{Cov}(X, Y)=\frac{1}{12}-\frac{1}{9}=-\frac{1}{36}. Cov(X,Y)=121−91=−361. E X 2 = 2 ∫ 0 1 ∫ 0 1 − y x 2 d x d y = 2 3 ∫ 0 1 ( 1 − y ) 3 d y = 1 6 , E X^{2}=2 \int_{0}^{1} \int_{0}^{1-y} x^{2} d x d y=\frac{2}{3}\int_{0}^{1}(1-y)^{3} d y=\frac{1}{6}, EX2=2∫01∫01−yx2dxdy=32∫01(1−y)3dy=61, so Var ( X ) = Var ( Y ) = 1 6 − 1 9 = 1 18 , \operatorname{Var}(X)=\operatorname{Var}(Y)=\frac{1}{6}-\frac{1}{9}=\frac{1}{18}, Var(X)=Var(Y)=61−91=181, And then there are ρ X Y = − 1 2 \rho_{X Y}=-\frac{1}{2} ρXY=−21.
5、 ... and 、(15 branch ) For two random variables with only two values X , Y , X, Y, X,Y, Try to prove X , Y X, Y X,Y Independent if and only if X , Y X, Y X,Y Unrelated .
Solution:
| X = x 1 X=x_{1} X=x1 | X = x 2 X=x_{2} X=x2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Y = y 1 Y=y_{1} Y=y1 | p 11 p_{11} p11 | p 21 p_{21} p21 | 1 − q 1-q 1−q |
| Y = y 2 Y=y_{2} Y=y2 | p 12 p_{12} p12 | p 22 p_{22} p22 | q q q |
| 1 − p 1-p 1−p | p p p |
Solution: Independence must not be relevant , Just prove the sufficiency . Just discuss X ′ = X − x 1 x 2 − x 1 X'=\frac{X-x_1}{x_2-x_1} X′=x2−x1X−x1, Y ′ = Y − y 1 y 2 − y 1 Y'=\frac{Y-y_1}{y_2-y_1} Y′=y2−y1Y−y1, X , Y X,Y X,Y Irrelevant and X ′ , Y ′ X',Y' X′,Y′ Irrelevance is equivalent . When X ′ , Y ′ X',Y' X′,Y′ When it's not relevant , explain p 22 = E ( X ′ Y ′ ) = E ( X ′ ) E ( Y ′ ) = p q , p_{22}=E(X'Y')=E(X')E(Y')=pq, p22=E(X′Y′)=E(X′)E(Y′)=pq, Further, there are p 21 = p − p 22 = p − p q = p ( 1 − q ) , p_{21}=p-p_{22}=p-pq=p(1-q), p21=p−p22=p−pq=p(1−q), p 12 = q − p 22 = q − p q = q ( 1 − p ) , p_{12}=q-p_{22}=q-pq=q(1-p), p12=q−p22=q−pq=q(1−p), p 11 = 1 − p − p 12 = ( 1 − p ) − q ( 1 − p ) = ( 1 − p ) ( 1 − q ) . p_{11}=1-p-p_{12}=(1-p)-q(1-p)=(1-p)(1-q). p11=1−p−p12=(1−p)−q(1−p)=(1−p)(1−q). therefore X ′ , Y ′ X',Y' X′,Y′ Independent , so X , Y X,Y X,Y Also independent .
6、 ... and 、(15 branch ) Set from the overall X ∼ N ( μ , σ 2 ) X \sim N\left(\mu, \sigma^{2}\right) X∼N(μ,σ2) Of 2 n 2 n 2n Random sample , Try to expect
E ( ∑ i = 1 n ( X i + X n + i − 2 X ˉ ) 2 ) . E\left(\sum_{i=1}^{n}\left(X_{i}+X_{n+i}-2 \bar{X}\right)^{2}\right). E(i=1∑n(Xi+Xn+i−2Xˉ)2).
