当前位置:网站首页>tensorRT教程——使用tensorRT OP 搭建自己的网络
tensorRT教程——使用tensorRT OP 搭建自己的网络
2022-08-04 05:29:00 【TigerZ*】
如下提供一个可以运行的使用tensorRT的OP来搭建自己定义的层或者直接重写自己网络,使用OP的场景:
1、自己的网络无法通过paser来直接转换为TRT的网络。如果自己写cuda实现,那么量化的操作也得自己实现,这样难度其实很高,建议还是使用TRT的OP搭建,搭建完支持量化等操作。
2、学习测试TRT的OP。
关于OP的一些我遇到的疑惑解读见我的另一篇博客:tensorRT教程——tensor RT OP理解(实现自定义层,搭建网络)_u012863603的博客-CSDN博客
import tensorrt as trt
import numpy
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import pycuda.autoinit
TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)
def generate_net(network, weights):
input_tensor = network.add_input(name="input", dtype=trt.float32, shape=(4, 5, 5))
print(input_tensor.shape)
# scale_1 = network.add_scale(input=input_tensor, mode=trt.tensorrt.ScaleMode.UNIFORM, shift=np.zeros((1), dtype=np.float32), scale=np.array([4], dtype=np.float32), power=np.ones((1), dtype=np.float32))
# unary_1 = network.add_unary(input=input_tensor, op=trt.tensorrt.UnaryOperation.EXP)
# print(unary_1.get_output(0).shape)
elemnet_1 = network.add_elementwise(input1=input_tensor, input2=input_tensor, op=trt.tensorrt.ElementWiseOperation.DIV)
print(elemnet_1.get_output(0).shape)
# reduce_1 = network.add_reduce(input=input_tensor, op=trt.tensorrt.ReduceOperation.MAX, axes=1, keep_dims=True)
# print(reduce_1.get_output(0).shape)
# network.mark_output(reduce_1.get_output(0))
# div_1 = network.add_elementwise(input1=input_tensor, input2=reduce_1.get_output(0), op=trt.tensorrt.ElementWiseOperation.DIV)
# network.mark_output(div_1.get_output(0))
# const_1 = network.add_constant(shape=[], weights=numpy.zeros((2,), dtype=numpy.int32))
# gather_1 = network.add_gather(input=input_tensor, indices=const_1.get_output(0), axis=2)
# print(const_1.get_output(0).shape)
# network.mark_output(gather_1.get_output(0))
# shuffle_1 = network.add_shuffle(input=gather_1.get_output(0))
# shuffle_1.reshape_dims=[1, 5, 5]
# print(shuffle_1.get_output(0).shape)
# concat_1 = network.add_concatenation(inputs=[input_tensor, gather_1.get_output(0)])
# print(concat_1.get_output(0).shape)
network.mark_output(elemnet_1.get_output(0))
def build_engine(weights):
# For more information on TRT basics, refer to the introductory samples.
with trt.Builder(TRT_LOGGER) as builder, builder.create_network() as network:
builder.max_workspace_size = 1 << 30
builder.max_batch_size = 8
# Populate the network using weights from the PyTorch model.
generate_net(network, weights)
# Build and return an engine.
return builder.build_cuda_engine(network)
def allocate_buffers(engine):
# Determine dimensions and create page-locked memory buffers (i.e. won't be swapped to disk) to hold host inputs/outputs.
h_input = cuda.pagelocked_empty(trt.volume(engine.get_binding_shape(0)) * engine.max_batch_size, dtype=trt.nptype(trt.float32))
h_output = cuda.pagelocked_empty(trt.volume(engine.get_binding_shape(1)) * engine.max_batch_size, dtype=trt.nptype(trt.float32))
# Allocate:device memory for inputs and outputs.
d_input = cuda.mem_alloc(h_input.nbytes)
d_output = cuda.mem_alloc(h_output.nbytes)
