当前位置:网站首页>Usage of test macro of GTEST
Usage of test macro of GTEST
2022-07-06 05:57:00 【panamera12】
1. TestCase Introduction to
Gtest There are several case Methods to test different use cases . The main common ones are TEST/TEST_F And TEST_P Use of macros . At every TestCase The method provided by assertions can be used to control whether the expected direction of the program is the expected result , So as to determine the correctness of the program . In the same TestCase Cannot appear at the same time TEST and TEST_F Mix the two ; secondly TEST_F Than TEST What is strong is that it will inherit ::testing::Test Generate a new class , And this is necessary . In the new class, you can use void SetUp(); and void TearDown(); Create and clear relevant resource data ;
2. TEST macro
TEST The macro is used to create a simple test , It defines a test function , You can use any... In this function C++ Code and use the provided assertions to check .
TEST Grammar definition :
TEST(test_case_name, test_name)
- test_case_name The first parameter is the test case name , Usually take the test function name or test class name
- test_name The second parameter is the test name, which is arbitrary , But it's better to take a meaningful name
- When the test is completed, the test results will be displayed in " Test case name . Test name " Given in the form of
// SharedUnique.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <gtest/gtest.h>
// A custom make_unique templete class
#include <Memory.h>
using namespace sampleCXX::common;
class Base {
public:
Base(std::string name):m_name{name} {
std::cout << "name: " << m_name << std::endl;
}
std::string getName() {
return m_name;
}
~Base() {
std::cout << "destory base" << std::endl;
}
private:
std::string m_name;
};
void getNameFunc(std::shared_ptr<Base> base) {
std::cout << __func__ << " : usercount: " << base.use_count() << std::endl;
std::cout << __func__ << " : name: " << base->getName() << std::endl;
// EXPECT_EQ(2, base.use_count());
}
TEST(Base, createInstance) {
std::unique_ptr<Base> instance = make_unique<Base>("SvenBaseUnique");
// Test created instance Whether the instance is not nullptr
EXPECT_NE(instance, nullptr);
instance.reset();
// test instance Whether the instance is nullptr
EXPECT_EQ(instance, nullptr);
}
TEST(Base, getName) {
std::unique_ptr<Base> instance = make_unique<Base>("BaseUnique");
EXPECT_NE(instance, nullptr);
auto name = instance->getName();
// Test acquired name Whether the value is equal to the given value
EXPECT_STREQ(name.c_str(), "BaseUnique");
instance.reset();
EXPECT_EQ(instance, nullptr);
}
TEST(Base, shared_ptr) {
std::shared_ptr<Base> instance = std::make_shared<Base>("BaseShared");
EXPECT_NE(instance, nullptr);
std::cout << "shared_ptr.use_count: " << instance.use_count() << std::endl;
// test instance Whether the number of citations is 1
EXPECT_EQ(1, instance.use_count());
getNameFunc(instance);
EXPECT_EQ(1, instance.use_count());
}
TEST(Base, unique_ptr) {
std::unique_ptr<Base> instance = make_unique<Base>("BaseUnique");
EXPECT_NE(instance, nullptr);
getNameFunc(std::move(instance));
EXPECT_EQ(instance, nullptr);
}

3. TEST_F macro
TEST_F It mainly carries out various tests , It's a test in many different situations TestCase It will only be used when the same test data will be used in .
That is to test different behaviors with the same data , If the TEST Macros will be tested for different tests case Create a data .TEST_F Macros will share one copy, avoiding duplicate copies and having flexibility .
The syntax is defined as :
TEST_F(test_case_name, test_name);
test_case_name The first parameter is the test case name , You must take the class name . This and TEST Macro different
test_name The second parameter is the test name, which is arbitrary , But it's better to take a meaningful name
Use TEST_F Must inherit ::testing::Test class . And this class provides two interfaces void SetUp(); void TearDown();
void SetUp() function , Prepare objects for testing .
void TearDown() function Destroy object resources after testing .
The following procedure tests one Base Class , They all share the same data (Base Class object ):
Procedure passed BaseTest Class to create a common data resource , This will not need to be created separately for no test cases when testing Base object .
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <gtest/gtest.h>
#include <Memory.h>
using namespace sampleCXX::common;
class Base {
public:
Base(std::string name):m_name{name} {
std::cout << "Create constructor name: " << m_name << std::endl;
}
std::string getName() {
return m_name;
}
void setName(const std::string &name) {
m_name = std::string(name);
}
~Base() {
std::cout << "Destory base" << std::endl;
}
private:
std::string m_name;
};
class BaseTest : public ::testing::Test {
protected:
// Prepare data objects for testing
void SetUp() override {
m_base = std::make_shared<Base>("SvenBaseTest");
}
// Clear resources
void TearDown() override {
m_base.reset();
}
std::shared_ptr<Base> m_base;
};
TEST_F(BaseTest, testCreateInstance) {
std::unique_ptr<Base> instance = make_unique<Base>("SvenBaseUnique");
EXPECT_NE(instance, nullptr);
instance.reset();
EXPECT_EQ(instance, nullptr);
}
TEST_F(BaseTest, testGetName) {
auto name = m_base->getName();
EXPECT_STREQ(name.c_str(), "SvenBaseTest");
}
TEST_F(BaseTest, testSetName) {
m_base->setName("NewSvenBase");
auto name = m_base->getName();
EXPECT_STREQ(name.c_str(), "NewSvenBase");
}

