当前位置:网站首页>AWS learning notes (III)
AWS learning notes (III)
2022-07-07 14:30:00 【51CTO】
Security group 、EBS、 Instance store 、AMI
Security team summary
In every one of them EC2 During instance creation , We will all be asked to designate one Security group (Security Group). This security group acts as the virtual firewall of the host , According to the agreement 、 port 、 Source IP Address to filter EC2 The incoming and outgoing flows of the instance .
In addition to using security groups , We can also keep the native firewall of the system (Linux Under the iptable and Windows The firewall of ).
Security group is Stateful
- If a certain flow is released by the rules of the incoming direction , No matter what its outbound rules are , Its exit direction Response traffic Will be unconditionally released
- If the outbound request sent from the host , Regardless of inbound rules , The requested Response traffic Will be unconditionally released
- We cannot use security groups to prohibit certain IP Address access host , To achieve this effect, you need to use the network access control list (NACL)
- Only allowed entries can be set in the security group , Rejected entries cannot be set
- Source of security group IP You can choose all addresses IP Address (0.0.0.0/0), specific IP Address ( such as 8.8.8.8/24), Or in the same VPC Other security groups in
- As long as a traffic is matched by any rule of the security group , Then this traffic will be allowed to release
- Security groups are associated with EC2 Example of ENI( Network interface ) On
Example
- Security group Can track TCP/22 In and out flow of , Because the source IP Address defines a specific address (194.233.74.243/32), Not all IP Address (0.0.0.0/0)
- Security group No tracking TCP/80 Of traffic , Because its incoming and outgoing flows are for all IP Address (0.0.0.0/0)
- Security group Can track ICMP Traffic , Because no matter what the rules are , Security groups track ICMP Traffic
| Inbound rules | ||
|---|---|---|
| Protocol type | Port number | Source IP |
| TCP | 22 (SSH) | 194.233.74.243/32 |
| TCP | 80 (HTTP) | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| ICMP | All | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Outbound rules | ||
| Protocol type | Port number | Source IP |
| All | All | 0.0.0.0/0 |
Security group (Security Group) And network access control list (Network Access Control List) Have played a similar firewall function .
EBS
EBS Characteristics
- Amazon EBS Volume provides High availability 、 reliable 、 Persistent block storage ,EBS It can be attached to a running EC2 For instance
- If our EC2 The instance needs to use a database or file system , Then it is recommended to use EBS As the preferred storage device
- EBS The survival of the volume can be separated EC2 The survival status of the instance . That is, when terminating an instance , We can choose to keep the instance bound EBS volume
- EBS The volume can be attached to ** Same zone (AZ)** On any instance within
- EBS Volumes can be encrypted , If it is encrypted, all existing data stored in it , Data transmitted , And the created image will be encrypted
- EBS Volumes can be snapshot (Snapshot) To carry out ( The incremental ) Backup , This snapshot will be saved in S3 (Simple Storage System) On
- We can use any snapshot to create a snapshot based EBS volume , And keep this EBS Volumes are applied to The area On any instance of
- EBS The availability zone has been fixed when the volume is created , also Can only be used for instances of this zone . If you need to use this in other zones EBS, Then you can create snapshots , And use this snapshot to create a new one in other zones EBS volume
- Snapshots can also be copied to other AWS Area
Different types of EBS volume
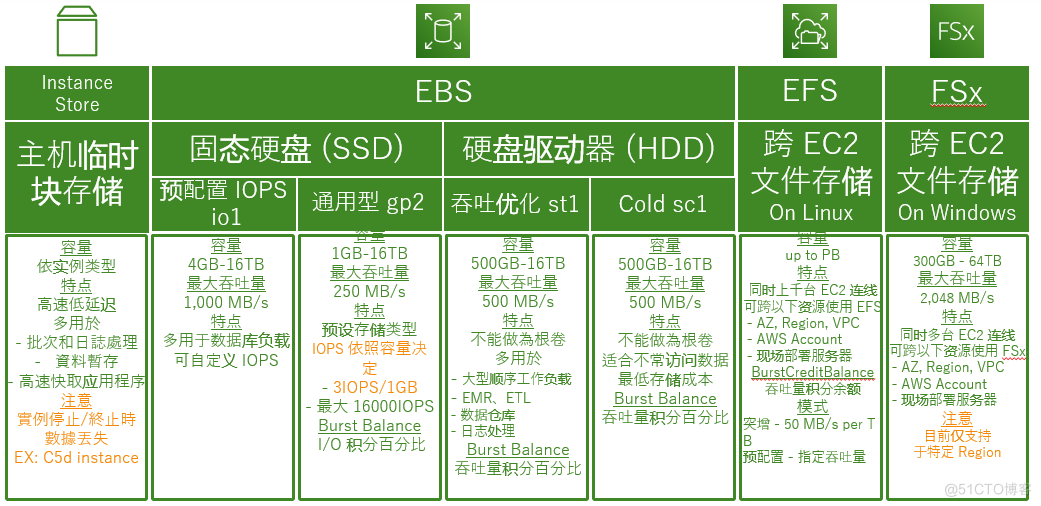
Instance store
- Instances are stored as EC2 Examples provide For a short time Block storage devices
- Instance store (Instance Store Volumes) Also called transient storage (Ephemeral Storage)
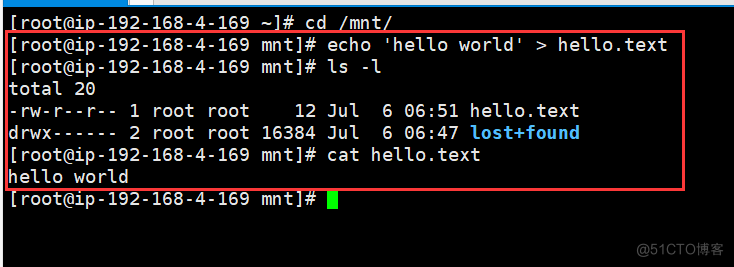
- The instance store is AWS The storage attached to the host ( It can be understood that instance storage is a disk installed on a real physical machine , Here's the picture ; and EBS It is another special storage device )
- Instance storage is more suitable for storing transient 、 Fast changing data , For example, cache 、 Crawler data and other transient data
- The size of the instance store depends on the type of instance
- The survival of the instance store is related to the state of the instance
- Instance restart , The data stored by the instance will not be affected
- Once the instance terminates , Instance storage will disappear forever
- The instance stored by the instance cannot enter the stop state (Stop), Can only restart (Reboot) Or terminate (Terminate).
