当前位置:网站首页>MNIST Handwritten Digit Recognition - Building a Perceptron from Zero for Two-Classification
MNIST Handwritten Digit Recognition - Building a Perceptron from Zero for Two-Classification
2022-08-04 06:20:00 【Learning Adventures】
From zero to build machine implementation handwritten Numbers two classification
Understand the nature of traditional programming method and machine learning method difference;Understand the mathematical expression of perceptron model;Grasp the formula of gradient descent method is derived by hand.
上一节,已经使用“统计非零像素占比,比较阈值” The traditional programming method based on image analysis to achieve the handwritten Numbers0和1的二分类,It is a very simple implementation strategy.This section started using machine learning methods to realize.There are many kinds of machine learning methods can achieve two classification problem,This section try using machine learning simple perceptron model,How to try the classification effect.
The birth of the perceptron model was inspired by the human brain neurons,As shown in the figure below is the structure of single neurons in the brain,Each neuron is connected to other neurons in,当神经元“兴奋”时,Will be connected to the neurons transmit chemical,Another is from dendrites receive other neurons chemicals input,Chemical change on axons potential,When the potential is greater than a certain threshold,The neurons are activated in the“兴奋”状态,Also passed on to other neurons axon endings chemicals.
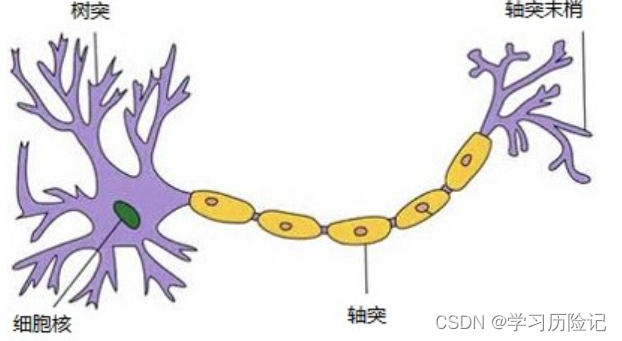
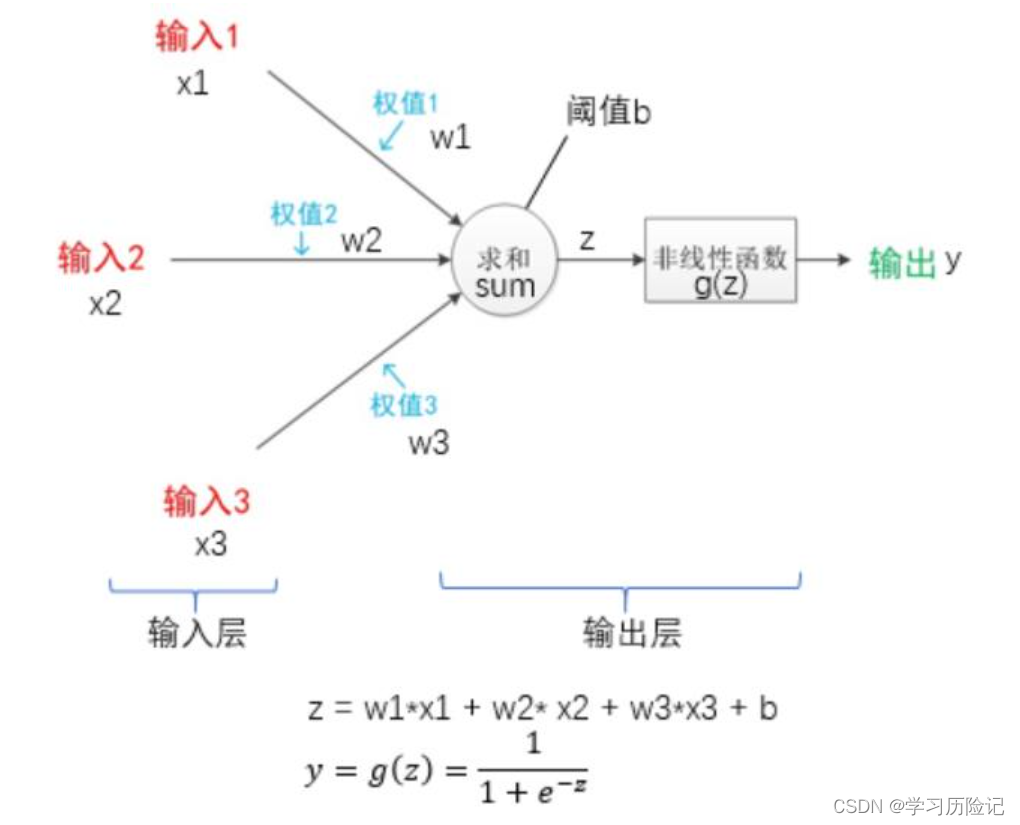
Perceptron model structure is similar to neurons,如下图所示,It has an input layer and output layer,The input layer is equivalent to neuron dendrites,用于接收输入,Output layer is the equivalent of axons and axonal endings,For the cumulative input and determine whether to activate the to“兴奋状态”.
