当前位置:网站首页>Stroke prediction: Bayesian
Stroke prediction: Bayesian
2022-07-03 10:24:00 【Why】
- Job requirements :
Stroke prediction : According to the World Health Organization (WHO) The data of , Stroke is the second leading cause of death in the world , About of the total deaths 11%. This data set is used according to the input parameters ( Such as gender , Age , Various diseases and smoking conditions ) Predict whether the patient may have a stroke . Each row provides information about the patient . The data download website is :https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QobTa9eN0snb9u2lXxX_iQ
Use data sets 70% Training Bayesian models ,30% forecast . - Data understanding ( Field description ):
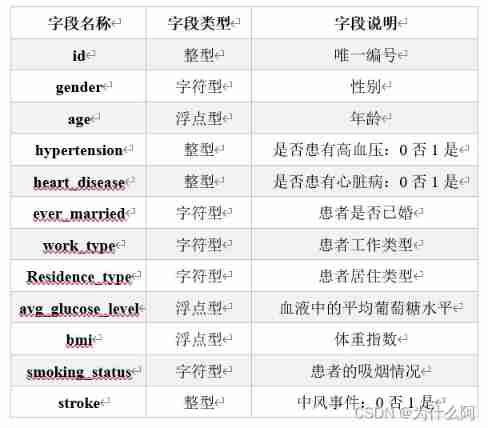
- Realize the idea
First, preprocess the data set , Remove a small number of gender outlier data entries , Use the mean to fill in the BMI (bmi) Missing values, etc . Randomly selected data sets 70% Train Bayesian model , be left over 30% Conduct model test , Compare and count the model test results with the original segmentation test data set , Calculate the prediction accuracy of the model .
Bayes' formula :

Maximum likelihood function :( Calculate the likelihood function value of stroke respectively and compare the size )
- Screenshot of operation result
Bayesian model test set test results ( The screenshot of the results of the three runs is as follows ):
The results of several runs show that the prediction accuracy of the model :94%-96%



