当前位置:网站首页>The difference between string constants and string objects when allocating memory
The difference between string constants and string objects when allocating memory
2022-07-07 06:24:00 【Pei Nanwei_】
Catalog
Understand memory distribution
elicit questions
Before understanding the difference between the two , Let's take a look at a piece of code
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = "abc";
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
String s3 = s2.intern();
System.out.println(s2 == s3);
}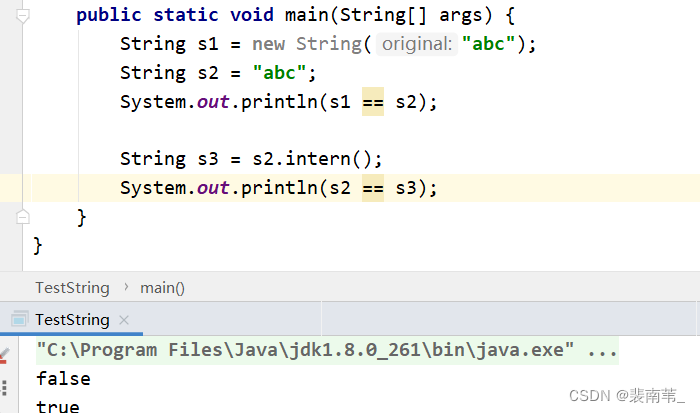
If you were to 2 If you have doubts about the output , After reading this article , I believe you will get something .
Understand memory distribution
Let's first understand the creation process of string constants, string variables and their objects , I believe it will be convenient for you to understand the above comparison .
String constant : It is placed in the string constant pool , In the code, that is "abc"
String object : It's an object , It's in the pile , In the code, that is "new String("abc")"
Next is their distribution in memory
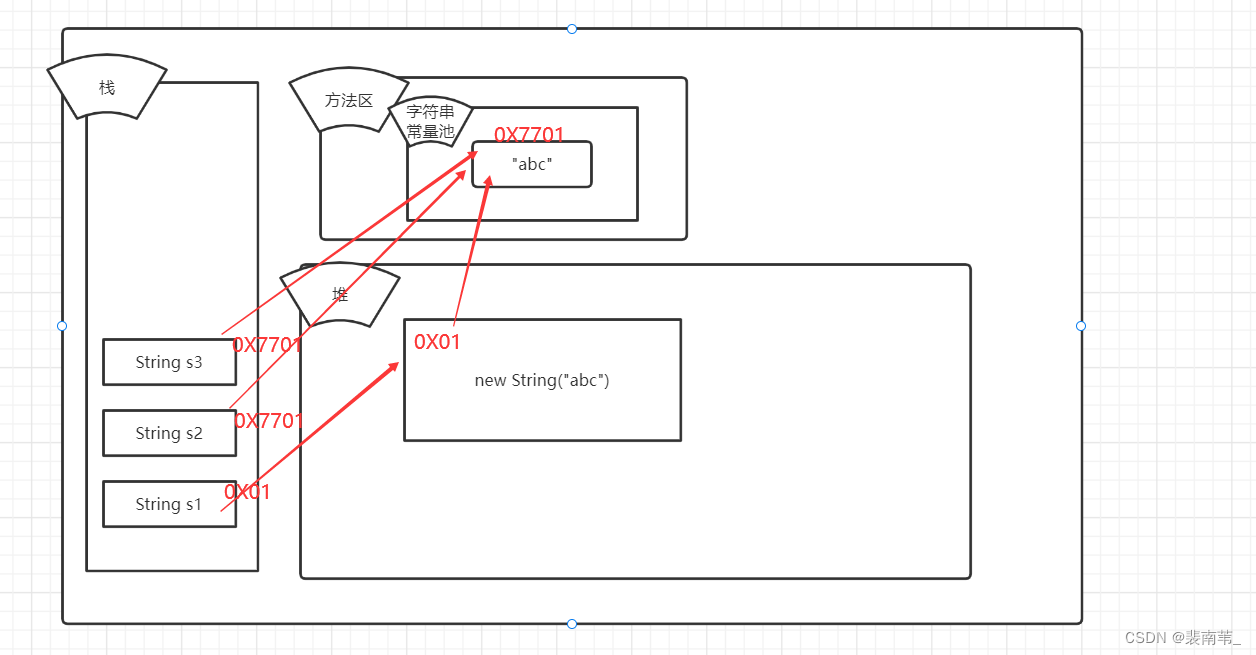
Explain and analyze :
Memory distribution analysis
String s1 = new String("abc")
First, open an address in the stack s1 In the pile new String("abc") The address of , then new This String The object of . stay new When this object , It is necessary to judge whether there is... In the string constant pool first "abc" This constant . If there is , Store the address of this constant directly in the object . without , You need to create this constant in the constant pool first , Then store the memory of this constant in the object .
String s2 = "abc"
First, open an address in the stack s2, The address of the constant to be stored . It is still to go to the constant pool to determine whether this constant exists , The difference is , This time, it is directly stored in the stack s1 quote .
String s3 = s2.intern()
Reference creation is as above ,String Object's intern Method , If the pool already contains one equal to this String Object's string ( The object is created by equals(Object) Method determination ), Then return the string in the pool . otherwise , Put this String Object added to pool , And return this String References to objects .
Result analysis
Compare s1 and s2 when , because s1 The object of is new Coming out , So it exists in the heap . and s2 The stored address is in the method area in the character constant pool , So it's more s1 and s2 Address comparison of , It must be false;
Compare s2 and s3 when , because s3 By s2.intern() Come to ,intern We already know that it is a reference to a constant returned directly . therefore s2 and s3 The storage address of is the same , Of course return true
Okay , That's all for this article , Favorite students can like the collection , Have a problem , Can comment , Or leave a message , I will give you feedback at the first time , Thank you for watching. !!
notes : This article is for me to share my learning experience , There are mistakes or areas that need to be corrected , Please correct me. , I will accept with an open mind
边栏推荐
- 力扣62 不同路径(从矩阵左上到右下的所有路径数量) (动态规划)
- 改变ui组件原有样式
- Navicat导入15G数据报错 【2013 - Lost connection to MySQL server during query】 【1153:Got a packet bigger】
- go-microservice-simple(2) go-Probuffer
- postgresql 数据库 timescaledb 函数time_bucket_gapfill()报错解决及更换 license
- rt-thread 中对 hardfault 的处理
- MySQL(十)
- 【OpenCV】形态学滤波(2):开运算、形态学梯度、顶帽、黑帽
- JMeter function assistant - random value, random string, fixed value random extraction
- 对称的二叉树【树的遍历】
猜你喜欢
Apple CMS V10 template /mxone Pro adaptive film and television website template
Peripheral driver library development notes 43: GPIO simulation SPI driver

