当前位置:网站首页>《牛客刷verilog》Part III Verilog企业真题
《牛客刷verilog》Part III Verilog企业真题
2022-07-05 23:07:00 【杰之行】
前言
之前刷过HDLbits上面的题目,点击链接可以查看详细笔记:verilog练习:hdlbits网站系列完结!
最近又想刷一下牛客上面的题目,可以点击链接与小编一起刷题:牛客刷题
小编不才,文中如有不当之处,可以在评论中互相交流。此处题目推荐看牛客的评论区,再提一嘴,注意积累自己的基本功
算法、设计模式、软件等
Part I Verilog快速入门
- 如果你想入门学习,可以点击链接:《牛客刷verilog》Part I Verilog快速入门
Part II Verilog进阶挑战
- 如果你想进阶学习,可以点击链接:《牛客刷verilog》Part II Verilog进阶挑战
Part III Verilog企业真题
01 哲K
VL59 根据RTL图编写Verilog程序
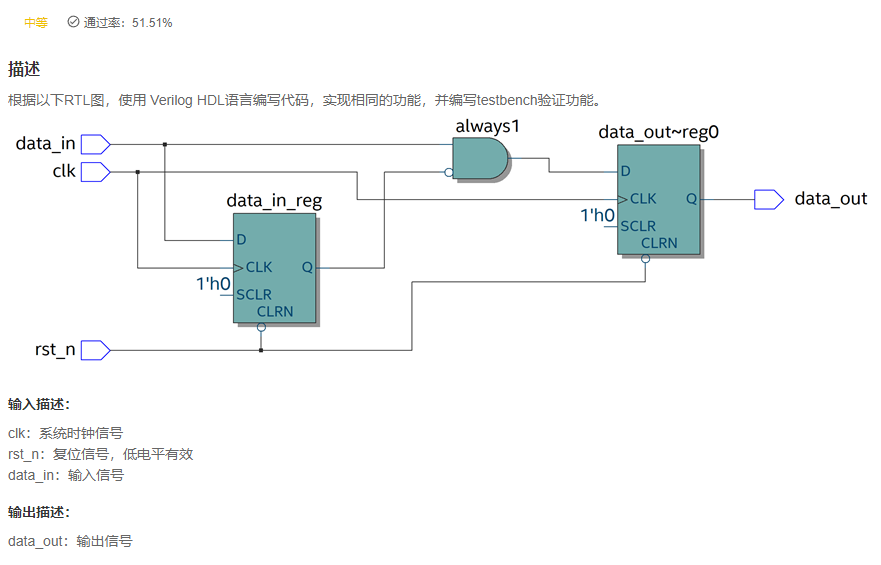
答案
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module RTL(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input data_in,
output reg data_out
);
reg data_in_reg;
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n)begin
data_in_reg <= 'd0;
end else begin
data_in_reg <= data_in;
end
end
assign always1 = data_in & ~data_in_reg;
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n)begin
data_out <= 'd0;
end else begin
data_out <= always1;
end
end
endmodule
VL60 使用握手信号实现跨时钟域数据传输
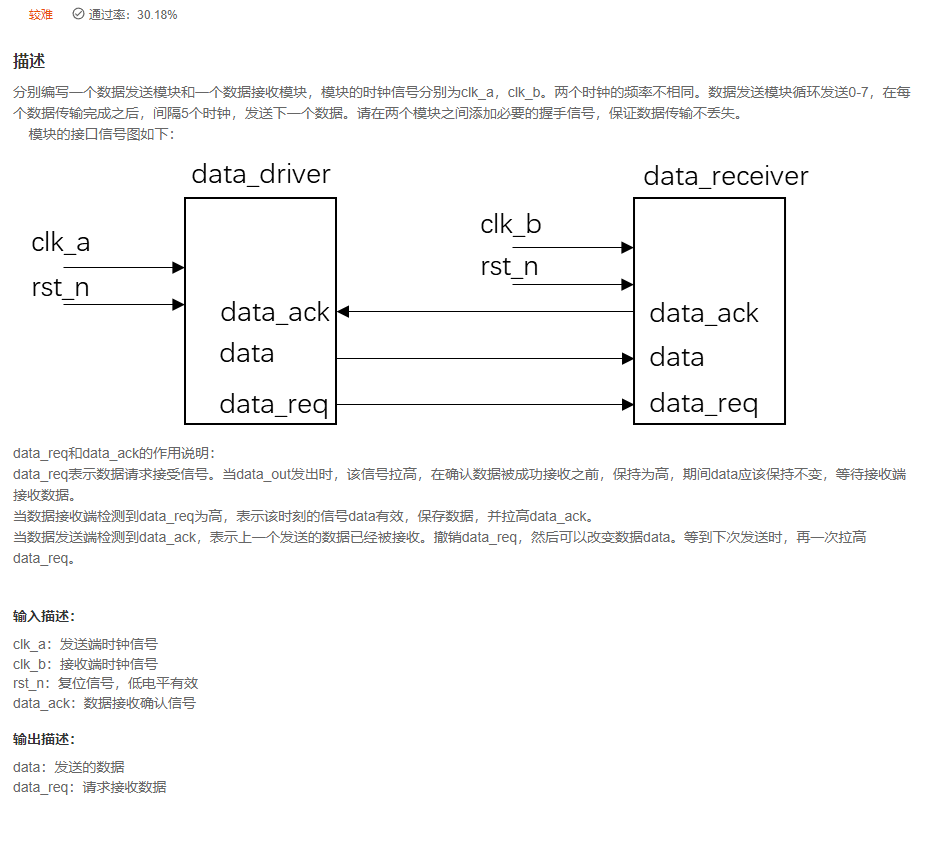
答案
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module data_driver(
input clk_a,
input rst_n,
input data_ack,
output reg [3:0]data,
output reg data_req
);
reg data_ack_reg_1,data_ack_reg_2;
always @ (posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)
if (!rst_n)
begin
{
data_ack_reg_1,data_ack_reg_2} <= 'd0;
end
else
begin
{
data_ack_reg_1,data_ack_reg_2} <= {
data_ack,data_ack_reg_1};
end
// wire flag = data_ack_reg_1 && !data_ack_reg_2;
wire flag = {
data_ack_reg_1,data_ack_reg_2} == 2'b10;
always @ (posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)
if (!rst_n) begin
data <= 0;
end
else if(flag)begin
// if(data == 'd7)
// data <= 'd0;
data <= data+1;
end
else begin
data <= data;
end
reg [2:0] cnt;
//同时在data_ack有效之后,开始计数五个时钟,之后发送新的数据,也就是再一次拉高data_req.
