当前位置:网站首页>4年工作经验,多线程间的5种通信方式都说不出来,你敢信?
4年工作经验,多线程间的5种通信方式都说不出来,你敢信?
2022-07-05 13:19:00 【罗汉翔】
问题
有两个线程,A 线程向一个集合里面依次添加元素“abc”字符串,一共添加十次,当添加到第五次的时候,希望 B 线程能够收到 A 线程的通知,然后 B 线程执行相关的业务操作。线程间通信的模型有两种:共享内存和消息传递,以下方式都是基本这两种模型来实现的。
一、使用 volatile 关键字
基于 volatile 关键字来实现线程间相互通信是使用共享内存的思想。大致意思就是多个线程同时监听一个变量,当这个变量发生变化的时候 ,线程能够感知并执行相应的业务。这也是最简单的一种实现方式
public class TestSync {
//定义共享变量来实现通信,它需要volatile修饰,否则线程不能及时感知
static volatile boolean notice = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//线程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
list.add("abc");
System.out.println("线程A添加元素,此时list的size为:" + list.size());
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (list.size() == 5)
notice = true;
}
});
//线程B
Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
if (notice) {
System.out.println("线程B收到通知,开始执行自己的业务...");
break;
}
}
});
//需要先启动线程B
threadB.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 再启动线程A
threadA.start();
}
}二、使用 Object 类的 wait()/notify()
Object 类提供了线程间通信的方法:wait()、notify()、notifyAll(),它们是多线程通信的基础,而这种实现方式的思想自然是线程间通信。
注意:wait/notify 必须配合 synchronized 使用,wait 方法释放锁,notify 方法不释放锁。wait 是指在一个已经进入了同步锁的线程内,让自己暂时让出同步锁,以便其他正在等待此锁的线程可以得到同步锁并运行,只有其他线程调用了notify(),notify并不释放锁,只是告诉调用过wait()的线程可以去参与获得锁的竞争了,但不是马上得到锁,因为锁还在别人手里,别人还没释放,调用 wait() 的一个或多个线程就会解除 wait 状态,重新参与竞争对象锁,程序如果可以再次得到锁,就可以继续向下运行。
public class TestSync {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个锁对象
Object lock = new Object();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 线程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
list.add("abc");
System.out.println("线程A添加元素,此时list的size为:" + list.size());
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (list.size() == 5)
lock.notify();//唤醒B线程
}
}
});
//线程B
Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
synchronized (lock) {
if (list.size() != 5) {
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("线程B收到通知,开始执行自己的业务...");
}
}
});
//需要先启动线程B
threadB.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//再启动线程A
threadA.start();
}
}由输出结果,在线程 A 发出 notify() 唤醒通知之后,依然是走完了自己线程的业务之后,线程 B 才开始执行,正好说明 notify() 不释放锁,而 wait() 释放锁。
wait() 和 notify()都是Object类的通讯方法,注意一点,wait和 notify必须搭配synchronized使用,并且notify()不会释放锁
public class SynchronizedTest {
//定义个year,用来记录某明星的练习年数
private static double year;
public void run() {
//线程A,练习唱跳rap
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (this) {
for (year = 0.5; year <= 5; year += 0.5) {
System.out.println("蔡徐鸡开始练习唱跳rap:已练习" + year + "年");
try {
Thread.sleep(288);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//众所周知,练习两年半即可出道
if (year == 2.5) {
System.out.println("===========================>成功练习两年半,出道!!!");
this.notify();
}
}
}
});
//线程B,练习打篮球
Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
synchronized (this) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("蔡徐鸡开始练习打篮球");
}
}
});
//注意,一定要先启动B,不然会导致B永远拿不到锁
threadB.start();
threadA.start();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynchronizedTest test = new SynchronizedTest();
test.run();
}
}
三、使用JUC工具类 CountDownLatch
jdk1.5 之后在java.util.concurrent包下提供了很多并发编程相关的工具类,简化了并发编程代码的书写,CountDownLatch 基于 AQS 框架,相当于也是维护了一个线程间共享变量 state。
public class TestSync {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//线程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
list.add("abc");
System.out.println("线程A添加元素,此时list的size为:" + list.size());
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (list.size() == 5)
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
});
//线程B
Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
if (list.size() != 5) {
try {
countDownLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("线程B收到通知,开始执行自己的业务...");
break;
}
});
//需要先启动线程B
threadB.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//再启动线程A
threadA.start();
}
}四、使用 ReentrantLock 结合 Condition
public class TestSync {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//线程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
list.add("abc");
System.out.println("线程A添加元素,此时list的size为:" + list.size());
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (list.size() == 5)
condition.signal();
}
lock.unlock();
});
//线程B
Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
if (list.size() != 5) {
try {
condition.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("线程B收到通知,开始执行自己的业务...");
lock.unlock();
});
threadB.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
threadA.start();
}
}这种方式使用起来并不是很好,代码编写复杂,而且线程 B 在被 A 唤醒之后由于没有获取锁还是不能立即执行,也就是说,A 在唤醒操作之后,并不释放锁。这种方法跟 Object 的 wait()/notify() 一样。
五、基本 LockSupport 实现线程间的阻塞和唤醒
LockSupport 是一种非常灵活的实现线程间阻塞和唤醒的工具,使用它不用关注是等待线程先进行还是唤醒线程先运行,但是得知道线程的名字。
public class TestSync {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//线程B
final Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> {
if (list.size() != 5) {
LockSupport.park();
}
System.out.println("线程B收到通知,开始执行自己的业务...");
});
//线程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
list.add("abc");
System.out.println("线程A添加元素,此时list的size为:" + list.size());
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (list.size() == 5)
LockSupport.unpark(threadB);
}
});
threadA.start();
threadB.start();
}
}边栏推荐
- Talking about fake demand from takeout order
- 私有地址有那些
- 使用Dom4j解析XML
- 事务的基本特性和隔离级别
- 阿里云SLB负载均衡产品基本概念与购买流程
- There is no monitoring and no operation and maintenance. The following is the commonly used script monitoring in monitoring
- Solve Unicode decodeerror: 'GBK' codec can't decode byte 0xa2 in position 107
- 不知道这4种缓存模式,敢说懂缓存吗?
- DataPipeline双料入选中国信通院2022数智化图谱、数据库发展报告
- Fragmented knowledge management tool memos
猜你喜欢

