当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode_Dec_2nd_Week
LeetCode_Dec_2nd_Week
2022-08-04 06:28:00 【KuoGavin】
December 13rd : 807. 保持城市天际线
December 14th : 630. 课程表 III
December 15th : 851. 喧闹和富有
December 16th : 1610. 可见点的最大数目
December 17th : 1518. 换酒问题
December 18th : 419. 甲板上的战舰
December 19th : 997. 找到小镇的法官
December 13rd : 807. 保持城市天际线
昨天把Porschefinished~Then the whole acrylic display cabinet will be happier!!!

今天的题,Calculate the maximum value of each row and column,Then traverse the entire city grid,Find the smaller value of the maximum value of the row and column minus the value of the grid, which is the maximum height increment of the grid,The accumulated results can be returned.
class Solution {
public:
int maxIncreaseKeepingSkyline(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size();
vector<int> rows = vector<int>(n, 0), cols = vector<int>(n, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
rows[i] = max(grid[i][j], rows[i]);
cols[i] = max(grid[j][i], cols[i]);
}
}
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
ret += min(rows[i], cols[j]) - grid[i][j];
return ret;
}
};
December 14th : 630. 课程表 III
Classic greedy algorithm problem,The course with the current minimum deadline is selected each time(排序后遍历):If the time after taking the course to study does not exceed the deadline,Then take this course;If the deadline is exceeded,Then select the course with the longest study time among the courses to be studied at present(优先队列/Large root heap storage acquisition),Replace it with the currently traversed class,That is, learning the same number of courses,The total time spent is shorter.
See the specific derivation process:方法一:优先队列 + 贪心.
class Solution {
public:
int scheduleCourse(vector<vector<int>>& courses) {
sort(courses.begin(), courses.end(),
[](vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b){
return a[1] < b[1];});
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int>> q;
int total = 0;
for(const auto& course : courses) {
int ti = course[0], di = course[1];
if(total + ti <= di) {
total += ti;
q.push(ti);
} else if(!q.empty() && q.top() > ti) {
total -= q.top() - ti;
q.pop();
q.push(ti);
}
}
return q.size();
}
};
December 15th : 851. 喧闹和富有
穷在闹市无人问,富在深山有远亲 .
不信但看宴中酒,杯杯先敬富贵人 .
门前拴着高头马,不是亲来也是亲.
门前放着讨饭棍,亲朋好友不上门 .
世上结交需黄金,黄金不多交不深 .
有钱有酒多兄弟,急难何曾见一人 .
三穷三富过到老,十年兴败多少人 .
谁人背后无人说,谁人背后不说人!
还是不忘初心,It is the same dust as the light!
Then this question,Who will be richer than who/Poverty has edges as graphs,Each person as a point in the graph,It's a graph related problem,See figure questions:图的遍历(DFS,BFS,Topology Sort),It just so happens that this problem also uses graph traversal and topological sorting,The knowledge link is above.
First of all, because the logic is self-consistent,So it is known that it isDAG图(有向无环图,It can be thought of as a multi-forked tree),那么有两种做法,The first is to build a map first:
- ① For drawing,Poorer points to richer situations,Then traverse the graph branch with the poorer human as the root node,Find the quietest of those richer than him(图的遍历,DFS和BFS);
- ② For drawing,Richer points to poorer situations,Start with the richest,for the richest(入度为0)有 a n s [ 最 富 的 ] = 最 富 的 ans[最富的]=最富的 ans[最富的]=最富的,will be poorer than him,related to him(相邻节点)的 a n s ans ans 进行更新,Then the in-degree of the richest adjacent point is 0,Then let him go,Updates the points adjacent to him a n s ans ans,until all people are admitted0,也即是DAG有拓扑排序,Topological sort determines whether it is an inverse application of a directed acyclic graph.This can be understood as the reverseBFS.
