当前位置:网站首页>C basic supplement
C basic supplement
2022-07-04 13:41:00 【Hua Weiyun】
C# Basic supplement
A. Allocation of value types .
There is an area called stack in the virtual memory , We don't know where it is in the address space , There is no need to know in the general development process , What we know is that the value type is assigned here . When the value type is allocated on the stack , It is filled from top to bottom , That is, starting from the high memory address .
For example, the current stack pointer is 100000, This shows that its next free storage space is from 99999 Start , When we're in C# Declare a int Variable of type A, because int The type is four bytes , So it will be allocated in 99996 To 99999 In this storage unit . If we go on to state double Variable B(8 byte ), This variable will be assigned to 99988 To 99995 This storage unit . If the code runs outside their scope , Now A and B Both variables will be deleted , At this time, the order is just the opposite , Delete variables first B, At the same time, the stack pointer will increment 8, That is to point back to 99996 This position ; Next, delete the variable A, The stack pointer points back to 10000. If two variables are declared at the same time . Such as int A,B, At this time, we don't know A and B The order of distribution of , But the compiler will ensure that their deletion order is exactly the opposite of the allocation order .
B. Allocation of reference types .
After understanding the allocation method on the stack , Obviously , Its performance is quite high , At the same time, we also found a disadvantage of it : The lifetime of variables must be nested . This is unacceptable in some cases , Sometimes we need to store some data and ensure that this part of data can be used after the method exits . So , Virtual memory allocates another part of the area , We call it managed heap . A big difference between managed heap and traditional heap is , The managed heap works under the control of the garbage collector . The reference type is allocated on the managed heap , Let's take a look at the allocation process of reference types .
Suppose we need to declare a Person Class and instantiate it .
Person p = new Person();
First , The system will give p This variable allocates storage space on the stack , Of course, it's just a reference , For storage Person The location of the instance on the managed heap , There is no real Person example . Because it just stores an address ( An integer value ), So it will occupy on the stack 4 Bytes of space . Next Person The instance will be stored on the managed heap . Different from the stack , Managed heap is allocated from bottom to top , Suppose this instance needs to occupy 10 Bytes , Suppose the address on the managed heap is 200000, Then it will be allocated in 200000 To 200009 This storage unit .
It should be noted that , This allocation is related to the size of the instance , If the instance is smaller than 85000 byte , It will be allocated to the managed heap . If you exceed 85000 byte , It will be assigned to LOH On .
C# Language does not support multiple inheritance .
1.4.3 Structure type
Structure types are the same as classes , Constructor can be declared 、 Data member 、 Method 、 Properties, etc . The fundamental difference between structure and class is that structure is a value type , Class is a reference type . Unlike classes , A structure cannot derive from another structure or class , Itself cannot be inherited , Therefore, abstract structures cannot be defined , Structure members cannot be controlled by access control words protected modification , You can't use virtual and abstract Modifying structural methods . Destructors cannot be defined in structures . Although structures cannot derive from classes and structures , But structures can inherit interfaces , The methods of structure inheritance interface and class inheritance interface are basically the same . The following example defines a point structure point:
using System;struct point// Structure definition { public int x,y;// Constructors and methods can also be declared in structures , Variables cannot be assigned initial values }class Test{ static void Main() { point P1; P1.x=166; P1.y=111; point P2; P2=P1;// Value passed , send P2.x=166,P2.y=111 point P3=new point();// use new Generate structural variables P3,P3 It is still a value type variable }// use new Generate structural variables P3 It only means calling the default constructor , send x=y==0.}Modifier :
One Access modifier Defines the scope and visibility of a class member .C# The supported access modifiers are as follows :
- public: All objects can access ;
- private: The object itself can be accessed inside the object ;
- protected: Only objects of this class and its subclasses can access
- internal: Objects of the same assembly can access ;
- protected internal: Access is limited to the current assembly or type derived from the containing class .
using Usage of :
1. using Instructions : Introduce namespace
This is the most common usage , for example :
using System;using Namespace1.SubNameSpace;2. using static Instructions : Specifies the type whose static members can be accessed without specifying a type name
using static System.Math;var = PI; // Use it directly System.Math.PI3. names
using Project = PC.MyCompany.Project;4. using sentence : Bind instance to code
using (Font font3 = new Font("Arial", 10.0f), font4 = new Font("Arial", 10.0f)){ // Use font3 and font4.}At the end of the snippet , Automatically call font3 and font4 Of Dispose Method , Release instance .
