当前位置:网站首页>SQL tuning notes
SQL tuning notes
2022-07-06 17:12:00 【Stray_ Lambs】
Catalog
Negative queries cannot use indexes
Leading fuzzy query cannot use index
When the data distinction is not obvious , There should be no indexing
The default value of the field should not be null
Calculation on a field cannot hit the index
Don't let the database cast automatically
join The field types of the two tables should be the same
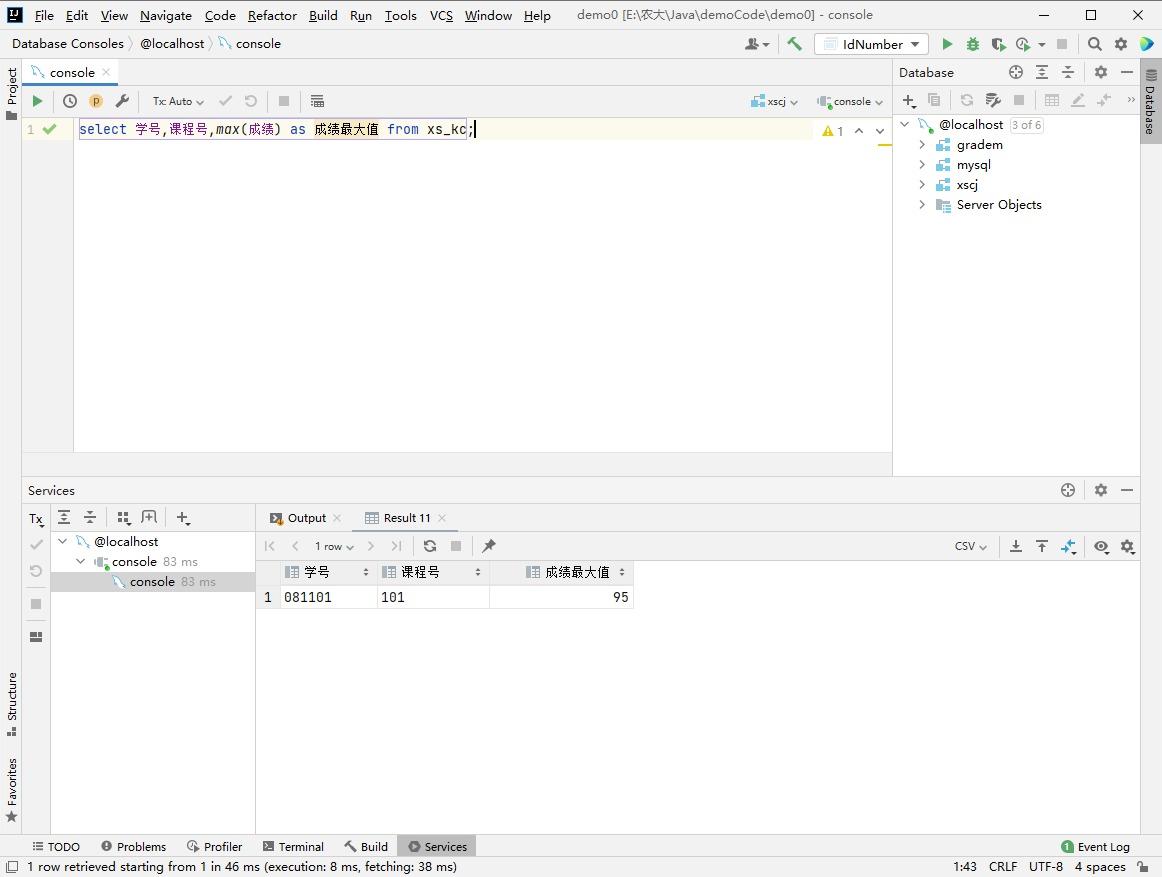
Use Explain Conduct SQL analysis
SQL Optimize
When there is slow SQL when , First we need to check SQL Whether the statement can be optimized ( Write SQL We need to think about whether we can optimize ), then , Then consider performance optimization .
SQL Statements to optimize
Negative queries cannot use indexes
When we use not in When , Even if it is indexed , It is also equivalent to failure .
select name from user where id not in (1,3,4);
-- It should be changed to
select name from user where id in (2,5,6);
Leading fuzzy query cannot use index
In the use of like When matching characters , if % in front , The index becomes invalid .
select name from user where name like '%zhangsan'
-- Try to change it to
select name from user where name like 'zhangsan%'
It is suggested to consider using Lucene And other full-text indexing tools to replace frequent fuzzy queries .
When the data distinction is not obvious , There should be no indexing
If the data fields cannot be clearly distinguished , Should not be indexed , Because indexing consumes space , Like a book 50 Pages of books have 50 Contents of pages .
The default value of the field should not be null
null It may occur during data query , Implicit conversion of types , Cause index to fail , And it may cause the result of the query to be inconsistent with the expectation .
Calculation on a field cannot hit the index
Try not to calculate functions on fields , namely Do not convert field types or operate on fields ( Calculation 、 function 、 Type conversion ( Manual or Automatically )), Can cause indexes to fail , Turn to full scan .