//dfs&bfs
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> loudAndRich(vector<vector<int>>& richer, vector<int>& quiet) {
int n = quiet.size();
vector<vector<int>> graph(n);
for(vector<int>& vec : richer) graph[vec[1]].push_back(vec[0]);
vector<int> ans(n, -1);
for(int x = 0; x < n; ++x) dfs(graph, quiet, ans, x);
//for(int x = 0; x < n; ++x) ans[x] = bfs(graph, quiet, x);
return ans;
}
private:
void dfs(const vector<vector<int>>& graph, const vector<int>& quiet,
vector<int>& ans, int x) {
if(ans[x] != -1) return;
ans[x] = x;
for(int y : graph[x]) {
dfs(graph, quiet, ans, y);
if(quiet[ans[x]] > quiet[ans[y]]) ans[x] = ans[y];
}
}
//超时
int bfs(const vector<vector<int>>& graph, const vector<int>& quiet, int x) {
queue<int> q; q.push(x);
while(!q.empty()) {
int y = q.front(); q.pop();
if(quiet[y] < quiet[x]) x = y;
for(int z : graph[y]) q.push(z);
}
return x;
}
};
/****************************************************************************************************/
//topology sort
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> loudAndRich(vector<vector<int>>& richer, vector<int>& quiet) {
int n = quiet.size();
vector<vector<int>> graph(n); //Record the edge connection of the graph,is a directed edge graph,DAG
vector<int> inDegree(n); //统计各个person的入度,That is, how many people have more money than him
for(auto& vec : richer) {
//Connect more money to less money
graph[vec[0]].push_back(vec[1]);
++inDegree[vec[1]];
}
vector<int> ans(n);
//ans[x]的产生,要么是x自己,or no less thanxmoney man,Initially it can be itself
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) ans[i] = i;
//iota(ans.begin(), ans.end(), 0);
queue<int> q;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if(inDegree[i] == 0) q.push(i);
//Start with the richest,The richest and quietest person must be himself,然后一直,next rich,再次的...
while(!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front(); q.pop();
for(int y : graph[x]) {
//如果比x没钱的人y,Its quiet value is greater than x的安静值,则更新yThe quiet value of ieans[y]=ans[x]
if(quiet[ans[x]] < quiet[ans[y]]) ans[y] = ans[x];
//更新后,将y的入度,即比xThe number of rich people is reduced by one,若是没有了,则加入队列,Impairment
if(--inDegree[y] == 0) q.push(y);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
December 16th : 1610. 可见点的最大数目
这道题,is a range sliding window problem for annular arrays(见).The main point is how to convert 2D scatter points to polar angles,这里使用了 atan2 \texttt{atan2} atan2 函数,也就是数学中的arctan.After sorting the obtained polar coordinates,Start with each polar angle,Finds the cis starting with the polar angle/逆时针angle范围内的点的个数,Take the maximum value inside.
需要注意的是:
- atan2 \texttt{atan2} atan2 的返回值范围为 [ − π , π ] [-\pi,\pi] [−π,π],Its coverage is 2 π 2\pi 2π,而 极角+angle \textit{极角+angle} 极角+angle 会出现大于 π \pi π 的情况,Then you can put each point in the original array 极 角 + 360 ° 极角 + 360\degree 极角+360°,Prevent inversion problems;
- 在求极角时,对于坐标刚好处于 location \textit{location} location 的元素需要单独进行统计,因为 arctan(0) \textit{arctan(0)} arctan(0) 未定义;
class Solution {
public:
int visiblePoints(vector<vector<int>>& points, int angle, vector<int>& location) {
int sameLoction = 0;
vector<double> degrees;
for(auto& point : points) {
if(point[0] == location[0] && point[1] == location[1]) {
sameLoction++;
continue;
}
double degree = atan2(location[1]-point[1], location[0]-point[0]);
//double degree = atan2(point[1] - location[1], point[0] - location[0]);
degrees.push_back(degree);
}
sort(degrees.begin(), degrees.end());
int n = degrees.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) degrees.push_back(degrees[i] + 2 * M_PI);
int maxVPnt = 0, right = 0;
double scope = angle * M_PI / 180 ;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
while(right < degrees.size() && degrees[right] <= degrees[i] + scope) right++;
maxVPnt = max(maxVPnt, right - i);
}
return sameLoction + maxVPnt;
}
};
December 17th : 1518. 换酒问题
Iterative process can be simulated,The number of empty bottles in the next round is based on the remaining amount after the original exchange,Add the number of bottles of wine you get after the exchange.
