当前位置:网站首页>MySQL - storage engine
MySQL - storage engine
2022-07-05 07:39:00 【Promise @ sunny day】
Storage engine
1.1 MySQL Architecture
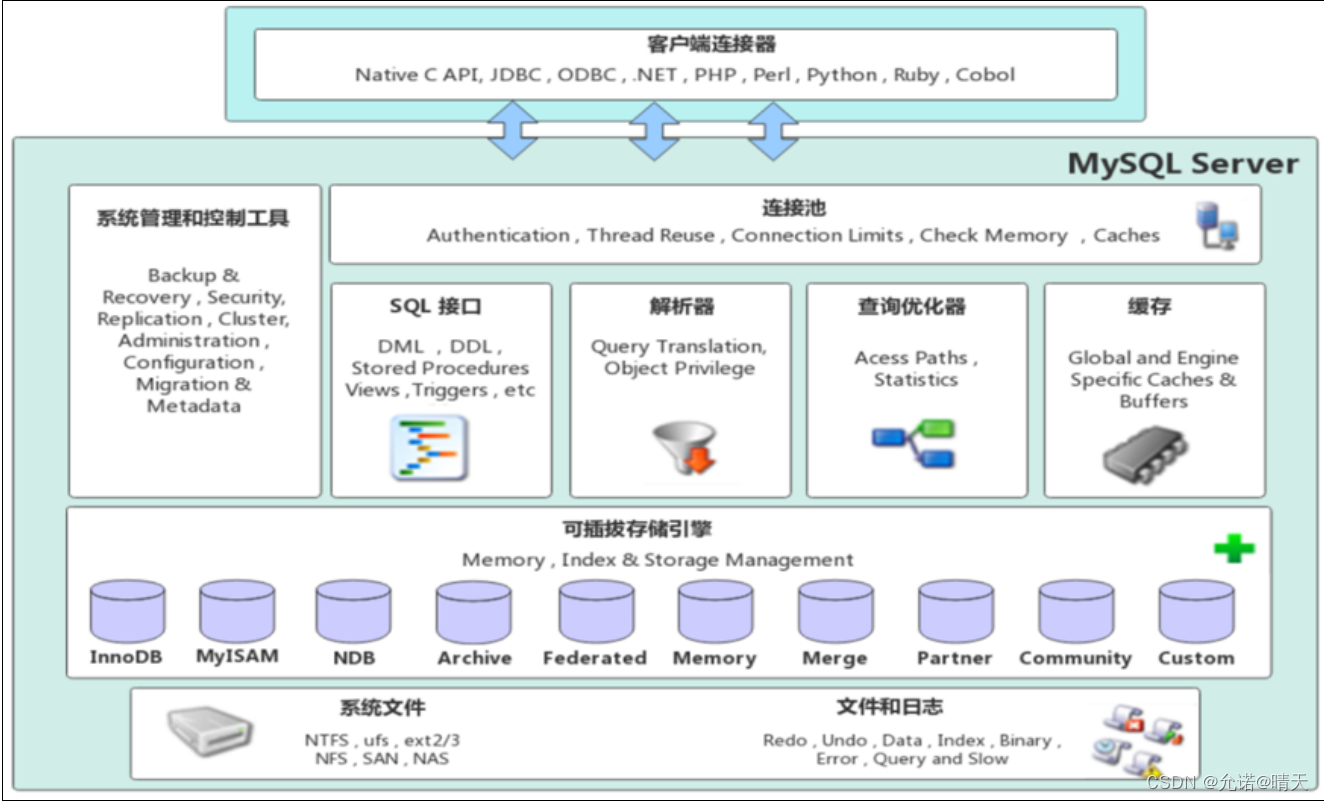
1). adjoining course
At the top are some clients and link services , Contains the local sock Communication and most are client based / The implementation of server-side tools is similar to TCP/IP Communication for . Mainly completes some similar to the connection processing 、 Authorized certification 、 And related safety programs . The concept of thread pool is introduced in this layer , Provide threads for clients accessing through authentication security . Also on this layer, we can implement the system based on SSL Security links for . The server will also verify the operation permissions it has for each client of secure access .
