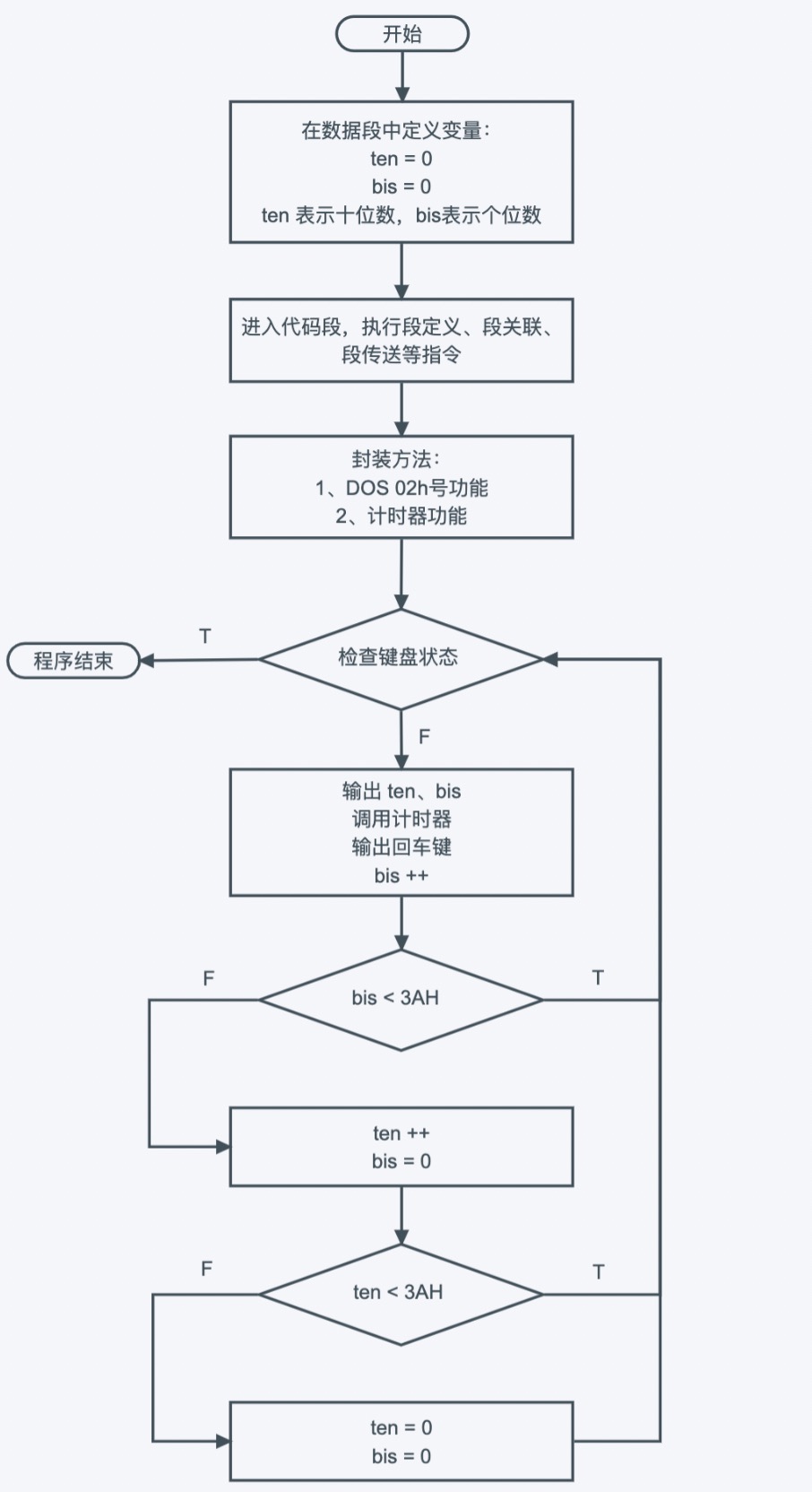
当前位置:网站首页>Notes on how the network is connected
Notes on how the network is connected
2022-07-06 16:58:00 【Xiaoxiamo】
Catalog
- Before the order
- One 、 Generate HTTP The request message
- Two 、 towards DNS Server query Web Server's IP Address
- 3、 ... and 、 Browser entrusts protocol stack to send message
- Four 、IP Packet sending and receiving operation with Ethernet
- 5、 ... and 、 A hub 、 Switch 、 Router
- 6、 ... and 、 What's the mystery of the LAN on the server side
- 7、 ... and 、 Request arrival Web The server , Response back to browser
