当前位置:网站首页>Makefile application
Makefile application
2022-07-05 07:54:00 【Soy sauce;】
1.Makefile The concept of
Use keil, mdk, avr When the tool develops the program, you can compile it with a little mouse
What is its internal mechanism ? How it organizes the management process ? How to decide which file to compile ?
gcc -o test a.c b.c
// Simple ,
// But all the files will be processed once ,
// When there are many files, if only one of them is modified, it will lead to low efficiency
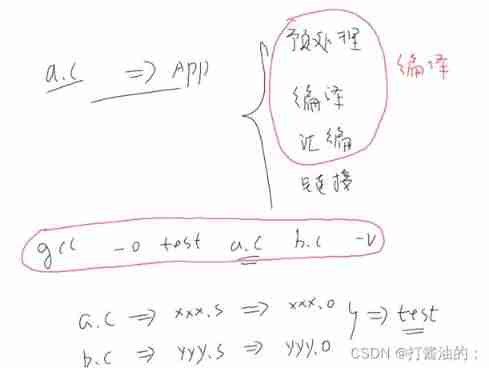


stay linux In the system make Is a very important compilation command , Whether it's project development or application software installation , We all use it a lot make or makeinstall. utilize make Tools , We can decompose large-scale development projects into more manageable modules , The source files in a project are not counted , By type 、 function 、 Modules are placed in several directories ,makefile A series of rules are defined to specify , Which files need to be compiled first , Which files need to be post compiled , Which files need to be recompiled , Even more complex functional operations , because makefile Like a Shell The script is the same , It can also execute operating system commands .makefile The benefit is “ Automated compilation ”, Once it's written , Just one make command , The whole project compiles completely automatically , Greatly improve the efficiency of software development .
2.Makefile Rules and usage
Conditions
When " Target file " non-existent ,
or
A dependent file is larger than the target file " new ",
be : perform " command "

The rules
One rule :
The goal is : rely on 1 rely on 2 …
[TAB] command
From top to bottom , Break down the task
perform :make
Two rules :
The pseudo target does not judge whether the target file exists or has been updated
Unconditionally execute the command
Fake target
.PHONY:
clean:( no need tab)
rm -rf $(OBJS) $(TARGET)
perform :make clean
Makefile Three elements of the basic rule :
The goal is : rely on 1 rely on 2 …
[TAB] command
notes : Take the names of these two documents casually , The purpose is to link
1) Target file :
Usually the name of the file to be generated , The target can be an executable or something else obj file , It can also be the name of an action ( There has to be )
Only one
2) Dependency file :
The file used to input and generate the target
A target usually has several dependent files ( There can be no )
One or more
3) command :
make The action performed , A rule can contain several commands ( There can be no )
When there are multiple commands , Every command takes a line
grammar :
make [ Fake target ]
If there is no false target , Default to the first target 
Use
Execute... In the current directory make command , I'll find it myself Makefile And execute
explain : When it is detected that no dependency needs to be updated, the following error will be reported 
3.Makefile Advanced Grammar
a. wildcard : %.o
[email protected] It means a goal
$< It means the first one 1 A dependency file
$^ Represents all dependent files
4.Makefile Variables in use
similar C Macro definition in language
stay Makefile It is a little similar to the variable in use C Macro definition in language , Using this variable is equivalent to replacing , Using variables can make Makefile Easy to maintain , The modification content becomes simple, variable definition and use .
