当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode-112: path sum
Leetcode-112: path sum
2022-07-03 10:10:00 【ITSOK_ U】
112. The sum of the paths
Give you the root node of the binary tree root And an integer representing the sum of goals targetSum . Determine if there is Root node to leaf node The path of , The sum of the values of all nodes in this path is equal to the target and targetSum .
If there is , return true ; otherwise , return false . A leaf node is a node that has no children .
This question and question 257. All paths of binary tree Very similar , The code is similar .
Depth first (O(N),O(N))
If you use depth first in this problem, you can use the previous sequence recursion simulation , But what we need to deal with in recursion is the calculation of the path sum of each node to ensure that it does not affect the path and calculation of other nodes , Therefore, if recursion is used, those redundant leaf nodes will need to be handled in the backtracking process .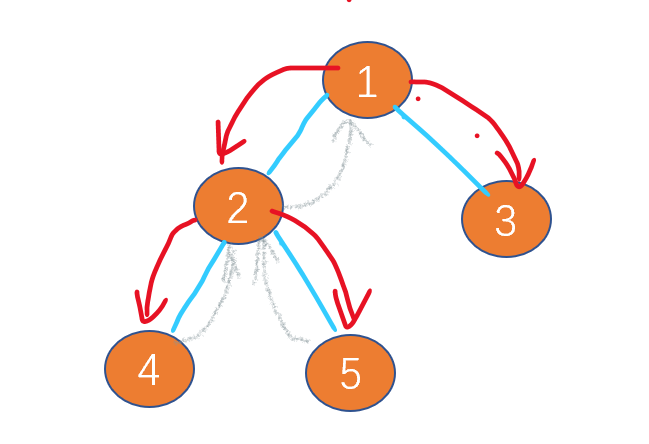
As in the above path and calculation , The path sum of the first leaf node is calculated as 1+2+4, If the requirements are not met at this time , You need to go back , So update the existing results to 1+2, Using recursion can solve this problem perfectly , As in the following code return You can achieve effective backtracking .
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr){
if(num == target) falg = true;
// Otherwise continue to recurse
return;
}
The specific problem-solving code is as follows :
class Solution {
public:
void findPath(TreeNode* root,int num,int target,bool &falg){
// The node update path and
num += root->val;
// To the leaf node
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr){
// Satisfy the solution conditions , Result flag is true
if(num == target){
falg = true;
}
// Otherwise continue to recurse
return;
}
// Left subtree recursion
if(root->left) findPath(root->left,num,target,falg);
// Right subtree recursion
if(root->right) findPath(root->right,num,target,falg);
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
// The root node is empty , return false
if(root == nullptr) return false;
// falg Used to mark the solution result
bool falg = false;
findPath(root,0,targetSum,falg);
return falg;
}
};
breadth-first (O(N),O(N))
Using breadth first is to simulate a sequence traversal . However, compared with ordinary printing path and other solutions , At this time, we need to maintain the existing paths and queues of each node . As shown in the figure below . Our path and queue are one-to-one corresponding to the tree node queue , in other words , The value of the path and queue at the same location as the tree node queue is the path and to the tree node .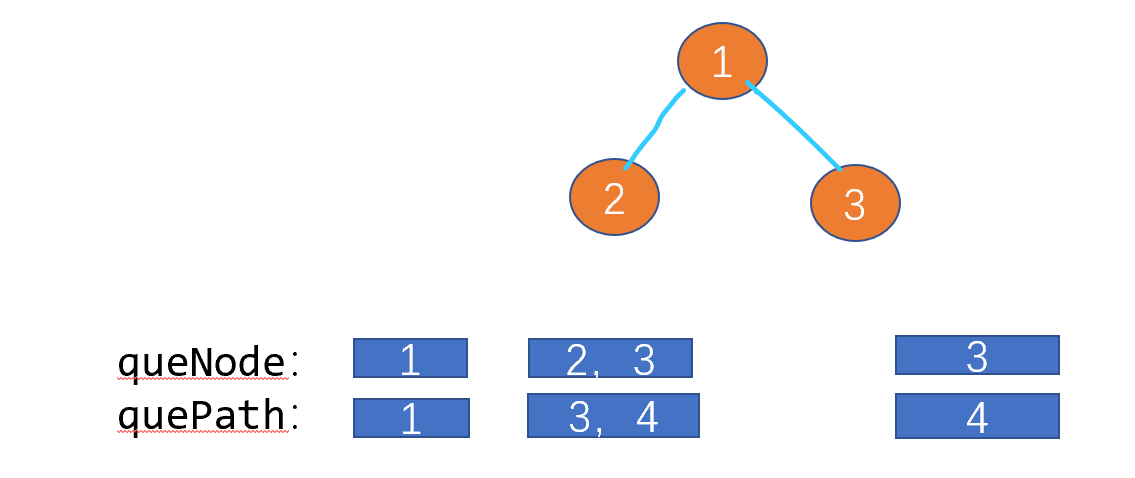
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
// The empty tree returns directly false
if(root == nullptr) return false;
// Initialize the tree node queue of breadth traversal
queue<TreeNode*> que;
queue<int> num;
que.push(root);
num.push(root->val);
// If the queue is not empty, the node has not finished processing
while(!que.empty()){
// Take out the tree node queue and the first element of the path and queue
TreeNode* node = que.front();
int res=num.front();
que.pop();
num.pop();
// If you reach the leaf node and the path and meet the requirements, you will directly jump out of the traversal , return true
if(node->left==nullptr && node->right==nullptr && res==targetSum)
return true;
if(node->left){
que.push(node->left);
// Next level nodes join the team , And the corresponding node path and storage
num.push(node->left->val + res);
}
if(node->right){
que.push(node->right);
// Next level nodes join the team , And the corresponding node path and storage
num.push(node->right->val + res);
}
}
// After the node is processed, the addition is still not found targetSum The path of , return false
return false;
}
};
边栏推荐
- 20220602数学:Excel表列序号
- The 4G module designed by the charging pile obtains NTP time through mqtt based on 4G network
- Markdown latex full quantifier and existential quantifier (for all, existential)
- 2.1 Dynamic programming and case study: Jack‘s car rental
- CV learning notes - image filter
- Basic knowledge of communication interface
- [combinatorics] combinatorial existence theorem (three combinatorial existence theorems | finite poset decomposition theorem | Ramsey theorem | existence theorem of different representative systems |
- Serial communication based on 51 single chip microcomputer
- LeetCode - 508. Sum of subtree elements with the most occurrences (traversal of binary tree)
- Deep learning by Pytorch
猜你喜欢