Put functions in modules
![[deep learning paper notes] hnf-netv2 for segmentation of brain tumors using multimodal MR imaging](/img/52/5e85743b1817de96a52e02b92fd08c.png)
[deep learning paper notes] hnf-netv2 for segmentation of brain tumors using multimodal MR imaging
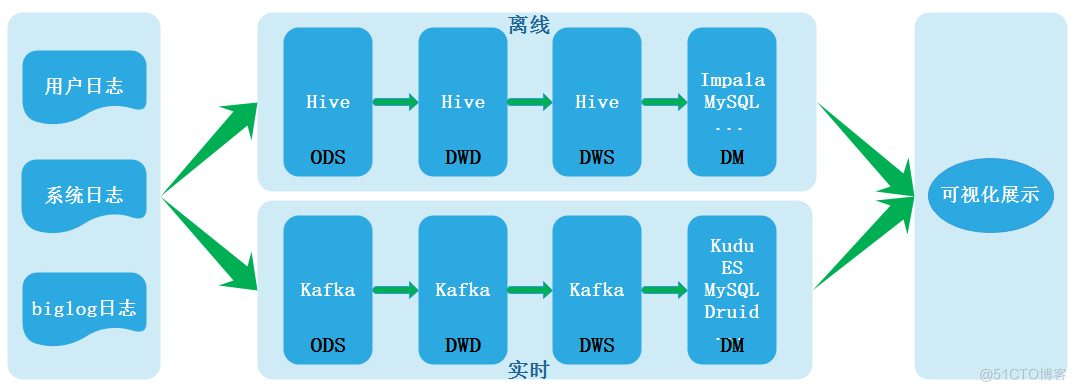
数据湖(七):Iceberg概念及回顾什么是数据湖

MySQL - database query - sort query, paging query
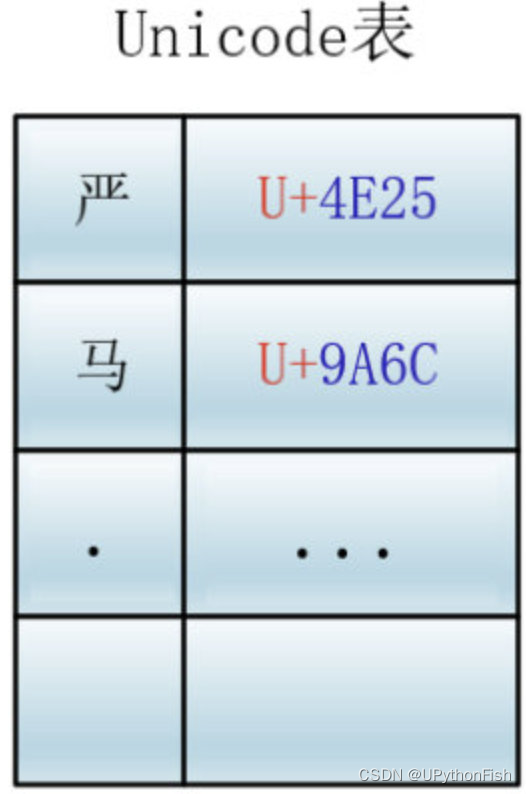
一文详解ASCII码,Unicode与utf-8

