当前位置:网站首页>Program simulation perceptron algorithm (gradient descent method sklearn.linear_ Perception method in model)
Program simulation perceptron algorithm (gradient descent method sklearn.linear_ Perception method in model)
2020-11-09 16:06:00 【Come on, get up】
Chapter two The original form simulation of the perceptron
- I'm Xiaobai ; This article code reprint address, there is a note at the end of the article ; Most of the notes are written by themselves , If you have any questions, please give me more advice .
- Simulated perceptron algorithm by gradient descent . The data comes from sklearn.datasets The classic dataset in the middle of .
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Import dataset load_iris.
# The first four columns are calyx length , Calyx width , Petal length , Petal width, etc 4 Attributes used to identify iris ,
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
# load data
iris = load_iris()
# Constructors DataFrame(data,index,columns),data For data ,index Index rows ,columns Index columns
# Construct data structures
df = pd.DataFrame(data=iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)
# stay df A new column has been added to : Name label The data of target, That's the type
# The first 5 In the category of iris ( Include Setosa,Versicolour,Virginica Three types of ).
# That is, by determining the calyx length , Calyx width , Petal length , The size of the petal width is used to identify the type of iris .
df['label'] = iris.target
df.columns = ['sepal length', 'sepal width', 'petal length', 'petal width', 'label']
# Print out label The number of column values . And column name 、 type
# print(df.label.value_counts())
# Create array ,
# The first parameter :100 It means take 0-99 That's ok , The former 100 That's ok ; Empathy 100: After 100 That's ok .
# The second parameter ,0,1 For the first and second columns ,-1 It means the last column
data = np.array(df.iloc[:100, [0, 1, -1]])
# Array cutting ,X Cut out the last column ;y Cut only the last column
X, y = data[:, :-1], data[:, -1]
# Data collation , take y Central African 1 Of is changed to -1
y = np.array([1 if i == 1 else -1 for i in y])
# The data are linearly separable , Two categories of data
# Here is a linear equation of one variable
class Model:
def __init__(self):
# w It starts with the same number of independent variables (1,1) front
self.w = np.ones(len(data[0]) - 1, dtype=np.float32)
self.b = 0
# The learning rate is set to 0.1
self.l_rate = 0.1
def sign(self, x, w, b):
# dot The function is a dot product , The difference in * ride .
# dot Matrix multiplication is the operation of matrix , One row by one column .
# * When you're doing matrix multiplication , It's the multiplication of the corresponding elements
y = np.dot(x, w) + b
return y
# Random gradient descent method
def fit(self, X_train, y_train):
is_wrong = False
while not is_wrong:
# Record the number of points of current classification errors , When the number of misclassification points returns to zero , That's the end of classification
wrong_count = 0
# d from 0-49 Traverse
for d in range(len(X_train)):
# there X For a row two column array
X = X_train[d]
y = y_train[d]
if y * self.sign(X, self.w, self.b) <= 0:
self.w = self.w + self.l_rate * np.dot(y, X)
self.b = self.b + self.l_rate * y
wrong_count += 1
if wrong_count == 0:
is_wrong = True
return 'Perceptron Model!'
def score(self):
pass
perceptron = Model()
# Yes perception Make a gradient descent
perceptron.fit(X, y)
print(perceptron.w)
x_points = np.linspace(4, 7, 10)
# The final fitting function is as follows :
# w1*x1 + w2*x2 + b = 0
# among x1 It's the one below x_points,x2 Namely y_
y_ = -(perceptron.w[0] * x_points + perceptron.b) / perceptron.w[1]
plot.plot(x_points, y_)
# scatter The two properties correspond to x,y.
# First draw the front 50 Calyx length and width of each point , The flower type is 0;
# And then draw 50-100, Now the flower type 1
plot.scatter(df[:50]['sepal length'], df[:50]['sepal width'], label='0')
plot.scatter(df[50:100]['sepal length'], df[50:100]['sepal width'], label='1')
# Abscissa name
plot.xlabel('sepal length')
# Ordinate name
plot.ylabel('sepal width')
plot.legend()
plot.show()
The result is shown in Fig.
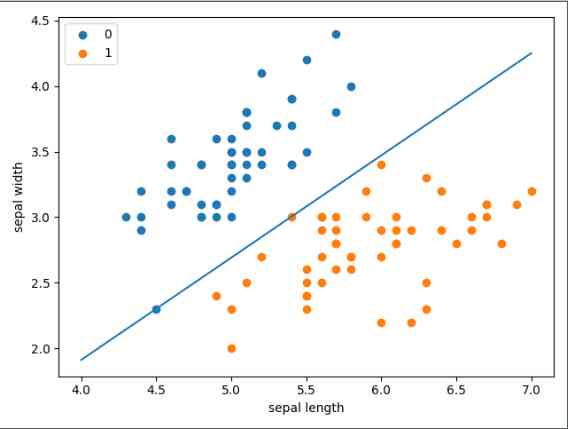
2. sklearn A ready-made perceptron method is provided in , We can call
import sklearn
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron
iris = load_iris()
df = pd.DataFrame(iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)
df['label'] = iris.target
# df.columns = [
# 'sepal length', 'sepal width', 'petal length', 'petal width', 'label'
# ]
data = np.array(df.iloc[:100, [0, 1, -1]])
X, y = data[:, :-1], data[:, -1]
y = np.array([1 if i == 1 else -1 for i in y])
clf = Perceptron(fit_intercept=True, # true Represents the estimated intercept
max_iter=1000, # The maximum number of training data
shuffle=True, # Whether to retrain after each training
tol=None) # If not set none Then the iteration will be less than 1e-3 end
clf.fit(X, y)
# Output after bonding w
print(clf.coef_)
# Output the intercept after fitting b
print(clf.intercept_)
# Canvas size
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
# Chinese title
# plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
# plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# plt.title(' Iris linear data example ')
plt.scatter(data[:50, 0], data[:50, 1], c='b', label='Iris-setosa',)
plt.scatter(data[50:100, 0], data[50:100, 1], c='orange', label='Iris-versicolor')
# Draw the wires of the sensor
x_ponits = np.arange(4, 8)
y_ = -(clf.coef_[0][0]*x_ponits + clf.intercept_)/clf.coef_[0][1]
plt.plot(x_ponits, y_)
# Other parts
plt.legend() # Show Legend
plt.grid(False) # Don't show grid
plt.xlabel('sepal length')
plt.ylabel('sepal width')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
The result is shown in Fig.
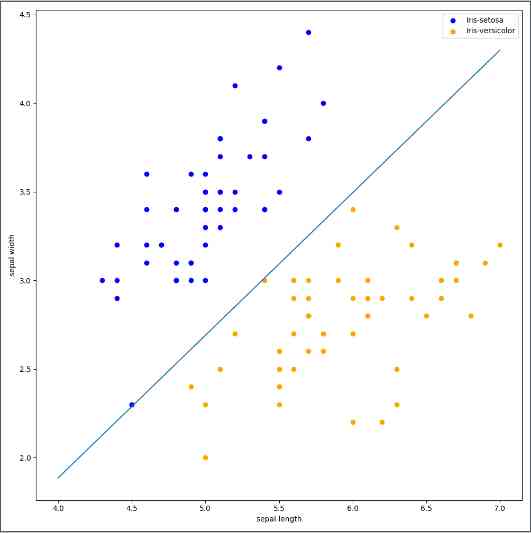
版权声明
本文为[Come on, get up]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- CAD2016下载AutoCAD2016下载安装详细教程CAD下载
- Equivalent judgment between floating point numbers
- 【运维思考】如何做好云上运维服务?
- MES系统在行业应用里区别于传统式管理
- SEO builders, what are the unspeakable hardships?
- QML Repeater
- Autocad2020 full version installation text course, registration activation cracking method
- Using art template to obtain weather forecast information
- Method of conversion between JS character and ASCII code
- What is website [new four modernizations]?
猜你喜欢