always @ (posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)
if (!rst_n)
cnt <= 0;
else if (flag)
cnt <= 0;
else if (data_req)
cnt <= cnt;
else
cnt <= cnt+1;
always @ (posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n)
if (!rst_n)
data_req <= 0;
else if (cnt == 3'd4)
data_req <= 1'b1;
else if (flag)
data_req <= 1'b0;
else
data_req <= data_req;
endmodule
module data_receiver(
input clk_b,
input rst_n,
output reg data_ack,
input [3:0]data,
input data_req
);
reg [3:0]data_in_reg;
reg data_req_reg_1, data_req_reg_2;
always @ (posedge clk_b or negedge rst_n)
if (!rst_n)begin
{
data_req_reg_1, data_req_reg_2} <= 'd0;
end
else begin
{
data_req_reg_1, data_req_reg_2} <= {
data_req, data_req_reg_1};
end
wire flag = {
data_req_reg_1, data_req_reg_2} == 2'b10;
always @ (posedge clk_b or negedge rst_n)
if (!rst_n)
data_ack <= 0;
else if (flag)
data_ack <= 1;
else data_ack <=0 ;
always @ (posedge clk_b or negedge rst_n)
if (!rst_n)
data_in_reg <= 0;
else if (flag)
data_in_reg <= data;
else data_in_reg <= data_in_reg ;
endmodule
复盘
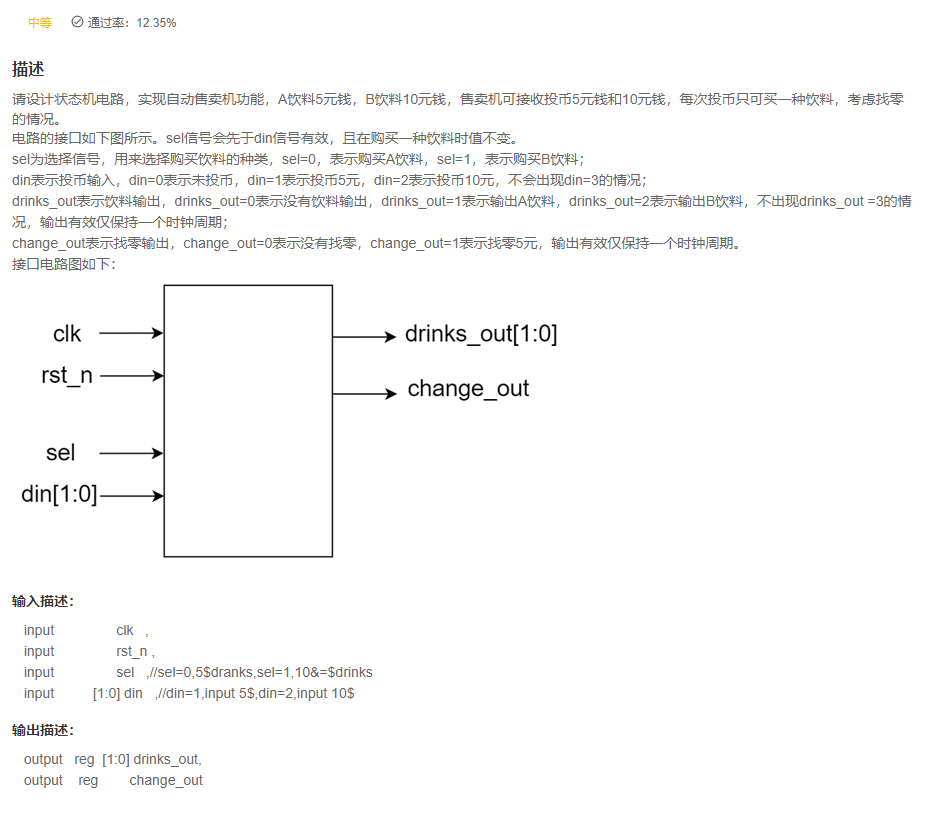
VL61 自动售卖机
答案
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module sale(
input clk ,
input rst_n ,
input sel ,//sel=0,5$dranks,sel=1,10&=$drinks
input [1:0] din ,//din=1,input 5$,din=2,input 10$
output reg [1:0] drinks_out,//drinks_out=1,output 5$ drinks,drinks_out=2,output 10$ drinks
output reg change_out
);
reg [2:0] c_state,n_state;
parameter IDLE = 3'd0;
parameter S1 = 3'd1;//5元买5元饮料
parameter S2 = 3'd2;//10元买5元饮料找5块
parameter S3 = 3'd3;//5元买十元饮料
parameter S4 = 3'd4;//加了5块,不找
parameter S5 = 3'd5;//加了10块,找5块
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
c_state<=IDLE;
else
c_state <= n_state;
[email protected](*)
if(sel== 1'b0)begin
case(c_state)
IDLE:begin
case(din)
2'b00: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b01: n_state <= S1;
2'b10: n_state <= S2;
endcase
end
S1:begin
case(din)
2'b00: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b01: n_state <= S1;
2'b10: n_state <= S2;
endcase
end
S2:begin
case(din)
2'b00: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b01: n_state <= S1;
2'b10: n_state <= S2;
endcase
end
S3:begin
case(din)
2'b00: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b01: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b10: n_state <= IDLE;
endcase
end
S4:begin
case(din)
2'b00: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b01: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b10: n_state <= IDLE;
endcase
end
S5:begin
case(din)
2'b00: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b01: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b10: n_state <= IDLE;
endcase
end
endcase
end
else begin
case(c_state)
IDLE:begin
case(din)
2'b00: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b01: n_state <= S3;
2'b10: n_state <= S4;
endcase
end
S1:begin
case(din)
2'b00: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b01: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b10: n_state <= IDLE;
endcase
end
S2:begin
case(din)
2'b00: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b01: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b10: n_state <= IDLE;
endcase
end
S3:begin
case(din)
2'b00: n_state <= S3;
2'b01: n_state <= S4;
2'b10: n_state <= S5;
endcase
end
S4:begin
case(din)
2'b00: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b01: n_state <= S3;
2'b10: n_state <= S4;
endcase
end
S5:begin
case(din)
2'b00: n_state <= IDLE;
2'b01: n_state <= S3;
2'b10: n_state <= S4;
endcase
end
endcase
end
[email protected](*)
if(!rst_n)begin
drinks_out <= 0;
change_out <=0;
end
else begin
case(c_state)
IDLE:begin
drinks_out <= 0;
change_out <=0;
end
S1:begin