哈趣投影黑馬之姿,僅用半年强勢突圍千元投影儀市場!

Three updates to build applications for different types of devices | 2022 i/o key review
Bypass open_ basedir
Jstat of JVM command: View JVM statistics
Subghz, lorawan, Nb IOT, Internet of things

字符串常量与字符串对象分配内存时的区别
Several key steps of software testing, you need to know
【GNN】图解GNN: A gentle introduction(含视频)
随机推荐
软件测试的几个关键步骤,你需要知道
外设驱动库开发笔记43:GPIO模拟SPI驱动
Solve pod install error: FFI is an incompatible architecture
693. 行程排序
[SOC FPGA] custom IP PWM breathing lamp
3428. Put apples
Navicat导入15G数据报错 【2013 - Lost connection to MySQL server during query】 【1153:Got a packet bigger】
Sequential storage of stacks
VIM mapping large K
"Parse" focalloss to solve the problem of data imbalance
tkinter窗口选择pcd文件并显示点云(open3d)
3531. Huffman tree
POI导出Excel:设置字体、颜色、行高自适应、列宽自适应、锁住单元格、合并单元格...
vim映射大K
c面试 加密程序:由键盘输入明文,通过加密程序转换成密文并输出到屏幕上。
Jstack of JVM command: print thread snapshots in JVM
How to set up in touch designer 2022 to solve the problem that leap motion is not recognized?
LM小型可编程控制器软件(基于CoDeSys)笔记二十三:伺服电机运行(步进电机)相对坐标转换为绝对坐标
win系统下安装redis以及windows扩展方法
Doctoral application | Professor Hong Liang, Academy of natural sciences, Shanghai Jiaotong University, enrolls doctoral students in deep learning