Solution: remember Y i = X i + X n + i , i = 1 , 2 , … , n Y_{i}=X_{i}+X_{n+i}, i=1,2, \ldots, n Yi=Xi+Xn+i,i=1,2,…,n, such Y 1 , Y 2 , … , Y n Y_{1}, Y_{2}, \ldots, Y_{n} Y1,Y2,…,Yn It comes from the whole N ( 2 μ , 2 σ 2 ) N\left(2 \mu, 2 \sigma^{2}\right) N(2μ,2σ2) Of n n n Random sample , Y ˉ = 2 X ˉ \bar{Y}=2 \bar{X} Yˉ=2Xˉ, According to the definition and nature of sample variance , We have 1 2 σ 2 ∑ i = 1 n ( X i + X n + i − 2 X ˉ ) 2 = 1 2 σ 2 ∑ i = 1 n ( Y i − Y ˉ ) 2 ∼ χ 2 ( n − 1 ) \frac{1}{2 \sigma^{2}} \sum_{i=1}^{n}\left(X_{i}+X_{n+i}-2 \bar{X}\right)^{2}=\frac{1}{2 \sigma^{2}} \sum_{i=1}^{n}\left(Y_{i}-\bar{Y}\right)^{2} \sim \chi^{2}(n-1) 2σ21i=1∑n(Xi+Xn+i−2Xˉ)2=2σ21i=1∑n(Yi−Yˉ)2∼χ2(n−1) therefore
E ∑ i = 1 n ( X i + X n + i − 2 X ˉ ) 2 = 2 ( n − 1 ) σ 2 . E \sum_{i=1}^{n}\left(X_{i}+X_{n+i}-2 \bar{X}\right)^{2}=2(n-1)\sigma^{2}. Ei=1∑n(Xi+Xn+i−2Xˉ)2=2(n−1)σ2.
7、 ... and 、(15 branch ) X 1 , X 2 , X 3 X_{1}, X_{2}, X_{3} X1,X2,X3, yes i.i.d. To obey U ( 0 , 1 ) U(0,1) U(0,1) Random variable of , Find order statistics X ( 1 ) X_{(1)} X(1) Distribution function and expectation of .
Solution: set up Y = X ( 1 ) Y=X_{(1)} Y=X(1), When y ∈ ( 0 , 1 ) y \in(0,1) y∈(0,1) when , P { Y ≥ y } = P ( min { X 1 , X 2 , X 3 } ≥ y ) = P 3 { X 1 ≥ y } = ( 1 − y ) 3 P\{Y \geq y\}=P\left(\min \left\{X_{1}, X_{2}, X_{3}\right\} \geq y\right)=P^{3}\left\{X_{1} \geq y\right\}=(1-y)^{3} P{ Y≥y}=P(min{ X1,X2,X3}≥y)=P3{ X1≥y}=(1−y)3 So the distribution function is
F ( y ) = { 0 , y < 0 , 1 − ( 1 − y ) 3 , 0 ≤ y < 1 , 1 , y ≥ 1. F(y)=\left\{\begin{array}{lc}0, & y<0, \\ 1-(1-y)^{3}, & 0 \leq y<1, \\ 1, & y \geq 1 .\end{array}\right. F(y)=⎩⎨⎧0,1−(1−y)3,1,y<0,0≤y<1,y≥1. This happens to be Beta ( 1 , 3 ) \operatorname{Beta}(1,3) Beta(1,3) Distribution function of . E Y = ∫ 0 1 y d F ( y ) = 1 ⋅ F ( 1 ) − ∫ 0 1 [ 1 − ( 1 − y ) 3 ] d y = 1 4 E Y=\int_{0}^{1} y d F(y)=1 \cdot F(1)-\int_{0}^{1}\left[1-(1-y)^{3}\right] d y=\frac{1}{4} EY=∫01ydF(y)=1⋅F(1)−∫01[1−(1−y)3]dy=41
8、 ... and 、(30 branch ) From X ∼ f ( x ) = { θ , 0 ≤ x < 1 1 − θ , 1 ≤ x < 2 , 0 , otherwise X \sim f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cl}\theta, & 0 \leq x<1 \\ 1-\theta, & 1 \leq x<2, \\ 0, & \text { otherwise }\end{array}\right. X∼f(x)=⎩⎨⎧θ,1−θ,0,0≤x<11≤x<2, otherwise Of n n n A simple random sample , seek
(1)(15 branch ) θ \theta θ The moment estimate of ;
(2)(15 branch ) θ \theta θ Maximum likelihood estimation of , It is known that m = ∑ i = 1 n I [ X i < 1 ] m=\sum_{i=1}^{n} I\left[X_{i}<1\right] m=∑i=1nI[Xi<1].
