当前位置:网站首页>[effective Objective-C] - block and grand central distribution
[effective Objective-C] - block and grand central distribution
2022-07-03 19:50:00 【Xiyou guofucheng】
When developing an application , The worst thing is that the program UI Thread blocked and hung , stay iOS In the system , Blocking for too long may cause the application to terminate execution , Fortunately, Apple has designed multithreading in a new way , And the core of multithreading is “ block ” And “ Large central distribution ”,“ block ” It's a kind of technology that can be used in C、C++ And OC Used in the code “ Lexical closure ”,GCD Is a block related technology , It provides an abstraction of threads , This abstraction is based on “ Distribution lines ”.
Block and GCD It's all current OC The cornerstone of programming , therefore , Must understand its working principle and function .
The first 37 strip : understand “ block ” The concept of
block Closures can be implemented , And it is as “ Expand ” To join GCD In the compiler .
1. Basic knowledge of blocks :
Blocks are like functions , It's just defined directly in another function , Share something in the same scope as the function that defines it . block use “^” A sign to indicate , Followed by a pair of curly braces , Inside the brackets is the implementation code of the block . for example :
^{
// Code
}
A block is actually a value , And it has its own related types . And int、float or OC object , You can also assign blocks to variables , Then use it like any other variable .** The syntax of block type is similar to that of function pointer .** The structural syntax of the block is as follows :
return_type (^block_name)(parameters)
for example :
int (^addBlock)(int a, int b) = ^(int a, int b){
return a + b;
};
If used, it is :
int add = addBlock(2, 5);
This is similar to the feeling of setting a function in a function , Then you can call this in this function block, And it can also capture all variables within its declared scope .
By default , Variables captured for the block , It can't be modified in the block , however , Variables can be declared with _block Modifier , In this way, it can be modified within the block .
for example :
_block NSIntger count = 0;
// Below is a block
So this count The value can be changed in the block , This is also “ Inline block ” Usage of .
If the variable captured by the block is an object type , Then it will be automatically retained . When the system releases this block , It will also be released . This leads to an important problem related to blocks . The block itself can be regarded as an object . And the block itself is like other objects , There are reference counts .
If the block is defined in OC Class , So except that you can access all instance variables of the class , You can also use self Variable . Blocks can always modify instance variables , So there is no need to add _block. however , If an instance variable is captured by a read or write operation , Then it will automatically self Variables are captured together , Because the instance variable is the same as self The instance of the reference is associated with . in other words , As long as you call the attribute value in the block. , Then the block will capture the class itself, that is self.
But remember :self It's also an object , So the block will keep it when it captures it . If self The object referred to also retains the block , Then this usually leads to “ Reserved ring ”.
2. The internal structure of the block :
The block itself is also an object , In the memory area where the block object is stored , The first variable is pointing to Class Object pointer , The pointer is called isa. The rest of the memory contains all kinds of information needed for the normal operation of the block object . Memory layout of block objects :
In memory layout , The most important thing is invoke Variable , This is a function pointer , Implementation code pointing to block . The function prototype needs to accept at least one void* The parameters of type , This parameter represents the block .
descriptor A variable is a pointer to a structure , Each block contains this structure , The overall size of the block object in the declaration , Also shengmingli copy And dispose The function pointer corresponding to these two auxiliary functions .
The block also copies all variables it captures . These copies are placed in descriptor After the variable , How many variables are captured , How much memory space to occupy . Please note that , It is not the object itself that is copied , It's a pointer variable to these objects .invoke Why does a function need to pass a block object as a parameter ? And the reason is that , When executing a block , To read these captured variables from memory .
3. Global block 、 Stack block and stack block :
When defining blocks , Its memory area is allocated in the stack . That is to say , A block is valid only in the range in which it is defined . Code like this can be dangerous :
It's defined in if And else Both blocks in the statement are allocated in stack memory . The compiler will allocate memory blocks to each stack , However, after leaving the corresponding scope , It is possible for the compiler to overwrite the memory allocated to the block . therefore , These two blocks can only be guaranteed in the corresponding if or else Valid within the scope of the statement . The code written in this way is sometimes correct , Sometimes wrong . If the compiler does not overwrite the block to be executed , Then the program runs as usual , If you overwrite , Then the program crashes . Generally speaking, it means , Because you are if Blocks defined within conditions ,if After execution, your block may be recycled , Then you're in if If you use it outside the condition, you will make an error .