- Complete code
# Import basic library
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import random
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# Do not limit the maximum number of columns displayed
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
# Do not limit the maximum number of lines displayed
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None)
# Data preprocessing
def dataProcessing(df):
# View the data as a whole
df.info()
# Statistical description of data characteristics
# print(df.describe())
# View missing values
print(df.isnull().sum())
# Delete duplicate values
df = df.drop_duplicates()
# print(df.shape)
# Exception handling
# View the number of gender outliers
print(df.gender.value_counts())
# There is only one other data for gender , Consider deleting
df = df.drop(df[df["gender"]=="Other"].index)
print(df.gender.value_counts())
# Fill in missing values bmi
df["bmi"].fillna(df["bmi"].mean(),inplace=True)
df.index = range(df.shape[0])
df.info()
return df
# Randomly assign proportionally split data sets
def randSplit(df,rate):
# Get the index of the data entry
extract=list(df.index)
# Randomly disorder the index of data
random.shuffle(extract)
df.index=extract
# Total number of data entries
n=df.shape[0]
# Calculate the number of segmented data entries in proportion
m=int(n * rate)
# 0-m As the training set
train=df.loc[range(m),:]
# m-n For test set
test=df.loc[range(m,n),:]
# Renumber the training set and test set data
df.index=range(df.shape[0])
test.index=range(test.shape[0])
# print(train)
return train,test
# Get the probability model , Input test set
def trainPbmodel_X(feats):
# Get the number of rows in the dataset ( Number of entries ) And number of columns ( dimension )
N,D=np.shape(feats)
model={
}
# Perform probability statistics on the attributes of each dimension
for i in range(D):
# Convert data to list format
data=feats[:,i].tolist()
# Creates an unordered set of non-repeating elements , Take out the non repeated value
keys=set(data)
# Get data length
N=len(data)
model[i]={
}
# Calculate the probability corresponding to each category in each dimension
for key in keys:
# Computation first i The probability corresponding to a certain value of dimension
model[i][key]=float(data.count(key)/N)
return model
# datas: list Format , Each element represents 1 Feature sequences
# labs: list Format , Each element represents a label
def trainPbmodel(datas,labs):
# Defining models
model={
}
# The last column , Get the category of classification (0 or 1)
keys=set(labs)
for key in keys:
# get P(Y)
Pbmodel_Y=labs.count(key)/len(labs)
# The collection category is 0,1( No stroke , Stroke ) Data tag number of
index=np.where(np.array(labs)==key)[0].tolist()
# According to the tag number, the category is 0,1 The data of
feats=np.array(datas)[index]
# get P(X|Y)
Pbmodel_X=trainPbmodel_X(feats)
# Dictionaries , Model preservation
model[key]={
}
model[key]["PY"]=Pbmodel_Y
model[key]["PX"]=Pbmodel_X
return model
# test
# feat: list Format , An input feature
# model: Probability model of training
# keys: Look at the types of labels
def getPbfromModel(feat,model,keys):
results={
}
# Replace with a minimum 0, The likelihood function is used to calculate without overflow
eps=0.00001
for key in keys:
# from model In order to get P(Y)
# Use get function , When cannot find the current key When the value of , return eps
PY=model.get(key,eps).get("PY")
# from model Get... Respectively P(X|Y)
model_X=model.get(key,eps).get("PX")
# Define the probability that the array stores the characteristics of each dimension
list_px=[]
for i in range(len(feat)):
# Get the probability of each dimension feature
pb=model_X.get(i,eps).get(feat[i],eps)
# Deposit in list_px Array
list_px.append(pb)
# The maximum likelihood function is used to obtain 0,1 Possible values of categories
result= np.log(PY) + np.sum(np.log(list_px))
# Will get the result corresponding 0,1 Category storage
results[key]=result
return results
if __name__== '__main__':
# Storage 0,1 Likelihood values of two categories , Key value pair
result=[]
# Used to store predictions 0,1 Category value
judge=[]
# Used to count the correct entries predicted in the test set
count=0
# Reading data sets
df = pd.read_csv("C:\\Users\\31998\\Downloads\\ Stroke prediction data set .csv")
# Data preprocessing
df=dataProcessing(df)
# Delete the first column of useless data in the dataset id
charges = df.drop(["id"], axis=1)
# Get the attribute labels of data
labels = list(charges.columns.values)
# according to 7:3 Proportional segmentation dataset
train,test=randSplit(df,0.7)
# Convert test set data to list format
dataSet = train.values.tolist()
# Data area for training
datas= [i[:-1] for i in dataSet]
# stroke Category data
labs=[i[-1] for i in dataSet]
# print(datas)
# print(labs)
# Use data and tags to train the model
model = trainPbmodel(datas,labs)
# print(model)
# Get the stroke of the test set , No stroke category value , Compare with the following calculation results
x=test[['stroke']]
# To array format
x=np.array(x)
# Delete test data stroke A column of
datadata=test.drop(["stroke"], axis=1)
# Standardize the collective test data
corrDf = datadata.apply(lambda x: pd.factorize(x)[0])
# Convert to list format
feat=corrDf.values.tolist()
keys=set(labs)
for i in range(len(feat)):
# Substitute into the test set one by one to calculate stroke In the column 0,1 Likelihood values of two categories , And store it in the array
result.append(getPbfromModel(feat[i],model,keys))
# print(result[i])
for key,value in result[i].items():
# Compare 0,1 The likelihood values of the two categories , The bigger the value is. , The higher the probability
if(value==max(result[i].values())):
# print(key)
# The result will be 0 or 1 Save to array
judge.append(key)
# Compare the predicted result array with the actual result array of the test set , If equal , The prediction is correct , Count +1
if (key == x[i][0]):
count=count+1
print(judge)
print(count)
# Print prediction accuracy
print(count/len(feat))
边栏推荐
- Leetcode-404:左叶子之和
- 20220606 Mathematics: fraction to decimal
- [LZY learning notes dive into deep learning] 3.1-3.3 principle and implementation of linear regression
- LeetCode - 1670 設計前中後隊列(設計 - 兩個雙端隊列)
- 2.2 DP: Value Iteration & Gambler‘s Problem
- Mise en œuvre d'OpenCV + dlib pour changer le visage de Mona Lisa
- Deep learning by Pytorch
- Neural Network Fundamentals (1)
- 20220609 other: most elements
- LeetCode - 933 最近的请求次数
猜你喜欢

Leetcode-106: construct a binary tree according to the sequence of middle and later traversal

CV learning notes - scale invariant feature transformation (SIFT)
Advantageous distinctive domain adaptation reading notes (detailed)
Opencv notes 17 template matching

Secure in mysql8.0 under Windows_ file_ Priv is null solution
Vgg16 migration learning source code
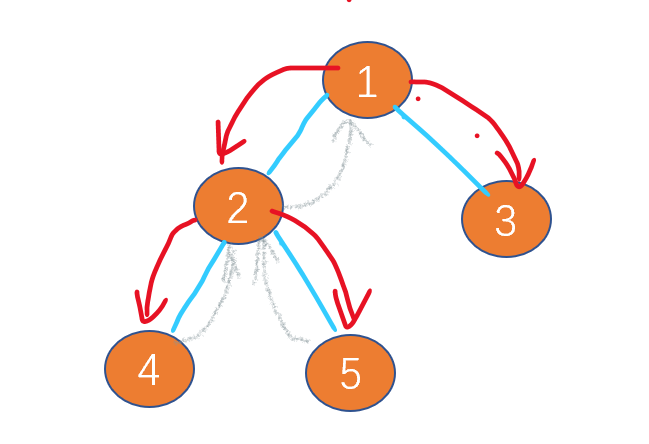
Leetcode-112: path sum