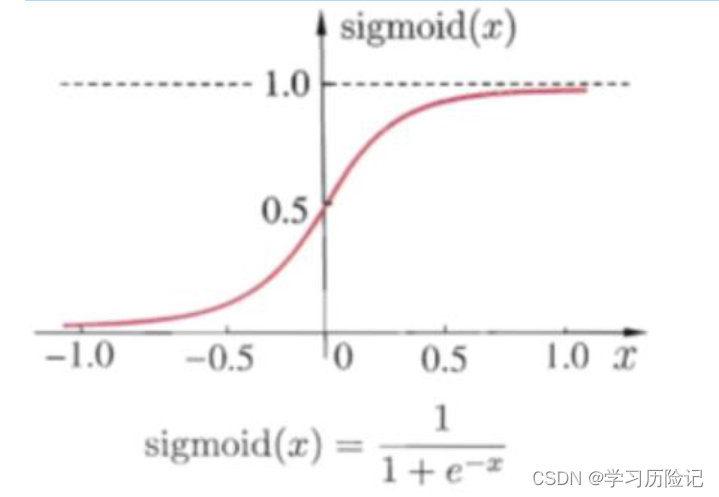
Perceptron can use activation function there are many kinds of,上图中使用的是sigmoid函数,Its function curve as shown in the figure below,It can be seen that function of agv is(0.0, 1.0).
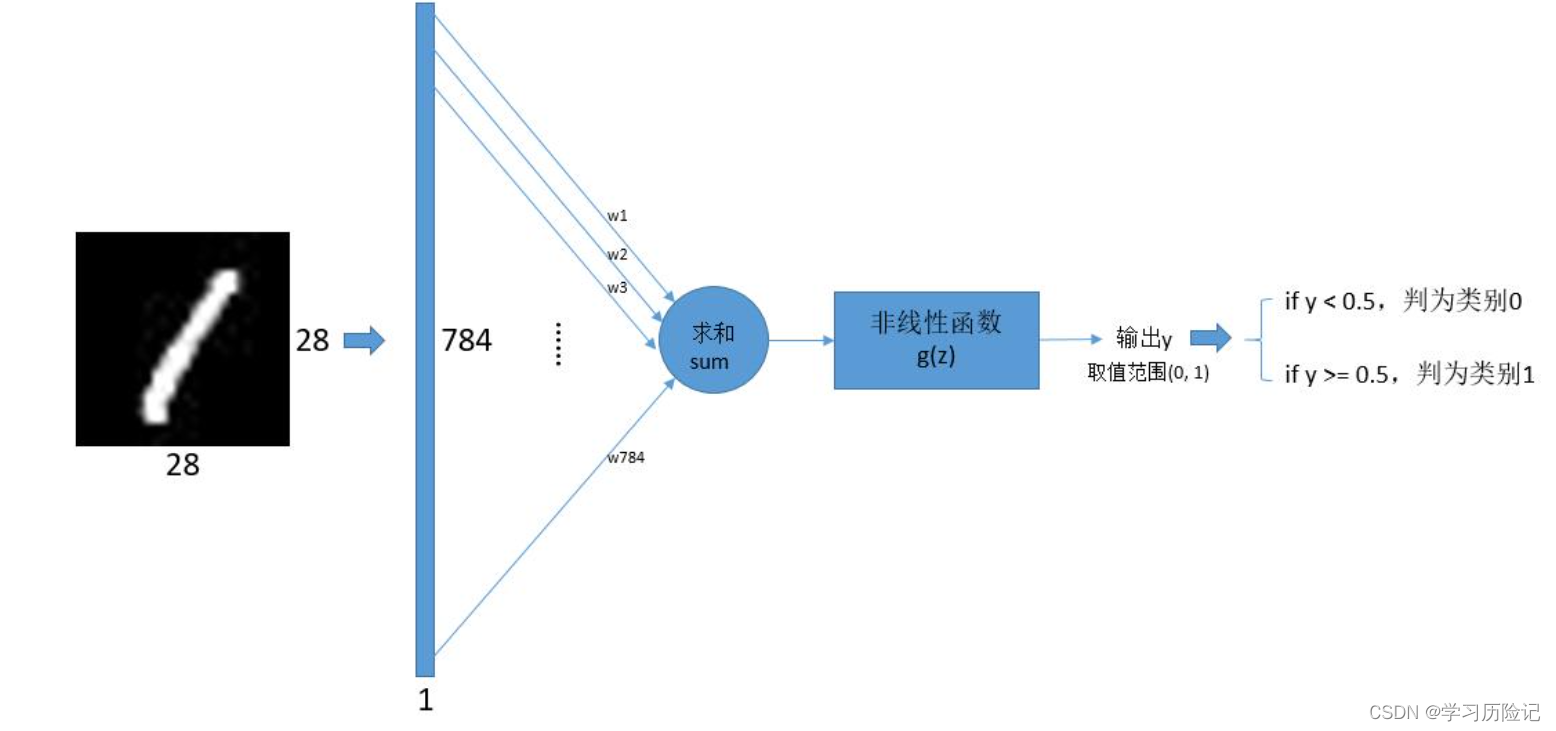
那么,How to use the perceptron to achieve handwritten Numbers0和1The binary classification? Known handwritten digital image data can be used28*28的数组来表示,You can convert the array to784*1的列向量,The column vector as input of perception machine,That is to say, the input and weights are784个.