To solve this problem , We can send to the block object copy Messages are copied . In this case , You can copy the block from the stack to the heap . And the copied block , Can be used outside the scope that defines it .

If you use manual reference counting , Then remember to release the outer block after using it .
except “ Stack block ” and “ Heaps ” outside , Another kind of block is called “ Global block ”. This block does not capture any state ( For example, peripheral variables ), The runtime does not need to have a state to participate . The entire memory area used by the block , It has been completely determined at compile time , therefore , Global blocks can be declared in global memory , It doesn't need to be created in the stack every time it is used . in addition , The global copy operation is an empty block , Because global blocks can never be reclaimed by the system . This block is actually equivalent to a single case . Here is a global block :
void (^block)() = ^{
NSLog(@"This is a block");
};
4. The main points of :
- Block is C、C++、OC Lexical closure in .
- Block acceptable parameters , You can also return a value .
- Blocks can be allocated on the stack or heap , It can also be global . Blocks allocated on the stack can be copied to the heap , In this case , Just like standard OC object , Reference count is available .
The first 38 strip : Create for common block types typedef
Each block has its own “ Intrinsic type ”, Therefore, it can be assigned to variables of appropriate types . This type consists of the parameters accepted by the block and its return value .
Because before, when we used or wrote blocks, the code was very complex , So in order to simplify the code, we use typedef, Just like this. :
typedef int (^EOCSomeBlock)(BOOL flag, int value);
In this way, you can rename a block , Now if you want to define this block, you can directly use EOCSomeBlock To define , This is equivalent to a new data type , It takes two arguments , Return to one int Data of type .
for example :
EOCSomeBlock block = ^(BOOL flag, int value) {
// Code
};
This time the code reads much more smoothly : Just like when defining other variables , The variable type is on the left , The variable name is on the right .
Of course, its use is more than that , When a function is accepting parameters , There are many parameters , We can use this method to write the parameter type in the method signature as a word , That makes it easier to read .
for example :
I can write this as :
It looks concise and clear in this way , Easy to understand , And it is more convenient when we want to change its receiving parameters , It's not easy to make mistakes. , We just need to change its typedef Just define the parameters in , If the parameters in some places are not adjusted, it will warn them , We can know clearly .
also , If there are several methods with the same receiving parameters , You can't use a substitute , You also have to define an alias for each method to receive parameters , Because if you use the same one , Modifying one is equivalent to modifying all of them , This will affect other methods .
The main points of :
- With typedef Redefine block type , Block variables can be used more easily .
- You should follow existing naming conventions when defining new types , Do not make its name conflict with other types .
- You can define multiple type aliases for the same block signature . If the code to be refactored uses an alias of the block type , Then you only need to modify the corresponding typedef Block signature in , No other changes are required typedef.
The first 39 strip : use handler Block reduces code dispersion
When coding the user interface , A common paradigm is “ Perform tasks asynchronously ”. This paradigm benefits lie in : The thread used to handle the display and touch operation of the user interface , Not because of the execution of I/O Or network communication . This thread is usually called the main thread .
In some cases , If the application does not respond within a certain period of time , Then it will automatically terminate .iOS This is the case with applications on the system ,“ System monitor ” After discovering that the main thread of an application has been blocked for some time , Will terminate it .
Usually, we want to notify the relevant code after the execution of a task, and various value transfer methods will be used for subsequent tasks , But we mentioned the various uses of blocks above , Here we can use , We change the method signature of a method to a block , Then can we achieve the desired effect through this block , Just like this. :
This method is very similar to the entrustment agreement , But it can be defined inline completion handler, Use... In this way “ Network data acquisition device ”, The code is much easier to understand than before .
