当前位置:网站首页>The mutual realization of C L stack and queue in I
The mutual realization of C L stack and queue in I
2022-07-05 07:23:00 【MT_ one hundred and twenty-five】
Catalog
One 、 Stack with pairs of columns
Two 、 Using stack to realize queue
One 、 Stack with pairs of columns
Question stem requirements :

Detail analysis : The queue is first in, first out ; The stack to be implemented is first in and last out .
Their thinking : hypothesis : First use a queue to store data N individual , And then N-1 Data is imported into another queue ,
here , There is only one left in the original queue , Is the last remaining data , You can export it , This is a last in, first out .
Minutiae : Every time you export data , You need one queue to transfer data to another queue , So input queues and output queues Rotation required , It should be judged .
The specific process gif The dynamic diagram is as follows :
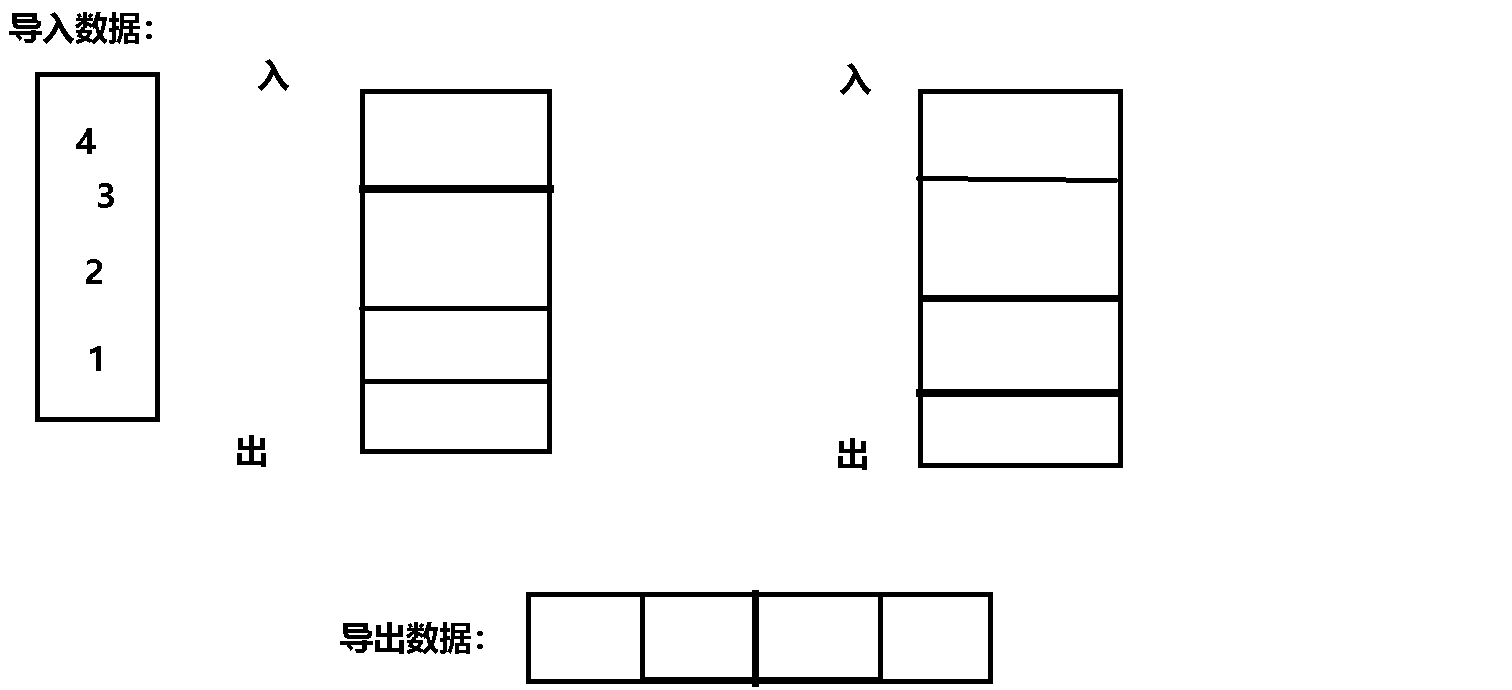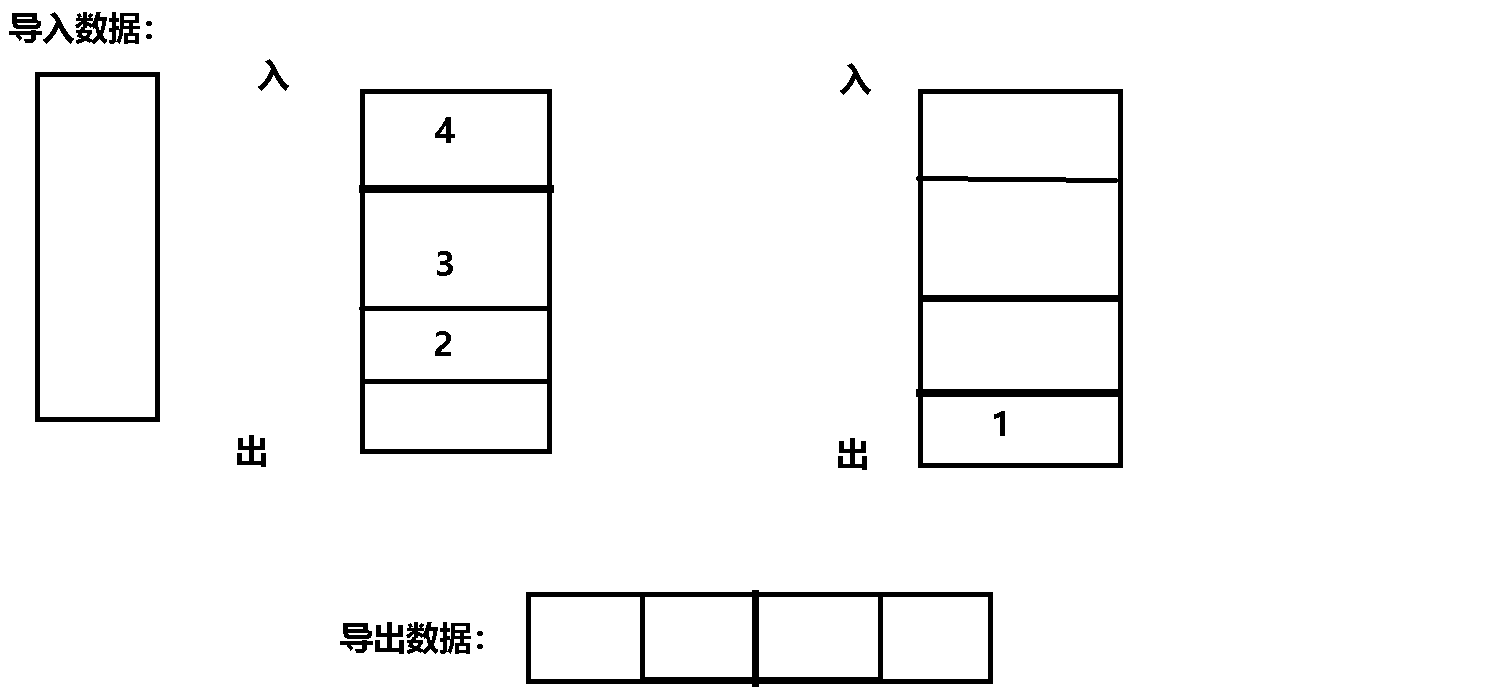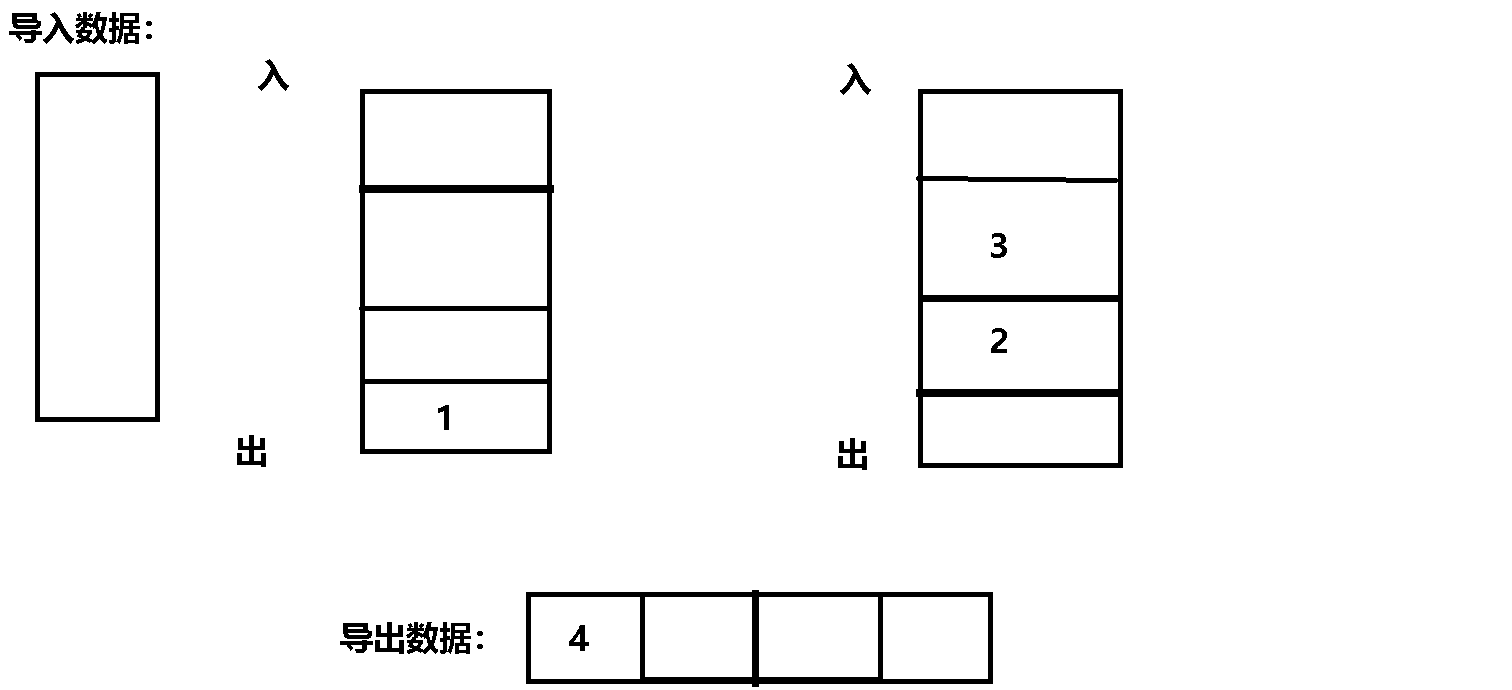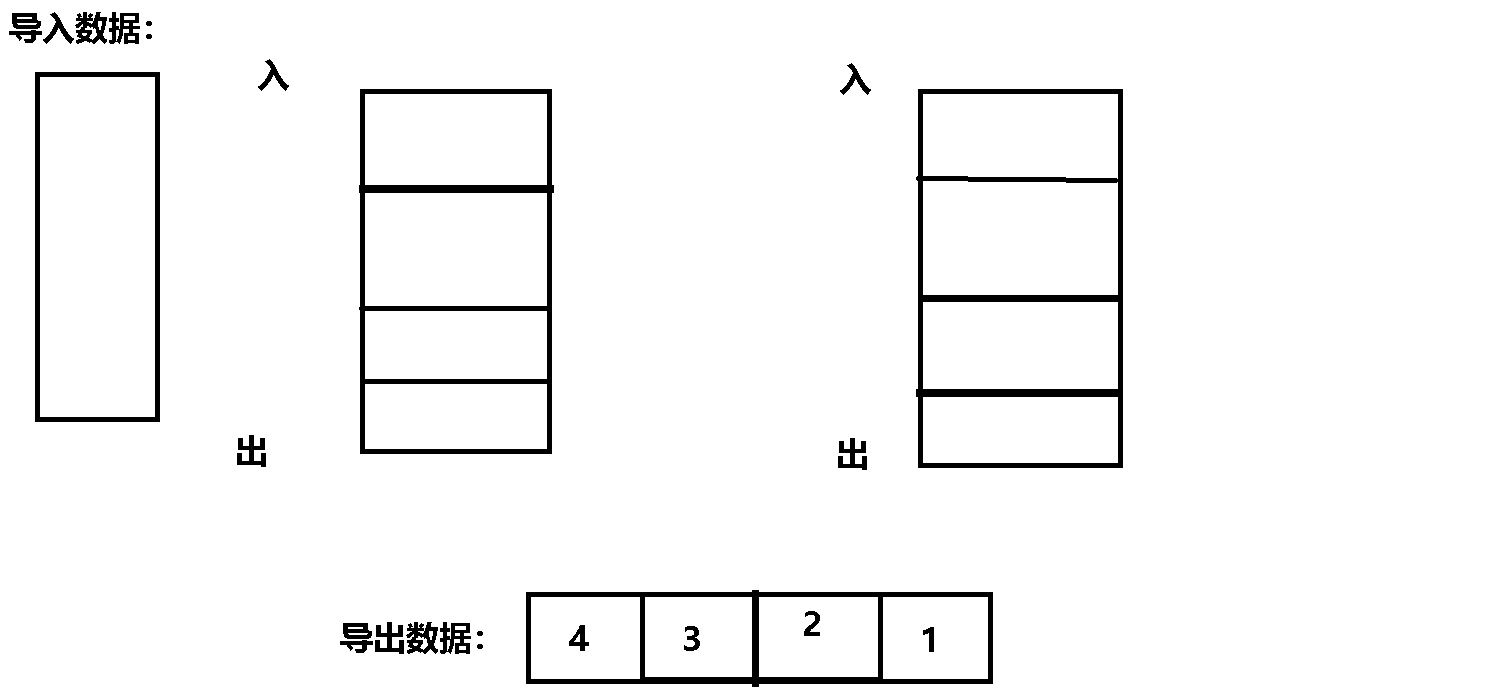
Code implementation :
