当前位置:网站首页>Powermanagerservice (I) - initialization
Powermanagerservice (I) - initialization
2022-07-05 07:00:00 【ʚ Xiansen of rabbit ɞ】
PowerManagerService( One )— initialization
1. brief introduction
PowerManagerServcie yes android The core service of system power management , It's in Framework Layer establishes a strategy control scheme , Downward decision HAL Layers and kernel Layer to control the standby state of the device , The main function is to control the standby state of the system , Screen display , Brightness adjustment , The light / Control of distance sensor, etc .
In addition to interacting with Applications , Also cooperate with other modules in the system , Provide good energy management and friendly user experience . For example, keep the system awake while listening to music , When the application notification comes, it wakes up the mobile screen and other scenes
Analyze a service , First of all, we should start from what it provides for the application layer api PowerManager Starting with , Observe which interface calls are provided ;
Wakeup(): Force the system to wake up from sleep , This interface is not open to applications , If an application wants to wake up the system, it must set the bright screen flag ( Later, I will talk about );gotoSleep(): Force the system to sleep , This interface is also not open to applications .userActivity(): towards PowerManagerService Report user activity that affects system hibernation , Recalculate the screen out time , Backlight brightness, etc , For example, touch screen , Scratch the screen ,power Key and other user activities ;Wakelock:wakelock yes PowerManager An inner class , Provides relevant interfaces to operate wakelock lock , such as newWakeLock() Method to create wakelock lock ,acquire() and release() Method to apply and release the lock . The following examples are introduced !isDeviceIdleMode(): Return to the current state of the device , If in the Idle state , Then return to true,Idle The status is when the mobile phone has not been used for a long time and has not moved , Mobile phones enter a Doze Low power consumption mode , In this state, the mobile phone may turn off network data access , By monitoring DEVICE_IDLE_MODE_CHANGED This broadcast message , To monitor the change of mobile phone status
1.1 System level diagram
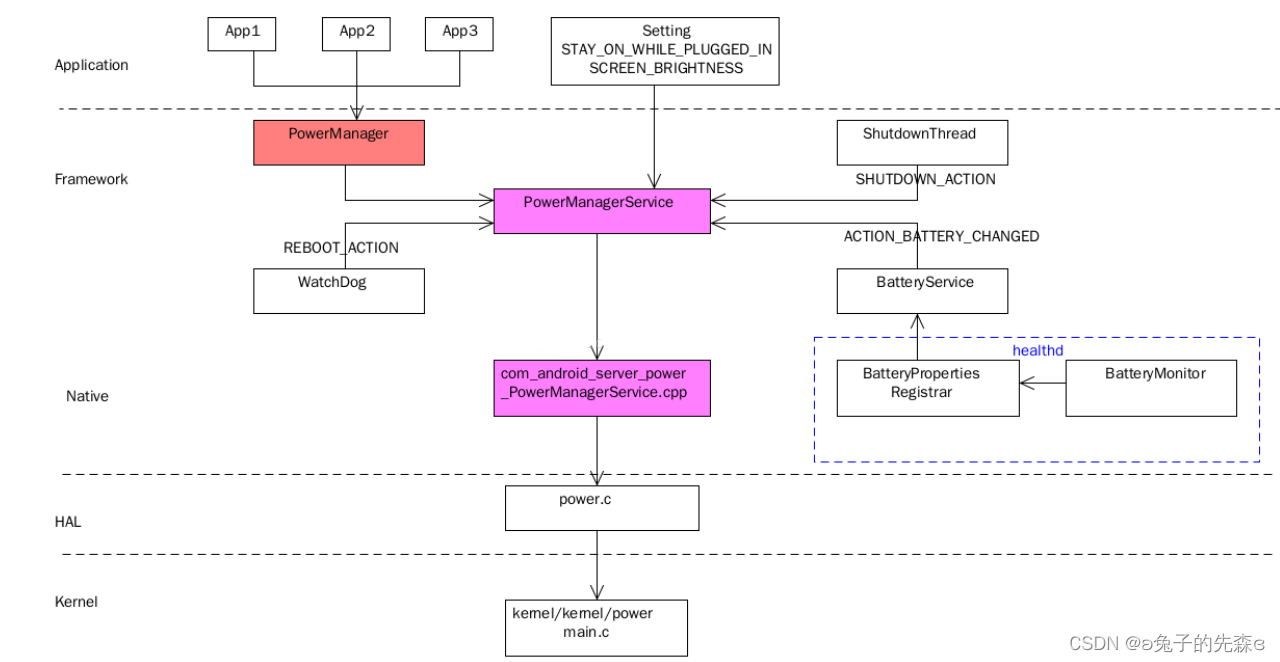
1.2 Power management architecture
It is mainly divided into four levels :
- Application interface layer :
PowerManager.javaOpen a series of interfaces to applications , Applications can call PM Interface application wakelock, arousal system , Put the system into sleep and other operations ; - Framework layer :
PowerManagerService.javaComputing system and Power Relevant calculations , It is the decision-making department of the whole power management ; - HAL layer : This layer has only one