Compared to code that uses the delegate pattern , The code written in blocks is obviously Cleaner . however Delegate pattern Another shortcoming : If the class needs to use multiple fetchers to download different data , Then you have to delegate The callback method switches according to the incoming getter parameters , Just like this. :

change to the use of sth. The benefits of writing in blocks yes : No need to save the getter , There is no need to switch in the callback method . Every completion handler Business logic of , They are defined together with the related getter objects :
And using this writing method can also deal with many error situations , This is divided into two ways . Two handlers can be used to deal with the failure of the operation and the success of the operation . You can also put the code needed to handle the failure , And the code used to deal with normal conditions , All encapsulated in the same completion handler Block inside . for example :
such API The design style is very good , Because success and failure should be dealt with separately , So call this API The code will follow the logic , Write the code for success and failure separately , This will make the code easier to read . and , If there is need to , You can also omit the code used to deal with failure or success .
And the other is like this :
This approach requires detection of incoming error Variable , And put the logic code in one place . It's written in this way shortcoming yes : Because all the logic is written together , So it will make the block longer , And it's complicated . However, there are also ways of using only one block benefits , That is more flexible .
Put success and failure in the same block, and there is another advantage : call API Your code may find errors in processing successful responses .
Sometimes it is necessary to perform callback operations at relevant event points , This situation can also be used handler block . For example, it is the progress bar of downloading applications . We add an observer to it , And when its value changes, we call the block .
The NSOperationQueue The parameter indicates the queue used to execute the block code when the notification is triggered . This is a “ Queue operation ”, Instead of “ Bottom GCD queue ”, However, the semantics of both are the same .
The main points of :
- When you create an object , You can use inline handler The block declares the relevant business logic together .
- When multiple instances need to be monitored , If the Commission mode is adopted , You often need to switch based on the incoming objects , And if you use handler Block , You can directly put the block together with related objects .
- Design API If you use handler block , Then you can add a parameter , Using this parameter, the caller can decide on which queue the block should be scheduled for execution .
The first 40 strip : Do not have a reserved ring when using a block to refer to its owning object
When using blocks , If you don't think carefully , It's easy to see “ Reserved ring ”. For example, the following code :

There is another class to reference him :
These two pieces of code look ok , But there is a retention ring , This is the case :
stay EOCClass Class , that start Method block references _fetchedData Instance variables are equivalent to the block referencing the class itself , Because if you want to get this instance variable, you can get this class .
It's actually very simple to crack this retention ring , Just let one of them break :
This kind of reservation ring is caused by the reservation of three parties , Of course, there is also a retention ring caused by the reservations of two parties , If completion handler The object referenced by the block finally refers to the block itself , Then there will be a retention ring . So when we write this kind of code , Be sure to pay attention to , Maybe you can't see , But it does exist .
The main points of :
- If the object captured by the block retains the block itself directly or indirectly , Then be careful about the retention ring problem .
- Be sure to find an appropriate time to release the reserved ring , Instead of putting the blame on API The caller .
The first 41 strip : Multi purpose distribution queue , Use less synchronization locks
stay OC in , If there are multiple threads to execute the same code , Then sometimes there will be problems . In this case , Locks are usually used to implement some kind of synchronization mechanism . stay GCD Before appearance , There are two ways , The first is to use built-in “ Synchronized block ”.
This way of writing will be based on the given object , Automatically create a lock , And wait for the code in the block to execute . Execute to the end of this code , The lock is released . However , The abuse of @synchronized(self) Will reduce code efficiency , Because those synchronization blocks that share a lock , Must be executed in order . If it's in self Frequent locking on objects , Then the program may have to wait for another unrelated piece of code to be executed , To continue executing the current code , There is no need to do so .
Another method is to use directly NSLock object :
You can also use NSRecursiveLock such “ Recursive lock ”, The thread can hold the lock more than once , Without deadlock .
Both methods are good , But it also has its drawbacks . For example , In extreme cases , Synchronization blocks can cause deadlocks , in addition , Its efficiency is not necessarily very high , If you use the lock object directly , Once you encounter a deadlock , It's going to be a lot of trouble .
The alternative is to use GCD, It can be simpler 、 A more efficient form is code locking .
Because I just said , The abuse of @synchronized(self) It will be very dangerous , Because all synchronization blocks will rob each other of the same lock . So we have a simple and efficient way to replace synchronous blocks or lock objects , That's it “ Serial synchronization queue ”. Usage is as follows :
The idea of this model is : Arrange the set operation and get operation to be executed in the serialized queue , In this case , All access operations for attributes are synchronized . But there is a Disadvantage : If you test the program performance , Then you may find that this writing method is slower than the original , Because when performing asynchronous dispatch , Need to copy block . If the time taken to copy the block significantly exceeds the time taken to execute the block , Then this practice will be slower than before .