Solution: (1) E X = ∫ 0 1 x θ d x + ∫ 1 2 x ( 1 − θ ) d x = 3 2 − θ E X=\int_{0}^{1} x \theta d x+\int_{1}^{2} x(1-\theta) d x=\frac{3}{2}-\theta EX=∫01xθdx+∫12x(1−θ)dx=23−θ, therefore θ ^ 1 = 3 2 − X ˉ . \hat{\theta}_{1}=\frac{3}{2}-\bar{X}. θ^1=23−Xˉ.(2) Likelihood function L ( x 1 , … , x n ; θ ) = θ m ( 1 − θ ) n − m , L\left(x_{1}, \ldots, x_{n} ; \theta\right)=\theta^{m}(1-\theta)^{n-m}, L(x1,…,xn;θ)=θm(1−θ)n−m,
ln L = m ln θ + ( n − m ) ln ( 1 − θ ) \ln L=m \ln \theta+(n-m) \ln(1-\theta) lnL=mlnθ+(n−m)ln(1−θ), Yes θ \theta θ Finding partial derivatives , have to ∂ ln L ∂ θ = m θ − n − m 1 − θ = l e t 0 , \frac{\partial \ln L}{\partial \theta}=\frac{m}{\theta}-\frac{n-m}{1-\theta} \stackrel{l e t}{=} 0, ∂θ∂lnL=θm−1−θn−m=let0, Solution θ ^ 2 = m n \hat{\theta}_{2}=\frac{m}{n} θ^2=nm.
边栏推荐
- 分支语句和循环语句
- 1. C language matrix addition and subtraction method