7.1 Custom variable
1) Define variable methods :
Variable name = A variable's value
2) How to reference variables :
( change The amount name ) or ( Variable name ) or ( Variable name ) or { Variable name }
3)makefile Variable name :
makefile Variable names can start with numbers
Variables are case sensitive
Variables are generally in makefile The head definition of
Variables can be found almost in makefile Anywhere
4) Variable type
Real time variables 、 Delay variable , export
Simple variable ( Real time variables ) :
A := xxx # A The value of is determined immediately , It is determined at the time of definition
B = xxx # B The value of is determined only when it is used 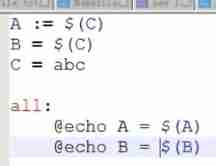

:= # Real time variables
= # Delay variable
?= # Delay variable , If it's No 1 The second definition works , If the variable has been defined before, ignore this sentence
+= # additional , Whether it's a real-time variable or a delay variable depends on the previous definition
5.Makefile function
a. $(foreach var,list,text)
b. $(filter pattern…,text) # stay text In accordance with patten Value of format
$(filter-out pattern…,text) # stay text It doesn't conform to patten Value of format
c. $(wildcard pattern) # pattern Defines the format of the file name ,
# wildcard Take out the existing files
d. ( p a t s u b s t p a t t e r n , r e p l a c e m e n t , (patsubst pattern,replacement, (patsubstpattern,replacement,(var)) # Take each value from the list
# If meet pattern
边栏推荐
- STM32 learning method