Multiple acquisition methods can be executed concurrently , The acquisition method and the setting method cannot be executed concurrently , Take advantage of this feature , We can write faster code . This time we use Concurrent queues .
Write code like this , Synchronization has not been achieved correctly . All read and write operations are performed on the same queue , But because it is a concurrent queue , So read and write operations can be performed at any time . And we just I don't want these operations to be performed at will . This problem uses a simple GCD Function can solve , He is fence . The following functions can dispatch blocks to the queue , Use it as a fence :
In the queue , Fence blocks must be executed separately , Cannot be in parallel with other blocks . This only makes sense for concurrent queues , Because the blocks of the serial queue are always executed in order . Concurrent queue if the block to be processed next is a fence block , Then wait until all current concurrent blocks are executed , Will execute this fence block alone . After the fence block is executed , Then continue to process downward in the normal way .
Because the get and write methods cannot be synchronized , So the above method can be written in this way :

Use concurrent queues for get methods , Use fence blocks for write methods . It is illustrated by a diagram :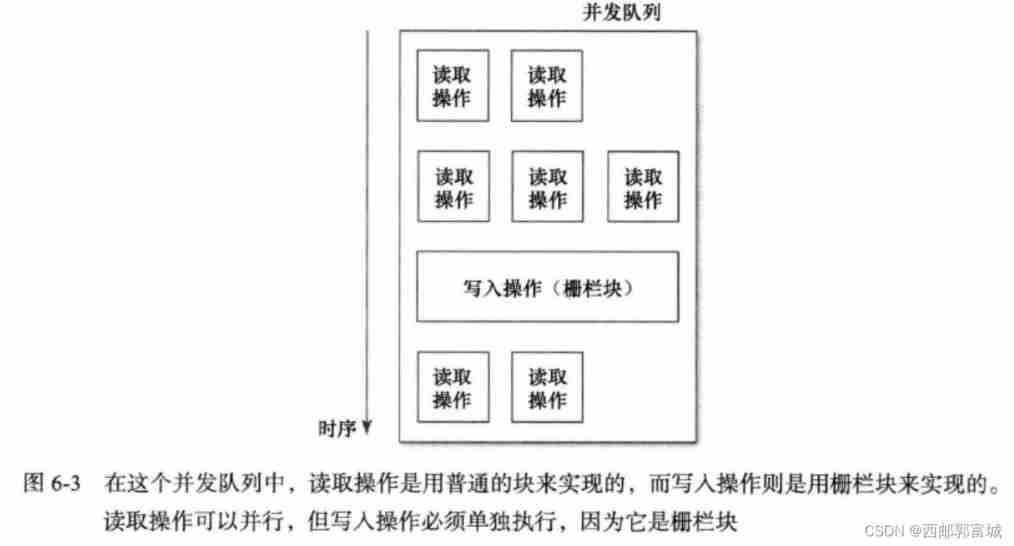
It must be faster than the previous serial queue . Be careful : The setting function can also be implemented by using synchronized fence blocks , That might be more efficient , The reason has just been explained .
The main points of :
- Dispatch queue can be used to express synchronization semantics , This method is better than using @synchronized Block or NSLock The object is simpler .
- Combining synchronous and asynchronous dispatch , It can achieve the same synchronization behavior as ordinary locking mechanism , This does not block the thread that performs the asynchronous dispatch .
- Using synchronous queues and fence blocks , Can make synchronous behavior more efficient .
The first 42 strip : multi-purpose GCD, To use less performSelector Series method
OC Is a very dynamic language ,NSObject Several methods are defined , So that developers can call any method at will . These methods can delay the execution of method calls , You can also specify the thread used to run the method . But it's better to use less now .