1. Initialization stack : First initialize two queues
// The stack structure is composed of two queues
typedef struct Nystack{
Quetail q1;
Quetail q2;
} MyStack;
// Initialization of stack
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* Newstack = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
Que_Init(&Newstack->q1);
Que_Init(&Newstack->q2);
return Newstack;
}2. insert data
Because the queue for storing data is not fixed , Therefore, on the premise that a queue has data , Continue to insert data into the queue ,
The empty queue is responsible for rotation when exporting data .( Which is not empty, which is inserted )
// insert data
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
//if((&obj->q1)->head == NULL) // Law 1 : Directly judge whether it is empty
if(Que_Empty(&obj->q1)) // Law two : Reuse of subsequent functions
Que_push(&obj->q2,x);
else
Que_push(&obj->q1,x);
}3. Derived data ( Achieve first in and last out )

First step : Divide the last data in the queue with data , Import to another empty queue in turn ;
Import empty queue , Delete the original queue , Keep the last data .
Second cloth : Export the last data in the original queue .
notes : Here we first assume two queues , One is the original queue and the other is the empty queue , And then judge , If it is inconsistent with the actual , be In exchange for .
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
int temp = 0;
// Suppose the original queue and the empty queue
Quetail* existque = &obj->q1,*nullque = &obj->q2;
if((&obj->q1)->head == NULL) // Judge whether it is consistent with the actual
{
existque = nullque;
nullque = &obj->q1;
}
for(;existque->head->Next;) // Keep the last data
{
Que_push(nullque,existque->head->data); // Import data to an empty queue
Que_pop(existque); // Delete the original queue data
}
temp = existque->head->data;
Que_pop(existque); // Export the last entered data
return temp;
}4. Find the data at the top of the stack
Find a queue that is not empty >> Return the data at the end of the queue
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if((&obj->q1)->head == NULL)
{
return (&obj->q2)->tail->data;
}
return (&obj->q1)->tail->data;
}5. Judge whether the stack is empty :
Judge whether both queues are empty
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
// Law 1 : Direct judgment
//if((&obj->q1)->head == NULL&& (&obj->q2)->head == NULL)
// Law two : Reuse queue empty function
if(Que_Empty(&(obj->q1))&&Que_Empty(&(obj->q2)))
return true;
return false;
}
6. Destroy the stack :
Destroy two queues
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
Que_Destory(&obj->q1);
Que_Destory(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}Two 、 Using stack to realize queue
Question stem requirements :

Detail analysis : This time we use two stacks , Achieve first in first out .
Their thinking : First , Divide the two stacks into entry stack and exit stack ,
secondly , Data positive order entry stack , Because the stack is first in and last out , Therefore, enter the data into the exit stack in reverse order ,
then , At this time, the data is in reverse order in the exit stack , therefore , Then it can be discharged from the exit stack in positive order .