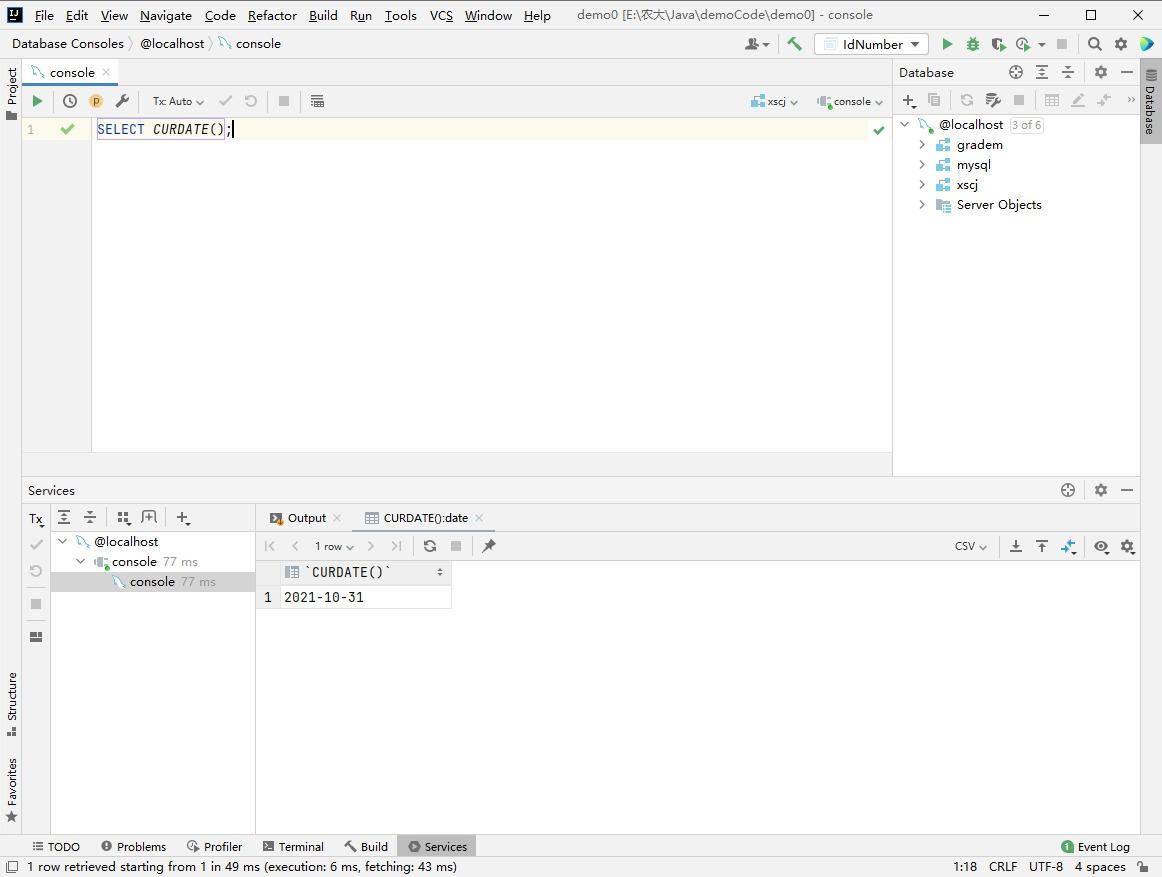
select name from user where FROM_UNIXTIME(create_time) < CURDATE();
-- It should be changed to
select name from user where create_time < FROM_UNIXTIME(CURDATE());
Leftmost prefix problem
-- If user In the table username pwd If the field creates a composite index, use the following SQL Can hit the index :
select username from user where username='zhangsan' and pwd ='axsedf1sd'
select username from user where pwd ='axsedf1sd' and username='zhangsan'
select username from user where username='zhangsan'
-- But use the following , Index failed to hit
select username from user where pwd ='axsedf1sd'
Specify the number of returns
If you explicitly return the number of entries , Then the quantity is constrained during query , Reduce the number of queries , Such as
select name from user where username='zhangsan' limit 1
Don't let the database cast automatically
If the types of left and right sides are inconsistent , Cast will be done , Then perform a full scan .
select name from user where telno=18722222222
-- It should be changed to
select name from user where telno='18722222222'
join The field types of the two tables should be the same
Otherwise, the index will be invalid , Can't hit .
Summary
The occurrence of index failure :
1、 Full value matching my favorite ;
2、 The best left prefix rule ;
3、 Do nothing on the index column ( Calculation 、 function 、 Type conversion ( Manual or Automatically )), Can cause indexes to fail , Turn to full scan ;
4、 The storage engine cannot use the column to the right of the range condition in the index ;
5、 Try to use overlay index ( Only access index columns ( The query column is consistent with the index column )), Reduce select *;
6、MySQL Using the not equal operator (!= or <>) when , Index not available , Causes a full table scan ;
7、is null and is not null, Index not available ;
8、like If it starts with a wildcard (’%aa’), The index becomes invalid , Full table scan ;***– resolvent :1、 Wildcards on the left 2、 Use overlay index ( see P40)***
9、 If the string is not quoted, the index will be invalid ( Equivalent to using implicit type conversion – See the first 3 strip );
10、 To use less or, When using it to connect conditions , Index failure .
formula
Full value matching my favorite , The leftmost prefix should follow ; Leading brother can't die , The middle brother can't break ; Less computation on index columns , After the range, it all fails ;LIKE 100% right , Overlay index without writing *; I don't want empty values and or, Index failure should be used less .