The simplest of them is “performSelector:”. The method is signed as follows , It takes a parameter , It's the choice to execute :
- (id)performSelector:(SEL)selector;
This method is equivalent to calling the selector directly . So the execution effect of the following two lines of code is the same :
This way looks like chicken ribs , But if the selector is determined during the run time , Then it can reflect the strength of this way . This is equivalent to using dynamic binding again on top of dynamic binding , It looks like this :
This method is extremely flexible , It can also be used to simplify code . There's another way , Is to save the selection first , Call... After an event occurs . Either way , The compiler doesn't even know what selector to execute , This can only be determined after the operation period . However , The cost of using this feature is , If in ARC Compile the code under , Then the compiler will issue the following warning message :
Because the compiler doesn't know what selector to call , You don't know its method signature and return value , I don't even know whether there is a return value , I don't know how to use ARC How much space to allocate . In view of this ,ARC Took a more cautious approach , That is, the release operation is not added . It is because of this that the memory leaks , This is because the method may have retained the object when it returns it . So we usually don't recommend using this method to access methods in programs .
And this method has many extended methods , Like the following , However, it is not recommended to use , Because its disadvantages outweigh its advantages , There are great limitations .
For example, the above two parameters can only pass two parameters at most , So what if you want to pass more parameters , And because it is id Parameters of type , So you can only pass objects , If you receive an integer or floating-point number, it is troublesome to convert . There are many similar ones, but they are not recommended because they have limitations and we can find better ways to replace .
Like , To postpone execution, you can use dispatch_after To achieve , Executing a task on another thread can be done through dispatch_sync And dispatch_async To achieve .
The main points of :
- performSelector In memory management, the serial methods are easy to miss . It cannot determine exactly what the selectors will be executed , thus ARC The compiler will not be able to insert appropriate memory management methods .
- performSelector The selectors that a series of methods can handle are too limited , The return value type of the selector and the number of parameters sent to the method are limited .
- If you want to put the task on another thread , Well, it's better not to use it performSelector Series method , Instead, you should encapsulate tasks into blocks , Then we call the relevant methods of the large central dispatching mechanism. .
The first 43 strip : master GCD And when to use the operation queue
When performing background tasks ,GCD Not necessarily the best way . There's another technology called NSOperationQueue, Although it is related to GCD Different , But it has something to do with it , Developers can operate as NSOperation In the form of subclasses in the queue , These operations can also be performed concurrently .
Among the many differences between the two , First of all Be careful :GCD Is pure C Of API, The operation queue is OC The object of . stay GCD in , Tasks are represented by blocks , And block is a lightweight data structure . By contrast ,“ operation ” Is a more heavyweight OC object .
Use NSOperation And NSOperationQueue Of benefits as follows :

NSOperation There are also objects. “ Thread priority ”, This determines the priority of the thread running this operation . use GCD This function can also be realized , It is simpler to use the operation queue , Just set a property .
All in all , still We should try to choose high-level API, Turn to the bottom only when necessary . But it has to be discussed according to the situation .
The main points of :
- When solving the problem of multithreading and task management , Dispatch queue is not the only solution .
- The operation queue provides a set of high-level OC API, Can achieve pure GCD Most of the functions , And it can do some more complicated operations , If those operations are changed to GCD To achieve , You need to write additional code .
The first 44 strip : adopt Dispatch Group Mechanism , Perform tasks according to system resource status
dispatch group yes GCD A feature of , Ability to group tasks . The caller can wait for this set of tasks to complete , You can also continue to execute after providing the callback function , When this set of tasks is completed , The caller will be notified . The most important usage , It is to combine multiple tasks to be executed concurrently , So the caller can know when all these tasks will be finished .
The following function can create dispatch group:
dispatch_group_tdispatch_group_create();
Want to group tasks , There are two ways . The first is the following function :
void dispatch_group_async(dispatch_group_t group, dispatch_queue_t queue, dispatch_block_t block);
He is ordinary dispatch_async Variations of functions , One more parameter than the original , Used to indicate the group to which the execution block belongs . There are also ways to specify which tasks belong to dispatch group, That is to use the following pair of functions :
void dispatch_group_enter(dispatch_group_t group);
void dispatch_group_leave(dispatch_group_t group);
The former can increase the number of tasks to be performed in the group , The latter makes it decrease . Thus we can see that , Called dispatch_group_enter in the future , There must be a corresponding dispatch_group_leave Talent . This is similar to reference counting . But in the use of dispatch group when , If the enter after , There is no corresponding leave operation , Then this group of tasks will never be completed .