The output of the perceptron is0.0到1.0之前的小数,And need is a binary classification problem,Expect the results of the final output is0或1.The output can be perceived in the machiney之后,Add a post-processing judgment,如果y>0.5,Is convicted of category1,Otherwise the sentence to category0,This is the perception machine is used to realize handwritten Numbers0和1Two classification method of,可以表示为下图:
1. The essential difference between traditional programming method and machine learning method
Perceptron to achieve two classification has been verified the feasibility of the,Before starting the implementation,First to understand the difference between the traditional programming method and machine learning method.
Traditional programming method of mode
Traditional programming method of model can be represented with below,Most programs can be seen as a box,Given a clear input,Had a clear output,And the program implementation logic is written by a programmer asm,Step by step, people tell the computer what to do,People can fully explain why give an input can get some output.
Machine learning method of mode
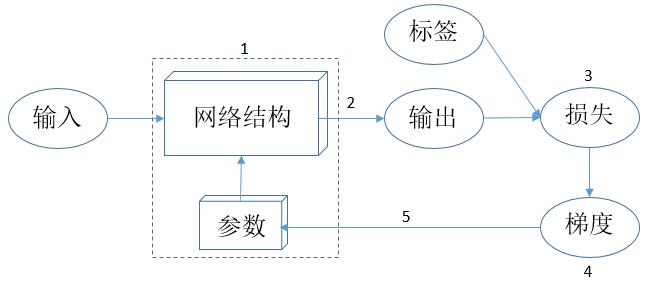
Machine learning method of model can be represented with below,核心在于“网络结构 + 参数”,Also can regard it as a special program,This program is not only by the programmer write out,People only defines the network structure,And parameters is through machine learning method by computer“学习”得来的,People can't explain why want to take these parameter values.
Machine learning methods of learning mode
Then the machine learning method is how to“学习”的呢?思想其实很简单,可以用下图来表示:
Above the learning mode can be summarized as the following:
(1)定义网络结构,And to all the parameters in the network w Give random value;
(2)Using the network to predict a batch of samples,得到预测值pred_y;
(3)定义一个损失函数,如 $loss=(pred\_y-true\_y)^2$,true_y是指标签,The purpose of the training model is made of all training data loss as much as possible to the sum of small;
(4)For all the loss function was obtained parameter gradient gradient_w;
(5)按照公式 w = w - lr * gradient_w 对所有参数w进行更新,其中lr是指学习率,常见的取值有0.01、0.001、0.0001等.
In accordance with the above summarized below points to realize the whole process of machine learning,After completing all code,Review the understanding.
2.加载数据集
Before starting machine learning process,Is still the first loading data set.由于整个MNIST数据集是包含0~9的所有图片,现在研究的是简化的0和1的二分类问题,所以先从整个数据集中将所有手写数字0和1的图片挑选出来,同样也需要区分训练集和测试集.
挑选数字0和1The training sample and test sample
import os
import numpy as np
import mindspore.dataset as ds
datasets_dir = '../datasets'
if not os.path.exists(datasets_dir):
os.makedirs(datasets_dir)
import moxing as mox
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(datasets_dir, 'MNIST_Data.zip')):
mox.file.copy('obs://modelarts-labs-bj4-v2/course/hwc_edu/python_module_framework/datasets/mindspore_data/MNIST_Data.zip',
os.path.join(datasets_dir, 'MNIST_Data.zip'))
os.system('cd %s; unzip MNIST_Data.zip' % (datasets_dir))
# 读取完整训练样本和测试样本
mnist_ds_train = ds.MnistDataset(os.path.join(datasets_dir, "MNIST_Data/train"))
mnist_ds_test = ds.MnistDataset(os.path.join(datasets_dir, "MNIST_Data/test"))
items_train = mnist_ds_train.create_dict_iterator(output_numpy=True)
train_data = np.array([i for i in items_train])
images_train = np.array([i["image"] for i in train_data])
labels_train = np.array([i["label"] for i in train_data])
items_test = mnist_ds_test.create_dict_iterator(output_numpy=True)
test_data = np.array([i for i in items_test])
images_test = np.array([i["image"] for i in test_data])
labels_test = np.array([i["label"] for i in test_data])
train_zeros = np.squeeze(images_train[labels_train==0])
train_ones = np.squeeze(images_train[labels_train==1])
test_zeros = np.squeeze(images_test[labels_test==0])
test_ones = np.squeeze(images_test[labels_test==1])
print('数字0,训练集规模:', len(train_zeros), ',测试集规模:', len(test_zeros))
print('数字1,训练集规模:', len(train_ones), ',测试集规模:', len(test_ones))数字0,训练集规模: 5923 ,测试集规模: 980
数字1,训练集规模: 6742 ,测试集规模: 1135
train_x = np.vstack((train_zeros, train_ones)) # 将数字0和1The sample collected together,np.vstackSaid the two arrays for vertical stitching
train_y = np.array([0] * len(train_zeros) + [1] * len(train_ones)).astype(np.uint8)
test_x = np.vstack((test_zeros, test_ones)) # 将数字0和1The sample collected together,np.vstackSaid the two arrays for vertical stitching
test_y = np.array([0] * len(test_zeros) + [1] * len(test_ones)).astype(np.uint8)train_x = train_x.reshape(-1, 28*28) # Each sample into a row vector,Because the row vector is convenient for calculation
train_y = train_y.reshape(-1, 1)
test_x = test_x.reshape(-1, 28*28) # Each sample into a row vector,Because the row vector is convenient for calculation
test_y = test_y.reshape(-1, 1)print(train_x.shape, train_y.shape, test_x.shape, test_y.shape)(12665, 784) (12665, 1) (2115, 784) (2115, 1)
3.Mixed wash data set
Because of machine learning method is through the training of the training sample to obtain a model of a classification ability,And this model will be more inclined to“记住”The last of the training sample.If to model of training data is a full digital before0,After a period of all digital1,This model will eventually tend to be more effective classification number1.因此,If you want to make the model for the balance of classification ability,Need to order training data.