- in addition **, It should be noted that , Not all instance types support instance storage .** When creating an instance , We can do it in AWS Select the image that supports instance storage in the market , Then in the next step, we can only select some specific instance type sizes ; And for EBS Come on , There are not so many restrictions , We can choose any instance type and size .
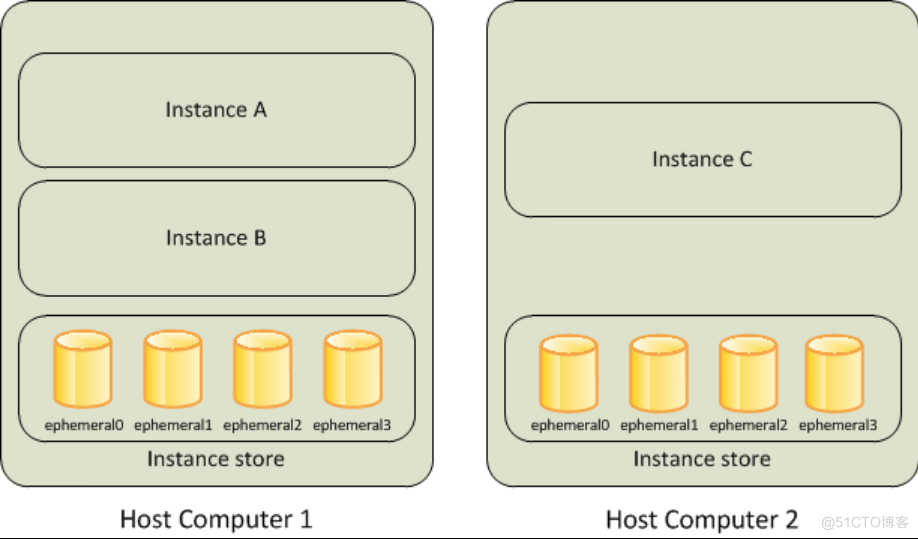
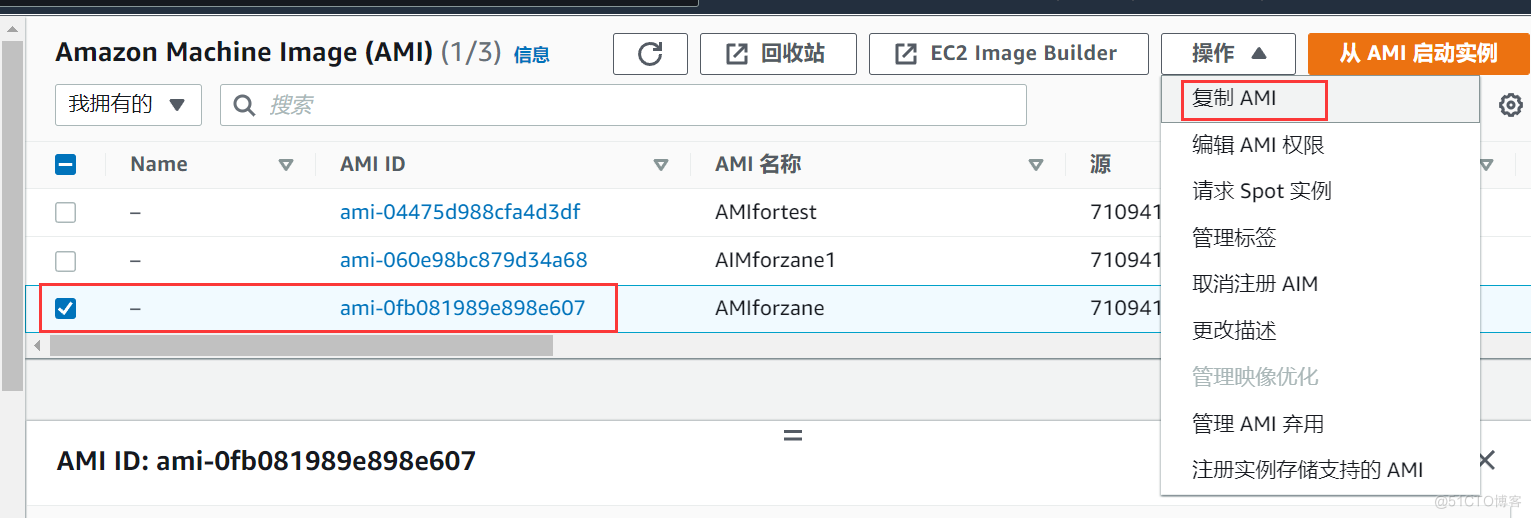
AMI System image and snapshot
Amazon Machine Image (AMI) It's Amazon AWS System image provided , This AMI It contains the following information :
- Operating system by instance 、 Template composed of application and application related configuration