drinks_out <= 2'd1;
change_out <=1'd0;
end
S2:begin
drinks_out <= 2'd1;
change_out <=1'd1;
end
S3:begin
drinks_out <= 0;
change_out <=0;
end
S4:begin
drinks_out <=2'd2;
change_out <=0;
end
S5:begin
drinks_out <= 2'd2;
change_out <=1'd1;
end
endcase
end
endmodule
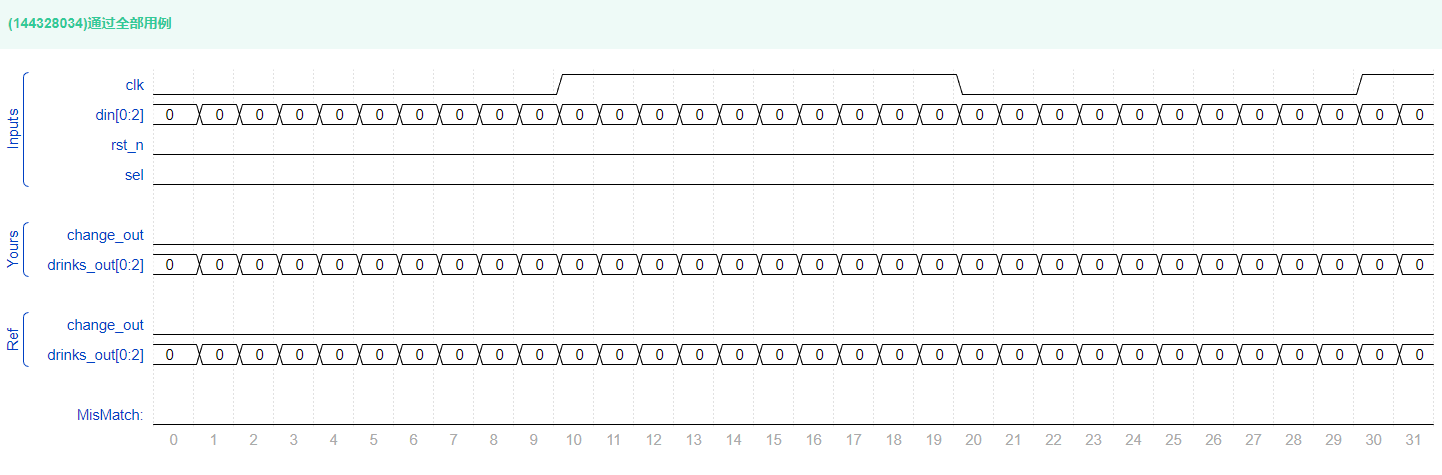

复盘
- 给一个没有通过的代码,可以修改一下。
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module sale(
input clk ,
input rst_n ,
input sel ,//sel=0,5$dranks,sel=1,10&=$drinks
input [1:0] din ,//din=1,input 5$,din=2,input 10$
output reg [1:0] drinks_out,//drinks_out=1,output 5$ drinks,drinks_out=2,output 10$ drinks
output reg change_out
);
parameter IDLE = 2'd0;//0元
parameter S1 = 2'd1;//5元
parameter S2 = 2'd2;//10元
parameter S3 = 2'd3;//15元
//第一段
reg [1:0] cur_state, next_state;
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
cur_state <= IDLE;
end
else begin
cur_state <= next_state;
end
end
//第二段
[email protected](*) begin
case(cur_state)
IDLE:begin
if(din == 2'b01)
next_state = S1;
else if(din == 2'b10)
next_state = S2;
else
next_state = next_state;
end
S1:begin
if(sel == 0)//买5元的
next_state = IDLE;
else if(din == 2'b01)
next_state = S2;
else if(din == 2'b10)
next_state = S3;
else
next_state = next_state;
end
S2:begin
next_state = IDLE;
end
S3:begin
next_state = IDLE;
end
default: next_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
//第三段
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
{
drinks_out,change_out} <= 3'b00_0;
end
else case(next_state)
IDLE:begin
{
drinks_out,change_out} <= 3'b00_0;
end
S1:begin
if(sel == 0)//买5元的
{
drinks_out,change_out} <= 3'b01_0;
else
{
drinks_out,change_out} <= 3'b00_0;
end
S2:begin
if(sel == 0)//买5元的
{
drinks_out,change_out} <= 3'b01_1;
else
{
drinks_out,change_out} <= 3'b10_0;
end
S3:begin
{
drinks_out,change_out} <= 3'b10_1;
end
default:{
drinks_out,change_out} <= 3'b00_0;
endcase
end
endmodule
VL62 序列发生器
答案
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module sequence_generator(
input clk,
input rst_n,
output reg data
);
reg [5:0] data_reg;
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n)
data_reg <= 6'b001011;
else
data_reg <= {
data_reg, data_reg[5]};
end
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n)
data <= 1'b0;
else
data <= data_reg[5];
end
endmodule
复盘
02 华W
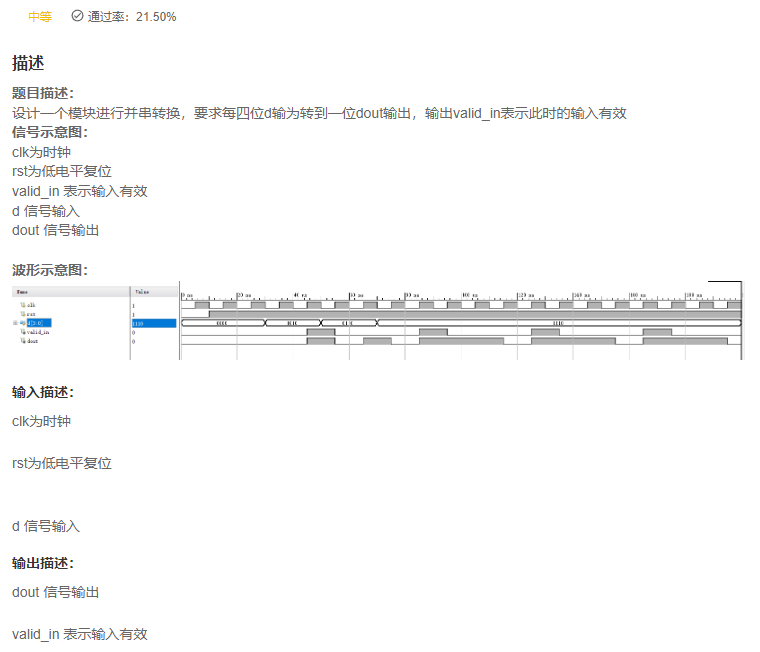
VL63 并串转换
答案
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module huawei5(
input wire clk ,
input wire rst ,
input wire [3:0]d ,
output wire valid_in ,
output wire dout
);
//*************code***********//
reg [3:0] data = 'd0;
reg [1:0]cnt;//计数
reg valid;
assign dout = data[3];//data的最高位接输出线
assign valid_in =valid;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst) begin
if(!rst)begin
data<= 'd0;
cnt <= 'd0;
valid <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if (cnt == 'd3) begin
data <= d;//d是在cnt清零时给到data上传的
cnt <= 'd0;
valid <= 1;
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt + 'd1;
valid <= 0;
data <= {
data[2:0],data[3]};//循环左移
end
end
end
//*************code***********//
endmodule
复盘
- 相关题目推荐《牛客刷verilog》Part II Verilog进阶挑战中有VL30 数据串转并电路
- 这个题目的核心就是,读懂题目:
从高位移位输出,4个bit为一个周期。具体的做法就是:利用循环左移将高位移动到低位,然后利用互相寄存的特性,使得最高位寄存输出。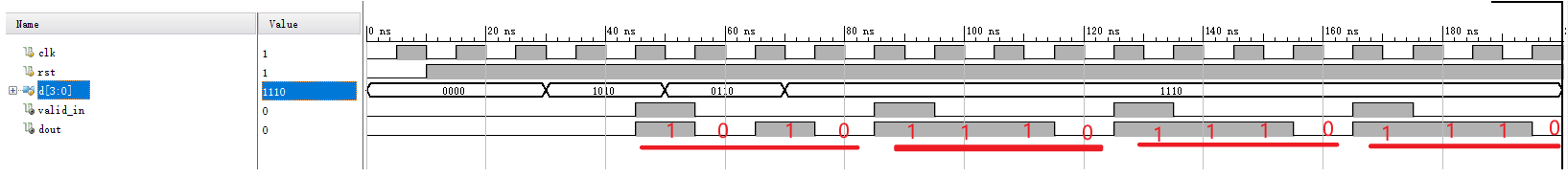
VL64 时钟切换
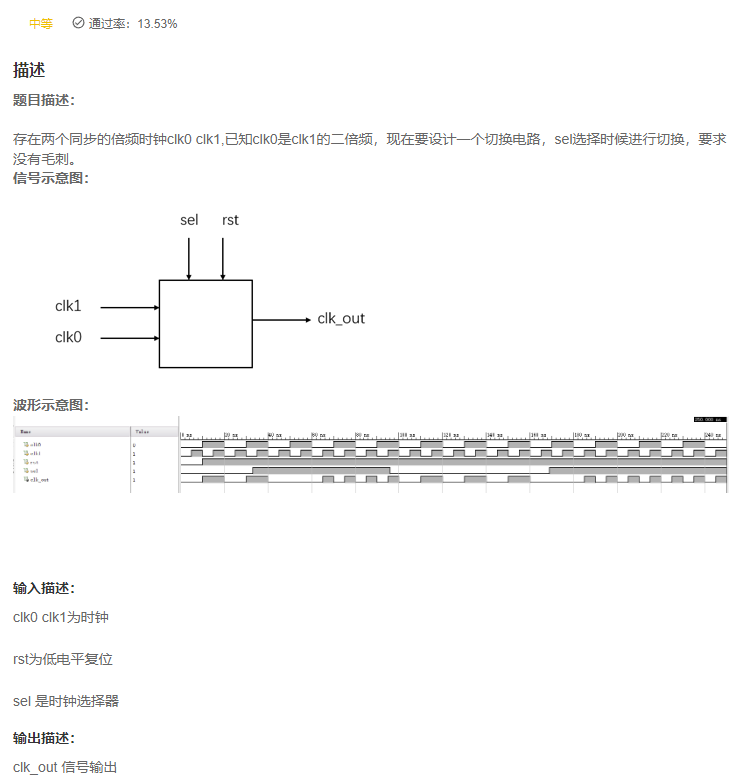
答案
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module huawei6(
input wire clk0 ,
input wire clk1 ,
input wire rst ,
input wire sel ,
output wire clk_out
);
reg q0, q1;
[email protected](negedge clk1 or negedge rst)
if(!rst)
q0 <= 0;
else
q0 <= ~sel & ~q1;
[email protected](negedge clk0 or negedge rst)
if(!rst)
q1 <= 0;
else
q1 <= sel & ~q0;
assign clk_out = (q0 & clk0) | (q1 & clk1);
endmodule
复盘
- 什么东西?