class Solution {
public:
int numWaterBottles(int numBottles, int numExchange) {
int numEmptyBottles = numBottles, numFullBottles = 0;
int ret = numBottles;
while(numEmptyBottles >= numExchange) {
numFullBottles = numEmptyBottles / numExchange;
numEmptyBottles = numEmptyBottles % numExchange + numFullBottles;
ret += numFullBottles;
}
return ret;
}
};
/*******************************************************************************************************/
class Solution {
public:
int numWaterBottles(int numBottles, int numExchange, int numEmptyBottles = 0) {
cout << "numBottles:" << numBottles << " numEmptyBottles:" << numEmptyBottles << endl;
//When the number of empty bottles and full bottles is less than the number of exchange bottles,则递归结束,Returns the number of full bottles
if(numEmptyBottles+numBottles < numExchange) return numBottles;
//If it is greater than or equal to the number of exchange bottles,Then the number of full bottles in the next round is the empty bottle+Divide the remaining empty bottles and floor from the previous round by the number of exchange bottles
//The number of empty bottles in the next round is this round of empty bottles+The remaining empty bottles in the previous round and the remainder of the number of exchanged bottles
return numBottles +
numWaterBottles((numBottles+numEmptyBottles)/numExchange,
numExchange,
(numBottles+numEmptyBottles)%numExchange);
}
};
December 18th : 419. 甲板上的战舰
Similar to the number of islands,使用dfs或bfsJust fill in the island,It's just that the islands here are horizontal or vertical,So the code for the number of islands is generic here,Discovery is not part of the battleship,dfs时返回即可.But here has changedboard地图.
Depending on whether the ship is horizontal or vertical,You can know that the battleship must have a top left corner,And there must be a space between the two battleships,There are no adjacent cases,According to this theme,We can count the number of the upper left corner of the battleship,That is the number of warships.
有点奇怪的是,The time and space complexity of the second method is actually similar to the first,Maybe the data is not strong enough.
//dfs
class Solution {
public:
int countBattleships(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
//The number of islands is similar,空间复杂度On,时间复杂度On
int ships = 0;
int m = board.size(), n = board[0].size();
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if(board[i][j] == 'X') {
ships++;
dfs(board, i, j);
}
}
}
return ships;
}
private:
vector<int> directions = {
-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& board, int r, int c) {
if(r == board.size() || r == -1 || c == board[0].size() || c == -1 || board[r][c] == '.') return;
board[r][c] = '.';
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
dfs(board, r+directions[i], c+directions[i+1]);
}
}
};
/****************************************************************************************************************/
//Statistics in the upper left corner
class Solution {
public:
int countBattleships(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
int m = board.size(), n = board[0].size();
int ships = 0;
if(board[0][0] == 'X') ships++;
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) if(board[0][i-1] != 'X' && board[0][i] == 'X') ships++;
for(int i = 1; i < m; ++i) if(board[i-1][0] != 'X' && board[i][0] == 'X') ships++;
for(int i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
for(int j = 1; j < n; ++j) {
if(board[i-1][j] != 'X' && board[i][j-1] != 'X' && board[i][j] == 'X')
ships++;
}
}
return ships;
}
};
December 19th : 997. 找到小镇的法官
Simple graph theory questions,Only the basic concepts of out-degree and in-degree of nodes in the basic graph are examined.For judges,其在trustThe out-degree after the entire traversal is 0(不信任任何人),入度为n-1(All people trust him,除了他自己),And there is only one judge in the title.So open two arrays to record each person's in-degree(被信任),出度(信任他人),Then iterate through everyone's trust and trust status,If the above-mentioned out-degree is met0,入度为n-1,Then that person is the town judge.
