当前位置:网站首页>Gilbert Strang's course notes on linear algebra - Lesson 2
Gilbert Strang's course notes on linear algebra - Lesson 2
2022-06-30 08:16:00 【GiantOceanicMantaray】
The topic of the second lesson is : Matrix Elimination operation
example 1: Two ways of solving equations
Let's start with a question , Suppose we now have a system of equations :
![]()
The first solution is : take 1 Equation to y = 5 - 2x, Then substitute it into 2 Formula solution x Solution , And then you get y Solution . That is, through " use x To express y" In order to eliminate y
The second solution is : take 1 The left and right of the equation are multiplied by 3 obtain :6x + 3y = 15, then 2 Form and 1 Formula subtraction , obtain -y = -7, namely y = 7, Dai Huide x = -1. That is, through “ Operate on the equations ” Eliminate from a formula x
“ take 1 The left and right of the equation are multiplied by 3, And will 2 Form and 1 Formula subtraction ” The process of , In fact, that is Matrix elimination
When the unknowns become more , Method 1 Our thinking methods are often inefficient and disorderly , Using the appropriate elimination method will significantly improve the efficiency of the operation
example 2: The elimination process of ternary equations
Now let's use a system of three variable equations as an example to decompose the process of elimination :
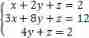
For the convenience of expression , It can be written as Ax = b In the form of :
Write it as Ax = b In the form of :

The first step of elimination , In fact, it is to eliminate the first unknown , Here it is. x
The operation steps are: : Put the equation 1 in x The coefficient of is based on the following equation x Transform and subtract the corresponding coefficients
For example, in equation 2 in ,x The coefficient before is 3, So we'll have the equation 1 multiply 3, And then by the equation 2 Subtractive form 1, obtain :

After calculation, we get :
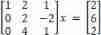
here , Except for the first element, the first column is 0, It means that we have finished the x The elimination of element !
And this 1 That's ok 1 The elements of the column "1" It can be called a ” Fulcrum ”(pivot): The fulcrum is that we need to be based on it , Operate on it and its row ( Multiply ) Go down ” cater to ” In other formulas, the coefficients corresponding to the unknowns to be eliminated in this round are used to get the objective of elimination .
And the fulcrum cannot be 0( Because it doesn't work 0 To eliminate other things )
It's easy to say , Each step of elimination is to find the relationship downward based on the fulcrum , Then, according to the relation, the multiplication and subtraction are performed to complete the elimination , Then take down a fulcrum and continue the downward operation , Until it can no longer be eliminated .
Take the example above ,1 And 3 The relationship between 3 times , In order to 3 Elimination requires progressive 2 - ( type 1 * 3) The operation of
Now turn to the next parameter y The elimination of element :
Let's get rid of the first line , take 2 That's ok 2 The elements of the column "2" It is called fulcrum , Use the second line to eliminate the third line , obtain :

After calculation, we get :

here , The values below the fulcrum of the second column are 0, It means that we have finished the y The elimination of element !
Yes x And y After the elimination , So the equation can be solved , At this point, we The elimination of the matrix is completed !
Solve the equation after elimination : from 5z = -10 Start to understand , Available z = -2, Replace the equation 2 Available y = 1, And then according to the equation 1 Available x = 2
The process of substituting into the solution is also called The process of retrogression (back substitution)
It needs to be mentioned that , In this case , Diagonal 1、2、5 All are fulcrum . Although the 5 There is no substantive operation , But if there is another line below ,5 Will become a fulcrum to eliminate the following Yuan , therefore 5 Belonging to a fulcrum in nature
Be careful , Elimination will also fail ( Causes the equation to be insoluble ):
In the process of elimination, if one or more lines appear 0, This will make m An unknown number m The first equation becomes m The number of unknowns is less than m An equation , Causes the equation to be insoluble
example 3: How to explain matrix multiplication by row column combination ?
We have seen the process of matrix elimination , So how to express the operation process of matrix elimination ?
Let's review one thing first , Suppose there's an equation :
![]()
Turn into Ax = b In the form of :
![]()
can Further written as :
![]()
To understand from the perspective of columns is :x The first column is related to y The second column can be combined to get the target vector
Now if I want to x Put it in A Left side , Then I will first perform an operation of left and right transposition of the equation ( Transpose related formulas :![]() ) Other operations of attached matrix :6.5 Matrix operation and its operation rules
) Other operations of attached matrix :6.5 Matrix operation and its operation rules
obtain ![]()
![]()
Explain in terms of vectors , We can say that the objective vector is composed of x individual ![]() And y individual
And y individual ![]() Composed of
Composed of
This is the same as before , It's just here in the behavioral dimension , Previously, columns were used as dimensions
What do you get from this example : When x stay A On the right , Our interpretation of the results is based on A Of Column according to x Are combined ; When x stay A On the left , Our interpretation of the results is based on A Of That's ok according to x Are combined
If it is x Is not a 1 x n or n x 1 The matrix of , Can matrix multiplication also be understood in the way of combination ?
Have a try :
![]() According to matrix multiplication, the result can be obtained
According to matrix multiplication, the result can be obtained ![]()
Suppose we treat each row on the left as a set of parameters ( That is to say, multiplication is xA,x On the left , Explain by line )
So for the first line ![]() , As 1 individual
, As 1 individual ![]() And 2 individual
And 2 individual ![]() The combination of , obtain
The combination of , obtain ![]()
For the second line ![]() , As 4 individual 2-1
, As 4 individual 2-1![]() And 0 individual
And 0 individual ![]() The combination of , obtain
The combination of , obtain ![]()
It works !
Conclusion : When x No 1 x n or n x 1 Matrix time , It can be explained that the matrix contains multiple sets of parameters ( For this example 2 Group parameters , Each line in a group ), Each set of parameters produces a result , The final target value is the combination of different parameters
example 4: Express the elimination process of matrix with matrix
In the first step of elimination , Let's look at the matrix A =  The operation result of is set to U1 =
The operation result of is set to U1 =
Hypothetical use E11 Matrix to represent the elimination operation ( The naming rule is E The subscript of is the position of the fulcrum ), Because the current composition is based on rows , Then put the E11 This matrix needs to be on the left ,E11A = U1
E11 The first line in comes from :1 individual A The first line in ,0 individual A The second line in ,0 individual A The third line in
E11 The second line in comes from :-3 individual A The first line in ,1 individual A The second line in ,0 individual A The third line in
E11 The third line in comes from :0 individual A The first line in ,0 individual A The second line in ,0 individual A The third line in
therefore E11 by