VL65 状态机与时钟分频
题目描述: 使用状态机实现时钟分频,要求对时钟进行四分频,占空比为0.25
信号示意图:
clk为时钟
rst为低电平复位
clk_out 信号输出
Ps 本题题解是按照1000的状态转移进行的,不按照此状态进行,编译器可能报错但没有影响。
波形示意图:
输入描述:
clk为时钟
rst为低电平复位
输出描述:
clk_out 信号输出
答案
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module huawei7(
input wire clk ,
input wire rst ,
output reg clk_out
);
//*************code***********//
parameter S0 = 'd0;
parameter S1 = 'd1;
parameter S2 = 'd2;
parameter S3 = 'd3;
reg [1:0] state;
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(!rst)
state <= S0;
else
case(state)
S0:state <= S1;
S1:state <= S2;
S2:state <= S3;
S3:state <= S0;
endcase
[email protected](*)
if(state == S1)
clk_out <= 'd1;
else
clk_out <= 'd0;
//*************code***********//
endmodule

复盘
- 上述状态机是有规律的循环,如果状态条件是独热码,我们
是否也可以使用移位得到状态。 - 如下得到的答案是错的,大家可以看看。
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module huawei7(
input wire clk ,
input wire rst ,
output reg clk_out
);
//*************code***********//
parameter S0 = 4'b0001;
parameter S1 = 4'b0010;
parameter S2 = 4'b0100;
parameter S3 = 4'b1000;
reg [3:0] state;
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(!rst)
state <= S0;
else
state <= state << 1;
[email protected](*)
if(state == S1)
clk_out <= 'd1;
else
clk_out <= 'd0;
//*************code***********//
endmodule
- 如果使用计数器呢?
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module huawei7(
input wire clk ,
input wire rst ,
output reg clk_out
);
//*************code***********//
reg [1:0] state;
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(!rst)
state <= 'd0;
else
state <= state + 1'b1;
[email protected](*)
if(state == 2'b01)
clk_out <= 'd1;
else
clk_out <= 'd0;
//*************code***********//
endmodule
VL66 超前进位加法器
描述
题目描述:
求两个四位的数据编写一个四位的超前进位加法器,建议使用子模块
提示:超前进位加法器的位公式如下
这里‘+’ ‘·’符号不是‘加’和‘乘’,是‘或’和 ‘与’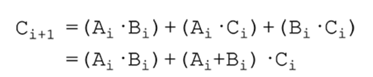
波形示意图:
输入描述:
A B 输入值
输出描述:
OUT 加法结果
答案
复盘
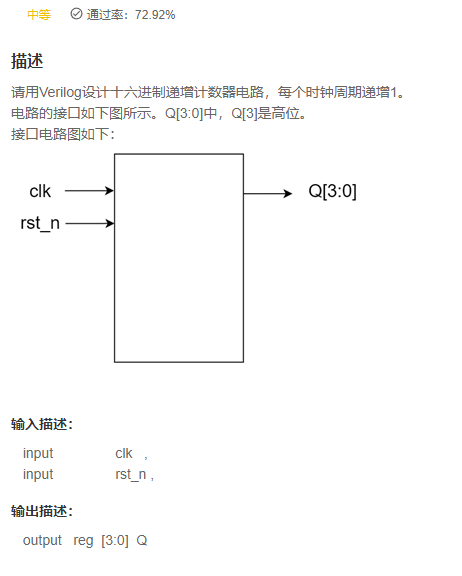
VL67 十六进制计数器
答案
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module counter_16(
input clk ,
input rst_n ,
output reg [3:0] Q
);
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n)
Q <= 'd0;
else
Q <= Q + 1'b1;
end
endmodule
复盘
- 自己能发散到什么吗?
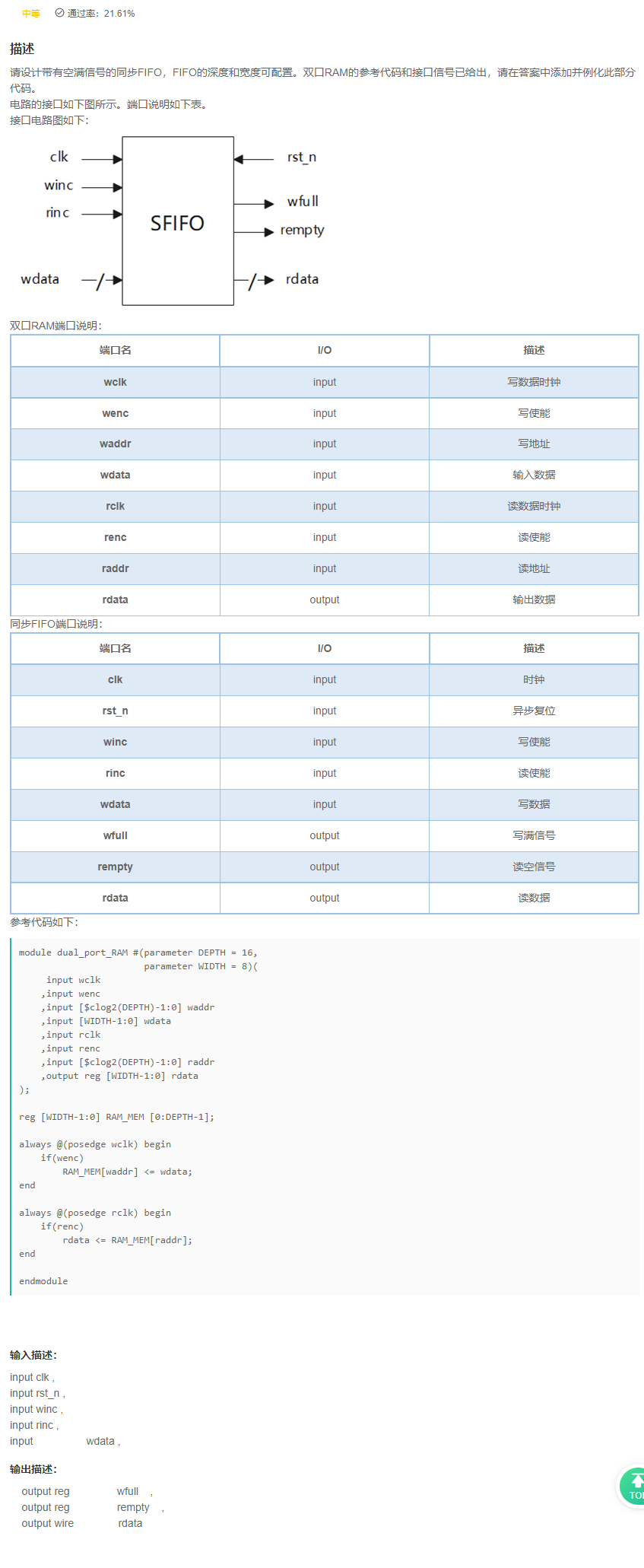