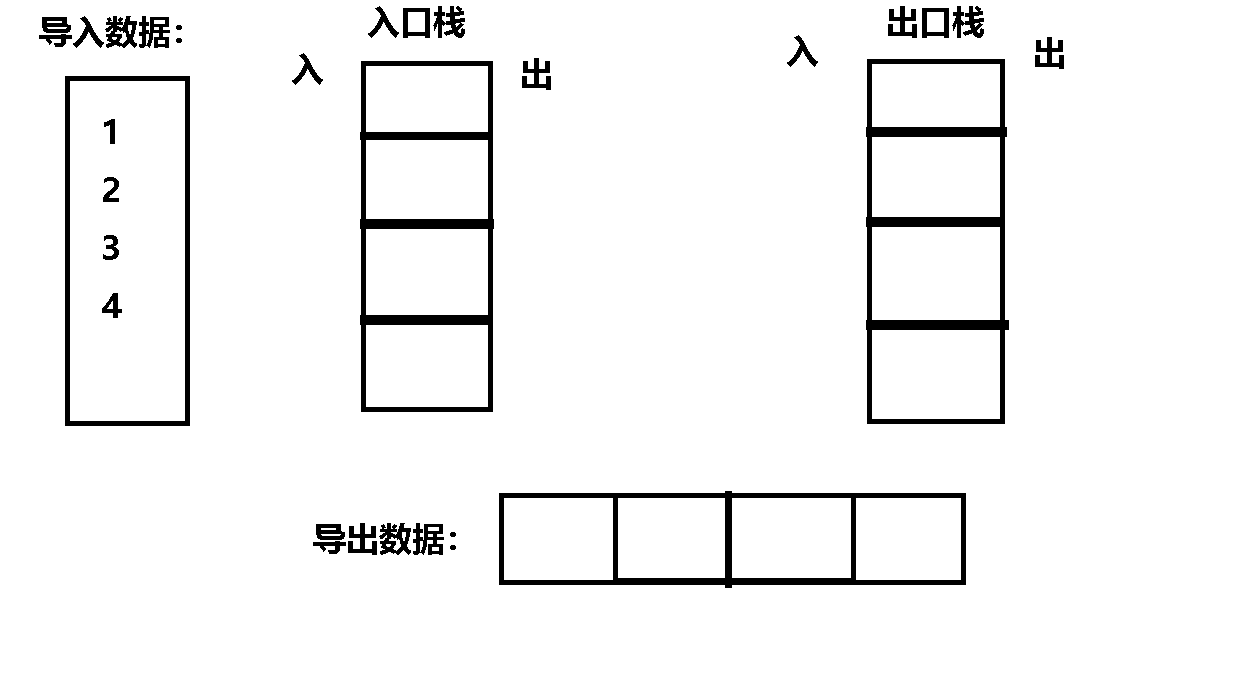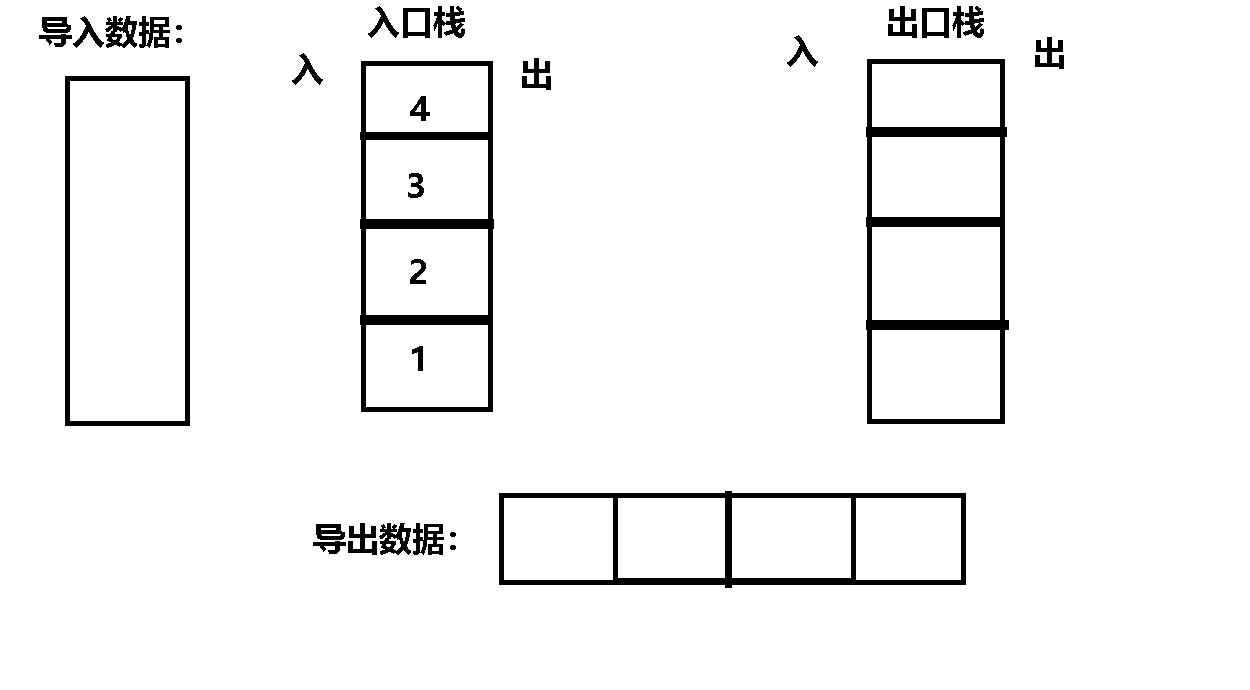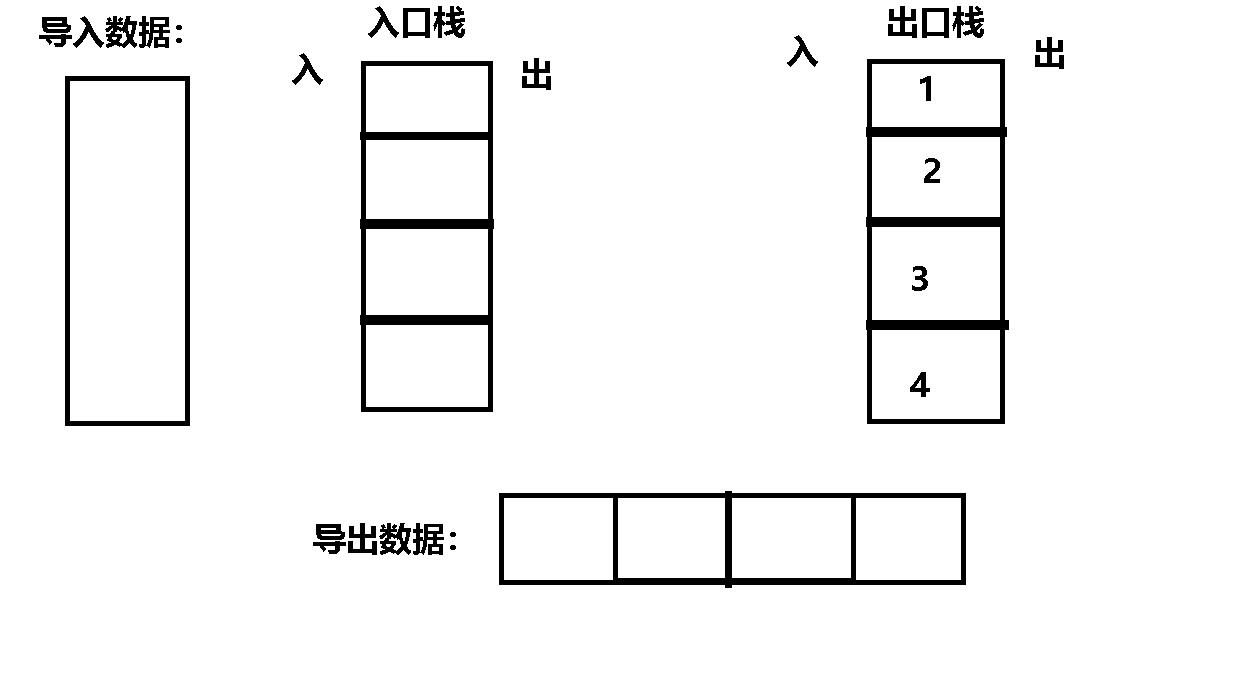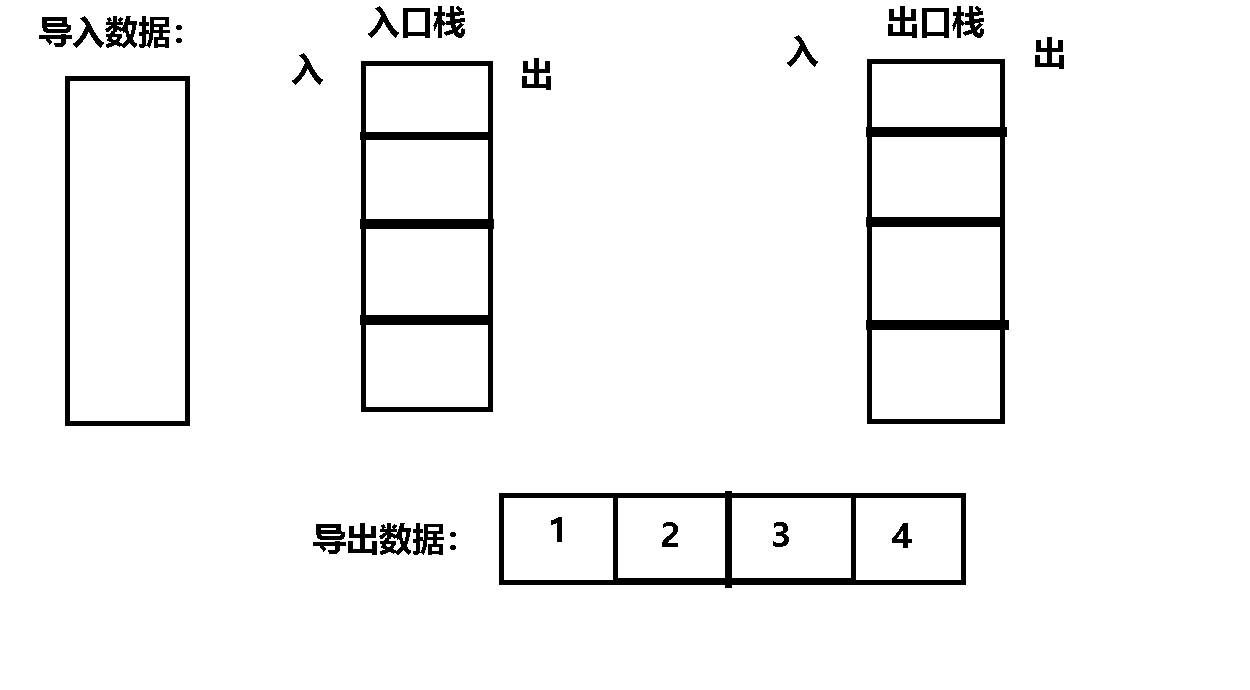
Code implementation :
1. Initialize the dual stack queue
typedef struct {
Stack T1;
Stack T2;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue *Q1;
Q1 = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
Stack_init(&(Q1->T1)); // T1 Do the entry stack
Stack_init(&(Q1->T2)); // T2 Make a mouth stack
return Q1;
}2. insert data
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
Stack_push(&obj->T1,x); // Here will stack T1 As an entry stack
}3. Delete data ( fifo )
Record the entry stack data >> Delete entry stack data >> Import exit stack >> Export data from exit stack

int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
if(Stack_Empty(&obj->T2)) // Determine whether it is null
{
int k = 0;
for(;!Stack_Empty(&obj->T1);)
{
k = Stack_Top(&obj->T1); // Record entry station data
Stack_pop(&obj->T1); // Delete entry stack data
Stack_push(&obj->T2,k); // Import exit stack