The overall structure
The book is mainly written around the following structure 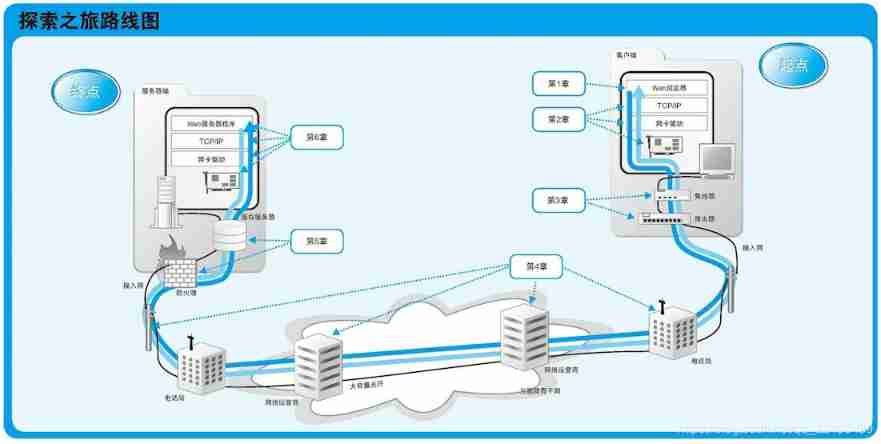
The journey of network package
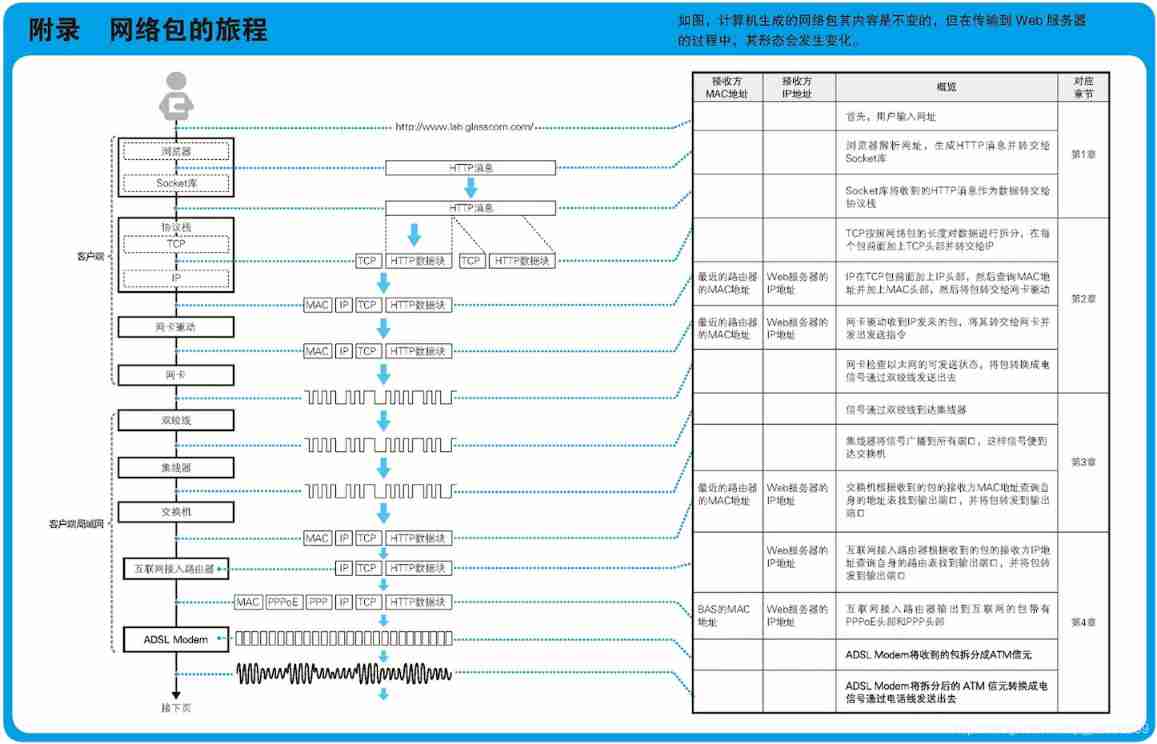
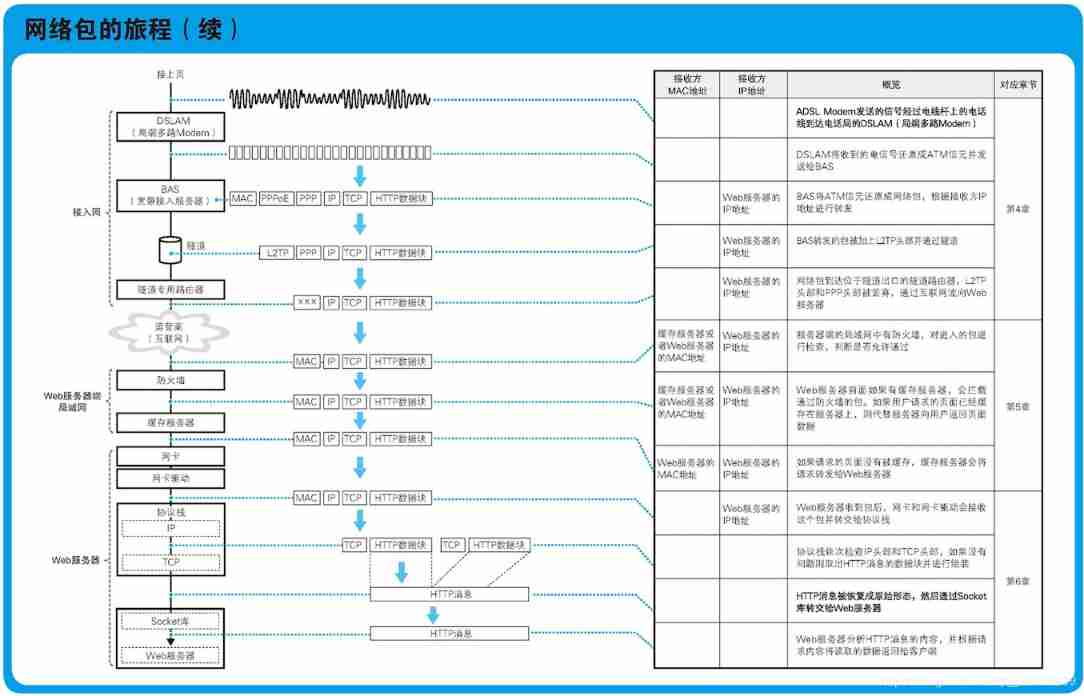
One 、 Generate HTTP The request message
1.1、 Browser input URL
http://www.baidu.com
1.2、 First of all, according to the HTTP The rules of , analysis URL
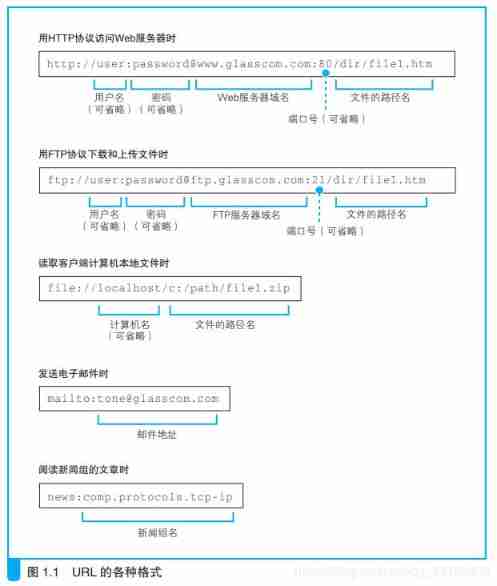
1.3、URL Several cases of omitting file names
- a) http://www.baidu.com/dir/
stay /dir/ The accessed file name is omitted later , The server has set the default file name to be accessed when the file name is omitted , Usually visit /dir/index.html perhaps /dir/default.html
- b) http://www.baidu.com/dir
General treatment scheme : If web There is... On the server dir file , Will dir Treat as file name ; If web There is a file named on the server dir The catalog of , Will dir Treat as a directory
- c) http://www.baidu.com/
This URL Express : It visits a person named / The catalog of . Because the file name is omitted , So according to the previous situation , The file it accesses is /index.html perhaps /default.html.