- UEFI development learning 2 - running ovmf in QEMU
- Day08 ternary operator extension operator character connector symbol priority
- 万字详解八大排序 必读(代码+动图演示)
- The printer encountered an abnormal configuration problem 0x8007007e (win10)
- MySQL - storage engine
- Software designer: 03 database system
- Some errors in configuring the environment
- 研究发现,跨境电商客服系统都有这五点功能!
- Gradle复合构建
猜你喜欢
Altium designer learning (I)
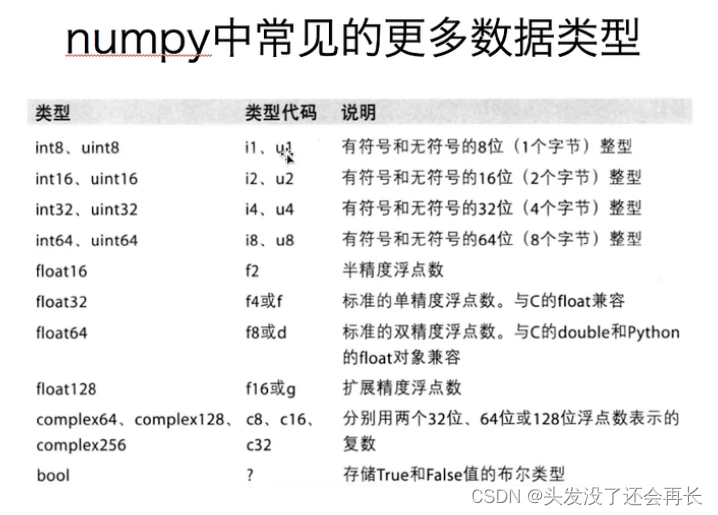
Numpy——1. Creation of array

Altium designer 19.1.18 - clear information generated by measuring distance
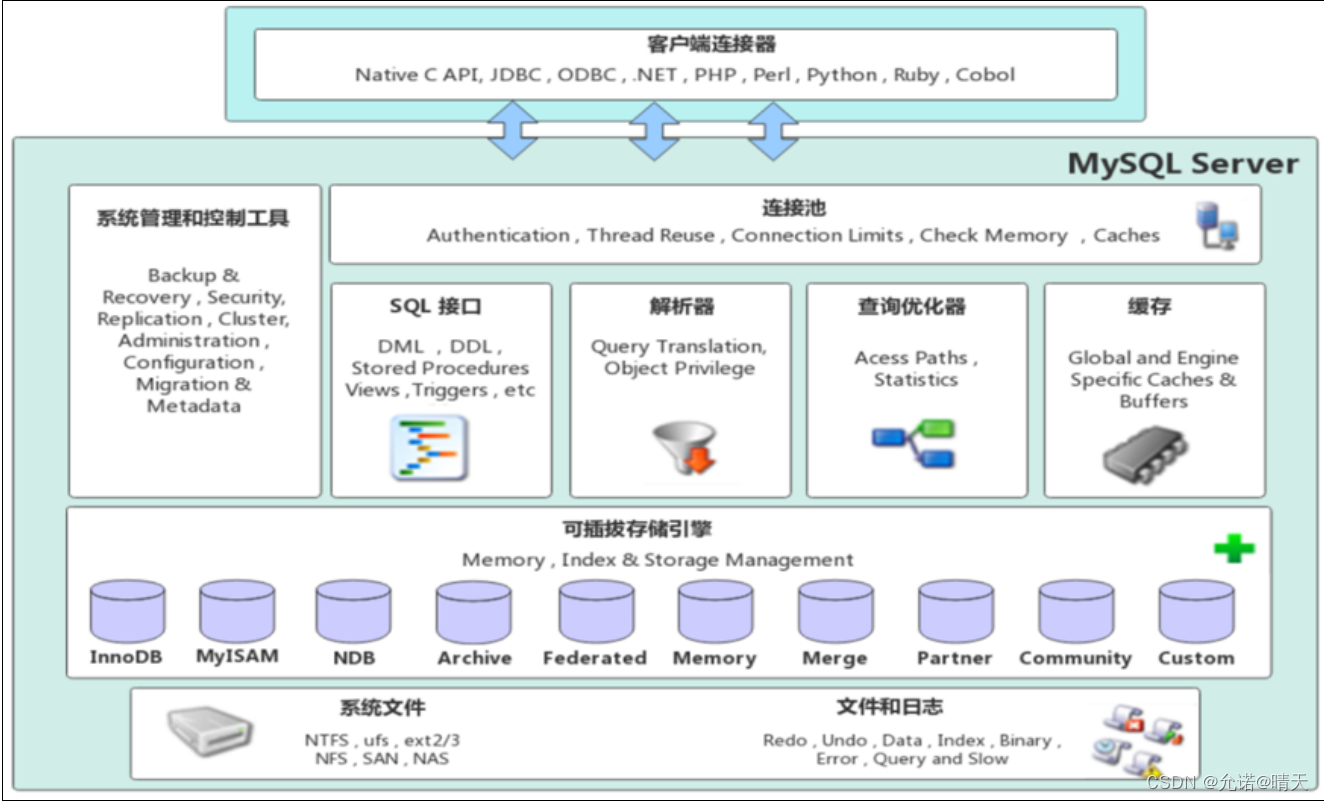
MySQL - storage engine
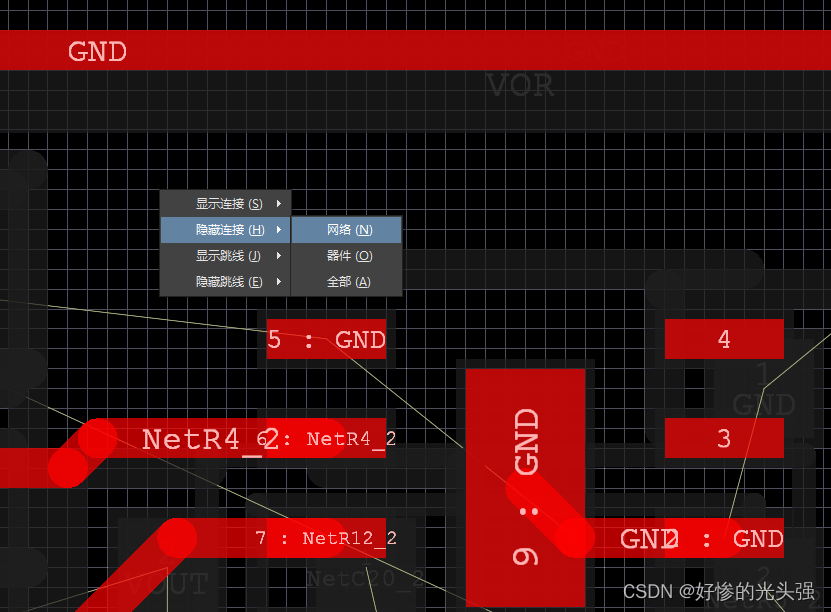
Altium Designer 19.1.18 - 隐藏某一个网络的飞线
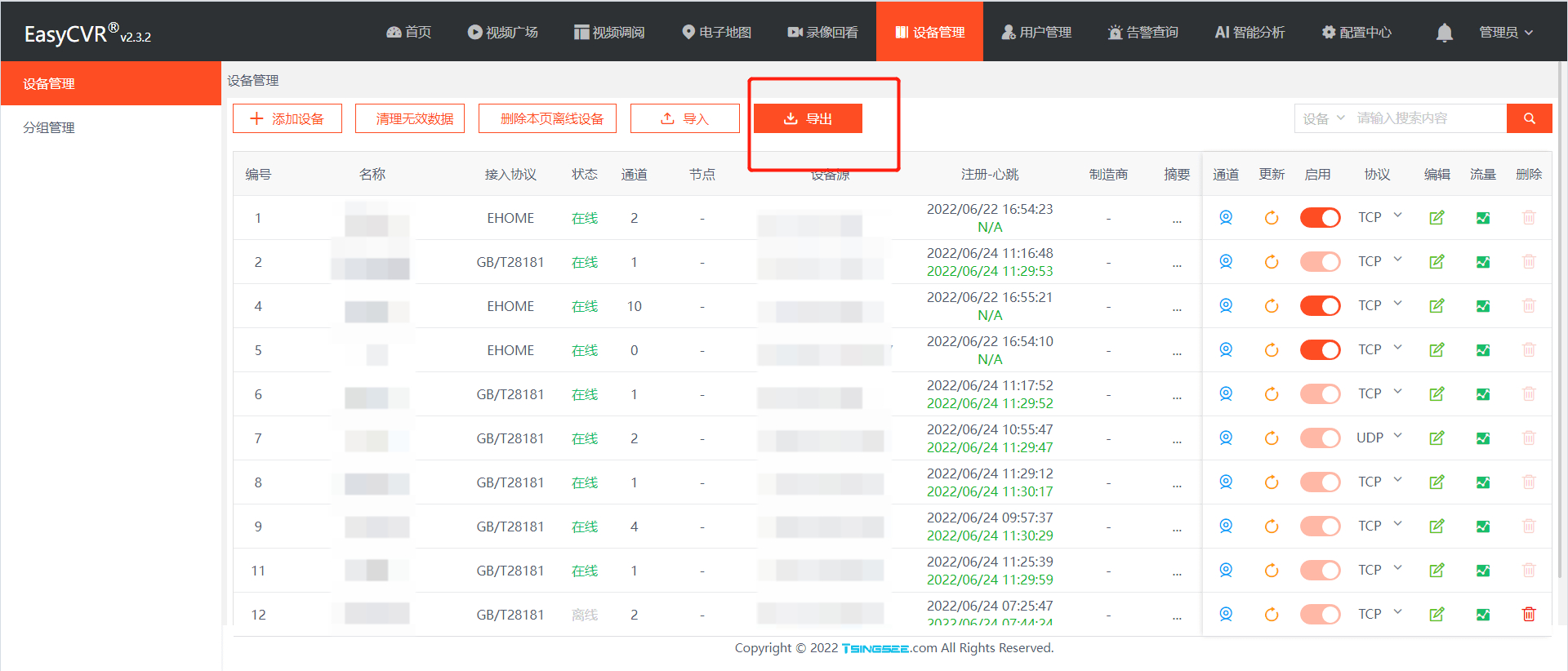
如何将EasyCVR平台RTSP接入的设备数据迁移到EasyNVR中?