power.cfile , The file passes the parameters from the upper layer , towards/sys/power/wake_lockperhaps/sys/power/wake_unlockFile nodes write data to communicate with kernel communicate , The main function is to apply / Release the lock , Keep the screen on and off . - Kernel layer : The scheme of power management in kernel layer mainly includes three parts :
Kernel/power/: The system power management framework mechanism is realized .Arch/arm(ormips or powerpc)/mach-XXX/pm.c: Realize the processor power management of a specific board .drivers/power: It is the basic framework of device power management , Power management interface is provided for the driver .
2. initialization
Like other system services ,PowerManagerService It is also inherited from SystemService And pass SystemServer start-up .
2.1 SystemServer start-up PowerManagerService service
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
private void startBootstrapServices() {
......
mPowerManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerManagerService.class);
......
}
2.2 PowerManagerService structure
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/power/PowerManagerService.java
public final class PowerManagerService extends SystemService
implements Watchdog.Monitor {
public PowerManagerService(Context context) {
super(context);
mContext = context;
// Create a message processing thread , And start the
mHandlerThread = new ServiceThread(TAG,
Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_DISPLAY, false /*allowIo*/);
mHandlerThread.start();
// establish Hanlder Object handles messages
mHandler = new PowerManagerHandler(mHandlerThread.getLooper());
mConstants = new Constants(mHandler);
mAmbientDisplayConfiguration = new AmbientDisplayConfiguration(mContext);
mBatterySaverPolicy = new BatterySaverPolicy(mHandler);
synchronized (mLock) {
// establish "PowerManagerService.WakeLocks" Of SuspendBlocker
mWakeLockSuspendBlocker = createSuspendBlockerLocked("PowerManagerService.WakeLocks");
// establish "PowerManagerService.Display" Of SuspendBlocker
mDisplaySuspendBlocker = createSuspendBlockerLocked("PowerManagerService.Display");
// request DisplaySuspendBlocker, Disable the system from entering sleep
mDisplaySuspendBlocker.acquire();
mHoldingDisplaySuspendBlocker = true;
mHalAutoSuspendModeEnabled = false;
mHalInteractiveModeEnabled = true;
// Set up mWakefulness In the wake-up state
mWakefulness = WAKEFULNESS_AWAKE;
sQuiescent = SystemProperties.get(SYSTEM_PROPERTY_QUIESCENT, "0").equals("1");
// Enter into native Layer initialization
nativeInit();
nativeSetAutoSuspend(false);
nativeSetInteractive(true);
nativeSetFeature(POWER_FEATURE_DOUBLE_TAP_TO_WAKE, 0);
}
}
......
}
PowerManagerService The constructor first creates the process of processing the message and the corresponding handler Object for message processing , Then create SuspendBlocker object , be used for WakeLocks And Display, And set up mWakefulness The initial state of is WAKEFULNESS_AWAKE, Finally, enter native Layer initialization . Now let's take a look at mWakefulness The definition of .