SQL performance optimization
Use Explain Conduct SQL analysis
Explain Used for analysis SELECT Query statement , Developers can analyze Explain Results to optimize the query statements .
The more important fields are :
- select_type : Query type , There is a simple query 、 The joint query 、 The subquery etc.
- key : Index used
- rows : Number of lines scanned
Optimize data access
Reduce the number of requested visits
- Only necessary columns are returned : Better not to use SELECT * sentence .
- Just go back to the necessary lines : Use LIMIT Statement to limit the data returned .
- Cache data from repeated queries : Using caching can avoid queries in the database , Especially when the data to be queried is often repeatedly queried , The query performance improvement brought by cache will be very obvious .
Reduce the number of server-side scan lines
The most efficient way is to use indexes to override queries .
Refactoring query methods
Cut big query
If a big query is executed at one time , It's possible to lock up a lot of data at a time 、 Full transaction log 、 Drain system resources 、 Block a lot of small but important queries . Limit the number of strips per time , It can effectively reduce congestion .
DELEFT FROM messages WHERE create < DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL 3 MONTH);
-- It should be revised to
rows_affected = 0
do {
rows_affected = do_query(
"DELETE FROM messages WHERE create < DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL 3 MONTH) LIMIT 10000")
} while rows_affected > 0
Break down large connection queries
Decompose a large join query into a single table query for each table , Then correlate the results in the application , The benefits of this are :
- Make caching more efficient . For connection queries , If one of the tables changes , Then the entire query cache cannot be used . And multiple queries after decomposition , Even if one of the tables changes , The query cache for other tables can still be used .
- Split into multiple single table queries , The cache results of these single table queries are more likely to be used by other queries , So as to reduce the query of redundant records .
- Reduce lock competition ;
- Connect at the application layer , It's easier to split the database , This makes it easier to achieve high performance and scalability .
- Query itself may also be more efficient . For example, in the following example , Use IN() Instead of a connection query , It can make MySQL according to ID Query in sequence , This may be more efficient than random connections .
SELECT * FROM tab
JOIN tag_post ON tag_post.tag_id=tag.id
JOIN post ON tag_post.post_id=post.id
WHERE tag.tag='mysql';
It is amended as follows ( A little distributed )
SELECT * FROM tag WHERE tag='mysql';
SELECT * FROM tag_post WHERE tag_id=1234;
SELECT * FROM post WHERE post.id IN (123,456,567,9098,8904);
边栏推荐
- 唯有学C不负众望 TOP2 p1变量
- Only learning C can live up to expectations Top1 environment configuration
- Shell_ 02_ Text three swordsman
- Assembly language segment definition
- How to configure hosts when setting up Eureka
- J'ai traversé le chemin le plus fou, le circuit cérébral d'un programmeur de saut d'octets
- Go language uses the thrift protocol to realize the client and service end reports not enough arguments in call to oprot Writemessagebegin error resolution
- DOS function call
- Resume of a microservice architecture teacher with 10 years of work experience
- Design of DS18B20 digital thermometer system
猜你喜欢

吴军三部曲见识(七) 商业的本质

Yao BanZhi and his team came together, and the competition experts gathered together. What fairy programming competition is this?
Activiti directory (V) reject, restart and cancel process
字节跳动海外技术团队再夺冠:高清视频编码已获17项第一
MySQL date function
Set up the flutter environment pit collection
MySQL digital function
arithmetic operation

我走過最迷的路,是字節跳動程序員的腦回路
Some instructions on whether to call destructor when QT window closes and application stops
随机推荐
redux使用说明
The daemon thread starts redis and modifies the configuration file
Set up the flutter environment pit collection
Ce n'est qu'en apprenant que c est à la hauteur des attentes Top5 s1e8 | s1e9: caractères et chaînes & opérateurs arithmétiques
關於Stream和Map的巧用
MySQL日期函数
MySQL string function
Shell_ 06_ Judgment and circulation
Assembly language addressing mode
In the command mode in the VI editor, delete the character usage at the current cursor__ Command.
姚班智班齐上阵,竞赛高手聚一堂,这是什么神仙编程大赛?
ByteDance open source Gan model compression framework, saving up to 97.8% of computing power - iccv 2021
暑假刷题嗷嗷嗷嗷
JVM类加载子系统
DOS function call
1. JVM入门介绍
100张图训练1小时,照片风格随意变,文末有Demo试玩|SIGGRAPH 2021
Activit零零碎碎要人命的坑
MySQL date function
Activit fragmented deadly pit