- [Topic terminator]
- 2.初识C语言(2)
- View UI Plus 发布 1.3.0 版本,新增 Space、$ImagePreview 组件
- 【快趁你舍友打游戏,来看道题吧】
- TYUT太原理工大学2022“mao gai”必背
- E-R graph to relational model of the 2022 database of tyut Taiyuan University of Technology
- 最新坦克大战2022-全程开发笔记-2
- TYUT太原理工大学2022软工导论大题汇总
猜你喜欢
3.猜数字游戏

3. Number guessing game

Smart classroom solution and mobile teaching concept description
凡人修仙学指针-2
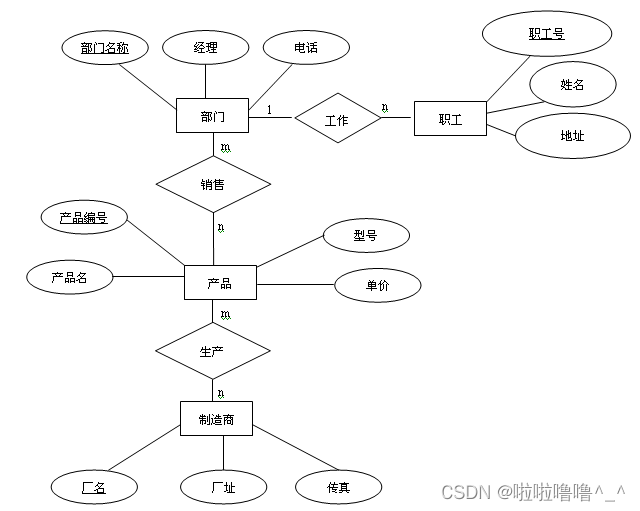
TYUT太原理工大学2022数据库大题之概念模型设计
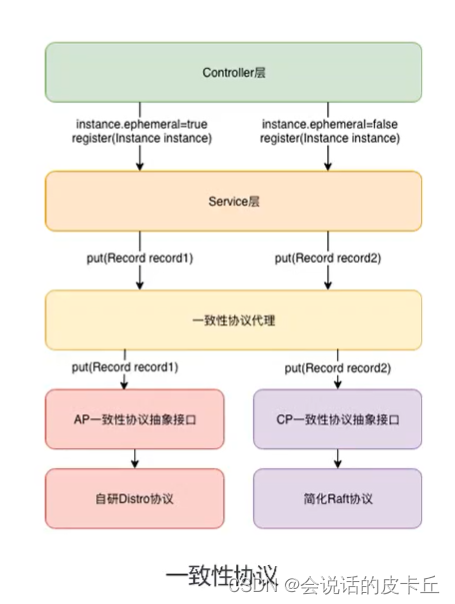
Alibaba cloud microservices (II) distributed service configuration center and Nacos usage scenarios and implementation introduction
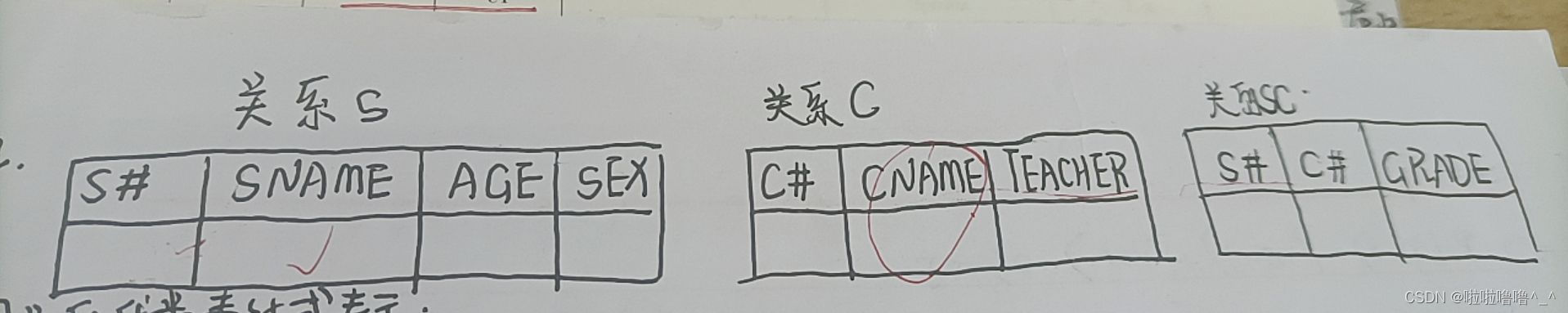
TYUT太原理工大学2022数据库题库选择题总结

The latest tank battle 2022 full development notes-1
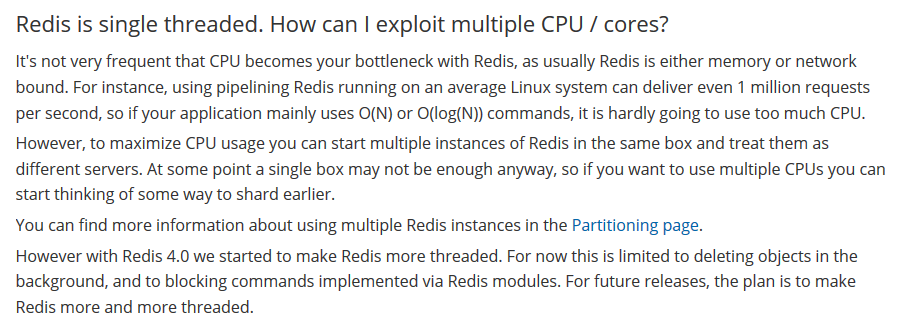
Counter attack of flour dregs: redis series 52 questions, 30000 words + 80 pictures in detail.