VL68 同步FIFO
答案
`timescale 1ns/1ns
/**********************************RAM************************************/
module dual_port_RAM #(parameter DEPTH = 16,
parameter WIDTH = 8)(
input wclk
,input wenc
,input [$clog2(DEPTH)-1:0] waddr
,input [WIDTH-1:0] wdata
,input rclk
,input renc
,input [$clog2(DEPTH)-1:0] raddr
,output reg [WIDTH-1:0] rdata
);
reg [WIDTH-1:0] RAM_MEM [0:DEPTH-1];
always @(posedge wclk) begin
if(wenc)
RAM_MEM[waddr] <= wdata;
end
always @(posedge rclk) begin
if(renc)
rdata <= RAM_MEM[raddr];
end
endmodule
/**********************************SFIFO************************************/
module sfifo#(
parameter WIDTH = 8,
parameter DEPTH = 16
)(
input clk ,
input rst_n ,
input winc ,
input rinc ,
input [WIDTH-1:0] wdata ,
output reg wfull ,
output reg rempty ,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] rdata
);
localparam ADDR_WIDTH = $clog2(DEPTH) - 1 + 1;
//通过深度换算出需要多少位宽,因为fifo在最高位需要一个标志位产生满信号,上述再+1
//第二步:给RAM申明缺少的端口信号
///
reg [ADDR_WIDTH:0] waddr,raddr;//写地址,读地址
wire wenc,renc;//写使能信号,读使能信号
//第三步:写地址操作,什么时候写
///
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
waddr <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(wenc) begin
waddr <= waddr + 1'b1;
end
else begin
waddr <= waddr;
end
end
end
assign wenc = winc && ~wfull;//写使能信号
//第四步:读地址操作,什么时候读
///
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
raddr <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(renc) begin
raddr <= raddr + 1'b1;
end
else begin
raddr <= raddr;
end
end
end
assign renc = rinc && ~rempty;//读使能信号
//第五步:产生空满信号
///
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
wfull <= 'd0;
rempty <= 'd0;
end
else begin
wfull <= ((waddr[ADDR_WIDTH] != raddr[ADDR_WIDTH]) && (waddr[ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] == raddr[ADDR_WIDTH-1:0]));
rempty <= raddr == waddr;
end
end
//第一步:例化双口RAM
///
dual_port_RAM
#(
.DEPTH(DEPTH)
,.WIDTH(WIDTH)
)
dual_port_RAM_inst
(
.wclk (clk )
,.wenc (wenc )
,.waddr (waddr ) //深度对2取对数,得到地址的位宽。
,.wdata (wdata ) //数据写入
,.rclk (clk )
,.renc (renc )
,.raddr (raddr ) //深度对2取对数,得到地址的位宽。
,.rdata (rdata ) //数据输出
);
endmodule
复盘
- 《牛客刷verilog》Part II Verilog进阶挑战中有同步fifo和异步fifo,此题目完全一致。
03 DJ
