当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode-106:根据中后序遍历序列构造二叉树
Leetcode-106:根据中后序遍历序列构造二叉树
2022-07-03 09:22:00 【ITSOK_U】
1.题目描述
给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal
示例1: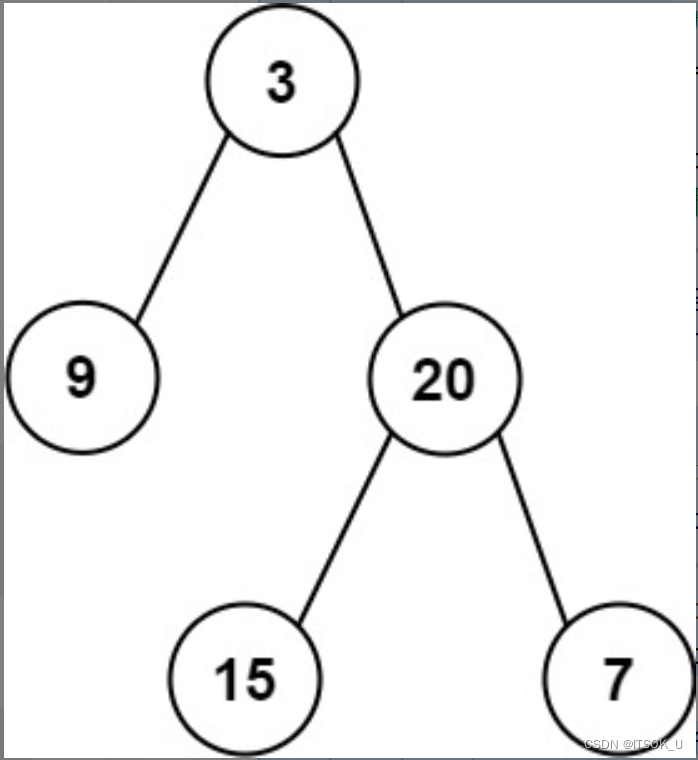
inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例2:
输入:inorder = [-1], postorder = [-1]
输出:[-1]
2.题目分析和解答
2.1 递归
2.1.1递归思路
这道题与前面105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树的解法基本一样,所以可以模拟上一题的递归实现来实现这道题的求解。这个过程对于下标变化的把握可以通过自己写一个序列来辅助分析,还是很容易理解的。
以下面的树的遍历结果为例,我们还是可以根据后序遍历的最后一个值确定根节点,然后再在中序遍历中根据这个根节点将中序序列划分为左右两部分,分别作为根节点的左子树和右子树的节点集群.根据这个思想我们就可以实现下面的递归过程。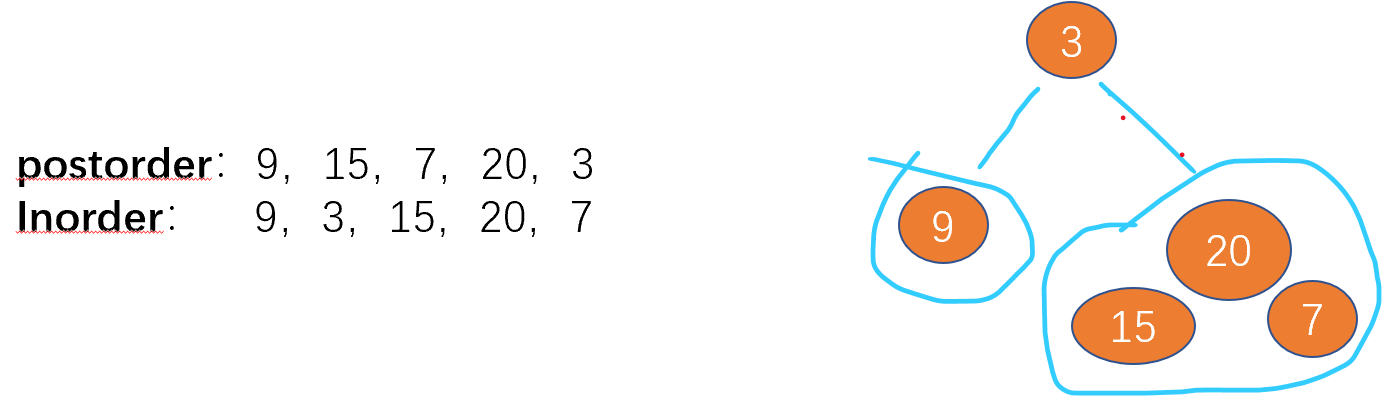
2.1.2递归代码(O(N),O(N))
class Solution {
// 前序遍历中树的节点值与下标值的map映射
unordered_map<int,int> index;
public:
TreeNode* build(vector<int>& inorder,vector<int>& postorder,int inLeft,int inRight,int postLeft,int postRight){
// 遍历列表为空返回空树
if(inLeft>inRight){
return nullptr;
}
// 记录后序遍历中的树的根节点以及中序遍历中的树的根节点
int postRoot = postRight;
int inorderRoot = index[postorder[postRoot]];
// 构造一颗只有根节点的树
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(postorder[postRoot]);
// 确定树的左子树的节点个数
int leftSize = inorderRoot - inLeft;
//构造左子树
root->left = build(inorder,postorder,inLeft,inorderRoot-1,postLeft,postLeft+leftSize-1);
//构造右子树
root->right = build(inorder,postorder,inorderRoot+1,inRight,postLeft+leftSize,postRoot-1);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
size_t size = postorder.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
index[inorder[i]] = i;
}
if(size == 0) return nullptr;
return build(inorder,postorder,0,size-1,0,size-1);
}
};
2.1.3递归代码2(O(N),O(N))
class Solution {
// 记录后序遍历中的根节点
int postIndex;
// 前序遍历中树的节点值与下标值的map映射
unordered_map<int,int> index;
public:
TreeNode* build(vector<int>& inorder,vector<int>& postorder,int inLeft,int inRight) {
// 遍历列表为空返回空树
if(inLeft>inRight) return nullptr;
// 记录当前根节点值
int rootVal = postorder[postIndex];
// 构建只有根节点的树
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
// 求出根节点在中序遍历中的下标值
int rootIndex = index[rootVal];
// 后序遍历根节点下标减一左移
postIndex--;
// 构建右子树,注意这里必须先构建右子树,
// 否则在构建左子树的时候的postIndex--会错误移动
// 由于遍历顺序的原因,后序中根节点左边最近的元素都处于右子树内
root->right = build(inorder,postorder,rootIndex+1,inRight);
// 构建左子树
root->left = build(inorder,postorder,inLeft,rootIndex-1);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