notes :/ The directory represents the top level in the directory hierarchy 『 root directory 』
- d)、http://www.baidu.com
When there is no path , Means to access the default folder set in advance under the root directory , That is to say /index.html perhaps /default.html
1.4、HTTP The basic idea of
HTTP agreement : It defines the content and steps of interactive information between the client and the server
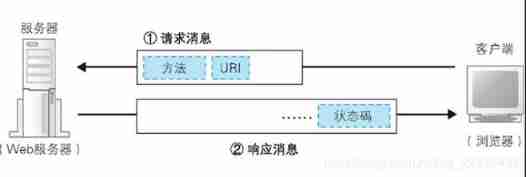
HTTP The request message contains 『 What to 』 and 『 How to operate 』 Two parts .
Which is equivalent to 『 What to 』 The part of is called URI. Generally speaking URI The content of a web page is a file name or a CGI The file name of the program , for example "/dir/file.html"、"/dir/program.cgi" etc. .
among 『 How to operate 』 The part of is called the method . Method means that you need to let web What does the server do , Typical examples include reading URI Data represented 、 Pass the data entered by the client to CGI Procedure, etc .
URI:Uniform Resource Identifier, Uniform resource identifiers
CGI Program : Yes web The rules for a server program to call other programs are defined as CGI, The program that installs this rule to work is CGI Program .
HTTP Main methods
| Method | meaning |
|---|---|
| GET | obtain URI Designated information , If URI Specified file , The contents of the file are returned ; If URI Specifies the CGI Program , The output data of the program is returned |
| POST | Send data from the client to the server . It is generally used to send the data filled in the form |
1.5、 Generate HTTP The request message
1.6、 Receive a response message after sending the request
Response status code 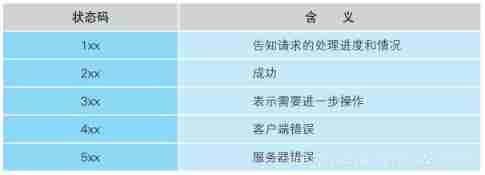
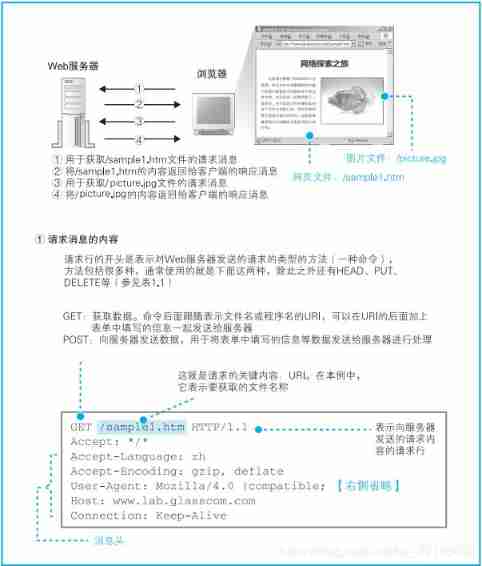
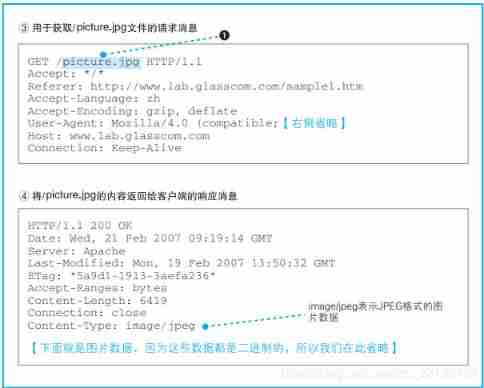
1.7、 Request that the page contain pictures
1 Only one request message can be written URI, If you need to get multiple files , Each file must be sent separately 1 The request
Two 、 towards DNS Server query Web Server's IP Address
The browser can parse the URL and generate HTTP news , But it does not have the function of sending messages to the network , Therefore, this function needs to be entrusted to the operating system . When delegating the operating system to send a message , The of the communication object must be provided IP Address , Not domain names , So in HTTP After message , We need to query according to the domain name IP Address