The same goes for the next step , You can get E22U1 = U2

in general ,A After two elimination, the final U2, Expressed as E22E11A = U2
notes : We can also put two E Merge , Put it on the right side of the equation and it turns into A = LU In the form of , Called matrix LU decompose , The details will not be expanded here
Add : Matrix permutation and matrix reversible operation
Matrix arrangement (Permute)
1. Line exchange
Operate on the line , It is necessary to multiply a transformation matrix to the left of the matrix to be transformed

Form the first line on the right ![]() need 0 individual
need 0 individual ![]() and 1 individual
and 1 individual ![]() , Form the second line on the right
, Form the second line on the right ![]() need 1 individual
need 1 individual ![]() and 0 individual
and 0 individual ![]() , therefore E The matrix of the
, therefore E The matrix of the ![]()
2. Column exchange
Operate on Columns , It is necessary to multiply a transformation matrix to the right of the matrix to be transformed

Forming the first column on the right requires 0 individual ![]() and 1 individual
and 1 individual ![]() , Forming the second column on the right requires 1 individual
, Forming the second column on the right requires 1 individual ![]() and 0 individual
and 0 individual ![]() , therefore E The matrix of the
, therefore E The matrix of the ![]()
Invertible operation of matrix (Inverses)
The inverse operation of a matrix is the process of restoring the matrix to the identity matrix through the inverse matrix , Expressed as :
AB = E
so to speak B yes A The inverse matrix , It can also be said that A yes B The inverse matrix ( It depends on whether you want to use rows or columns to explain , That is, which one is regarded as x)
The solution of inverse matrix can also be understood by row column combination , It is much more convenient than hard calculation
Gilbert Strang The teaching video of is ( Need scientific Internet ):https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QVKj3LADCnA&list=PL49CF3715CB9EF31D&index=2
边栏推荐
- Wechat applet reports errors using vant web app
- Redis设计与实现(一)| 数据结构 & 对象
- Experiment 2 LED button PWM 2021/11/15
- C preliminary chapter learning route
- Transformer architecture understanding
- mysql无法连接内网的数据库
- F12 packet capture is used for the whole process analysis of postman interface test
- 【NVMe2.0b 14-4】Directive Send/Receive command
- [flower carving experience] 12 build the Arduino development environment of esp32c3
- Emoji icons supported by markdown
猜你喜欢

Using typera+picgo to realize automatic uploading of markdown document pictures

Cesium learning notes (VI) particle system

Oracle expansion table space installed in docker

An example of a single service in a cloud project driven by a domain

Cesium learning notes (V) custom geometry and appearance

Construction of energy conservation supervision system for campus buildings of ankery University

vulfocus入门靶机

Deep learning -- using word embedding and word embedding features

Deep learning - residual networks resnets
直击产业落地 | 飞桨重磅推出业界首个模型选型工具
随机推荐
Deep learning - goal orientation
What are the Amazon evaluation terms?
涂鸦Wi-Fi&BLE SoC开发幻彩灯带
CRM&PM如何帮助企业创造最优销售绩效
MIME type Encyclopedia
Unity 基础光照模型
1162 Postfix Expression
Halcon12+vs2013 C # configuration
How CRM & PM helps enterprises create optimal sales performance
Dlib library blink
亚马逊测评术语有哪些?
mysql无法连接内网的数据库
鲸探NFT数字臧品系统开发技术分享
Redis设计与实现(二)| 数据库(删除策略&过期淘汰策略)
ACM. Hj48 delete the node with the specified value from the one-way linked list ●●
Final review -php learning notes 2-php language foundation
Experiment 2 LED button PWM 2021/11/15
Introduction to opencv (I): image reading and display
一次cpu 跌底排查
Redis设计与实现(三)| 服务器与客户端的交互(事件IO模型)