2). Service layer
The second layer architecture mainly completes most of the core service functions , Such as SQL Interface , And complete the cache query ,SQL Analysis and optimization of , Execution of some built-in functions . All the cross storage engine functions are also implemented in this layer , Such as : The process 、 Functions, etc . On this floor , The server parses the query and creates the corresponding internal parse tree , And it completes the corresponding optimization, such as determining the query order of the table , Whether to use index, etc , Finally, the corresponding execution operation is generated . If it is select sentence , The server also queries the internal cache , If the cache space is large enough , In this way, it can improve the performance of the system in the environment of solving a large number of read operations .
3). Engine layer
Storage engine layer ,
The storage engine is really responsible for MySQL The storage and extraction of data in , Server pass API Communicating with the storage engine . Different storage engines have different functions , So that we can according to our own needs , To choose the right storage engine . The index in the database is implemented in the storage engine layer .
4). Storage layer
Data storage layer , The main thing is to put the data ( Such as : redolog、undolog、 data 、 Indexes 、 Binary log 、 Error log 、 Query log 、 Slow query logs, etc ) Stored on the file system , And complete the interaction with the storage engine .
Compared with other databases ,MySQL It's a little different , Its architecture can be applied in many different scenarios and play a good role . Mainly in the storage engine , Plug in storage engine architecture , Separate query processing from other system tasks and data storage and extraction . This architecture can choose the right storage engine according to the needs of the business and the actual needs .
1.2 Storage engine introduction

- You may not have heard of storage engines , But I must have heard the word engine , The engine is the engine , It is the core component of a machine . such as , For carrier aircraft 、 The helicopter 、 For rockets , They all have their own engines , Is their core component . When we choose the engine , Need to be in the right scenario , Choose the right storage engine , Like in a helicopter , You can't choose the engine of the carrier plane
equally . - For storage engines , Is the same , He is mysql The core of the database , We also need to choose the right storage engine in the right scenario . Next, let's introduce the storage engine .
- The storage engine is to store data 、 Index 、 to update / Implementation of query data and other technologies . The storage engine is table based , Not library based , So a storage engine can also be called a table type . We can create the table , To specify the selected storage engine , If not specified, the default storage engine will be automatically selected .
1). Specify the storage engine when creating the table
CREATE TABLE Table name (
Field 1 Field 1 type [ COMMENT Field 1 notes ] ,
......
Field n Field n type [COMMENT Field n notes ]
) ENGINE = INNODB [ COMMENT Table annotation ] ;
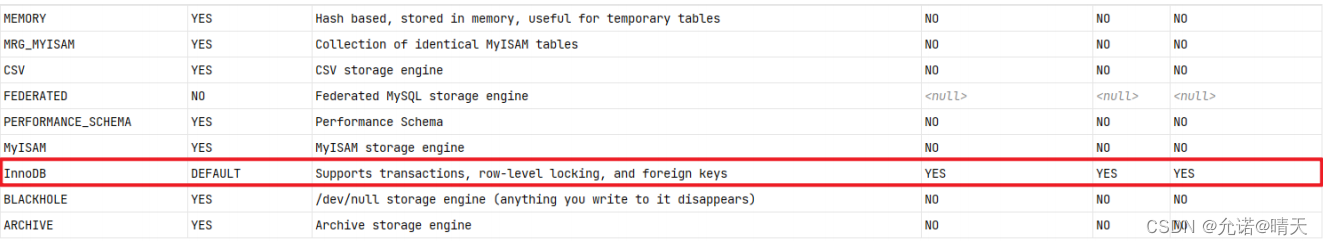
2). Query the storage engine supported by the current database
show engines;
Demonstration of examples :
A. Query table creation statement — Default storage engine : InnoDB
show create table account;

We can see , Create table time , Even if we don't specify storage , The database will also automatically select the default storage engine .
B. Query the storage engine supported by the current database
show engines ;
C. Create table my_myisam , And designate MyISAM Storage engine
create table my_myisam(
id int,
name varchar(10)
) engine = MyISAM ;
D. Create table my_memory , Appoint Memory Storage engine
create table my_memory(
id int,
name varchar(10)
) engine = Memory ;
1.3 Storage engine features
Above, we introduced what is a storage engine , And how to specify the storage engine when creating tables , Next, let's introduce the three storage engines mentioned above InnoDB、MyISAM、Memory Characteristics .
## 1.3.1 InnoDB
1). Introduce
InnoDB It is a general storage engine with high reliability and high performance , stay MySQL 5.5 after ,InnoDB By default MySQL Storage engine .