5. EXPECT_* and ASSERT_* Macro introduction of
5.1.gtest The assertion of
To test a class or function , We need to make assertions about their behavior . When an assertion fails ,Google Test The source file where the code is located and its location line number will be output on the screen , And error messages . You can also write assertions , Provide a custom error message , This information will be appended to... In case of failure Google Test After the error message .
Assertions often come in pairs , They all test the same class or function , But it has different effects on the current functions .ASSERT_* A fatal failure occurs when a version of the assertion fails , And end the current function .EXPECT_* Version of the assertion produces a non fatal failure , It does not abort the current function . Generally, it is more recommended to use EXPECT_* Assertion , Because they run a test and more than one error can be reported . But if you are writing an assertion, if it fails , There is no need to continue the test , You should use ASSERT_* Assertion . Because of the failure ASSERT_* The assertion will immediately return from the current function , You may skip some of the cleaning code that follows , This may lead to space leakage .
gtest The macro of interrupt words can be divided into two types : One is ASSERT macro , The other category is EXPECT Macro .
1、ASSERT_* series : Exit the current function if the current point detection fails
2、EXPECT_* series : If the current point detection fails, continue to execute
5.2. gtest Assertion classification 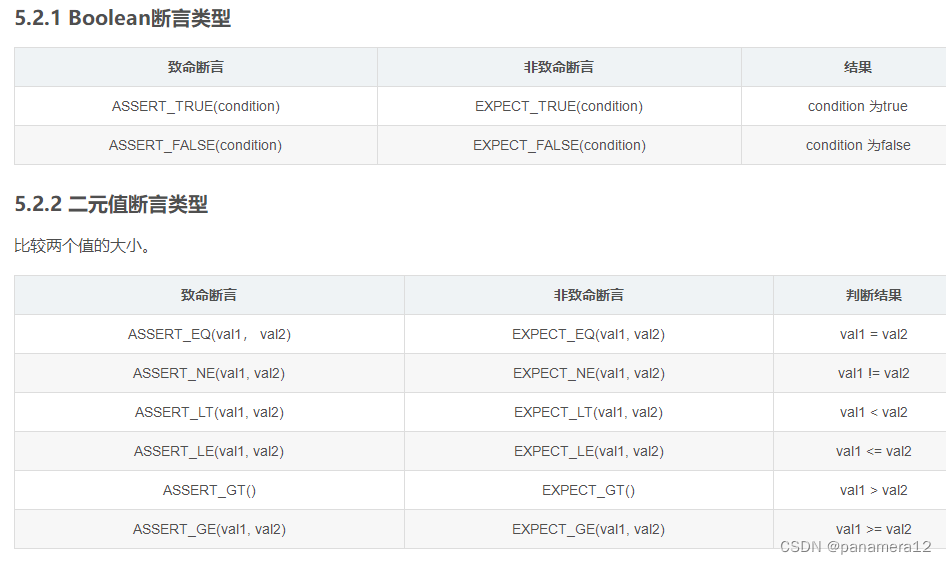
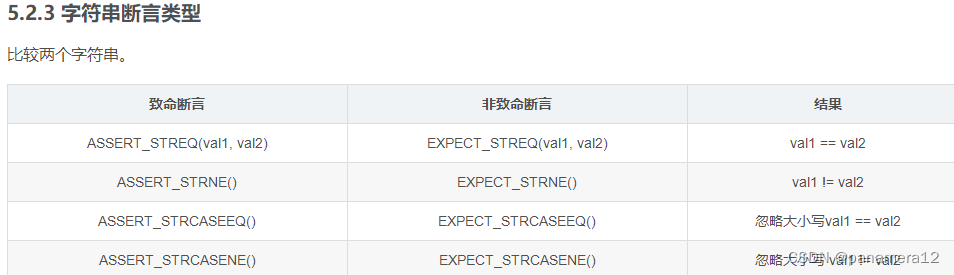
7. Call notes
TEST() and TEST_F() Use googletest Implicitly register their tests . therefore , With many others C ++ Different test framework , You don't have to list all the defined tests again to run them .
After defining the test , You can use RUN_ALL_TESTS() It runs them ,0 If all tests are successful ,1 Then return them . Please note that , In linked cells RUN_ALL_TESTS() Run all tests - They can come from different test cases , Even different source files .
Invocation time ,RUN_ALL_TESTS() macro :
Save all googletest Flag status
Create a test fixture object for the first test .
By initializing it SetUp().
Run the test on the fixture object .
By cleaning the fixture TearDown().
Delete fixture .
Restore all googletest Flag status
Repeat the above steps for the next test , Until all tests have been run .
If a fatal failure occurs , Next steps will be skipped .
Important note : You cannot ignore the return value RUN_ALL_TESTS(), Otherwise, you will receive a compiler error . The basic principle of this design is that the automated test service determines whether the test has passed according to its exit code , Not according to its stdout / stderr Output ; So your main() Function must return value RUN_ALL_TESTS().
Besides , You should RUN_ALL_TESTS() Call only once . Calling it multiple times will be associated with some advanced googletest function ( For example, thread safe death test ) Conflict , So not supported .
Actually Gtest comparison Gmock The use of is much simpler , The main reasonable use of the above assertions can write an automated test process for their own programs ;
边栏推荐
- Station B, Master Liu Er - back propagation
- C language learning notes (mind map)
- H3C firewall rbm+vrrp networking configuration
- [C language syntax] the difference between typedef struct and struct
- Sequoiadb Lake warehouse integrated distributed database, June 2022 issue
- Installation de la Bibliothèque de processus PDK - csmc
- Yygh-11-timing statistics
- continue和break的区别与用法
- 局域网同一个网段通信过程
- Auto.js学习笔记17:基础监听事件和UI简单的点击事件操作
猜你喜欢