The following function can be used to wait dispatch group completion of enforcement :
long dispatch_group_wait(dispatch_group_t group, dispatch_time_t timeout);
This function takes two arguments , One is to wait group, The other one represents waiting time timeout value .timeout The argument indicates that the function is waiting dispatch group At the end of execution , How long should it be blocked . If you execute dispatch group The time required is less than timeout, Then return to 0, Otherwise return to non 0. This parameter can also take a constant dispatch_time_forever, This means that the function will wait dispatch group After execution , It doesn't time out .
In addition to using the above function to wait dispatch group After execution , You can also use another method , Use the following functions :
void dispatch_group_notify(dispatch_group_t group, dispatch_queue_t queue, dispatch_block_t block);
And wait Function slightly Different Yes. : Developers can pass in blocks to this function , etc. dispatch group After execution , The block will execute on a specific thread . also notify The queue selected for callback , It should be decided according to the specific situation .
Why “ Perform tasks according to system resource status ” Well ?
To execute blocks in the queue ,GCD It will automatically create new threads or reuse old threads at the appropriate time . If you use concurrent queues , Then there may be multiple threads , This also means that multiple blocks can be executed concurrently . In the concurrent queue , The number of concurrent threads used to execute the task , Depends on various factors , and GCD These factors are mainly determined according to the status of system resources .
We want to traverse collection, And perform tasks on each of its elements , And this can also use another GCD Function to implement :
void dispatch_apply(size_t iterations, dispatch_queue_t queue, void(^block)(size_t));
This function will repeatedly execute the block a certain number of times , Every time the parameters passed to the block are incremented , from 0 Start , until “iterations - 1”, Its usage is as follows :
There is one thing to Be careful :dispatch_apply The queue used can be a concurrent queue . If concurrent queues are used , Then the system can execute these blocks in parallel according to the resource status , This is with the use of dispatch group The example code of is the same .
In short, we still have to be flexible , It's not like learning one and using one method , We should discuss it according to the situation , Choose the best way .
The main points of :
- A series of tasks can be grouped into one dispatch group In . Developers can be notified when this set of tasks is completed .
- adopt dispatch group, Multiple tasks can be performed simultaneously in a parallel dispatch queue . here GCD These concurrent tasks will be scheduled according to the system resource status . If developers implement this function by themselves , You need to write a lot of code .
The first 45 strip : Use dispatch_once To execute thread safe code that only needs to be run once
Singleton mode is no stranger to us , The common implementation method is : Write a class called sharedInstance Methods , This method will only return the singleton instance shared by the whole class , Instead of creating a new instance every time you call .
But there are still controversies , however GCD Introduced a feature , It can make the implementation of singleton easier :
void dispatch_once(dispatch_once_t *token, dispatch_block_t block);
This function accepts type dispatch_once_t The special function of , be called Mark , Block parameters are also accepted . For a given tag , This function is bound to execute the pillow related block , And only once . When this function is called for the first time , The code in the block must be executed , The most important point is this , This operation is completely thread safe . Please note that , For blocks that only need to be executed once , The tags passed in must be exactly the same each time the function is called . therefore , Developers usually declare tags in static or global In scope .
Then a single example can be written like this :
The main points of :
- Often need to write “ Thread safe code that only needs to be executed once ”. adopt GCD Provided by the dispatch_once function , It's easy to do this .
- Tags should be declared in static or global Scope , In this case , Pass a block that only needs to be executed once to the dispatch_once Function time , The same token was passed in .
The first 46 strip : Do not use dispatch_get_current_queue
Use GCD when , We often need to determine which queue the current code is executing on , We will find that Apple gave us this function :
dispatch_queue_t dispatch_get_current_queue();
This function will return the queue in which the code is currently executing . But we'd better not use , Because a hierarchy will be formed between queues , This means that blocks in a queue , Will be in its parent queue (“ Parent queue ”) Internal execution . The queue with the highest status in the hierarchy is always “ Global concurrent queues ”. So when we test again , What he returned was not the queue we wanted , It may be its sub queue , If we judge the condition, it may cause “ Deadlock ”.
To solve this problem , The best way is through GCD The functions provided to set “ Queue specific data ”, This function can associate any data to the queue in the form of key value pairs . The most important thing is , If the associated data cannot be obtained according to the specified key , Then the system will look up the hierarchy , Until the data is found or reaches the root queue .
void dispatch_queue_set_specific(dispatch_queue_t queue, const void *key, void *context, dispatch_function_t destructor);
The first parameter of this function indicates the queue of data to be set , The next two parameters are keys and values . Keys and values are opaque void The pointer . For keys , There is a problem that must be Be careful : The function compares keys by pointer value , Not according to its content .