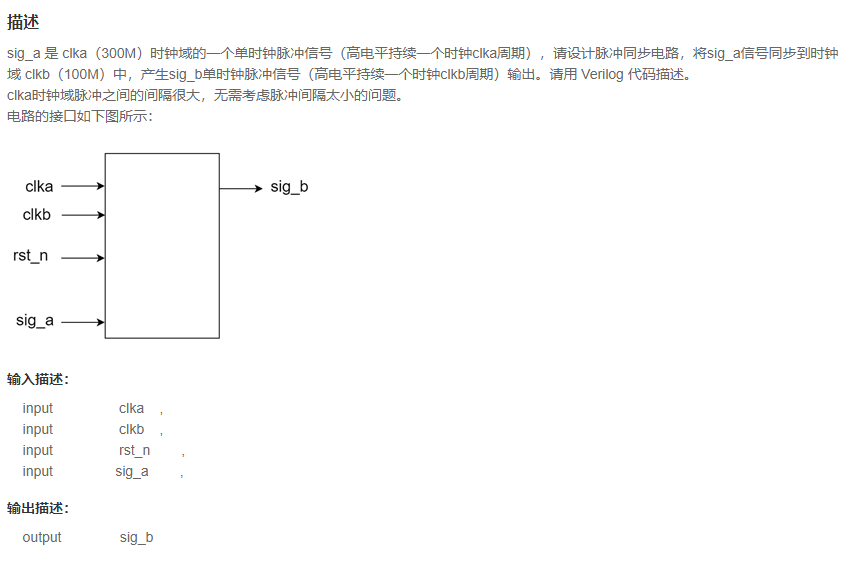
VL69 脉冲同步器(快到慢)
答案
复盘
VL70 序列检测器(Moore型)
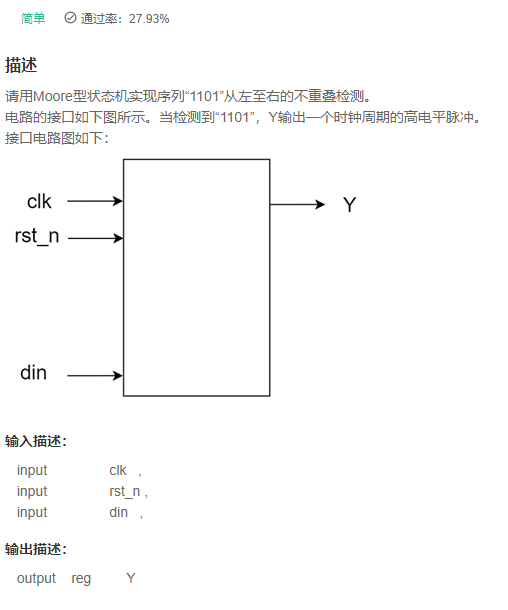
答案
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module det_moore(
input clk ,
input rst_n ,
input din ,
output reg Y
);
reg [3:0] din_reg;
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
din_reg <= 'd0;
else
din_reg <= {
din_reg,din};
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
Y <= 'd0;
else
Y <= din_reg == 4'b1101;
endmodule
复盘
- 《牛客刷verilog》Part II Verilog进阶挑战中很多题目,小编都用的这种方法。
VL71 乘法与位运算

答案
复盘
04 A里
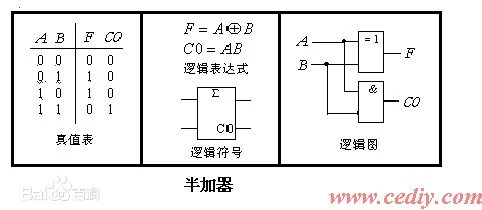
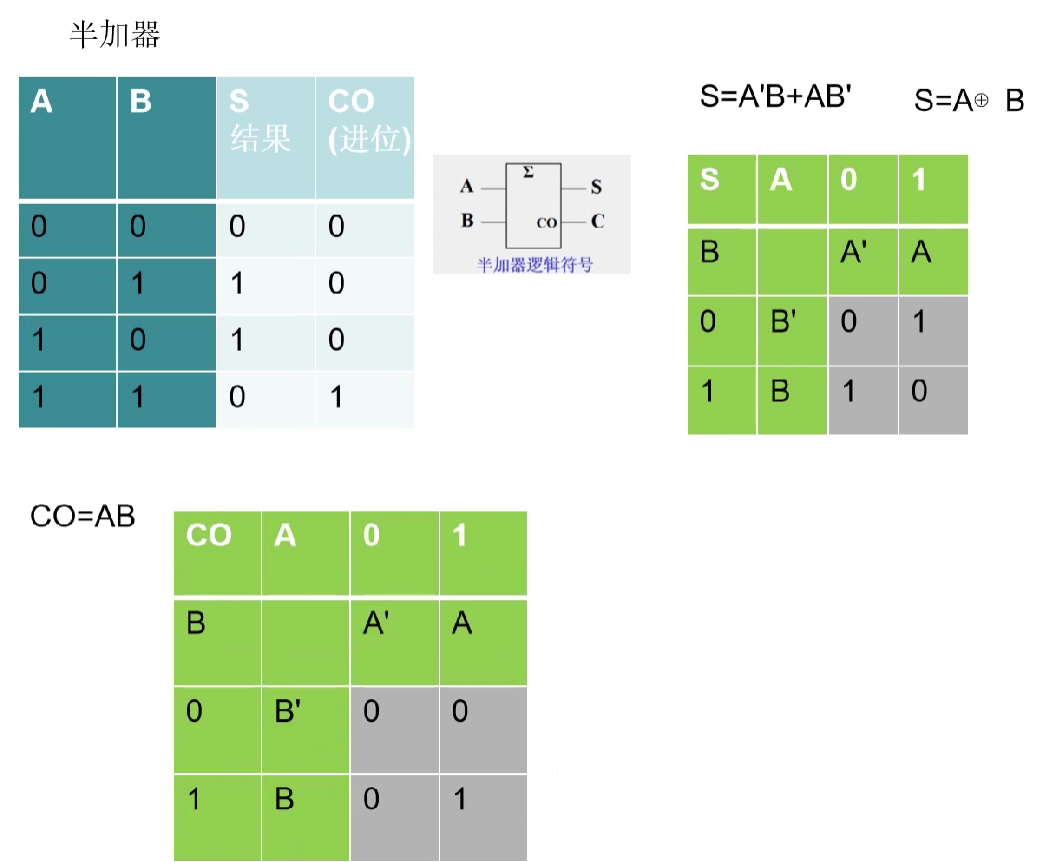
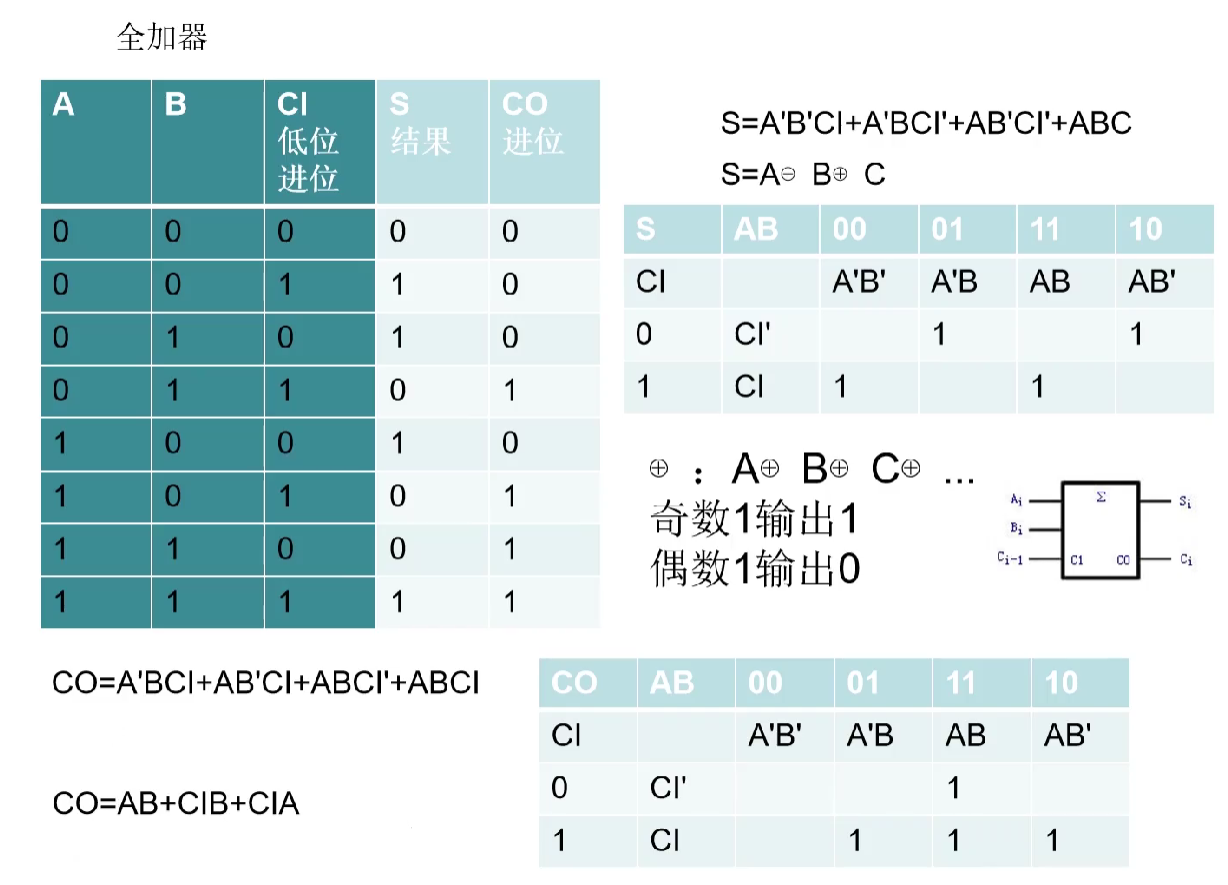
VL72 全加器

答案
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module add_half(
input A ,
input B ,
output wire S ,
output wire C
);
assign S = A ^ B;
assign C = A & B;
endmodule
/***************************************************************/
module add_full(
input A ,
input B ,
input Ci ,
output wire S ,
output wire Co
);
wire [1:0] s,c;
add_half add_half_U1(A,B,s[0],c[0]);
add_half add_half_u2(Ci,s[0],s[1],c[1]);
assign S = s[1];
assign Co = |c;
endmodule
复盘

- 在刚开始学习的时候,大家应该都知道,
半加器是不考虑进位的,但是很多人肯定会想到,好像是有进位的,就比如1'b1+1'b1 = 2'b10.注意了,此处的进位指的是,在1'b1+1'b1时考虑低位的进位吗?没有! - 半加器和全加器的区别主要是
半加器没有接收进位的输入端,全加器有进位输入端,在将两个多位二进制数相加时,除了最低位外,每一位都要考虑来自低位的进位,半加器则不用考虑,只需要考虑两个输入端相加即可。 半加器是实现两个一位二进制数加法运算的器件。它具有两个输入端(被加数A和加数B)及输出端Y。全加器是用门电路实现两个二进制数相加并求出和的组合线路,称为一位全加器。一位全加器可以处理低位进位,并输出本位加法进位。多个一位全加器进行级联可以得到多位全加器。
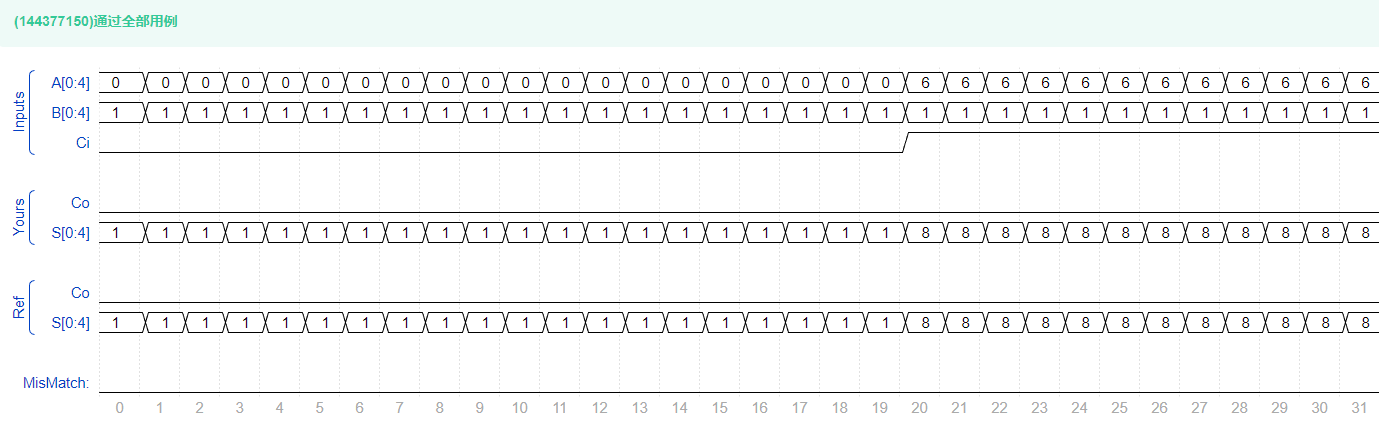
VL73 串行进位加法器
描述
② 请用全加器电路①实现串行进位的4位全加器电路
1位全加器参考代码如下:
module add_half(
input A ,
input B ,
output wire S ,
output wire C
);
assign S = A ^ B;
assign C = A & B;
endmodule
/***************************************************************/
module add_full(
input A ,
input B ,
input Ci ,
output wire S ,
output wire Co
);
wire c_1;
wire c_2;
wire sum_1;
add_half add_half_1(
.A (A),
.B (B),
.S (sum_1),
.C (c_1)
);
add_half add_half_2(
.A (sum_1),
.B (Ci),
.S (S),
.C (c_2)
);
assign Co = c_1 | c_2;
endmodule
输入描述:
input [3:0] A ,
input [3:0] B ,
input Ci ,
输出描述:
output wire [3:0] S ,
output wire Co
答案
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module add_4(
input [3:0] A ,