2.1、TCP/IP The Internet
The Internet and the company's internal LAN are based on TCP/IP The idea to design ,TCP/IP The structure of is composed of some small subnets , A large network connected by a router , The subnet here can be understood as several computers connected by hubs , We regard it as a unit , It's called a subnet , Connect subnets through routers , It forms a network .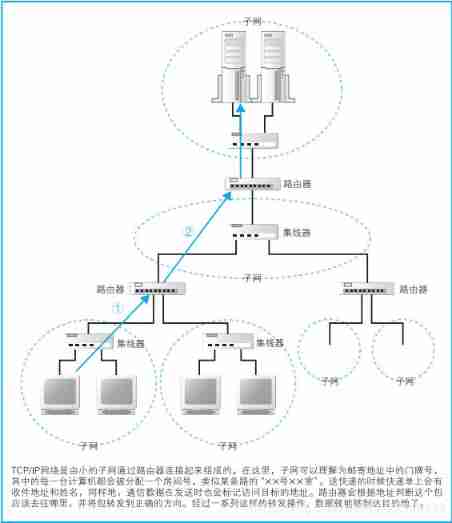
2.2、IP Address
In the network , All devices will be assigned an address , This address is equivalent to a certain road in the display "XX Number XX room ", among " Number " The corresponding number is assigned to the whole subnet , and " room " The corresponding number is assigned to computers in the subnet , This is the address in the network ." Number " Called network number ," room " Called host number , The entire address is called IP Address .
IP Address = network number + Host number
preheating : Data transfer process
adopt IP Address we can determine the location of the access object server , This sends the message to the server . The specific process of message transmission is explained in detail in the following chapters , But now let's have a brief look . The message sent by the sender first passes through the hub in the subnet , Forward to the router closest to the sender ( Upper figure ①). Next , The router will determine the location of the next router according to the destination of the message , Then send the message to the next router , That is, the message is forwarded to the next router through the hub in the subnet again ( Upper figure ②). The previous process is repeated , Finally, the message is delivered to the destination .
2.3、IP Address structure
Actually IP The address is a string of 32 The bit (bit) The number of , according to 8bit=1byte( byte ) Divide into groups 4 Group , They are expressed in decimal system . That's what we see IP Address format , But we can't tell which part of the network number is based on this string of numbers , Which part is the host number . stay IP In the rules of address , Connecting the network number and the host number, the total is 32 The bit , But the specific structure of these two parts is not fixed . When building a network , Users can decide the allocation relationship between them , therefore , We also need additional information to indicate IP Internal structure of address .