# Create a stream in which to copy inputs/outputs and run inference.
stream = cuda.Stream()
return h_input, d_input, h_output, d_output, stream
def inference(batch_size_inference, h_input, d_input, h_output, d_output, stream, context):
cuda.memcpy_htod_async(d_input, h_input, stream)
context.execute_async(batch_size=batch_size_inference, bindings=[int(d_input), int(d_output)], stream_handle=stream.handle)
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(h_output, d_output, stream)
stream.synchronize()
return h_output
#result_trt = numpy.reshape(h_output, (8, -1))[:batch_size_inference, ]
#return result_trt
def main():
input_array = numpy.array(range(300), dtype=numpy.float32).reshape(3,4,5,5)
weights = None
with build_engine(weights) as engine:
h_input, d_input, h_output, d_output, stream = allocate_buffers(engine)
with engine.create_execution_context() as context:
h_input = input_array
result = inference(3,h_input, d_input, h_output, d_output, stream, context)
print(result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()边栏推荐
- [CV-Learning] Semantic Segmentation
- TensorFlow:tf.ConfigProto()与Session
- 空洞卷积
- Learning curve learning_curve function in sklearn
- The use of the attribute of the use of the animation and ButterKnife
- Jupyter Notebook安装库;ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘plotly‘解决方案。
- 【CV-Learning】线性分类器(SVM基础)
- YOLOV4流程图(方便理解)
- 简单明了,数据库设计三大范式
- (十)树的基础部分(一)
猜你喜欢
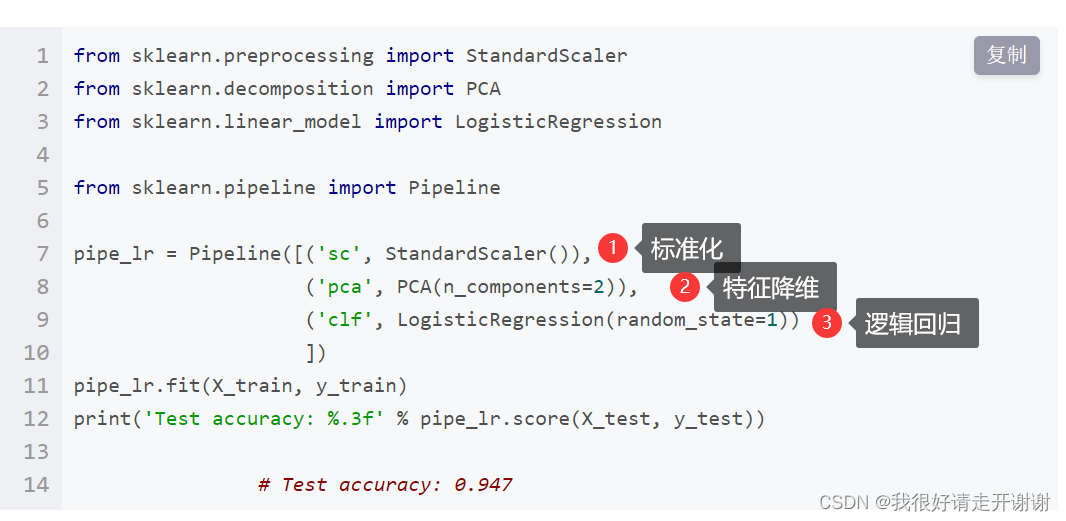
sklearn中的pipeline机制

【论文阅读】Mining Cross-Image Semantics for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
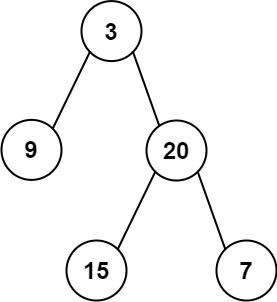
剑指 Offer 2022/7/1
Pytorch问题总结
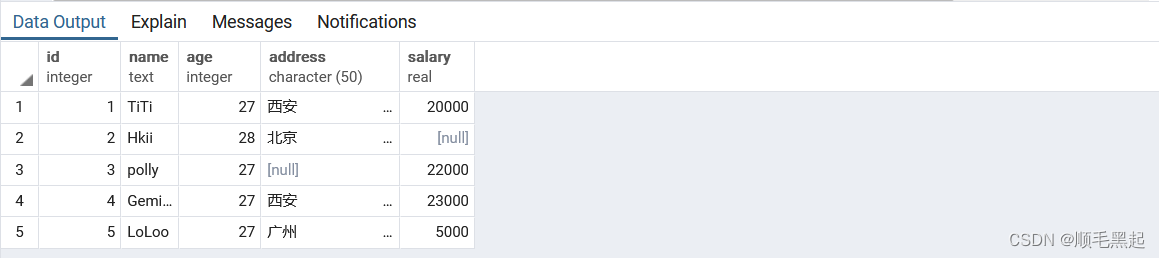
with recursive用法
![[Deep Learning 21-Day Learning Challenge] 3. Use a self-made dataset - Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) Weather Recognition](/img/d0/3b8549b9704278e8ec1df03a90f80e.png)
[Deep Learning 21-Day Learning Challenge] 3. Use a self-made dataset - Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) Weather Recognition
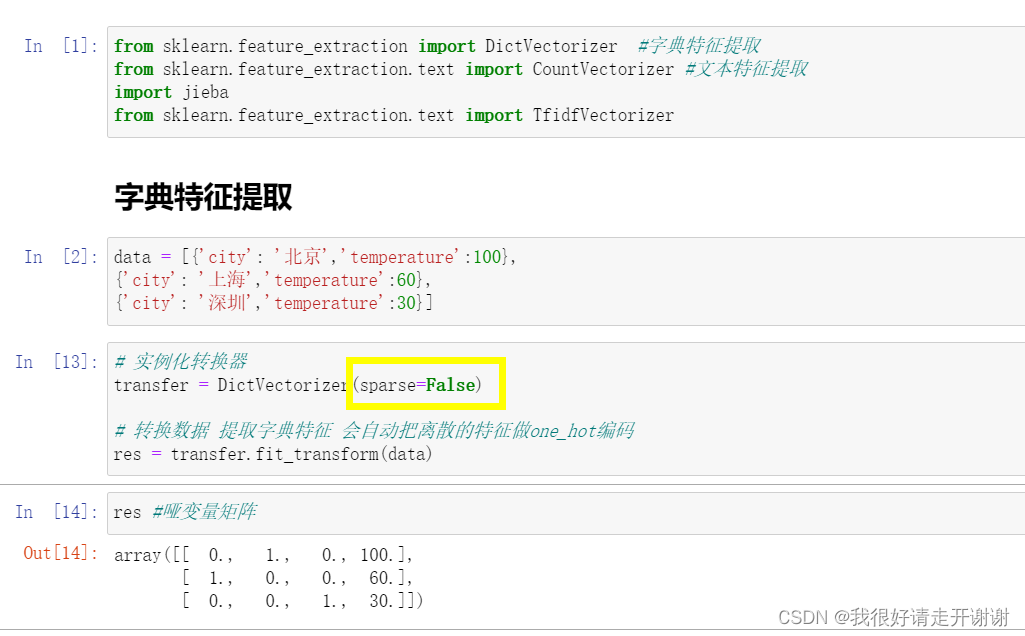
Dictionary feature extraction, text feature extraction.