2). characteristic
- DML Operation follows ACID Model , Support transactions ;
- Row-level locks , Improve concurrent access performance ;
- Support foreign keys FOREIGN KEY constraint , Ensure the integrity and correctness of data ;
3). file
xxx.ibd:xxx Represents the table name ,innoDB Each table of the engine will correspond to such a tablespace file , The table structure that stores the table (frm- In the early 、sdi- New version of the )、 Data and index .
Parameters :innodb_file_per_table
show variables like 'innodb_file_per_table';
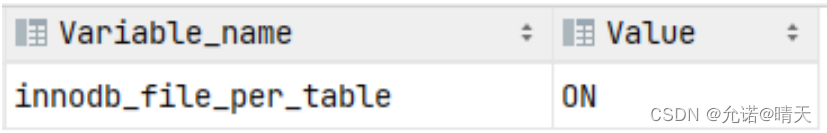
If this parameter is on , For InnoDB The engine's table , Each table corresponds to a ibd file . Let's turn on MySQL Data storage directory : C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\Data , There are many folders in this directory , Different folders represent different databases , Let's turn on itcast Folder .

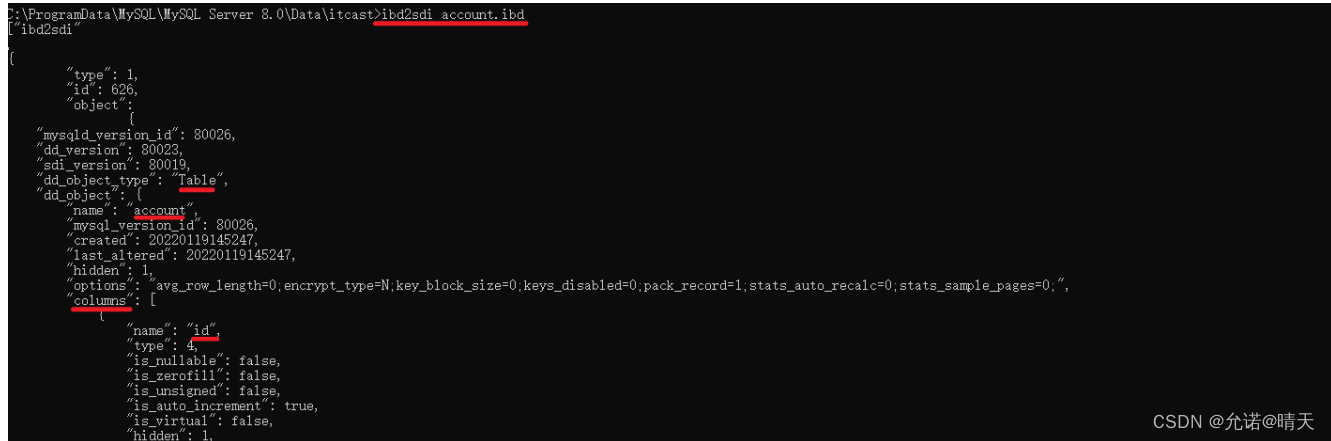
You can see there are a lot of ibd file , every last ibd The file corresponds to a table , such as : We have a table account, There is such a account.ibd file , And in this ibd The file not only stores the table structure 、 data , It also stores the index information corresponding to the table . The file is based on binary storage , Cannot open directly from Notepad , We can use mysql An instruction provided ibd2sdi , Through this instruction, you can start from ibd Extract in file sdi Information , and sdi The data dictionary information contains the table structure of the table .