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/PowerManagerInternal.java
/** * The device is in sleep state , Can only be wakeUp() Wake up the . */
public static final int WAKEFULNESS_ASLEEP = 0;
/** * The equipment is in normal operation (fully awake) state . */
public static final int WAKEFULNESS_AWAKE = 1;
/** * The device is in the state of playing screensaver . */
public static final int WAKEFULNESS_DREAMING = 2;
/** * Device in doze state , Only low power screensavers can run , Other apps are suspended . */
public static final int WAKEFULNESS_DOZING = 3;
Continue to back PowerManagerService Constructor's native In the initialization , First of all to see nativeInit The implementation of the .
frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_power_PowerManagerService.cpp
static void nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj) {
// Create a global object , quote PMS
gPowerManagerServiceObj = env->NewGlobalRef(obj);
// utilize hw_get_module load power modular
status_t err = hw_get_module(POWER_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
(hw_module_t const**)&gPowerModule);
if (!err) {
gPowerModule->init(gPowerModule);
} else {
ALOGE("Couldn't load %s module (%s)", POWER_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, strerror(-err));
}
}
nativeInit The main task when loading power modular , This module is implemented by the manufacturer , Take Qualcomm as an example , as follows .
device/qcom/common/power/power.c
tatic struct hw_module_methods_t power_module_methods = {
.open = NULL,
};
struct power_module HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.module_api_version = POWER_MODULE_API_VERSION_0_2,
.hal_api_version = HARDWARE_HAL_API_VERSION,
.id = POWER_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "QCOM Power HAL",
.author = "Qualcomm",
.methods = &power_module_methods,
},
.init = power_init,
.powerHint = power_hint,
.setInteractive = set_interactive,
};
power_module Implemented in the init,powerHint,setInteractive,nativeInit Finally call to HAL power Modular power_init Concrete implementation . Then look at native initialization nativeSetAutoSuspend The implementation of the .
frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_power_PowerManagerService.cpp
static void nativeSetAutoSuspend(JNIEnv* /* env */, jclass /* clazz */, jboolean enable) {
if (enable) {
ALOGD_IF_SLOW(100, "Excessive delay in autosuspend_enable() while turning screen off");
autosuspend_enable();
} else {
ALOGD_IF_SLOW(100, "Excessive delay in autosuspend_disable() while turning screen on");
autosuspend_disable();
}
}
static void nativeSetInteractive(JNIEnv* /* env */, jclass /* clazz */, jboolean enable) {
if (gPowerModule) {
if (enable) {
ALOGD_IF_SLOW(20, "Excessive delay in setInteractive(true) while turning screen on");
gPowerModule->setInteractive(gPowerModule, true);
} else {
ALOGD_IF_SLOW(20, "Excessive delay in setInteractive(false) while turning screen off");
gPowerModule->setInteractive(gPowerModule, false);
}
}
}
static void nativeSetFeature(JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz, jint featureId, jint data) {
int data_param = data;
if (gPowerModule && gPowerModule->setFeature) {
gPowerModule->setFeature(gPowerModule, (feature_t)featureId, data_param);
}
}
system/core/libsuspend/autosuspend.c
int autosuspend_disable(void)
{
int ret;
ret = autosuspend_init();
if (ret) {
return ret;
}
ALOGV("autosuspend_disable\n");
if (!autosuspend_enabled) {
return 0;
}
ret = autosuspend_ops->disable();
if (ret) {
return ret;
}
autosuspend_enabled = false;
return 0;
}
Same as nativeInit equally , In the end, it's all called to HAL power In the concrete implementation of the module .
3. start-up
Let's continue PowerManagerService Callback during system startup onStart(),onBootPhase(),systemReady() The implementation of the .
3.1 Start the service SystemServiceManager.onStart
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/power/PowerManagerService.java
public void onStart() {
publishBinderService(Context.POWER_SERVICE, new BinderService());
publishLocalService(PowerManagerInternal.class, new LocalService());
Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this);
Watchdog.getInstance().addThread(mHandler);
}
private final class BinderService extends IPowerManager.Stub {
......
}
private final class LocalService extends PowerManagerInternal {
......
}
onStart() Released in BinderService,LocalService For other processes , Other in-process service calls , And will PowerManagerService Add to Watchdog Monitoring .