- A specified information that needs to be attached to the volume of the instance when the instance is started ( For example, it defines the use 8 GB Of General Purpose SSD volume )
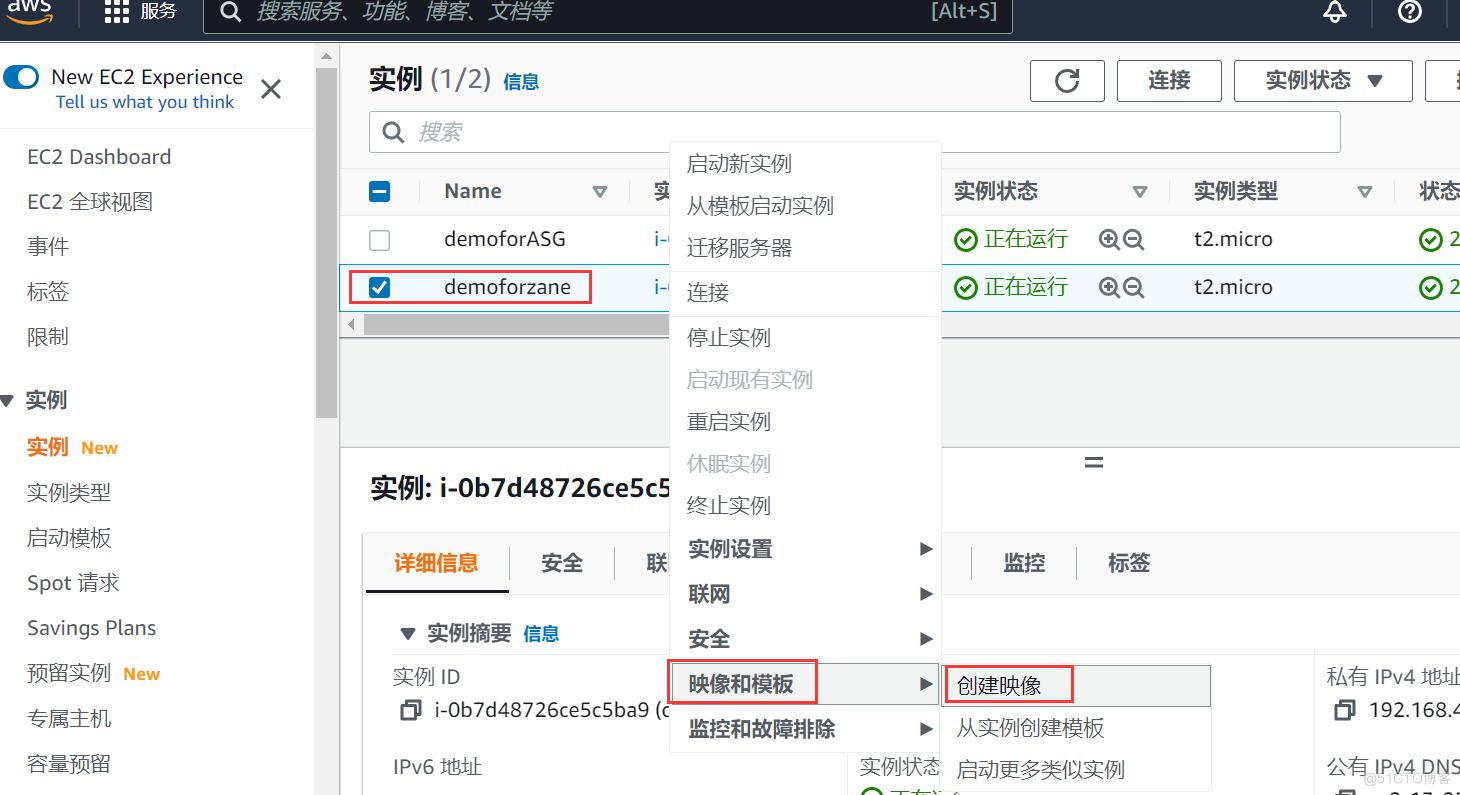
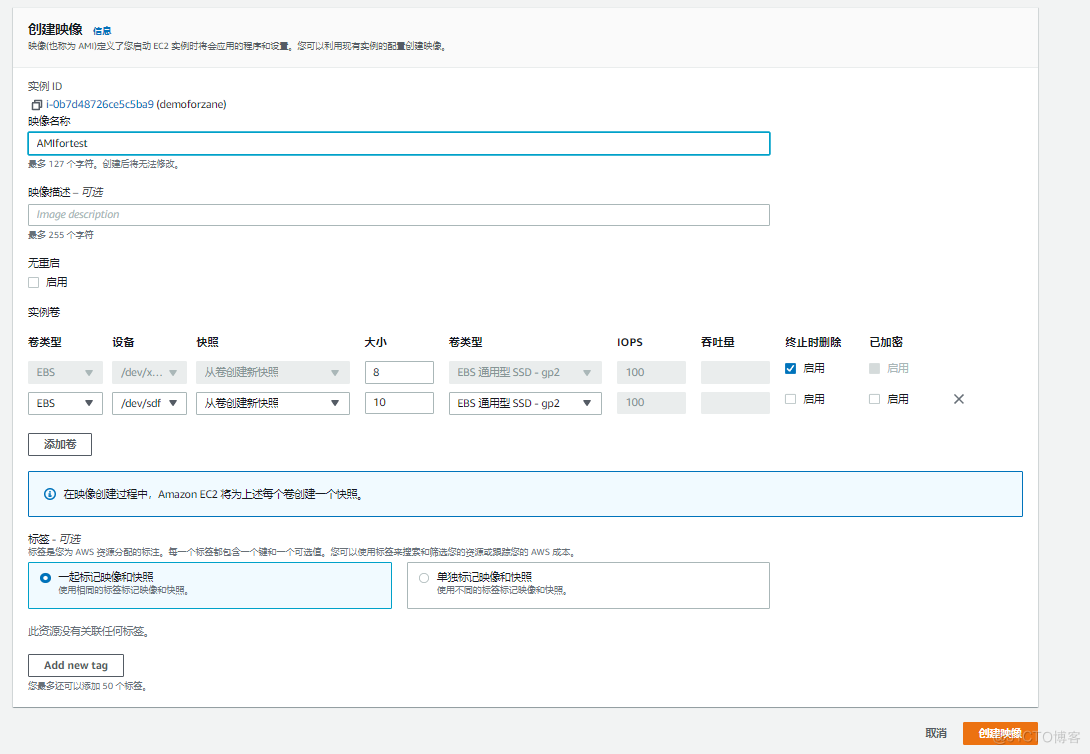
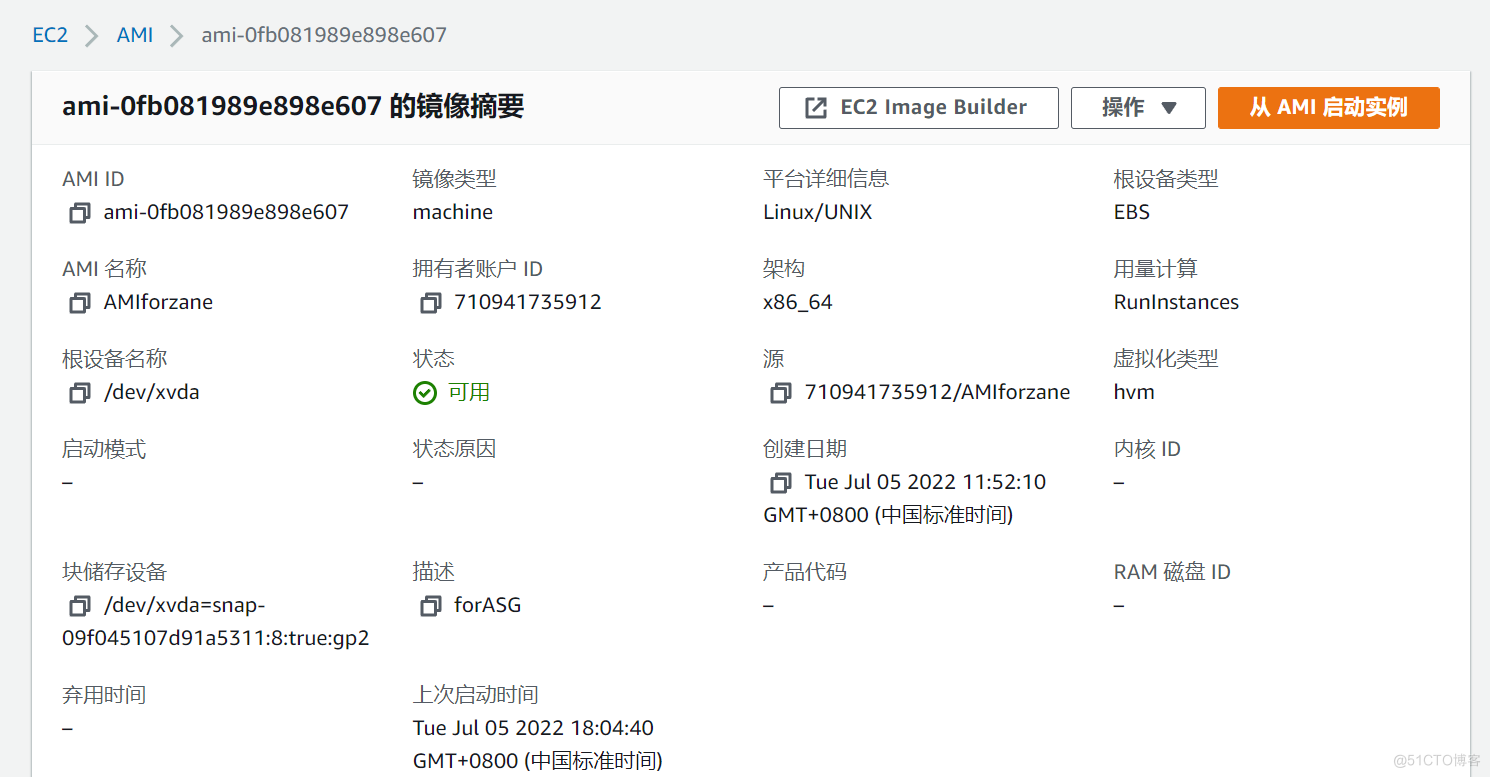