3.2 Off-Policy Monte Carlo Methods & case study: Blackjack of off-Policy Evaluation
Opencv Harris corner detection

Leetcode-112:路径总和

2.1 Dynamic programming and case study: Jack‘s car rental

Installation and removal of MySQL under Windows
CV learning notes - deep learning

CV learning notes ransca & image similarity comparison hash

Leetcode 300 最长上升子序列
Opencv notes 17 template matching

Leetcode - 933 number of recent requests
随机推荐
LeetCode - 900. RLE 迭代器
【C 题集】of Ⅵ
2. Elment UI date selector formatting problem
CV learning notes - deep learning
The underlying principle of vector
CV learning notes convolutional neural network
CV learning notes alexnet
使用密钥对的形式连接阿里云服务器
LeetCode - 933 最近的请求次数
[combinatorics] Introduction to Combinatorics (combinatorial idea 3: upper and lower bound approximation | upper and lower bound approximation example Remsey number)
Opencv Harris corner detection
Tensorflow2.0 save model
LeetCode - 705 设计哈希集合(设计)
Mise en œuvre d'OpenCV + dlib pour changer le visage de Mona Lisa
CV learning notes - clustering
Deep learning by Pytorch
Leetcode - 933 number of recent requests
4G module board level control interface designed by charging pile
Openeuler kernel technology sharing - Issue 1 - kdump basic principle, use and case introduction
Leetcode-106:根据中后序遍历序列构造二叉树