此外,You can also open only one array,入度++,出度–,这样,Only the last in-degree is n-1That man is the town judge.
class Solution {
public:
int findJudge(int n, vector<vector<int>>& trust) {
vector<pair<int, int>> vec(n+1);
for(int i = 0; i < trust.size(); ++i) {
vec[trust[i][0]].second++;
vec[trust[i][1]].first++;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if(vec[i].first == n-1 && vec[i].second == 0)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
};
/*********************************************************************/
//Only open an array
class Solution {
public:
int findJudge(int n, vector<vector<int>>& trust) {
vector<int> inDegree(n+1);
for(auto& vec : trust) {
inDegree[vec[0]]--;
inDegree[vec[1]]++;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if(inDegree[i] == n-1)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
};
边栏推荐
- Transformer
- No matching function for call to 'RCTBridgeModuleNameForClass'
- [开发杂项][VS Code]remote-ssd retry failed
- LeetCode_Nov_2nd_Week
- LeetCode_Dec_1st_Week
- MNIST Handwritten Digit Recognition - Lenet-5's First Commercial Grade Convolutional Neural Network
- LeetCode_Nov_5th_Week
- LeetCode_Dec_2nd_Week
- 题目1000:输入两个整数a和b,计算a+b的和,此题是多组测试数据
- Rules.make-适合在编辑模式下看
猜你喜欢
yoloV5 使用——训练速度慢,加速训练
【五一专属】阿里云ECS大测评#五一专属|向所有热爱分享的“技术劳动者”致敬#

【论文阅读】SPANET: SPATIAL PYRAMID ATTENTION NETWORK FOR ENHANCED IMAGE RECOGNITION

CSDN spree -- college round table spree

MNIST handwritten digit recognition, sorted by from two to ten
Code to celebrate the Dragon Boat Festival - Zongzi, your heart
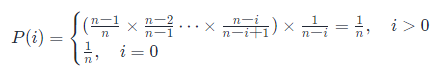
LeetCode_Nov_4th_Week
PP-LiteSeg
![[Copy Siege Lion Log] Flying Pulp Academy Intensive Learning 7-Day Punch Camp-Study Notes](/img/af/05caea638de8d75f6d3b42b3d8e28f.png)
[Copy Siege Lion Log] Flying Pulp Academy Intensive Learning 7-Day Punch Camp-Study Notes
浅谈外挂常识和如何防御
随机推荐
数据库的简述与常用操作指南
【论文阅读】Multi-View Spectral Clustering with Optimal Neighborhood Laplacian Matrix
多层LSTM
The second official example analysis of the MOOSE platform - about creating a Kernel and solving the convection-diffusion equation
[开发杂项][编辑器][代码阅读]ctags&vim
第三章 标准单元库(上)
集合---ArrayList的底层
第一章 绪论
基于asp.net的法律援助平台的设计与实现(附项目链接)
如何用Pygame制作简单的贪吃蛇游戏
Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks
基于BiGRU和GAN的数据生成方法
Windows10重置MySQL用户密码
fuser 使用—— YOLOV5内存溢出——kill nvidai-smi 无pid 的 GPU 进程
【论文阅读】TransReID: Transformer-based Object Re-Identification
MNIST Handwritten Digit Recognition - Image Analysis Method for Binary Classification
bind()系统调用的用处
Copy Siege Lions "sticky" to AI couplets
集合--LinkedList
Copy Siege Lion 5-minute online experience MindIR format model generation