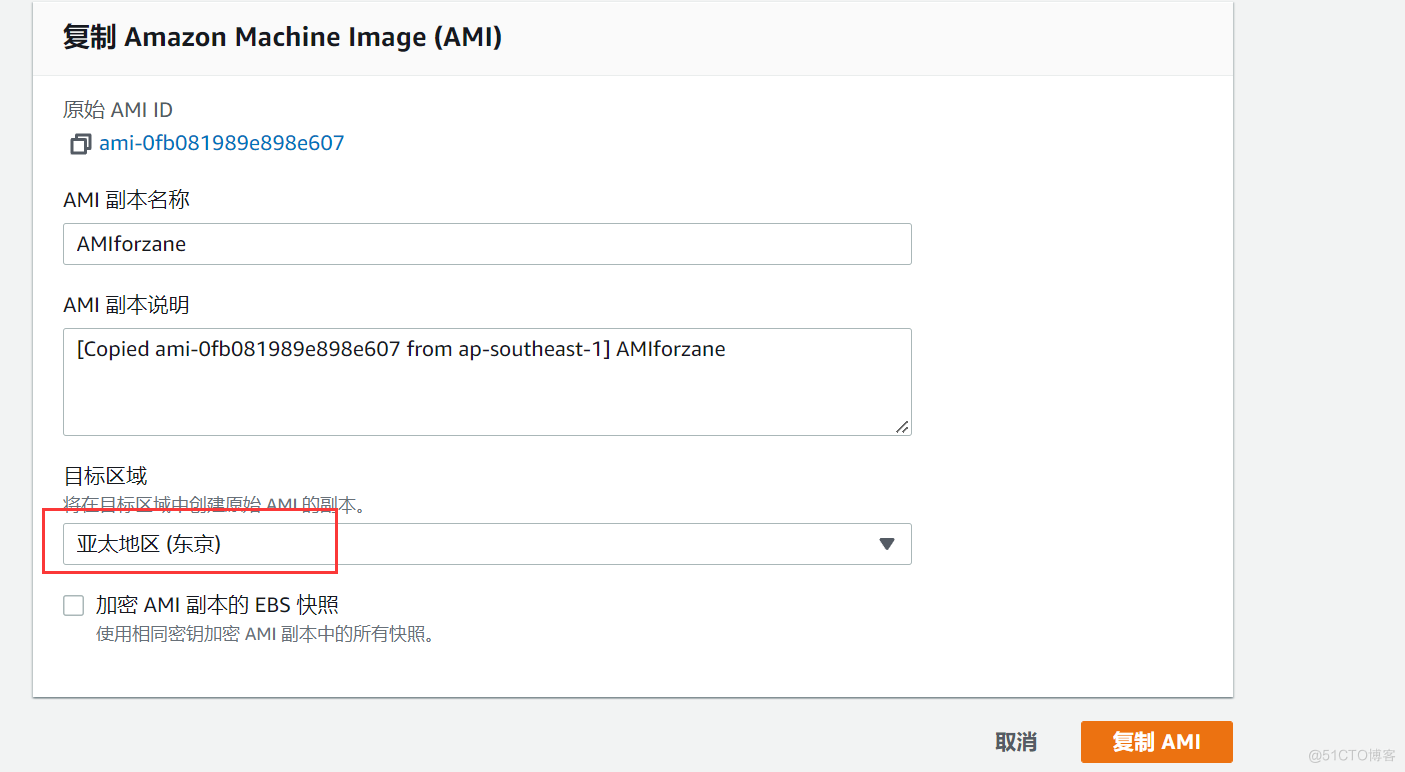
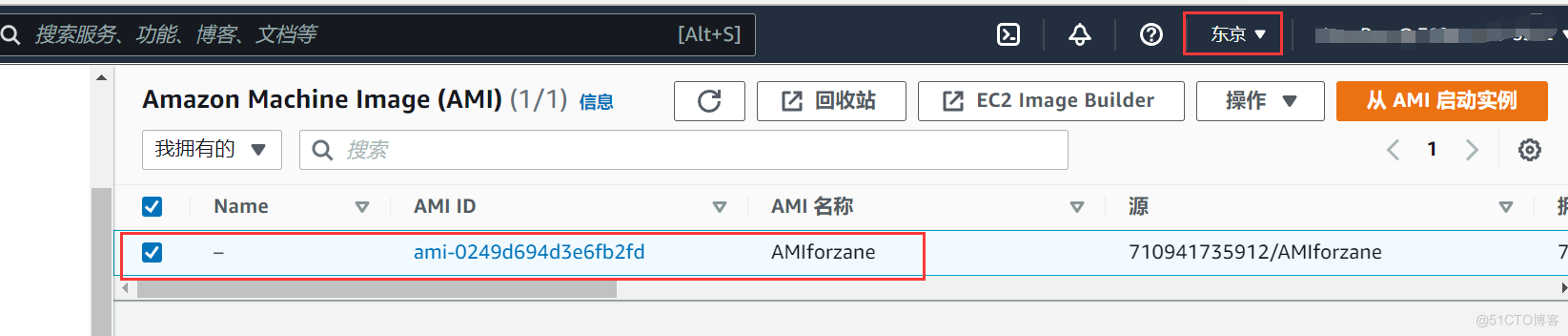
The picture below shows AMI Life cycle of , We can create and register one AMI, And you can use this AMI To create a EC2 example . At the same time, we can also put this AMI Copy to the same AWS Area or different AWS Area . We can also cancel this AMI Mirror image .