4). Logical storage structure 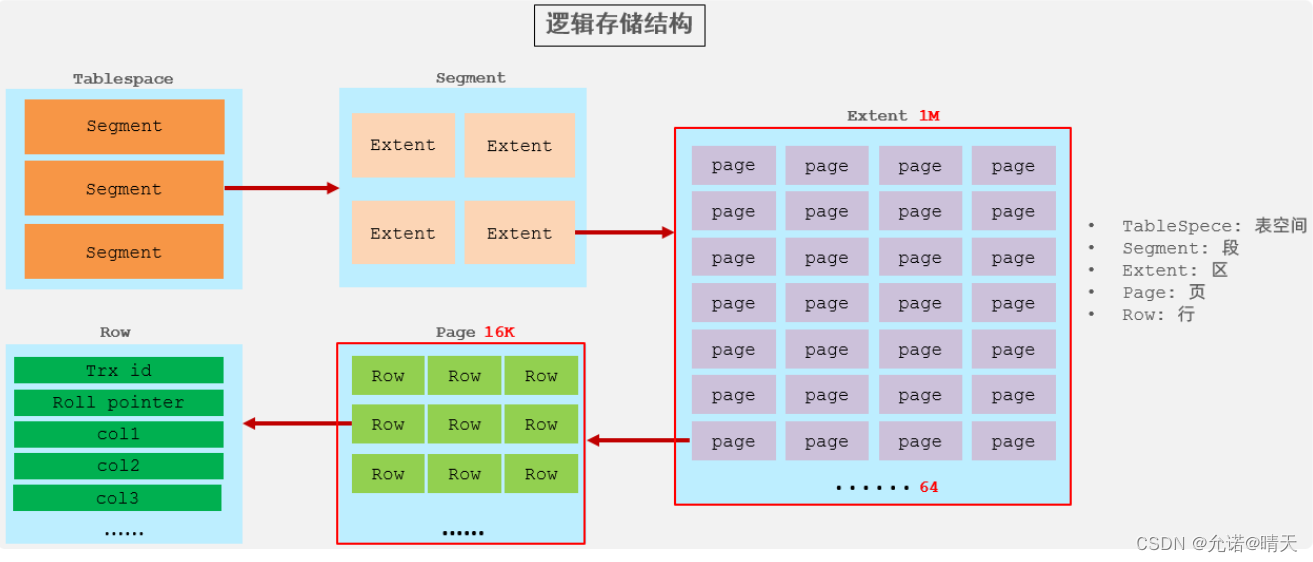
- Table space : InnoDB The highest level of the logical structure of the storage engine ,ibd A file is actually a tablespace file , A tablespace can contain multiple Segment paragraph .
- paragraph : Table spaces are made up of segments , Common segments have data segments 、 Index segment 、 Rollback segments, etc .InnoDB Management of segments in , It's all done by the engine itself , It doesn't need to be controlled artificially , A segment contains multiple sections .
- District : A region is the unit structure of a table space , The size of each zone is 1M. By default , InnoDB The storage engine page size is 16K, That is, there are... In a district 64 Consecutive pages .
- page : A page is the smallest unit that makes up a region , Pages are also InnoDB The smallest unit of storage engine disk management , The default size of each page is 16KB. To ensure page continuity ,InnoDB Every time the storage engine requests from disk 4-5 Districts .
- That's ok : InnoDB The storage engine is row oriented , That is to say, data is stored in rows , In each row, except for the fields specified when defining the table , It also contains two hidden fields ( More on that later ).
1.3.2 MyISAM
1). Introduce
MyISAM yes MySQL Early default storage engine .
2). characteristic
Unsupported transaction , Foreign key not supported
Support table lock , Row locks are not supported
Fast access
3). file
xxx.sdi: Store table structure information
xxx.MYD: Store the data
xxx.MYI: Storage index 
1.3.3 Memory
1). Introduce
Memory The table data of the engine is stored in memory , Due to hardware problems 、 Or the impact of power failure , These tables can only be used as temporary tables or caches .
2). characteristic
Memory storage
hash Indexes ( Default )
3). file
xxx.sdi: Store table structure information
1.3.4 Differences and characteristics
| characteristic | InnoDB | MyISAM | Memory |
|---|---|---|---|
| Storage limits | 64TB | Yes | Yes |
| Transaction security | Support | - | - |
| Locking mechanism | Row lock | Table locks | Table locks |
| B+tree Indexes | Support | Support | Support |
| Hash Indexes | - | - | Support |
| Full-text index | Support (5.6 After the version ) | Support | - |
| Space use | high | low | N/A |
| Memory usage | high | low | secondary |
| Batch insertion speed | low | high | high |
| Support foreign keys | Support | - | - |
Interview questions :
InnoDB The engine and MyISAM The difference between engines ?
①. InnoDB engine , Support transactions , and MyISAM I won't support it .
②. InnoDB engine , Support row lock and table lock , and MyISAM Only table locks are supported , Row locks are not supported .