About the supplement of constructor :
For parent and child classes , When subclasses call constructors, they will first call the parent constructor and then the subclass constructor . alike , If it is multiple inheritance , Then when the later subclasses call the constructor, they will call it from the constructor of the uppermost parent class once to the next , Until your constructor .
enumeration
C# Enumeration learning needs attention :
System.Enum Type is the abstract base class of all enumeration types ( It is a unique type different from the base type of enumeration type ), And from System.Enum Inherited members are available in any enumeration type . There are from any enumeration type to System.Enum Packing conversion for , And there are System.Enum Unboxing conversion to any enumeration type .System.Enum Itself is not an enumeration type . contrary , It is a class type , All enumeration types are derived from it . type System.Enum From the type System.ValueType The derived , The latter is from type object The derived . At run time , type System.Enum The value of can be null Or a reference to a boxed value of any enumeration type .
边栏推荐
- Agile development / agile testing experience
- Runc hang causes the kubernetes node notready
- ASP.NET Core入门一
- SQL语言
- Personalized online cloud database hybrid optimization system | SIGMOD 2022 selected papers interpretation
- 面向个性化需求的在线云数据库混合调优系统 | SIGMOD 2022入选论文解读
- 使用宝塔部署halo博客
- AI 绘画极简教程
- Besides, rsync+inotify realizes real-time backup of data
- Apache服务器访问日志access.log设置
猜你喜欢
![[leetcode] 96 and 95 (how to calculate all legal BST)](/img/d5/788c88064bce6a7c4499017908b3f2.jpg)
[leetcode] 96 and 95 (how to calculate all legal BST)
Reinforcement learning - learning notes 1 | basic concepts
CVPR 2022 | transfusion: Lidar camera fusion for 3D target detection with transformer
Cann operator: using iterators to efficiently realize tensor data cutting and blocking processing
高质量软件架构的唯一核心指标
CTF竞赛题解之stm32逆向入门
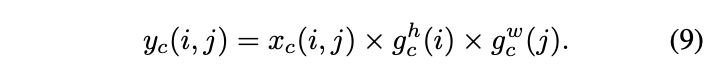
CA:用于移动端的高效坐标注意力机制 | CVPR 2021
Talk about the design and implementation logic of payment process
runc hang 导致 Kubernetes 节点 NotReady

Runc hang causes the kubernetes node notready
随机推荐
游戏启动后提示安装HMS Core,点击取消,未再次提示安装HMS Core(初始化失败返回907135003)
runc hang 导致 Kubernetes 节点 NotReady
阿里云有奖体验:用PolarDB-X搭建一个高可用系统
WPF双滑块控件以及强制捕获鼠标事件焦点
CANN算子:利用迭代器高效实现Tensor数据切割分块处理
Using nsproxy to forward messages
AI painting minimalist tutorial
PostgreSQL 9.1 飞升之路
Interviewer: what is the difference between redis expiration deletion strategy and memory obsolescence strategy?
Read the BGP agreement in 6 minutes.
Solution: how to delete the information of Jack in two tables with delete in one statement in Oracle
Commvault 和 Oracle 合作,在 Oracle 云上提供 Metallic数据管理即服务
C#基础深入学习一
干货整理!ERP在制造业的发展趋势如何,看这一篇就够了
C#基础补充
「小技巧」给Seurat对象瘦瘦身
WPF double slider control and forced capture of mouse event focus
Definition of cognition
Configure WebDAV server on Apache
Iptables foundation and Samba configuration examples