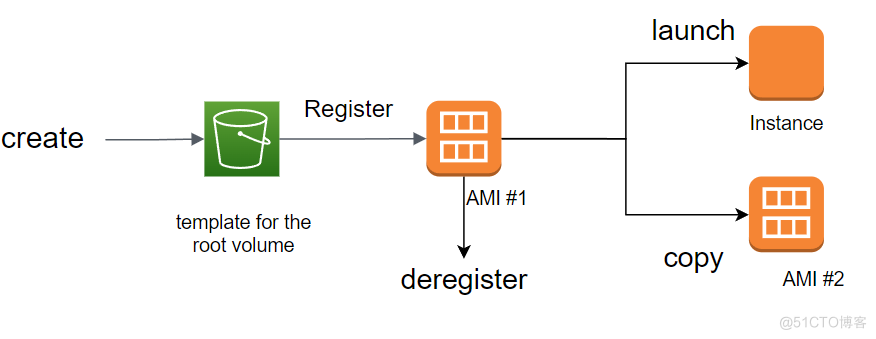
EBS Image made of snapshot
We can create a about EBS The snapshot of will Amazon EBS Back up the data on the volume , Then create a new one based on this snapshot EBS volume . Snapshots also have the following features :
- The backup snapshot will be saved in ** Amazon S3 (Simple Storage System)** On
- EBS The snapshot belongs to Incremental backup , That is, the snapshot after the second time will only update the changed part of the data
- We can do it in EC2 The instance is running EBS Snapshot operations for , But will give EC2 The system of brings a certain delay (CPU, Memory utilization will increase )
- The best practice is to EC2 Instance stop , And then EBS from EC2 It's up and down , Perform snapshot operation
- We can base it on EBS The snapshot is The same AWS Area Create a new EBS volume , This volume can be any EBS type , Any supported size
- We can also copy snapshots to other AWS Area
- We can share snapshots with others AWS user
- Encrypted EBS Volume after snapshot creation , The snapshot will also be automatically encrypted
- Created by encrypting snapshots EBS It is also automatically encrypted
- When copying an unencrypted snapshot , We can encrypt it during replication
AMI and EBS Usage scenarios of snapshots
There are several common scenarios that we need to use AMI and EBS Snapshot function .
If we want to put one EC2 Example from a AWS The region moves to another AWS Area , We need to :
- Create based on this EC2 Example of AMI
- Put this AMI replicate , Copy to another AWS Area
- Through this AMI Innovate to create a EC2 example
- Acting as a data disk EBS It also needs to be done EBS snapshot
- Put this EBS Snapshot for replication , Copy to another AWS Area
- Through this EBS Snapshot creation EBS volume , And attached to EC2 In fact