The test set is used only for testing,不参与训练,Don't force the mixed wash,是一个可选的操作.
train_data = np.hstack((train_x, train_y)) # np.hstackSaid the two arrays horizontally splicing
test_data = np.hstack((test_x, test_y)) # np.hstackSaid the two arrays horizontally splicing
np.random.seed(0)
np.random.shuffle(train_data) # 打乱train_dataAn array of row order
np.random.shuffle(test_data) # 打乱test_dataAn array of row order
train_x = train_data[:, :-1] # 重新取出train_x和train_y
train_y = train_data[:, -1].reshape(-1, 1)
test_x = test_data[:, :-1] # 重新取出train_x和train_y
test_y = test_data[:, -1].reshape(-1, 1)Review images and whether the label has been upset
from PIL import Image
batch_size = 10 # 查看10个样本
print(train_y.flatten()[:batch_size].tolist())
batch_img = train_x[0].reshape(28, 28)
for i in range(1, batch_size):
batch_img = np.hstack((batch_img, train_x[i].reshape(28, 28))) # 将一批图片水平拼接起来,方便下一步进行显示
Image.fromarray(batch_img)[1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0]
4.数据预处理
Most machine learning method to the data preprocessing and then to learn,Pretreatment methods there are many kinds of,This case only the data normalization preprocessing.
Normalization is refers to the scope of training data into[0, 1].Data normalization has many advantages,Can make the learning process faster,Can also prevent some cases training process from calculating overflow.
There are many kinds of normalized image data way,This case is the entire array divided by255的方式,Because the image array of a maximum of255,除以255You can make the scope of image data into[0, 1].
train_x = train_x.astype(np.float) / 255.0
train_y = train_y.astype(np.float)
test_x = test_x.astype(np.float) / 255.0
test_y = test_y.astype(np.float)5. 封装成load_data函数
到此,Completed the training data preparation,可以将以上操作封装成load_data函数,以便后面再次用到.
%%writefile ../datasets/MNIST_Data/load_data_zeros_ones.py
def load_data_zeros_ones(datasets_dir):
import os
import numpy as np
import mindspore.dataset as ds
# 读取完整训练样本和测试样本
datasets_dir = '../datasets'
mnist_ds_train = ds.MnistDataset(os.path.join(datasets_dir, "MNIST_Data/train"))
mnist_ds_test = ds.MnistDataset(os.path.join(datasets_dir, "MNIST_Data/test"))
items_train = mnist_ds_train.create_dict_iterator(output_numpy=True)
train_data = np.array([i for i in items_train])
images_train = np.array([i["image"] for i in train_data])
labels_train = np.array([i["label"] for i in train_data])
items_test = mnist_ds_test.create_dict_iterator(output_numpy=True)
test_data = np.array([i for i in items_test])
images_test = np.array([i["image"] for i in test_data])
labels_test = np.array([i["label"] for i in test_data])
train_zeros = np.squeeze(images_train[labels_train==0])
train_ones = np.squeeze(images_train[labels_train==1])
test_zeros = np.squeeze(images_test[labels_test==0])
test_ones = np.squeeze(images_test[labels_test==1])
print('数字0,训练集规模:', len(train_zeros), ',测试集规模:', len(test_zeros))
print('数字1,训练集规模:', len(train_ones), ',测试集规模:', len(test_ones))
train_x = np.vstack((train_zeros, train_ones)) # 将数字0和1The sample collected together,np.vstackSaid the two arrays for vertical stitching