openCV+dlib實現給蒙娜麗莎換臉
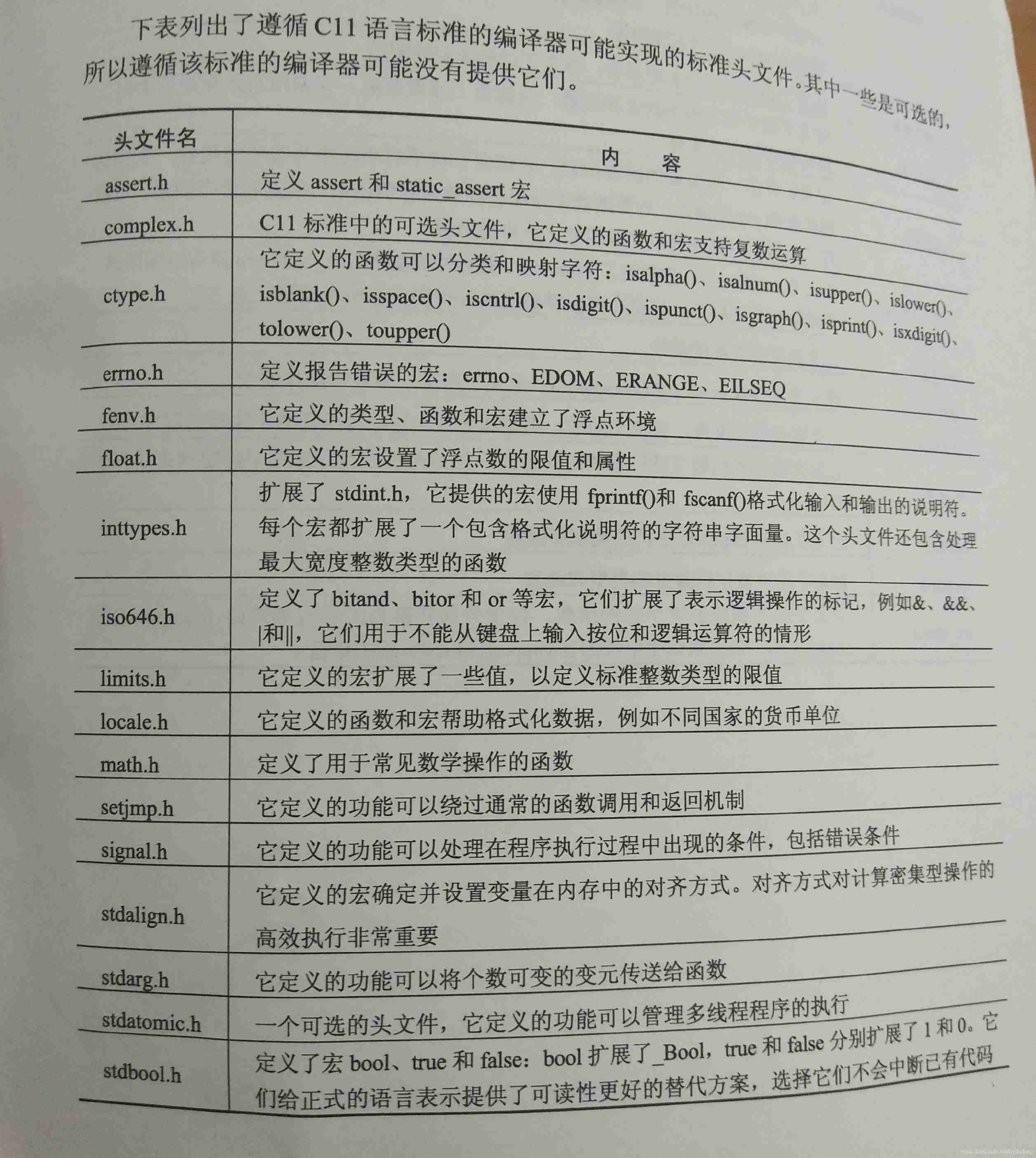
Standard library header file
Leetcode - 1670 design front, middle and rear queues (Design - two double ended queues)
随机推荐
【C 题集】of Ⅵ
2021-11-11 standard thread library
[LZY learning notes dive into deep learning] 3.5 image classification dataset fashion MNIST
What useful materials have I learned from when installing QT
Tensorflow built-in evaluation
LeetCode - 895 最大频率栈(设计- 哈希表+优先队列 哈希表 + 栈) *
Dictionary tree prefix tree trie
LeetCode - 715. Range module (TreeSet)*****
Pytorch ADDA code learning notes
Octave instructions
Opencv image rotation
20220603 Mathematics: pow (x, n)
Leetcode - 705 design hash set (Design)
One click generate traffic password (exaggerated advertisement title)
Neural Network Fundamentals (1)
20220608其他:逆波兰表达式求值
Leetcode 300 longest ascending subsequence
2.2 DP: Value Iteration & Gambler‘s Problem
Leetcode-513:找树的左下角值
OpenCV Error: Assertion failed (size.width>0 && size.height>0) in imshow