If we want to copy one EBS Roll to this AWS Different zones of the area , We can :
- Create a EBS snapshot
- adopt EBS Snapshot creates a new EBS volume , And define the size 、 Volume type 、 Whether to encrypt and other attributes
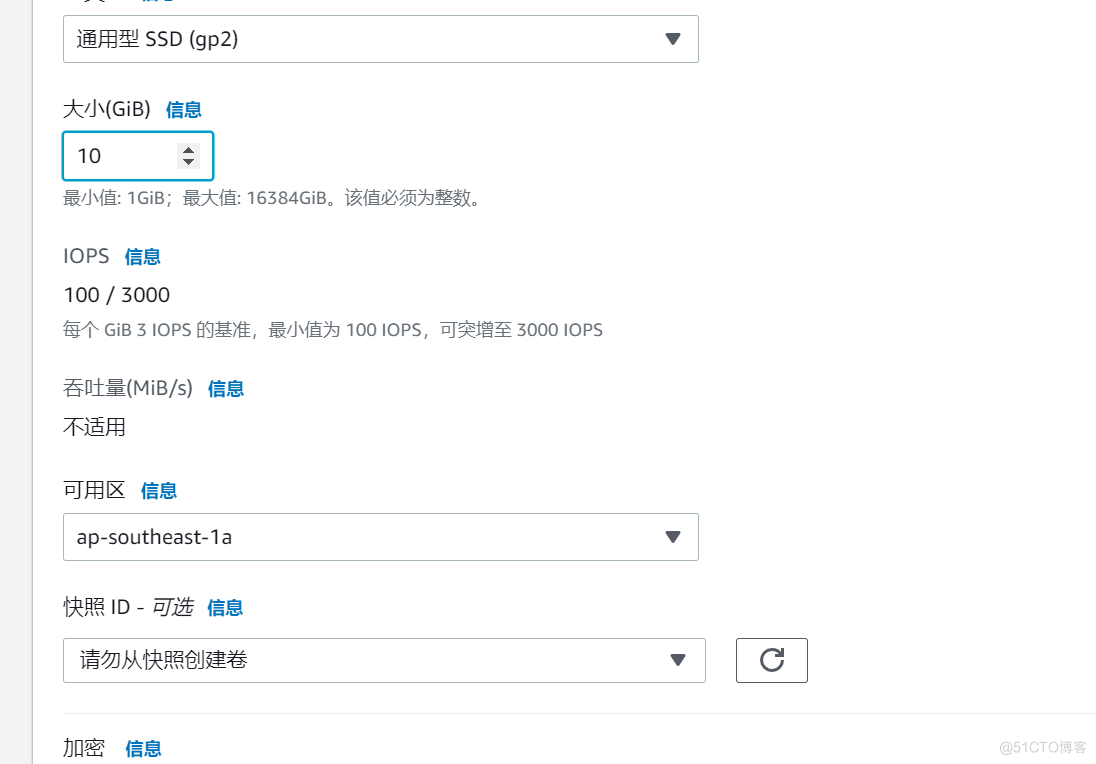
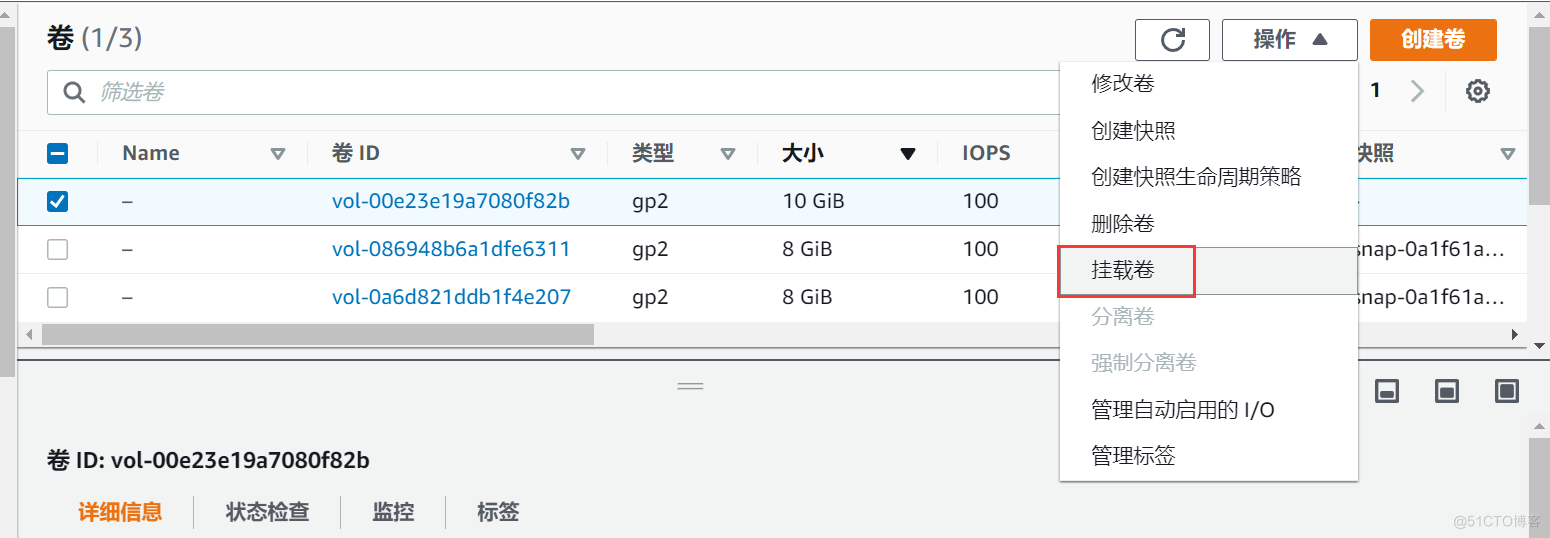
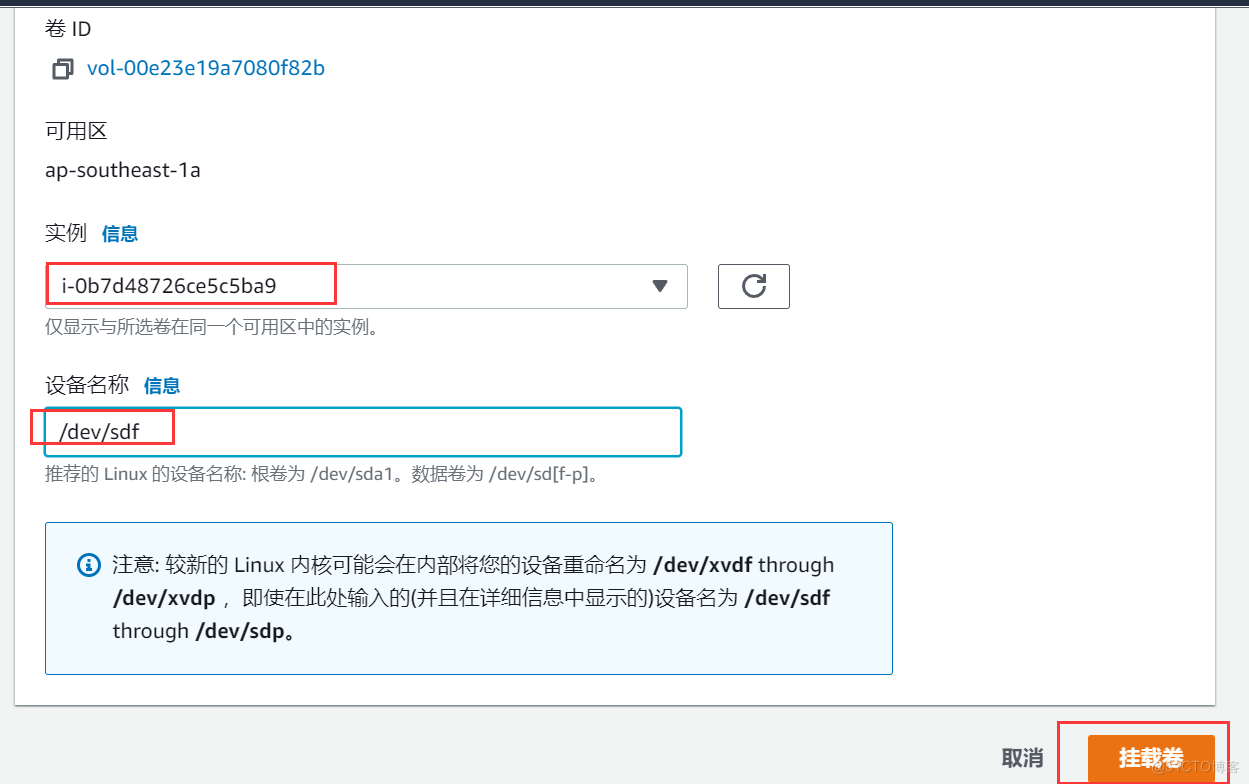
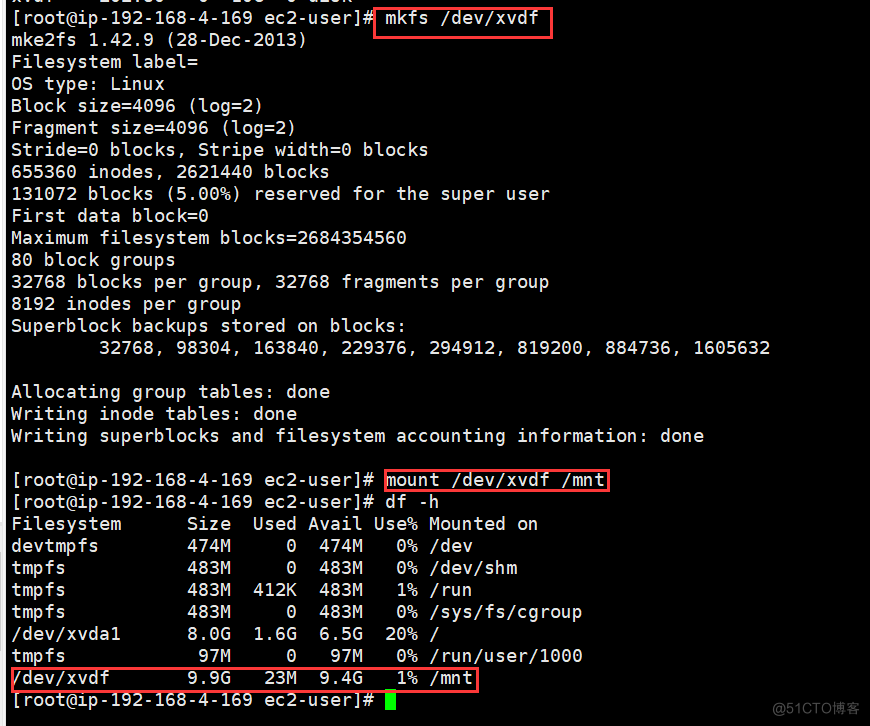
EBS (Elastic Block Storage) Summary
- EBS Different types of , Need to understand different types of EBS Main usage scenarios
- Universal SSD – GP2 ( the height is 10,000 IOPS), Applicable to startup disk , Low latency applications, etc
- Preconfigured SSD – IO1 ( exceed 10,000 IOPS), Apply to IO Intensive database
- Throughput optimized HDD -ST1, Applicable to data warehouse , Log processing
- HDD Cold – SC1 – Suitable for less used cold data
- HDD, Magnetic
- Can't be EBS Mount to multiple EC2 For instance , One EBS Can only be attached to 1 individual EC2 For instance .
- If there is a need to share data disks , Please use EFS (Elastic File System)
- root EBS By default, a volume cannot be encrypted , But you can use third-party encryption tools ( for example BitLocker) Encrypt it
- Volumes other than the root disk can be encrypted
EBS snapshot (Snapshot) Summary
- EBS The snapshot of will be saved to S3(Simple Storage System) On
- We can have a EBS Create a snapshot of the volume , This snapshot will be saved to S3 On
- Snapshots are actually Incremental backup , Only data changed after the last snapshot will be added S3 On
- Therefore, the first snapshot takes a long time
- The time taken for snapshots after the second time is relatively short
- For encrypted EBS Create snapshots of volumes , The created snapshot will also be encrypted
- Recovered from an encrypted snapshot EBS The volume will also be encrypted
- We can share snapshots with other accounts or AWS market , But only this snapshot is not encrypted