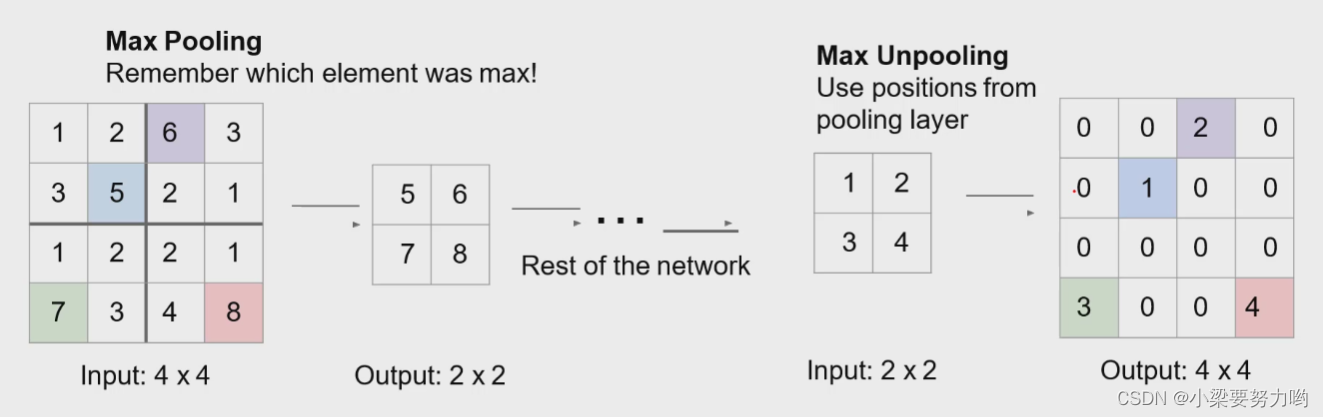
【CV-Learning】语义分割
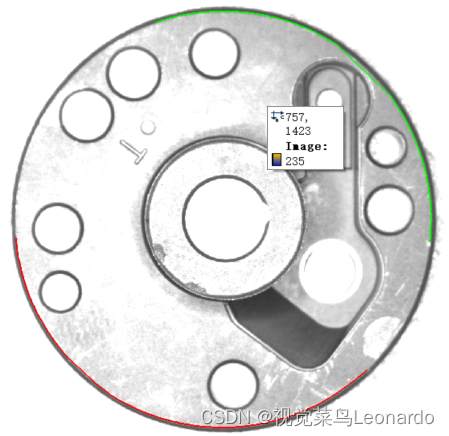
Halcon缺陷检测
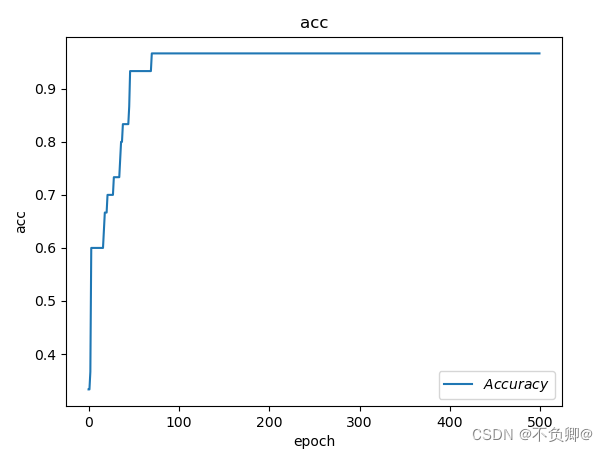
TensorFlow2 study notes: 4. The first neural network model, iris classification
随机推荐
属性动画的用法 以及ButterKnife的用法
postgresql中创建新用户等各种命令
TensorFlow2 study notes: 6. Overfitting and underfitting, and their mitigation solutions
【CV-Learning】Object Detection & Instance Segmentation
TensorFlow2 study notes: 4. The first neural network model, iris classification
Briefly say Q-Q map; stats.probplot (QQ map)
thymeleaf中 th:href使用笔记
Use of double pointers
postgres 递归查询
Jupyter Notebook安装库;ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘plotly‘解决方案。
pytorch学习-没掌握的点
【论文阅读】TransReID: Transformer-based Object Re-Identification
视图、存储过程、触发器
动手学深度学习_线性回归
sql中group by的用法
【深度学习21天学习挑战赛】2、复杂样本分类识别——卷积神经网络(CNN)服装图像分类
WARNING: sql version 9.2, server version 11.0. Some psql features might not work.
(十二)树--哈夫曼树
with recursive用法
计算某像素点法线