乘风破浪的技术大咖再次集结 | 腾讯云TVP持续航行中
AE(After Effects)的简单使用——记一次模板套用的过程
超简单集成华为系统完整性检测,搞定设备安全防护

Application of EMQ X in the Internet of things platform of China Construction Bank

cad教程 cad2016安装教程

Do programmers pay too much to work overtime? Should programmer's salary be reduced? Netizen: let go of other hard pressed programmers

Full stack technology experience tells you: how much does it cost to develop a mall small program?

MES系统在行业应用里区别于传统式管理

听说你一夜之间变了户籍,依萍如洗的打工人该如何自救?
5 minutes get I use GitHub's 5-year summary of these operations!
随机推荐
高质量的缺陷分析:让自己少写 bug
Full link stress testing of moral integrity -- the evolution of corpus intelligence
百万年薪架构师之路:谈应用系统架构设计
cad教程 cad2016安装教程
Super discount, cloud server 88 yuan seconds
[share] interface tests how to transfer files in post request
高质量的缺陷分析:让自己少写 bug
Express yourself with wechat expression translation, programmer's little romance, get up quickly!
瞧瞧,这样的『函数』才叫 Pythonic
Method of conversion between JS character and ASCII code
5 minutes get I use GitHub's 5-year summary of these operations!
International top journal radiology published the latest joint results of Huawei cloud, AI assisted detection of cerebral aneurysms
超简单集成华为系统完整性检测,搞定设备安全防护
In depth analysis of the multi-user shopping mall system from search to create a profit point
MES system plays an important role in the factory production management
Guest interview: Wang Jian
I do digital transformation in traditional industries (1)
谈谈敏捷开发概念和迭代开发方案
Do you think it's easy to learn programming? In fact, it's hard! Do you think it's hard to learn programming? In fact, it's very simple!
HomeLede 2020.11.08 v5.4.72内核 UPnP+NAS+多拨+网盘+DNS优化+帕斯沃 无缝集成+软件包