train_y = np.array([0] * len(train_zeros) + [1] * len(train_ones)).astype(np.uint8)
test_x = np.vstack((test_zeros, test_ones)) # 将数字0和1The sample collected together,np.vstackSaid the two arrays for vertical stitching
test_y = np.array([0] * len(test_zeros) + [1] * len(test_ones)).astype(np.uint8)
train_x = train_x.reshape(-1, 28*28) # Each sample into a row vector,Because the row vector is convenient for calculation
train_y = train_y.reshape(-1, 1)
test_x = test_x.reshape(-1, 28*28) # Each sample into a row vector,Because the row vector is convenient for calculation
test_y = test_y.reshape(-1, 1)
train_data = np.hstack((train_x, train_y)) # np.hstackSaid the two arrays horizontally splicing
test_data = np.hstack((test_x, test_y)) # np.hstackSaid the two arrays horizontally splicing
np.random.seed(0)
np.random.shuffle(train_data) # 打乱train_dataAn array of row order
np.random.shuffle(test_data) # 打乱test_dataAn array of row order
train_x = train_data[:, :-1] # 重新取出train_x和train_y
train_y = train_data[:, -1].reshape(-1, 1)
test_x = test_data[:, :-1] # 重新取出train_x和train_y
test_y = test_data[:, -1].reshape(-1, 1)
train_x = train_x.astype(np.float) / 255.0
train_y = train_y.astype(np.float)
test_x = test_x.astype(np.float) / 255.0
test_y = test_y.astype(np.float)
return train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y6. 定义网络结构
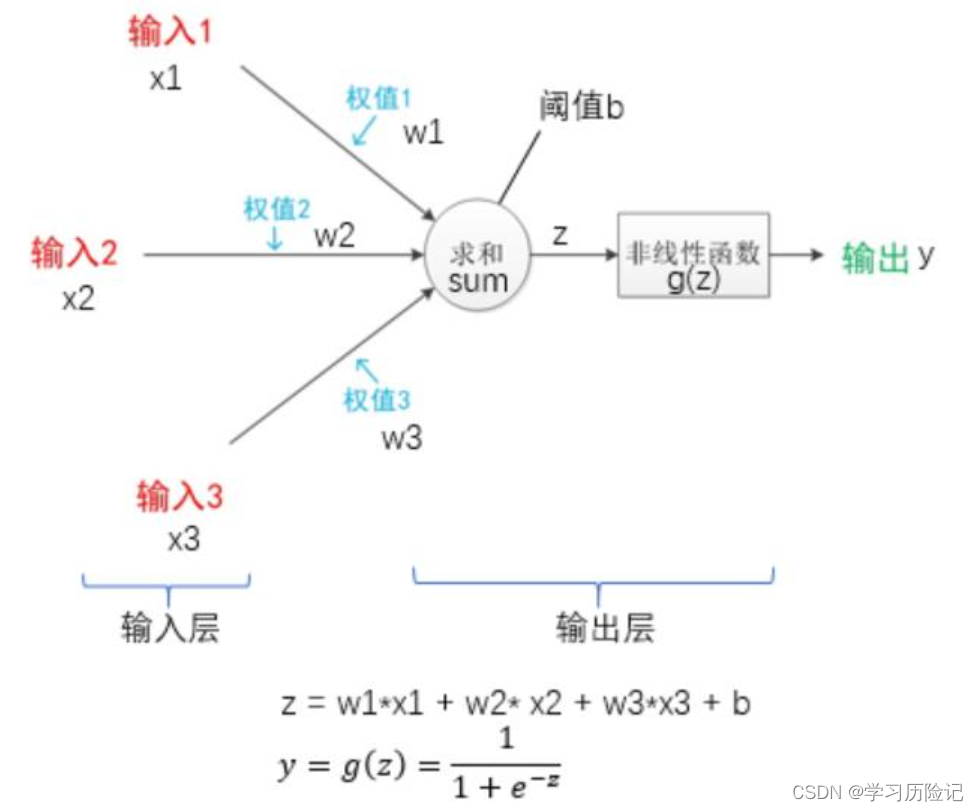
The case of network adopts perceptron structure as shown in the above,除去输入X和输出y之外,The weight value of figureW、阈值b、The weighted sum function unit、Need to define the nonlinear function unit,Through the definition of the following code to implement network structure.
np.random.seed(0)class Network(object):
def __init__(self, num_of_weights):
self.w = np.random.randn(num_of_weights, 1) # 使用np.random.randn随机生成一个 num_of_weights*1 的列向量,The vector is the weightw
self.b = 0.
def forward(self, x): # 加权求和单元和非线性函数单元通过定义计算过程来实现
z = np.dot(x, self.w) + self.b # 加权求和
pred_y = 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-z)) # 非线性函数sigmoid
return pred_yRandom initialization two network,And the forecast of the same sample
net1 = Network(28*28)
sample = train_x[0]
true_y = train_y[0]
pred_y_1 = net1.forward(sample)
print('true_y:', true_y, 'pred_y:', pred_y_1)true_y: [1.] pred_y: [0.00037376]
net2 = Network(28*28)
sample = train_x[0]
true_y = train_y[0]
pred_y_2 = net2.forward(sample)
print('true_y:', true_y, 'pred_y:', pred_y_2)true_y: [1.] pred_y: [0.96392999]
7.定义损失函数
The above two networks for the same label as1The samples is forecasted,net1The predicted value is0.00006124,net2The predicted value is0.99999943,显然net2Forecasts are closer to the true value,Can make evaluation:net2对train_x[0]The predicted effect of the sample thannet1更好.
To design a can self learning、Self improvement of network,Have to tell the computer the current network whether good or not,And to have a quantitative indicators to measure“好”或“不好”的程度,The quantitative index of machine learning is called loss valueloss.