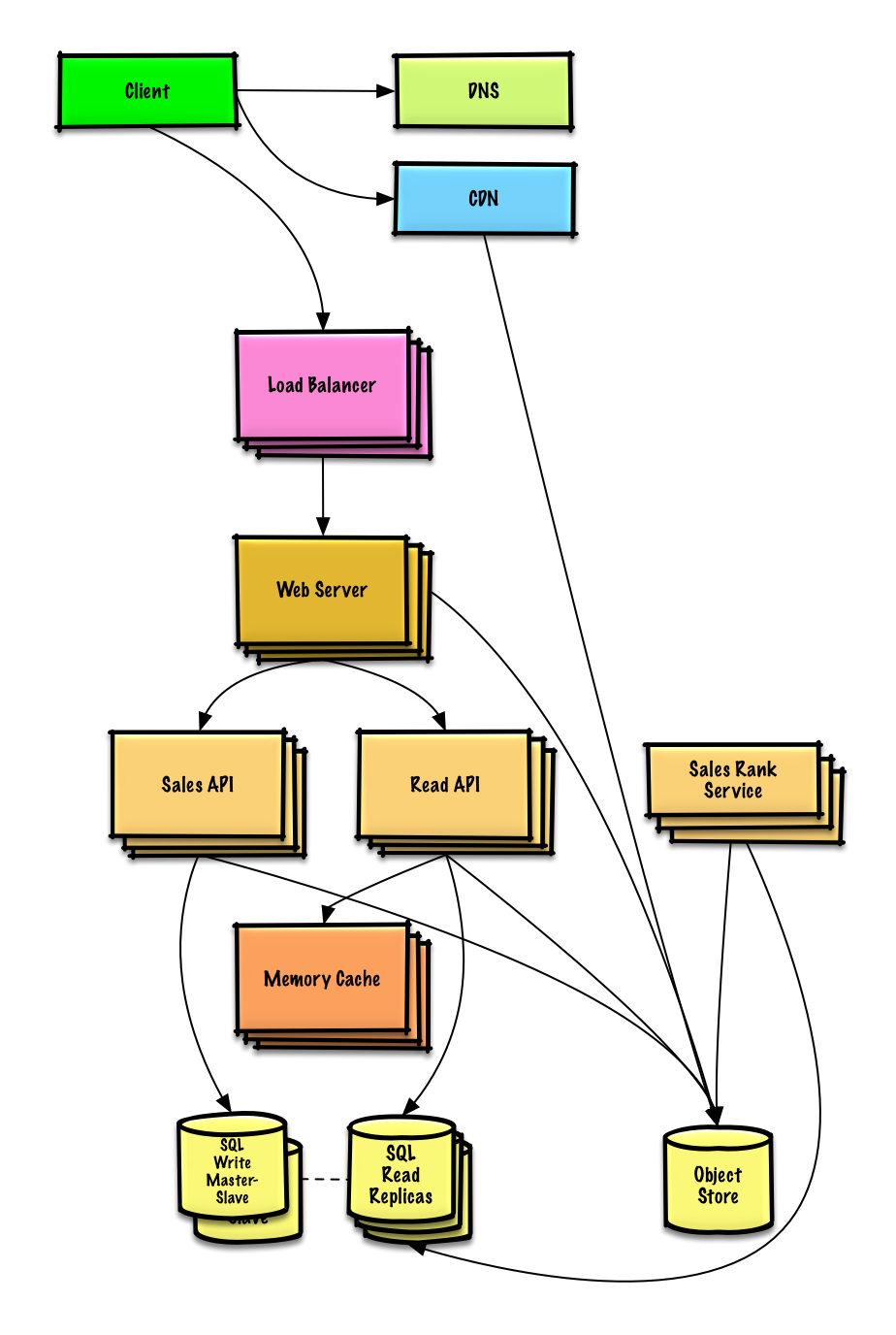
System design learning (III) design Amazon's sales rank by category feature
随机推荐
View UI Plus 发布 1.3.0 版本,新增 Space、$ImagePreview 组件
ROS machine voice
Rich Shenzhen people and renting Shenzhen people
2. Preliminary exercises of C language (2)
3. Number guessing game
TYUT太原理工大学2022数据库大题之分解关系模式
3.C语言用代数余子式计算行列式
9.指针(上)
JS interview questions (I)
4. Binary search
CorelDRAW plug-in -- GMS plug-in development -- Introduction to VBA -- GMS plug-in installation -- Security -- macro Manager -- CDR plug-in (I)
分支语句和循环语句
2.C语言初阶练习题(2)
Application architecture of large live broadcast platform
MySQL limit x, -1 doesn't work, -1 does not work, and an error is reported
Inheritance and polymorphism (I)
The latest tank battle 2022 - full development notes-3
Tyut Taiyuan University of technology 2022 introduction to software engineering
1.初识C语言(1)
Design a key value cache to save the results of the most recent Web server queries