- To be a root device EBS Create a snapshot of the volume , It is recommended to stop this instance and take a snapshot
Instance store (Instance Store)
- Instance storage is also called Transient storage (Ephemeral Storage)
- Instances stored by instances cannot be stopped ( Only restart or terminate ), If this instance fails , Then all the data above will be lost
- Use EBS Instances of can be stopped , After the stop EBS Data on will not be lost
- Restart the instance stored by the instance or restart the use EBS No instance of will cause data loss
Amazon system image (AMI)
- AMI It's regional , Only use AMI To create an instance ; But we can put AMI Copy from one area to another
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
2022年13个UX/UI/UE最佳创意灵感网站
GAN发明者Ian Goodfellow正式加入DeepMind,任Research Scientist

UML 状态图
Pert diagram (engineering network diagram)
Reverse non return to zero code, Manchester code and differential Manchester code of common digital signal coding
通过 iValueConverter 给datagrid 的背景颜色 动态赋值
多商戶商城系統功能拆解01講-產品架構
Introduction to sakt method
OAuth 2.0 + JWT 保护API安全
今日睡眠质量记录78分
随机推荐
潘多拉 IOT 开发板学习(HAL 库)—— 实验12 RTC实时时钟实验(学习笔记)
设备故障预测机床故障提前预警机械设备振动监测机床故障预警CNC震动无线监控设备异常提前预警
因员工将密码设为“123456”,AMD 被盗 450Gb 数据?
属性关键字OnDelete,Private,ReadOnly,Required
大厂做开源的五大痛点
IP address home location query
AWS学习笔记(三)
LeetCode每日一题(636. Exclusive Time of Functions)
CVPR2022 | 医学图像分析中基于频率注入的后门攻击
【服务器数据恢复】某品牌StorageWorks服务器raid数据恢复案例
Mmkv use and principle
最长上升子序列模型 AcWing 1014. 登山
MLGO:Google AI发布工业级编译器优化机器学习框架
ARM Cortex-A9,MCIMX6U7CVM08AD 处理器应用
杭电oj2054 A == B ? ???
JS get the current time, month, day, year, and the uniapp location applet opens the map to select the location
一个简单LEGv8处理器的Verilog实现【四】【单周期实现基础知识及模块设计讲解】
VSCode 配置使用 PyLint 语法检查器
Oracle non automatic submission solution
libSGM的horizontal_path_aggregation程序解读