3.2 Start the service SystemServiceManager.onBootPhase
public void onBootPhase(int phase) {
synchronized (mLock) {
if (phase == PHASE_THIRD_PARTY_APPS_CAN_START) {
......
} else if (phase == PHASE_BOOT_COMPLETED) {
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
// Set up mBootCompleted state
mBootCompleted = true;
mDirty |= DIRTY_BOOT_COMPLETED;
// to update userActivity And PowerState, Back analysis
userActivityNoUpdateLocked(
now, PowerManager.USER_ACTIVITY_EVENT_OTHER, 0, Process.SYSTEM_UID);
updatePowerStateLocked();
// perform mBootCompletedRunnables Medium runnable Method
if (!ArrayUtils.isEmpty(mBootCompletedRunnables)) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Posting " + mBootCompletedRunnables.length + " delayed runnables");
for (Runnable r : mBootCompletedRunnables) {
BackgroundThread.getHandler().post(r);
}
}
mBootCompletedRunnables = null;
}
}
}
onBootPhase() Main settings in mBootCompleted state , to update PowerState state , And implement mBootCompletedRunnables Medium runnables Method ( Low battery mode will be set ).
3.3 Start the service SystemServiceManager.systemReady
public void systemReady(IAppOpsService appOps) {
synchronized (mLock) {
mSystemReady = true;
// obtain AppOpsService
mAppOps = appOps;
// obtain DreamManager Screen saver
mDreamManager = getLocalService(DreamManagerInternal.class);
// obtain DisplayManagerService Screen display
mDisplayManagerInternal = getLocalService(DisplayManagerInternal.class);
// Window strategy
mPolicy = getLocalService(WindowManagerPolicy.class);
// obtain mBatteryService battery level
mBatteryManagerInternal = getLocalService(BatteryManagerInternal.class);
PowerManager pm = (PowerManager) mContext.getSystemService(Context.POWER_SERVICE);
// Get screen defaults , Maximum , Minimum brightness
mScreenBrightnessSettingMinimum = pm.getMinimumScreenBrightnessSetting();
mScreenBrightnessSettingMaximum = pm.getMaximumScreenBrightnessSetting();
mScreenBrightnessSettingDefault = pm.getDefaultScreenBrightnessSetting();
// obtain SensorManager
SensorManager sensorManager = new SystemSensorManager(mContext, mHandler.getLooper());
mBatteryStats = BatteryStatsService.getService();
// establish Notifier object , For broadcast power state The change of
mNotifier = new Notifier(Looper.getMainLooper(), mContext, mBatteryStats,
mAppOps, createSuspendBlockerLocked("PowerManagerService.Broadcasts"),
mPolicy);
// Wireless charging detection
mWirelessChargerDetector = new WirelessChargerDetector(sensorManager,
createSuspendBlockerLocked("PowerManagerService.WirelessChargerDetector"),
mHandler);
// Monitor for changes in settings
mSettingsObserver = new SettingsObserver(mHandler);
mLightsManager = getLocalService(LightsManager.class);
mAttentionLight = mLightsManager.getLight(LightsManager.LIGHT_ID_ATTENTION);
// Initialize display power management.
mDisplayManagerInternal.initPowerManagement(
mDisplayPowerCallbacks, mHandler, sensorManager);
// Register for settings changes.
final ContentResolver resolver = mContext.getContentResolver();
resolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.Secure.getUriFor(
Settings.Secure.SCREENSAVER_ENABLED),
......
IVrManager vrManager =
(IVrManager) getBinderService(VrManagerService.VR_MANAGER_BINDER_SERVICE);
try {
vrManager.registerListener(mVrStateCallbacks);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failed to register VR mode state listener: " + e);
}
// Reading configuration
readConfigurationLocked();
updateSettingsLocked();
mDirty |= DIRTY_BATTERY_STATE;
updatePowerStateLocked();
}
// Register for broadcasts from other components of the system.