input [3:0] B ,
input Ci ,
output wire [3:0] S ,
output wire Co
);
// assign {Co,S} = A + B + Ci;
wire C[3:0];
generate
genvar i ;
for(i=0;i<=3;i=i+1)
begin: Li
if(i==0) begin
add_full add_full_li(
.A(A[i]),
.B(B[i]),
.Ci(Ci),
.S(S[i]),
.Co(C[i]));
end
else begin
add_full add_full_li(
.A(A[i]),
.B(B[i]),
.Ci(C[i-1]),
.S(S[i]),
.Co(C[i]));
end
end
endgenerate
assign Co = C[3];
endmodule
module add_half(
input A ,
input B ,
output wire S ,
output wire C
);
assign S = A ^ B;
assign C = A & B;
endmodule
/***************************************************************/
module add_full(
input A ,
input B ,
input Ci ,
output wire S ,
output wire Co
);
wire c_1;
wire c_2;
wire sum_1;
add_half add_half_1(
.A (A),
.B (B),
.S (sum_1),
.C (c_1)
);
add_half add_half_2(
.A (sum_1),
.B (Ci),
.S (S),
.C (c_2)
);
assign Co = c_1 | c_2;
endmodule
复盘
- 全加器也可以不使用例化半加器的方式实现
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module add_4(
input [3:0] A ,
input [3:0] B ,
input Ci ,
output wire [3:0] S ,
output wire Co
);
// assign {Co,S} = A + B + Ci;
wire C[3:0];
generate
genvar i ;
for(i=0;i<=3;i=i+1)
begin: Li
if(i==0) begin
add_full add_full_li(
.A(A[i]),
.B(B[i]),
.Ci(Ci),
.S(S[i]),
.Co(C[i]));
end
else begin
add_full add_full_li(
.A(A[i]),
.B(B[i]),
.Ci(C[i-1]),
.S(S[i]),
.Co(C[i]));
end
end
endgenerate
assign Co = C[3];
endmodule
module add_full(
input A,
input B,
input Ci,
output S,
output Co
);
assign S = A^B^Ci;
assign Co = ((A^B)&Ci)|(A&B);
endmodule
VL74 异步复位同步释放
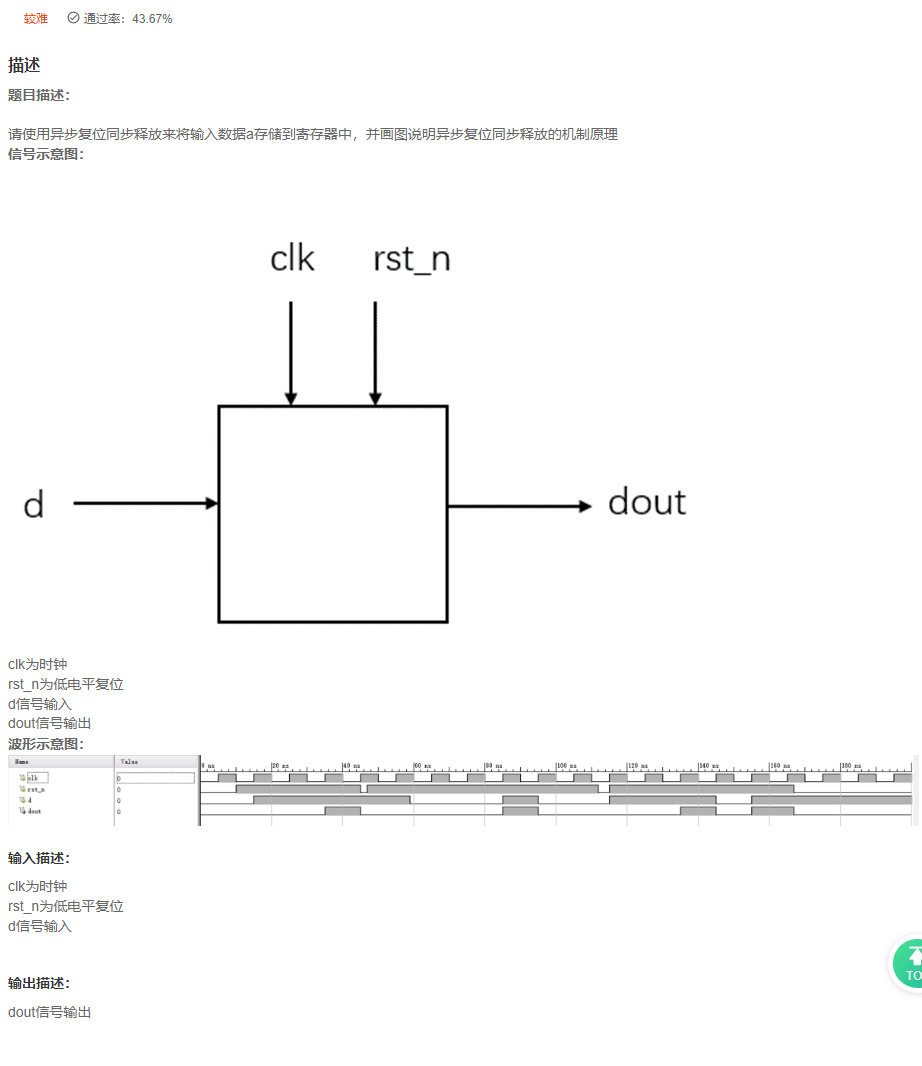
答案
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module ali16(
input wire clk,
input wire rst_n,
input wire d,
output reg dout
);
reg rst0,rst1;
always @ (posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
{
rst0,rst1} <= 'd0;
end
else begin
{
rst0,rst1} <= {
1'b1,rst0};
end
end
always @ (posedge clk or negedge rst1)begin
if(!rst1) begin
dout <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
dout <= d;
end
end
endmodule
复盘
- 异步复位,同步释放?
VL75 求最小公倍数
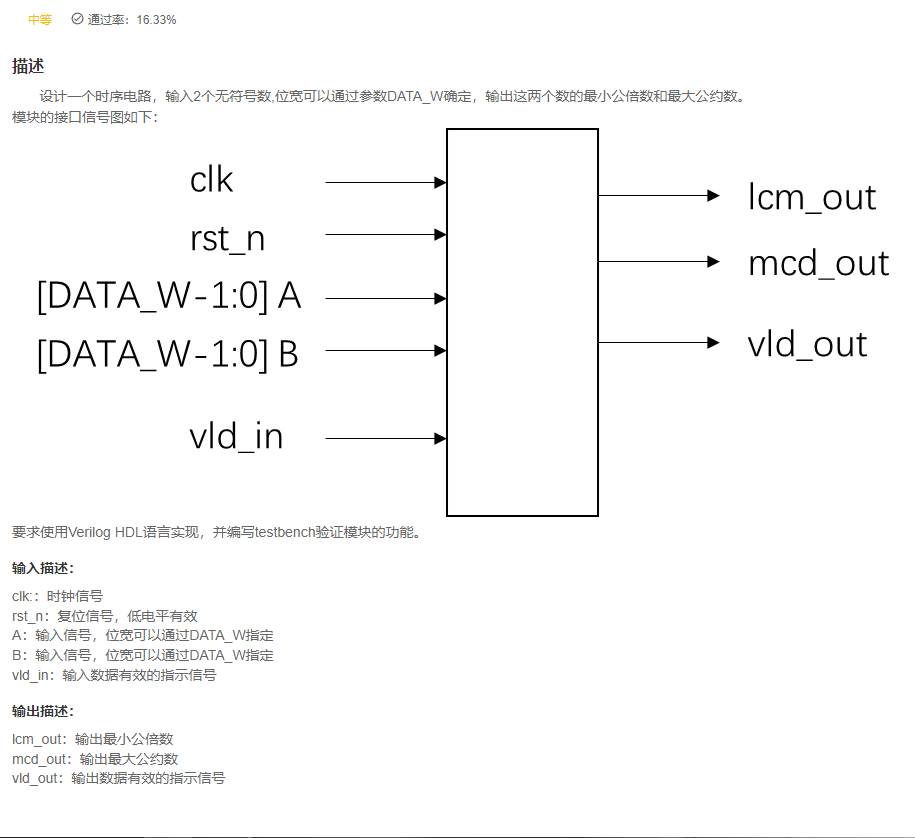
答案
VL76 任意奇数倍时钟分频
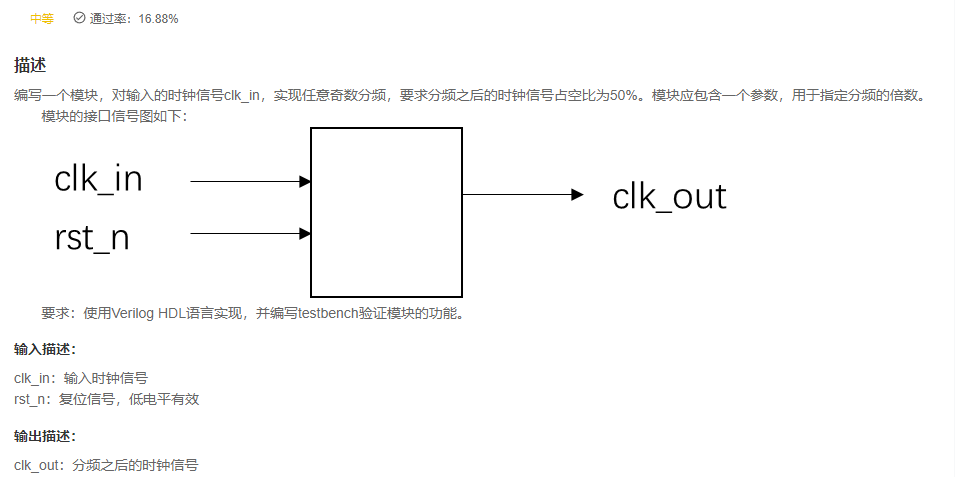
05 Z兴
VL77 编写乘法器求解算法表达式
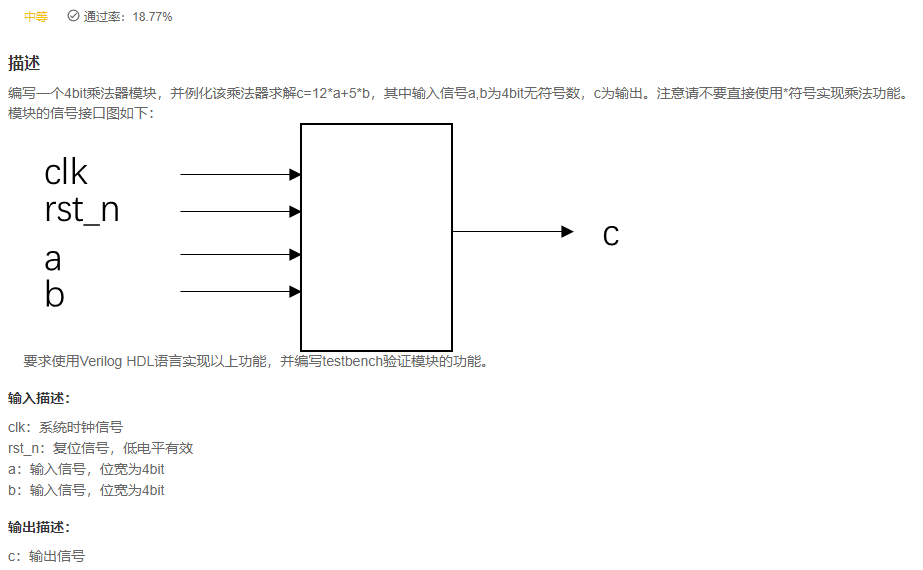
后记
推荐相关文章
- 可以点击链接与小编一起刷题:牛客刷题