size_t size = postorder.size();
postIndex = size -1;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
index[inorder[i]] = i;
}
if(size == 0) return nullptr;
return build(inorder,postorder,0,size-1);
}
};
2.2迭代
迭代也是与前面105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树基本相同的,我们分析后序遍历中节点的关系。假设在后序遍历序列中有两个相邻节点u和v,那么他们的关系只有以下两种情况:
- u是v的右孩子
- u是v的某个祖先的左孩子
也就是说,只要u是v的孩子,那必然是右孩子,否则不可能为u的孩子。这是跟二叉树的后序遍历次序相关的,因为后序遍历的顺序是左孩子-右孩子-根,座椅对于相邻的节点关系只能是以上两种之一。
因此我们就可以根据这个来实现迭代的逻辑。
但是我们如何在求解过程中确定是两种情况中的哪一种呢,这就需要借助中序遍历了。对于中序遍历来说,其第一个节点值必然是当前树的最左边的节点值,最后一个节点值必然是当前树的最右边的节点值。我们继续来看下面的一个树
将其中序遍历的遍历序列从后往前移动,我们就会发现,每一个节点都是去除其后所有结点之后的树的最右边节点。我们知道如果一个节点是最右边节点,那么他就没有左孩子。知道了这一点我们就可以利用这个来判断新加入的节点是属于哪一种情况。
- 如果新加入的节点在当前中序遍历的最右边,那么其下一个节点必然不是一个右孩子
- 如果新加入的节点不在当前中序序列的最右边,那么下一个节点就还是一个右孩子。
所以我们可以通过维护一个栈来保存所有未添加左孩子的节点以便于后面添加右孩子,通过inorderIndex来标记当前中序序列所维护的树。具体代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
size_t size = postorder.size();
// 空树的情况
if(size == 0) return nullptr;
// 以size记录后序访问下标值
size--;
// 构造只有根节点的树
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(postorder[size]);
stack<TreeNode*> st;
// 根节点入栈
st.push(root);
// 中序访问下标
int inorderIndex = size;
// 处理除根节点之外的节点
while(size--){
// 取新访问的后序遍历节点(从后往前)
int postVal = postorder[size];
// 取栈顶结点
TreeNode* node = st.top();
// 新的节点是栈顶结点的右孩子
if(node->val != inorder[inorderIndex]){
node->right = new TreeNode(postVal);
st.push(node->right);
}else{
// 新的节点不是栈顶结点的孩子
// 那就是栈顶结点的某个祖先的左孩子
while(!st.empty() && st.top()->val == inorder[inorderIndex]){
node = st.top();
st.pop();
--inorderIndex;
}
node->left = new TreeNode(postVal);
st.push(node->left);
}
}
return root;
}
};
总结:递归求解二叉树相关还是比较容易理解的
边栏推荐
- Markdown latex full quantifier and existential quantifier (for all, existential)
- It is difficult to quantify the extent to which a single-chip computer can find a job
- LeetCode - 703 数据流中的第 K 大元素(设计 - 优先队列)
- 4G module IMEI of charging pile design
- Serial communication based on 51 single chip microcomputer
- Do you understand automatic packing and unpacking? What is the principle?
- 4G module board level control interface designed by charging pile
- My openwrt learning notes (V): choice of openwrt development hardware platform - mt7688
- Vscode markdown export PDF error
- Vgg16 migration learning source code
猜你喜欢