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter();
filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_CHANGED);
filter.setPriority(IntentFilter.SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY);
mContext.registerReceiver(new BatteryReceiver(), filter, null, mHandler);
filter = new IntentFilter();
filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_DREAMING_STARTED);
filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_DREAMING_STOPPED);
mContext.registerReceiver(new DreamReceiver(), filter, null, mHandler);
filter = new IntentFilter();
filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_USER_SWITCHED);
mContext.registerReceiver(new UserSwitchedReceiver(), filter, null, mHandler);
filter = new IntentFilter();
filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_DOCK_EVENT);
mContext.registerReceiver(new DockReceiver(), filter, null, mHandler);
}
In short, in SystemReady The main work accomplished in the method is as follows :
- 1. To obtain and PowerManagerServcie Relevant system services and local services ;
Get the maximum screen size , Minimum and default brightness values ; - 2. establish SensorManager object , Used for and SensorService Interaction ;
- 3. establish Notifier object , It is used to notify the change of power status in the system ;
- 4. establish WirelessChargerDetector object , Sensor for detecting wireless charging ( There are few mobile phones supported on the market )
- 5. call DisplayManagerService Of initPowerManagement() Method to initialize Power Display module .
- 6. register SettingsObserver Changes in monitoring system settings
3.4 userActivity
userActivity Is defined in PowerManager Medium SystemApi, The user to PowerManagerService Report user activity , To update PowerManagerService Internal time / The status value , Postpone the time of system hibernation .
PowerManager in userActivity Request to call the server PowerManagerService BinderService Of userActivity, That is, call internal methods userActivityNoUpdateLocked.
private boolean userActivityNoUpdateLocked(long eventTime, int event, int flags, int uid) {
// If the occurrence time is before the last sleep or wake-up , Or the current boot is not completed until systemReady, Return without taking action
if (eventTime < mLastSleepTime || eventTime < mLastWakeTime
|| !mBootCompleted || !mSystemReady) {
return false;
}
try {
// to update mLastInteractivePowerHintTime Time
if (eventTime > mLastInteractivePowerHintTime) {
powerHintInternal(POWER_HINT_INTERACTION, 0);
mLastInteractivePowerHintTime = eventTime;
}
// adopt mNotifier notice BatteryStats UserActivity event
mNotifier.onUserActivity(event, uid);
if (mUserInactiveOverrideFromWindowManager) {
mUserInactiveOverrideFromWindowManager = false;
mOverriddenTimeout = -1;
}
// If the system is dormant , No processing
if (mWakefulness == WAKEFULNESS_ASLEEP
|| mWakefulness == WAKEFULNESS_DOZING
|| (flags & PowerManager.USER_ACTIVITY_FLAG_INDIRECT) != 0) {
return false;
}
// according to flag Whether to restart the activity timeout update when it is dimmed mLastUserActivityTimeNoChangeLights or mLastUserActivityTime
// And set up mDirty DIRTY_USER_ACTIVITY
if ((flags & PowerManager.USER_ACTIVITY_FLAG_NO_CHANGE_LIGHTS) != 0) {
if (eventTime > mLastUserActivityTimeNoChangeLights
&& eventTime > mLastUserActivityTime) {
mLastUserActivityTimeNoChangeLights = eventTime;
mDirty |= DIRTY_USER_ACTIVITY;
return true;
}
} else {
if (eventTime > mLastUserActivityTime) {
mLastUserActivityTime = eventTime;
mDirty |= DIRTY_USER_ACTIVITY;
return true;
}
}
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_POWER);
}
return false;
}
4. Application scenarios
for example : Long connections need to be in the background and services need to be continuously online ; The underlying optimization strategy of Android system will be adjusted during the period of system hibernation CPU Operation , We need to keep the application CPU Keep running .
mqtt perhaps websocket Equal length connection frame is needed !
PowerManager pm = (PowerManager) getSystemService(Context.POWER_SERVICE);
PowerManager.WakeLock w1 = pm.newWakeLock(PowerManager.SCREEN_DIM_WAKE_LOCK, "MyTag");
w1.acquire();
// In the process , The screen will remain bright !
// Or the network protocol executes heartbeat packets
w1.release();
Above newWakeLock( ) One of the first flag Mark , These marks affect the system power supply to varying degrees .