A complete set of indicators for the 10000 class clean room of electronic semiconductors
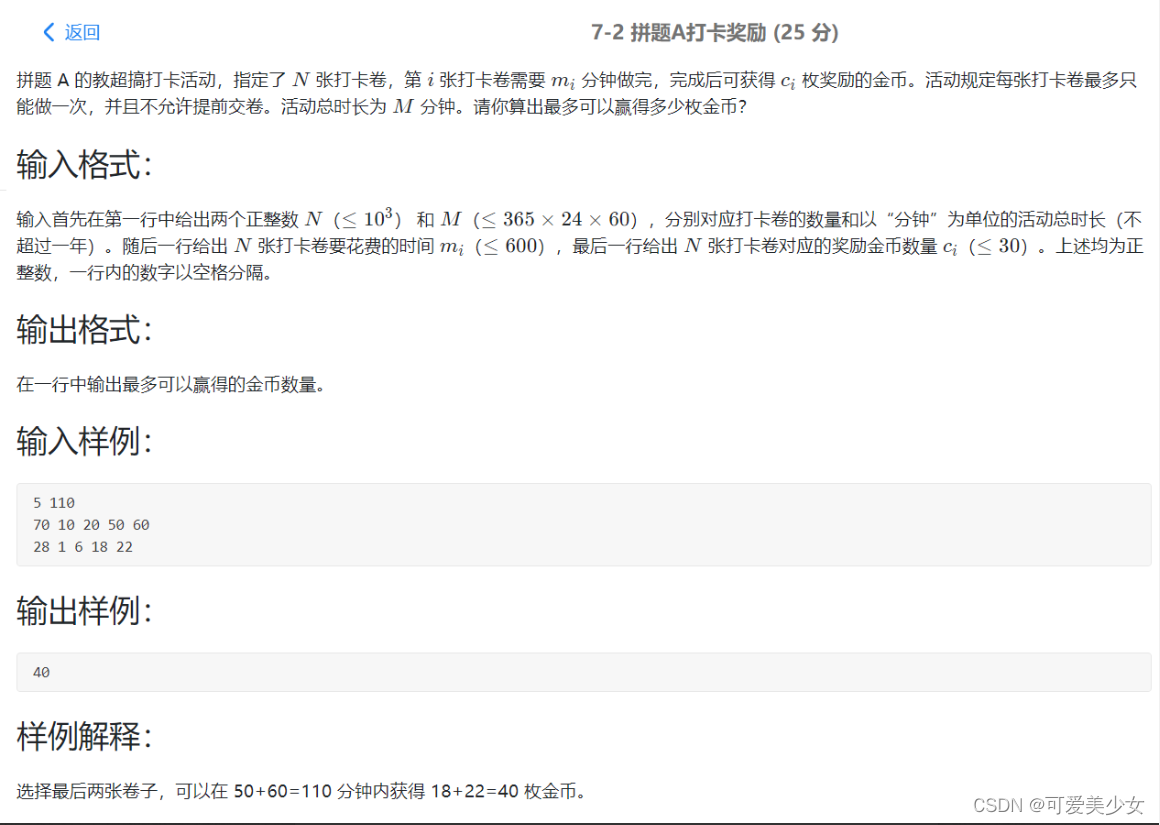
Acwing - the collection of pet elves - (multidimensional 01 Backpack + positive and reverse order + two forms of DP for the answer)
mysql 盲注常见函数
Opendrive ramp
随机推荐
SQL JOINS
NSIS finds out whether the file exists and sets the installation path
QT's excellent articles
Altium Designer 19.1.18 - 隐藏某一个网络的飞线
Package ‘*****‘ has no installation candidate
Function and usage of function pointer
Use stm32cubemx tool to write the demo program of FreeRTOS
Query the table name used by kettle in Oracle
About the problem that MySQL connector net cannot be cleared in MySQL
软件设计师:03-数据库系统
Consul安装
Apple system optimization
Altium Designer 19.1.18 - 导入板框
From then on, I understand convolutional neural network (CNN)
LED display equipment records of the opening ceremony of the Beijing Winter Olympics
C#,数值计算(Numerical Recipes in C#),线性代数方程的求解,LU分解(LU Decomposition)源程序
研究發現,跨境電商客服系統都有這五點功能!
Programming knowledge -- basis of C language
Global and Chinese market of plastic recycling machines 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Altium designer learning (I)