DataPipeline双料入选中国信通院2022数智化图谱、数据库发展报告

How to protect user privacy without password authentication?

【每日一题】1200. 最小绝对差
jenkins安装
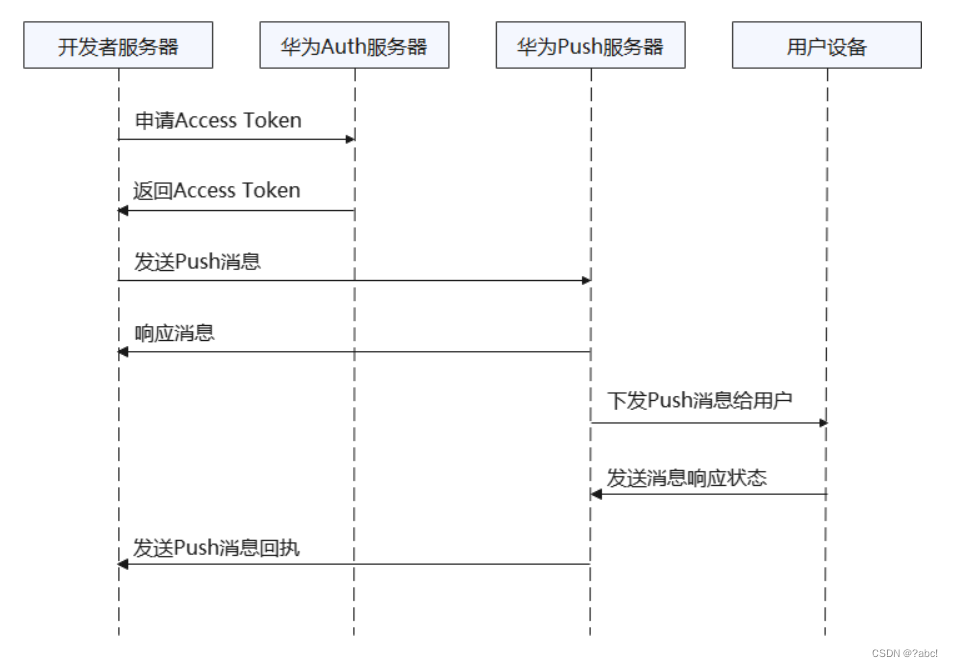
华为推送服务内容,阅读笔记
随机推荐
前缀、中缀、后缀表达式「建议收藏」
My colleague didn't understand selenium for half a month, so I figured it out for him in half an hour! Easily showed a wave of operations of climbing Taobao [easy to understand]
leetcode 10. Regular expression matching regular expression matching (difficult)
一文详解ASCII码,Unicode与utf-8
MySQL --- 数据库查询 - 排序查询、分页查询
“百度杯”CTF比赛 九月场,Web:Upload
#从源头解决# 自定义头文件在VS上出现“无法打开源文件“XX.h“的问题
go map
MMSeg——Mutli-view时序数据检查与可视化
There is no monitoring and no operation and maintenance. The following is the commonly used script monitoring in monitoring
聊聊异步编程的 7 种实现方式
APICloud Studio3 API管理与调试使用教程
手把手带你入门Apache伪静态的配置
Natural language processing from Xiaobai to proficient (4): using machine learning to classify Chinese email content
《2022年中国银行业RPA供应商实力矩阵分析》研究报告正式启动
Flutter draws animation effects of wave movement, curves and line graphs
Overflow toolbar control in SAP ui5 view
OpenHarmony应用开发之Navigation组件详解
The solution of outputting 64 bits from printf format%lld of cross platform (32bit and 64bit)
Solve Unicode decodeerror: 'GBK' codec can't decode byte 0xa2 in position 107