计算loss有很多种方法,A common way is to均方误差,公式:$loss=(pred\_y-true\_y)^2$ 于是,You can calculate the abovenet1和net2两个网络在train_x[0]The loss value on the sample,可以看到loss2比loss1小 .
loss1 = (pred_y_1 - true_y)**2
loss2 = (pred_y_2 - true_y)**2
print('loss1:', loss1, 'loss2:', loss2)loss1: [0.99925262] loss2: [0.00130105]
但是,Evaluation of a network is good,Not on a single sample evaluation,But on a batch of samples to evaluate,So will calculate a batch of sample loss value.On top of a single sample loss value calculation formula to improve the,就可以得到A number of sample loss value calculation formula,具体如下: $ loss=\frac{1}{N}\sum^{N}_{i=0}{(pred\_y-true\_y)^2} $
于是,We can use the following code to define the loss function of network :
class Network(object):
def __init__(self, num_of_weights):
np.random.seed(0)
self.w = np.random.randn(num_of_weights, 1) # 使用np.random.randn随机生成一个 num_of_weights*1 的列向量,The vector is the weightW
self.b = 0.
def forward(self, x): # 加权求和单元和非线性函数单元通过定义计算过程来实现
z = np.dot(x, self.w) + self.b # 加权求和
pred_y = 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-z)) # 非线性函数sigmoid
return pred_y
def loss_fun(self, pred_y, true_y):
"""
pred_y:Network of a batch of samples of column vector of the predicted values of
true_y:A sample of real label
"""
error = pred_y - true_y
num_samples = error.shape[0]
cost = error * error
cost = np.sum(cost) / num_samples
return costThe following ten samples we can calculate the overall loss value:
net3 = Network(28*28)
sample = train_x[0:10]
true_y = train_y[0:10]
pred_y = net3.forward(sample)
print('loss:', net3.loss_fun(pred_y, true_y))loss: 0.39990529371765265
8.定义评价函数
After defined loss function,To define evaluation function.These two functions are used to evaluate model performance,Easy to confuse their meaning,Here to explain the difference between the two:
(1)Loss function is used to measure the deviation between the predicted value and true value of the model,偏差越大,梯度就越大,To update parameters of the,Goal of the whole process of machine learning is the value of the loss function as small as possible;
(2)Evaluation function has a variety of evaluation index,The commonly used indicator is accurate,It is used in statistical models to predict the results of the time,比如有100个测试样本,其中有99All right,准确率就是99%;
言而简之,Loss function's role in the process of the gradient descent,Evaluation function is a statistical model of evaluation index to people.
class Network(object):
def __init__(self, num_of_weights):
np.random.seed(0)
self.w = np.random.randn(num_of_weights, 1) # 使用np.random.randn随机生成一个 num_of_weights*1 的列向量,The vector is the weightW
self.b = 0.
def forward(self, x): # 加权求和单元和非线性函数单元通过定义计算过程来实现
z = np.dot(x, self.w) + self.b # 加权求和
pred_y = 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-z)) # 非线性函数sigmoid
return pred_y
def loss_fun(self, pred_y, true_y):
"""
pred_y:Network of a batch of samples of column vector of the predicted values of
true_y:A sample of real label
"""
error = pred_y - true_y
num_samples = error.shape[0]
cost = error * error
cost = np.sum(cost) / num_samples
return cost
def evaluate(self, pred_y, true_y, threshold=0.5):
pred_y[pred_y < threshold] = 0 # 预测值小于0.5,Is convicted of category0
pred_y[pred_y >= threshold] = 1
acc = (pred_y == true_y).float().mean()
return acc9. Manual gradient descent algorithm is derived
Realize the gradient descent algorithm is two steps:
(1)For all the loss function was obtained parameter gradient gradient_w;
(2)按照公式 w = w - lr * gradient_w 对所有参数w进行更新
The key steps in the first step,If need from zero loss function for all parameters calculation method of the gradient,Requires a certain mathematical basis for the formulas,Can see in the code below gradient 函数.The implementation of the second step is simple,See below in the code update 函数.
class Network(object):
def __init__(self, num_of_weights):
np.random.seed(0)
self.w = np.random.randn(num_of_weights, 1) # 使用np.random.randn随机生成一个 num_of_weights*1 的列向量,The vector is the weightW
self.b = 0.
def forward(self, x): # 加权求和单元和非线性函数单元通过定义计算过程来实现
z = np.dot(x, self.w) + self.b # 加权求和
pred_y = 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-z)) # 非线性函数sigmoid
return pred_y
def loss_fun(self, pred_y, true_y):
"""
pred_y:Network of a batch of samples of column vector of the predicted values of
true_y:A sample of real label
"""
error = pred_y - true_y
num_samples = error.shape[0]
cost = error * error
cost = np.sum(cost) / num_samples
return cost
def evaluate(self, pred_y, true_y, threshold=0.5):
pred_y[pred_y < threshold] = 0 # 预测值小于0.5,Is convicted of category0
pred_y[pred_y >= threshold] = 1
acc = (pred_y == true_y).float().mean()
return acc
def gradient(self, x, y, pred_y):
gradient_w = (pred_y-y)*pred_y*(1-pred_y)*x
gradient_w = np.mean(gradient_w, axis=0)
gradient_w = gradient_w[:, np.newaxis]
gradient_b = (pred_y - y)*pred_y*(1-pred_y)
gradient_b = np.mean(gradient_b)
return gradient_w, gradient_b
def update(self, gradient_w, gradient_b, eta = 0.01):
self.w = self.w - eta * gradient_w
self.b = self.b - eta * gradient_b10.实现训练函数

The process of training function,就是把上图中的2、3、4、5Skewer idea process,Details see the following code train 函数.