The last argument to the function is “ Destructor ”, For a given key , When the memory occupied by the queue is reclaimed by the system , Or when a new value is associated with a key , The original value object will be removed , The destructor will also run at this time .dispatch_function_t The type is defined as follows :
typedef void (*dispatch_function_t)(void*);
The main points of :
- dispatch_get_current_queue Functions often behave differently than developers expect . This function is obsolete . Only debugging should be done .
- Because the distribution queue is organized by hierarchy , Therefore, it cannot be described by a single queue object “ The current queue ” The concept of .
- dispatch_get_current_queue Function is used to solve the deadlock caused by non reentrant code , However, this function can be used to solve the problem , It can also be used “ Queue specific data ” To solve .
边栏推荐
- Luogu-p1107 [bjwc2008] Lei Tao's kitten
- Professional interpretation | how to become an SQL developer
- Common text labels
- P1891 crazy LCM (Euler function)
- FPGA learning notes: vivado 2019.1 project creation
- Titles can only be retrieved in PHP via curl - header only retrieval in PHP via curl
- Geek Daily: the system of monitoring employees' turnover intention has been deeply convinced off the shelves; The meta universe app of wechat and QQ was actively removed from the shelves; IntelliJ pla
- Sentinel source code analysis part II - sentinel dashboard console startup and configuration
- Chapter 2: 4-digit Kaplan number, search even digit Kaplan number, search n-digit 2-segment sum square number, m-digit ingenious square number without 0, specify the number to form a 7-digit square nu
- Phpstudy set LAN access
猜你喜欢
![2022-06-30 advanced network engineering (XIV) routing strategy - matching tools [ACL, IP prefix list], policy tools [filter policy]](/img/b6/5d6b946d8001e2d73c2cadbdce72fc.png)
2022-06-30 advanced network engineering (XIV) routing strategy - matching tools [ACL, IP prefix list], policy tools [filter policy]

What is the content of game modeling

NFT without IPFs and completely on the chain?

2022-07-02 advanced network engineering (XV) routing policy - route policy feature, policy based routing, MQC (modular QoS command line)

Chapter 1: drinking soft drinks, step tariff calculation, step tariff calculation function, personal income tax, solving square root inequality, simplifying solving square root inequality, solving dem
IPv6 experiment

PR 2021 quick start tutorial, how to create a new sequence and set parameters?

Today's work summary and plan: February 14, 2022
第一章:三位阶乘和数,图形点扫描
BUUCTF
随机推荐
WPF format datetime in TextBlock- WPF format DateTime in TextBlock?
Chapter 1: recursively find the factorial n of n!
Day11 ---- 我的页面, 用户信息获取修改与频道接口
BOC protected alanine zinc porphyrin Zn · TAPP ala BOC / alanine zinc porphyrin Zn · TAPP ala BOC / alanine zinc porphyrin Zn · TAPP ala BOC / alanine zinc porphyrin Zn · TAPP ala BOC supplied by Qiyu
4. Data splitting of Flink real-time project
Chapter 1: King Shehan miscalculated
PR 2021 quick start tutorial, how to create a new sequence and set parameters?
Microservice knowledge sorting - search technology and automatic deployment technology
What is the difference between a kill process and a close process- What are the differences between kill process and close process?
kubernetes集群搭建efk日志收集平台
Chapter 1: extend the same code decimal sum s (D, n)
Micro service knowledge sorting - cache technology
Typora charges, WTF? Still need support
Chapter 1: seek common? Decimal and S (D, n)
Chapter 1: simplify the same code decimal sum s (D, n)
Day11 - my page, user information acquisition, modification and channel interface
Part 28 supplement (XXVIII) busyindicator (waiting for elements)
Octopus online ecological chain tour Atocha protocol received near grant worth $50000
Chapter 2: find the box array, complete number in the specified interval, and improve the complete number in the specified interval
Microsoft: the 12th generation core processor needs to be upgraded to win11 to give full play to its maximum performance