These tags are exclusive , And only one of them can be specified at a time .
PARTIAL_WAKE_LOCK: keep CPU Work , The screen and keyboard lights may be off .SCREEN_DIM_WAKE_LOCK: keep CPU Work , Allow to keep the screen display, but it may be gray , Allow to turn off the keyboard lightSCREEN_BRIGHT_WAKE_LOCK: keep CPU Work , Allows you to keep the screen highlighted , Allow to turn off the keyboard lightFULL_WAKE_LOCK: keep CPU Work , Keep the screen highlighted , The keyboard lights also stay bright
5. Control system sleep
Android The sleep and wake-up of devices are mainly based on WakeLock Mechanism .WakeLock It is a locking mechanism , As long as a process gets WakeLock The lock system will not enter Go to sleep . for example , When downloading files or playing music , Even if it's time to sleep , The system cannot sleep .WakeLock Timeout can be set , It will unlock automatically after timeout , Specific about wake lock I will write another article after the introduction of , Here is only a brief introduction .
Application and use WakeLock Before function , You need to use it first new WakeLock() Interface to create a WakeLock Class object , And then call it. acquire() Method disable system hibernation , After the application completes its work, call release() Method to restore the sleep mechanism , Otherwise, the system will not sleep , Until all the electricity is consumed .
WakeLock In the class implementation acquire() and release() Method is actually called PowerManagerService Of acquireWakeLock() and releaseWakeLock() Method .
updatePowerStateLocked() by PowerManagerService Core function of ; Apply for lock after execution , Release the lock , User events , Forced wakeup / Sleep and other operations need to be called updatePowerStateLocked() To update the power status
5.1 wakelock
Wakelock yes android Unique power management mechanism on the system , As long as an application holds this lock , The system cannot go to sleep , At the upper level, different applications can hold multiple different wakelock lock , But there are only three kinds of reflection on the bottom : Control system sleep PowerManagerService.WakeLock, Control what the screen displays PowerManagerService.Display And control power status change notification PowerManagerService.Broadcasts.
PowerManagerService Yes acquire() Lock and release() Unlock Two kinds of state , There are two ways to lock :
- The first is permanent locking , Unless such a lock is explicitly released , Otherwise, it will not be unlocked , So this kind of lock should be used very carefully ( Default ).
acquire(): apply wakelock Permanent lock ( Default ), Manual required release - The second kind of lock is timeout lock , This kind of lock will be unlocked for a period of time after locking .
acquire(long timeout): apply wakelock Timeout lock ,timeout Set the timeout for , Timeout Auto release Drop that wakelock.
The application is using wakelock front , Must be in its manifest.xml Register in the file android.permission.WAKE_LOCK jurisdiction ;
边栏推荐
- 全局变量和静态变量的初始化
- IPage能正常显示数据,但是total一直等于0
- Skywalking全部
- Sum of two numbers, the numbers in the array are converted to decimal, added, and output inversely
- Marvell 88E1515 PHY loopback模式测试
- PHY drive commissioning - phy controller drive (II)
- Ros2 - common command line (IV)
- Redis-02. Redis command
- Some classic recursion problems
- 2022年中纪实 -- 一个普通人的经历
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
IPage能正常显示数据,但是total一直等于0
U-Boot初始化及工作流程分析
[algorithm post interview] interview questions of a small factory
mysql设置触发器问题
ROS2——安装ROS2(三)
SRE核心体系了解
Using handler in a new thread
【软件测试】06 -- 软件测试的基本流程
Vscode editor
Ros2 - Service Service (IX)
Redis-02. Redis command
Lexin interview process
The problem of Chinese garbled code in the vscode output box can be solved once for life
【obs】x264编码:“buffer_size“
Xiaomi written test real question 1
LSA Type Explanation - lsa-5 (type 5 LSA - autonomous system external LSA) and lsa-4 (type 4 LSA - ASBR summary LSA) explanation
GDB code debugging
Application of recyclerview
【软件测试】05 -- 软件测试的原则
Marvell 88E1515 PHY loopback模式测试