class Network(object):
def __init__(self, num_of_weights):
np.random.seed(0)
self.w = np.random.randn(num_of_weights, 1) # 使用np.random.randn随机生成一个 num_of_weights*1 的列向量,The vector is the weightW
self.b = 0.
def forward(self, x): # 加权求和单元和非线性函数单元通过定义计算过程来实现
z = np.dot(x, self.w) + self.b # 加权求和
pred_y = 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-z)) # 非线性函数sigmoid
return pred_y
def loss_fun(self, pred_y, true_y):
"""
pred_y:Network of a batch of samples of column vector of the predicted values of
true_y:A sample of real label
"""
error = pred_y - true_y
num_samples = error.shape[0]
cost = error * error
cost = np.sum(cost) / num_samples
return cost
def evaluate(self, pred_y, true_y, threshold=0.5):
pred_y[pred_y < threshold] = 0 # 预测值小于0.5,Is convicted of category0
pred_y[pred_y >= threshold] = 1
acc = np.mean((pred_y == true_y).astype(np.float))
return acc
def gradient(self, x, y, pred_y):
gradient_w = (pred_y-y)*pred_y*(1-pred_y)*x
gradient_w = np.mean(gradient_w, axis=0)
gradient_w = gradient_w[:, np.newaxis]
gradient_b = (pred_y - y)*pred_y*(1-pred_y)
gradient_b = np.mean(gradient_b)
return gradient_w, gradient_b
def update(self, gradient_w, gradient_b, lr = 0.01):
self.w = self.w - lr * gradient_w
self.b = self.b - lr * gradient_b
def train(self, train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y, max_epochs=100, lr=0.01):
train_losses = []
test_losses = []
train_accs = []
test_accs = []
for epoch in range(1, max_epochs + 1):
pred_y_train = self.forward(train_x)
gradient_w, gradient_b = self.gradient(train_x, train_y, pred_y_train)
self.update(gradient_w, gradient_b, lr)
if (epoch == 1) or (epoch % 200 == 0):
pred_y_test = self.forward(test_x)
train_loss = self.loss_fun(pred_y_train, train_y)
test_loss = self.loss_fun(pred_y_test, test_y)
train_acc = self.evaluate(pred_y_train, train_y)
test_acc = self.evaluate(pred_y_test, test_y)
print('epoch: %d, train_loss: %.4f, test_loss: %.4f, train_acc: %.4f, test_acc: %.4f' % (epoch, train_loss, test_loss, train_acc, test_acc))
train_losses.append(train_loss)
test_losses.append(test_loss)
train_accs.append(train_acc)
test_accs.append(test_acc)
return train_losses, test_losses, train_accs, test_accs11.开始训练
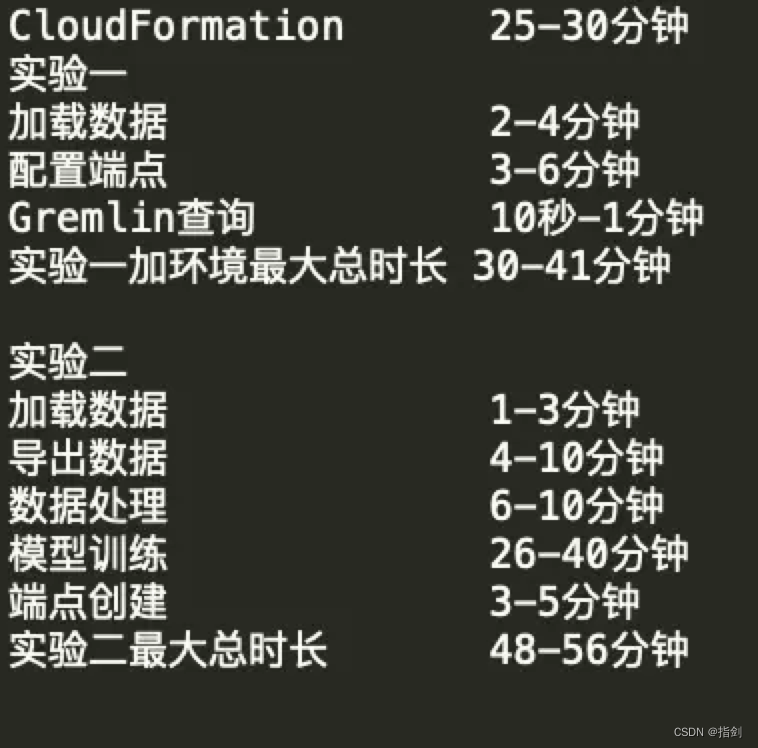
Training takes about615秒
import time
start_time = time.time()
# 创建网络
net = Network(28*28)
max_epochs = 3000
# 启动训练
train_losses, test_losses, train_accs, test_accs = net.train(train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y, max_epochs=max_epochs, lr=0.01)
print('cost time: %.1f s' % (time.time() - start_time))epoch: 1, train_loss: 0.5230, test_loss: 0.5282, train_acc: 0.4707, test_acc: 0.4652