}
}
int temp = 0;
temp = Stack_Top(&obj->T2);
Stack_pop(&obj->T2); // Export data from exit stack
return temp; // The stem of the question requires that the exported value be returned
}4. Find queue header data
The header data here is the header data in positive order , Therefore, first import the reverse order data in the entry stack into the exit stack ,
Become positive , Then return the top data of the exit stack .
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if(Stack_Empty(&obj->T2)) // Judge whether there is data in the exit stack
{
int k = 0;
for(;!Stack_Empty(&obj->T1);) // Import data to the exit stack
{
k = Stack_Top(&obj->T1);
Stack_pop(&obj->T1);
Stack_push(&obj->T2,k);
}
}
return Stack_Top(&obj->T2); // Return exit stack top data
}5. Determines if the queue is empty And Destroy queue
// Determines if the queue is empty
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
// Determine whether both stacks are empty
return Stack_Empty(&obj->T1)&&Stack_Empty(&obj->T2);
}
// Destroy the release queue
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
Stack_pop(&obj->T1);
Stack_pop(&obj->T2);
free(obj);
}Thank you for your support !!!
边栏推荐
- ImportError: No module named ‘Tkinter‘
- What if the DataGrid cannot see the table after connecting to the database
- PowerManagerService(一)— 初始化
- Simple operation of nixie tube (keil5)
- NPM and package common commands
- Use of Pai platform
- Altimeter data knowledge point 2
- 611. 有效三角形的个数
- Matlab在线性代数中的应用(四):相似矩阵及二次型
- Netease to B, soft outside, hard in
猜你喜欢
Ros2 - common command line (IV)
Matrix and TMB package version issues in R

Netease to B, soft outside, hard in
Today, share the wonderful and beautiful theme of idea + website address
【idea】Could not autowire. No beans of xxx type found
![When jupyter notebook is encountered, erroe appears in the name and is not output after running, but an empty line of code is added downward, and [] is empty](/img/fe/fb6df31c78551d8908ba7964c16180.jpg)
When jupyter notebook is encountered, erroe appears in the name and is not output after running, but an empty line of code is added downward, and [] is empty