③. InnoDB engine , Support foreign keys , and MyISAM Is not supported .
The main differences are the above three points , Of course, you can also use the index structure 、 Storage limitations, etc , A deeper answer , Specific reference Refer to the following official documents :
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/innodb-introduction.html
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/myisam-storage-engine.html
1.4 Storage engine selection
When choosing a storage engine , The appropriate storage engine should be selected according to the characteristics of the application system . For complex applications , You can also select a variety of storage engines to combine according to the actual situation .
- InnoDB: yes Mysql The default storage engine for , Support transactions 、 Foreign keys . If the application has higher requirements for transaction integrity , Data consistency is required under concurrent conditions , Data operations in addition to inserts and queries , It also contains a lot of updates 、 Delete operation , that InnoDB The storage engine is a better choice .
- MyISAM : If the application is based on read operation and insert operation , There are very few update and delete operations , And the integrity of the transaction 、 Concurrency requirements are not very high , So it's very appropriate to choose this storage engine .
- MEMORY: Keep all data in memory , Fast access , Usually used for temporary tables and caches .MEMORY The drawback is that there is a limit on the size of the table , Too large tables cannot be cached in memory , And can't guarantee the security of data .
边栏推荐
- Use stm32cubemx tool to write the demo program of FreeRTOS
- Using GEE plug-in in QGIS
- RF ride side door processing of prompt box
- Reading literature sorting 20220104
- Apple animation optimization
- Idea shortcut key
- What is Bezier curve? How to draw third-order Bezier curve with canvas?
- Process (P) runs, and idle is different from pycharm
- [neo4j] common operations of neo4j cypher and py2neo
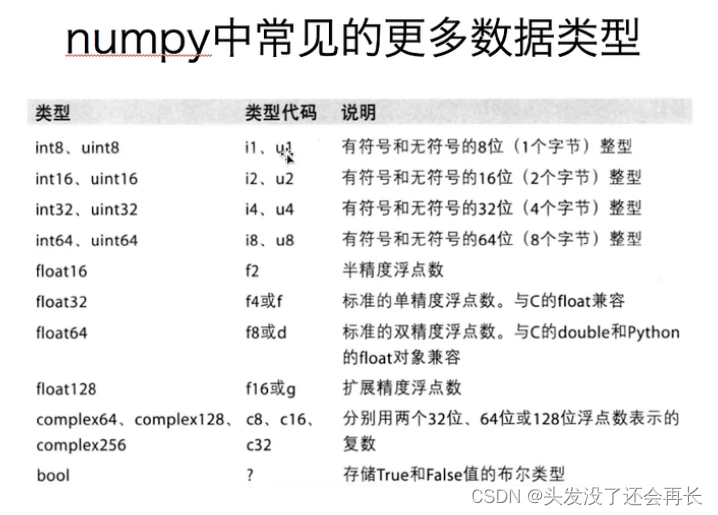
- Numpy——1. Creation of array
猜你喜欢
Rough notes of C language (2) -- constants

MySql——存储引擎
CADD course learning (5) -- Construction of chemosynthesis structure with known target (ChemDraw)
Graduation thesis project local deployment practice
Nombre - 1. Création de tableaux
With the help of Navicat for MySQL software, the data of a database table in different or the same database link is copied to another database table
Today, share the wonderful and beautiful theme of idea + website address
Differences between pycharm and idle and process -- join() in vs Code
From then on, I understand convolutional neural network (CNN)

CADD课程学习(5)-- 构建靶点已知的化合结构(ChemDraw)
随机推荐
Batch convert txt to excel format
Explanation of parallel search set theory and code implementation
Batch modify the txt file code to UTF-8 (notepad++)
deepin 20 kivy unable to get a window, abort
The golang timer uses the stepped pit: the timer is executed once a day
PIL's image tool image reduction and splicing.
行测--资料分析--fb--高照老师
Basic series of SHEL script (II) syntax + operation + judgment
Selenium element positioning
[idea] common shortcut keys
Don't confuse the use difference between series / and / *
Day08 ternary operator extension operator character connector symbol priority
static的作用
msys2
Clickhouse database installation deployment and remote IP access
Numpy——1.数组的创建
arcgis_ spatialjoin
How to delete the virus of inserting USB flash disk copy of shortcut to
Apple system shortcut key usage
Typescript get timestamp