Opencv notes 20 PCA
Vgg16 migration learning source code

Serial communication based on 51 single chip microcomputer

2.1 Dynamic programming and case study: Jack‘s car rental

LeetCode - 705 设计哈希集合(设计)
CV learning notes - image filter

CV learning notes - scale invariant feature transformation (SIFT)
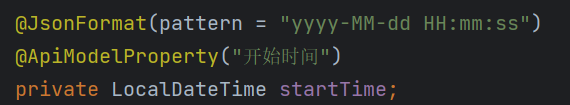
2.Elment Ui 日期选择器 格式化问题

2. Elment UI date selector formatting problem

CV learning notes alexnet
随机推荐
STM32 general timer 1s delay to realize LED flashing
01 business structure of imitation station B project
Swing transformer details-2
Google browser plug-in recommendation
Wireshark use
Qcombox style settings
4G module IMEI of charging pile design
Windows下MySQL的安装和删除
Markdown latex full quantifier and existential quantifier (for all, existential)
1. Finite Markov Decision Process
Yocto Technology Sharing Phase 4: Custom add package support
One click generate traffic password (exaggerated advertisement title)
QT detection card reader analog keyboard input
Application of 51 single chip microcomputer timer
Of course, the most widely used 8-bit single chip microcomputer is also the single chip microcomputer that beginners are most easy to learn
2312. Selling wood blocks | things about the interviewer and crazy Zhang San (leetcode, with mind map + all solutions)
[untitled] proteus simulation of traffic lights based on 89C51 Single Chip Microcomputer
(2)接口中新增的方法
yocto 技术分享第四期:自定义增加软件包支持
2021-10-28