数字经济破浪而来 ,LTD是权益独立的Web3.0网站?

What is independent IP and how about independent IP host?

HCIA review
Redis message queue

Yunxiaoduo software internal test distribution test platform description document
How Huawei routers configure static routes

Hongliao Technology: how to quickly improve Tiktok store

HCIA复习
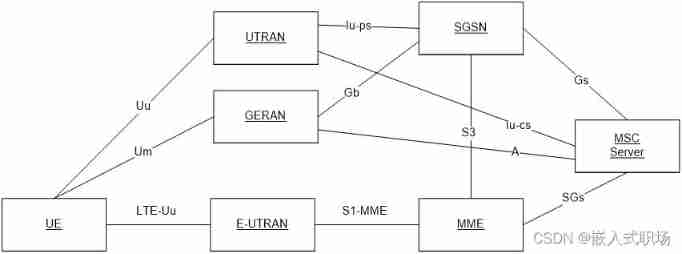
LTE CSFB process
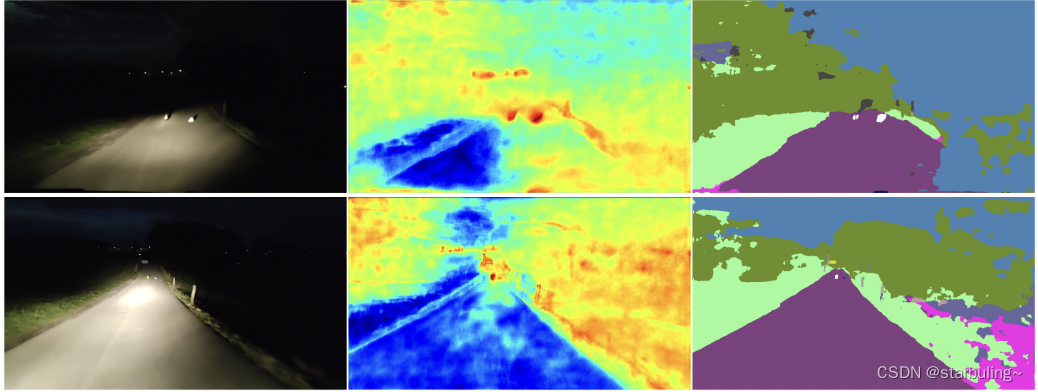
【论文阅读】NFlowJS:基于鲁棒学习的合成负数据密集异常检测
随机推荐
Clock in during winter vacation
【无标题】
如何在业务代码中使用 ThinkPHP5.1 封装的容器内反射方法
Winter 2021 pat class B problem solution (C language)
网站进行服务器迁移前应做好哪些准备?
[paper reading] nflowjs: synthetic negative data intensive anomaly detection based on robust learning
Redis消息队列
High quality coding tool clion
Migrate Infones to stm32
[Jiudu OJ 07] folding basket
Luogu [Beginner Level 4] array p1427 number game of small fish
What preparations should be made for website server migration?
B站刘二大人-线性回归 Pytorch
[SQL Server fast track] - authentication and establishment and management of user accounts
(column 22) typical column questions of C language: delete the specified letters in the string.
Implementation of linked list in address book management system
Hongliao Technology: Liu qiangdong's "heavy hand"
Auto.js学习笔记17:基础监听事件和UI简单的点击事件操作
[Tang Laoshi] C -- encapsulation: classes and objects
什么是独立IP,独立IP主机怎么样?