边栏推荐
- TVS管 与 稳压二极管参数对比
- UVA – 11637 Garbage Remembering Exam (组合+可能性)
- Golang code checking tool
- 动态规划 之 打家劫舍
- Media query: importing resources
- PLC编程基础之数据类型、变量声明、全局变量和I/O映射(CODESYS篇 )
- (4) UART application design and simulation verification 2 - RX module design (stateless machine)
- Expectation, variance and covariance
- 数学公式截图识别神器Mathpix无限使用教程
- (4)UART应用设计及仿真验证2 —— TX模块设计(无状态机)
猜你喜欢
LeetCode145. Post order traversal of binary tree (three methods of recursion and iteration)
The method and principle of viewing the last modification time of the web page
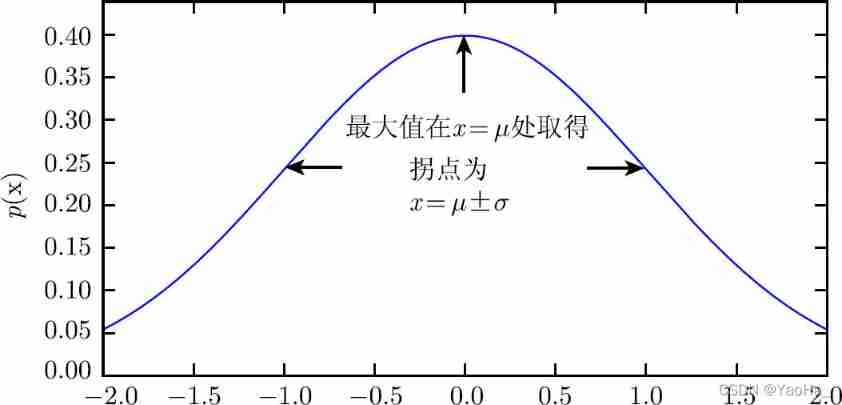
Commonly used probability distributions: Bernoulli distribution, binomial distribution, polynomial distribution, Gaussian distribution, exponential distribution, Laplace distribution and Dirac delta d
Matlab smooth curve connection scatter diagram
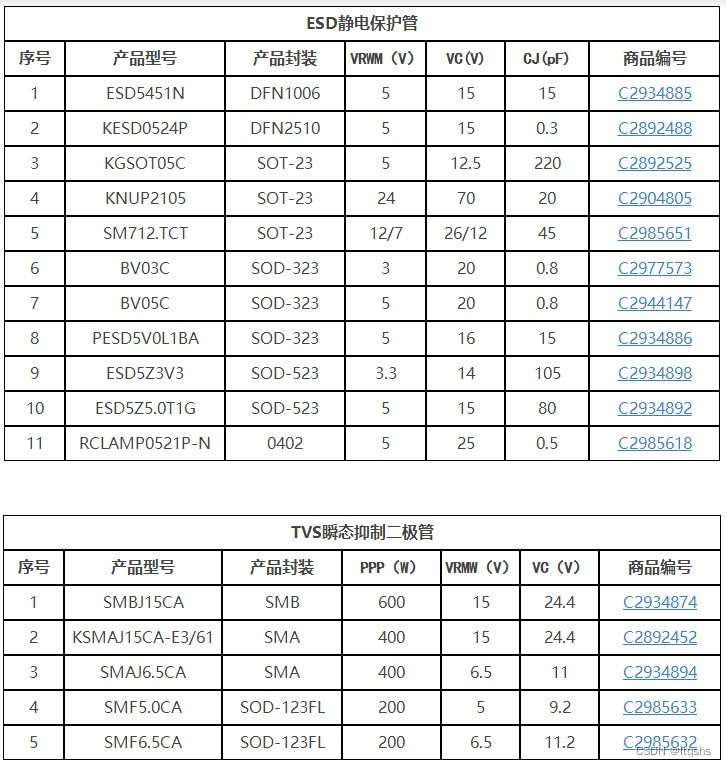
TVS管和ESD管的技術指標和選型指南-嘉立創推薦
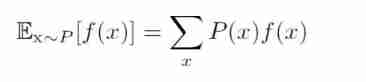
Expectation, variance and covariance
Simple and beautiful method of PPT color matching
Three. Js-01 getting started

YML configuration, binding and injection, verification, unit of bean
并查集实践
随机推荐
CJ mccullem autograph: to dear Portland
poj 2762 Going from u to v or from v to u? (infer whether it is a weak link diagram)
asp. Net pop-up layer instance
Golang code checking tool
There are 14 God note taking methods. Just choose one move to improve your learning and work efficiency by 100 times!
Mathematical formula screenshot recognition artifact mathpix unlimited use tutorial
(4) UART application design and simulation verification 2 - TX module design (stateless machine)
Idea rundashboard window configuration
进击的技术er——自动化
CIS基准测试工具kube-bench使用
openresty ngx_ Lua request response
openresty ngx_ Lua regular expression
Hj16 shopping list
From the perspective of quantitative genetics, why do you get the bride price when you get married
Three.JS VR看房
Calculating the number of daffodils in C language
Detailed explanation of pointer and array written test of C language
The method and principle of viewing the last modification time of the web page
Initial experience | purchase and activate typora software
无刷驱动设计——浅谈MOS驱动电路