epoch: 200, train_loss: 0.5216, test_loss: 0.5268, train_acc: 0.4715, test_acc: 0.4652 epoch: 400, train_loss: 0.5199, test_loss: 0.5251, train_acc: 0.4726, test_acc: 0.4657 epoch: 600, train_loss: 0.5177, test_loss: 0.5228, train_acc: 0.4736, test_acc: 0.4681 epoch: 800, train_loss: 0.5148, test_loss: 0.5199, train_acc: 0.4753, test_acc: 0.4704 epoch: 1000, train_loss: 0.5109, test_loss: 0.5161, train_acc: 0.4776, test_acc: 0.4733 epoch: 1200, train_loss: 0.5057, test_loss: 0.5110, train_acc: 0.4815, test_acc: 0.4761 epoch: 1400, train_loss: 0.4987, test_loss: 0.5039, train_acc: 0.4870, test_acc: 0.4813 epoch: 1600, train_loss: 0.4891, test_loss: 0.4938, train_acc: 0.4949, test_acc: 0.4870 epoch: 1800, train_loss: 0.4752, test_loss: 0.4787, train_acc: 0.5047, test_acc: 0.4983 epoch: 2000, train_loss: 0.4532, test_loss: 0.4548, train_acc: 0.5197, test_acc: 0.5191 epoch: 2200, train_loss: 0.4166, test_loss: 0.4169, train_acc: 0.5529, test_acc: 0.5499 epoch: 2400, train_loss: 0.3610, test_loss: 0.3630, train_acc: 0.5998, test_acc: 0.6014 epoch: 2600, train_loss: 0.2896, test_loss: 0.2913, train_acc: 0.6692, test_acc: 0.6638 epoch: 2800, train_loss: 0.2191, test_loss: 0.2173, train_acc: 0.7447, test_acc: 0.7428 epoch: 3000, train_loss: 0.1631, test_loss: 0.1582, train_acc: 0.8032, test_acc: 0.8061
cost time: 615.7 s
12.训练过程可视化
将训练过程中的train_loss, test_loss, train_acc, test_acc绘制成曲线图,Analysis the change trend of these indicators
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
# The index change trend of draw
plot_x = np.arange(0, max_epochs+1, 200)
plot_y_1 = np.array(train_losses)
plot_y_2 = np.array(test_losses)
plot_y_3 = np.array(train_accs)
plot_y_4 = np.array(test_accs)
plt.plot(plot_x, plot_y_1)
plt.plot(plot_x, plot_y_2)
plt.plot(plot_x, plot_y_3)
plt.plot(plot_x, plot_y_4)
plt.show() 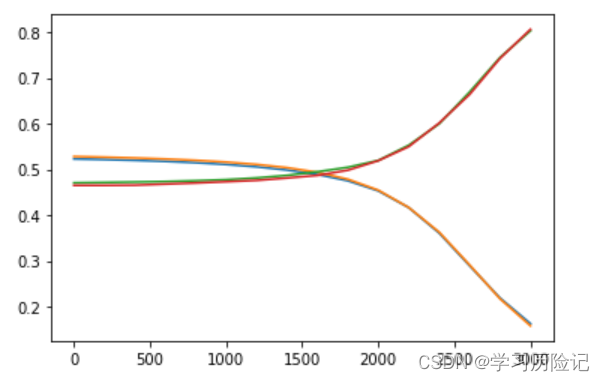
边栏推荐
- 2020-10-19
- target has libraries with conflicting names: libcrypto.a and libssl.a.
- SQL注入详解
- Briefly say Q-Q map; stats.probplot (QQ map)
- Pytorch语义分割理解
- 图像形变(插值方法)
- Lee‘s way of Deep Learning 深度学习笔记
- 动手学深度学习__数据操作
- [Deep Learning 21 Days Learning Challenge] 1. My handwriting was successfully recognized by the model - CNN implements mnist handwritten digit recognition model study notes
- TensorFlow2 study notes: 5. Common activation functions
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Qt日常学习
亚马逊云科技 Build On 2022 - AIot 第二季物联网专场实验心得
ConnectionRefusedError: [Errno 111] Connection refused问题解决
(Navigation page) OpenStack-M version - manual construction of two nodes - with video from station B
ValueError: Expected 96 from C header, got 88 from PyObject
【CV-Learning】Image Classification
多层LSTM
计算某像素点法线
Learning curve learning_curve function in sklearn
Copy攻城狮的年度之“战”|回顾2020
MFC 打开与保存点云PCD文件
YOLOV4流程图(方便理解)
tensorRT教程——tensor RT OP理解(实现自定义层,搭建网络)
AWS使用EC2降低DeepRacer的训练成本:DeepRacer-for-cloud的实践操作
Copy攻城狮信手”粘“来 AI 对对联
Deep Adversarial Decomposition: A Unified Framework for Separating Superimposed Images
迅雷关闭自动更新
MNIST手写数字识别 —— ResNet-经典卷积神经网络
Androd Day02
动手学深度学习_softmax回归



![[Deep Learning Diary] Day 1: Hello world, Hello CNN MNIST](/img/06/6f49260732e5832edae2ec80aafc99.png)