Jenkins reported an error. Illegal character: '\ufeff'. Class, interface or enum are required
U-boot initialization and workflow analysis
C learning notes
Ros2 - configuration development environment (V)
随机推荐
[untitled]
Install deeptools in CONDA mode
[untitled]
Target detection series - detailed explanation of the principle of fast r-cnn
Three body goal management notes
SOC_ SD_ DATA_ FSM
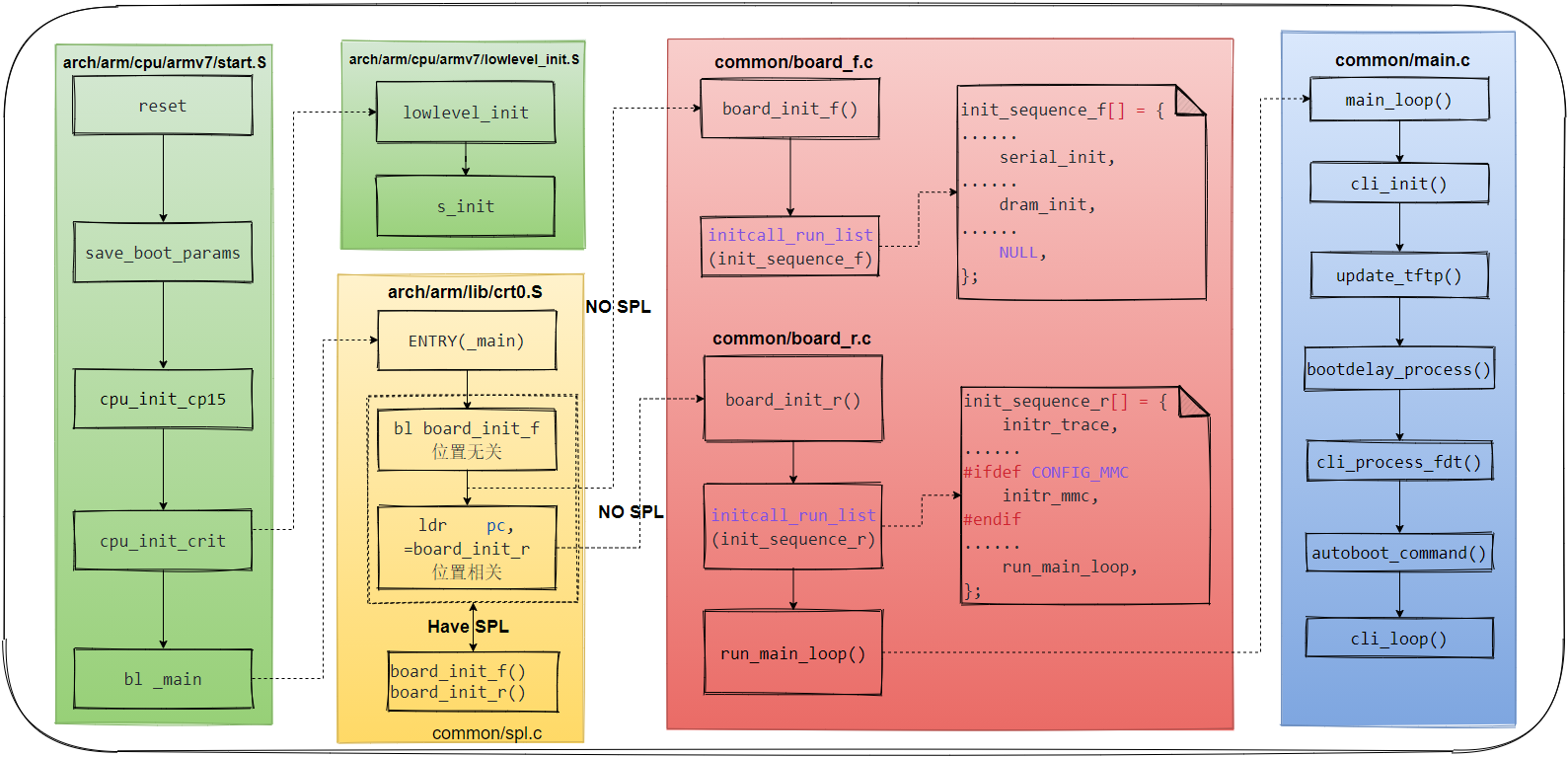
U-boot initialization and workflow analysis
[software testing] 04 -- software testing and software development
Solve tensorfow GPU modulenotfounderror: no module named 'tensorflow_ core. estimator‘
[software testing] 03 -- overview of software testing
Simple operation of nixie tube (keil5)
并查集理论讲解和代码实现
CADD课程学习(5)-- 构建靶点已知的化合结构(ChemDraw)
ImportError: No module named ‘Tkinter‘
NPM and package common commands
Ros2 - first acquaintance with ros2 (I)
公安基础知识--fb
And play the little chestnut of dynamic agent
Cookie operation
[vscode] recommended plug-ins