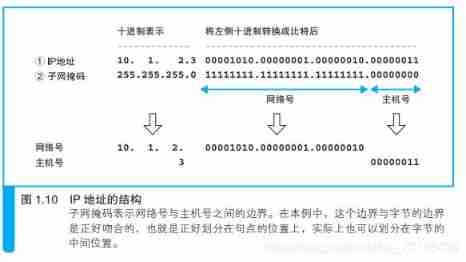
IP Host number of the address :
whole 0: Represents the entire subnet
whole 1: Means to send packets to all devices on the subnet , namely 『 radio broadcast 』
2.4、 How browsers send messages to DNS The server sends out the query ?
DNS Parser
towards DNS The server sends a query , That is to say, to DNS The server sends a query message , And receive the response message returned by the server . let me put it another way , about DNS The server , There must be a corresponding on our computer DNS client , And it's equivalent to DNS The part of the client is called DNS Parser , Or parser for short . adopt DNS Inquire about IP The operation of address is called domain name resolution , So it's responsible for performing parsing ( resolution) This operation is called parser ( resolver) 了 . The parser is actually a program , It's included in the operating system's Socket In the library .
library
First , What on earth is a library ? A library is a collection of common program components , Other applications need to use components . Libraries have many benefits . First , Using ready-made components to build applications can save programming workload ; secondly , The standardization of programs can be achieved by using the same components in multiple programs . In addition, there are many other benefits , Therefore, the idea of using libraries for software development has been very popular , There are also many kinds and quantities of libraries .
Socket library
Socket Library is also a kind of Library , It is a collection of program components used to call network functions . It contains program components that allow other applications to call the network functions of the operating system , The parser is one of the program components in this library .
2.5、 How to use the parser to DNS The server sends a query

According to the domain name IP Address time , The browser will use Socket The parser in the library .
After calling the parser , The parser will go to DNS The server sends a query message , then DNS The server will return a response message . The response message contains the IP Address , The parser will take out IP Address , And write it to the memory address specified by the browser . As long as the train diagram 1.11 This line of program in , You can complete all the previous work , We're done, too IP Address query . Next , The browser is looking at Web When the server sends a message , Just take it out of the memory address IP Address , And connect it with HTTP The request message is delivered to the operating system .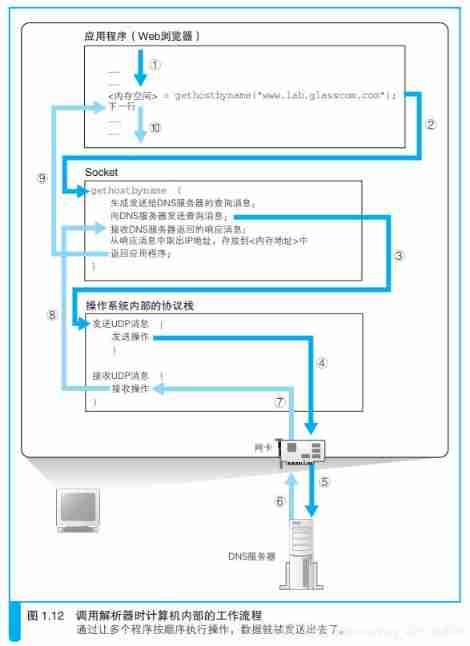
2.6、 How to get DNS The server IP Address ?(Domain Name System, The domain name system )
towards DNS When the server sends a message , We also need to know DNS Server's IP Address . It's just this IP The address is for TCP/ IP It's a pre-set item of , There's no need to look it up any more . In different operating systems TCP/ IP There are also differences in the setting methods of ,Windows The settings in are shown in the following figure , The parser will be based on the settings here DNS The server IP Address to send messages .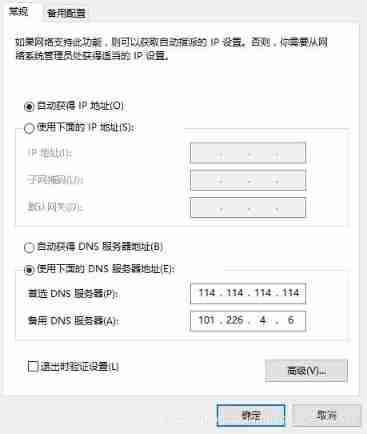
2.7、DNS How the server works
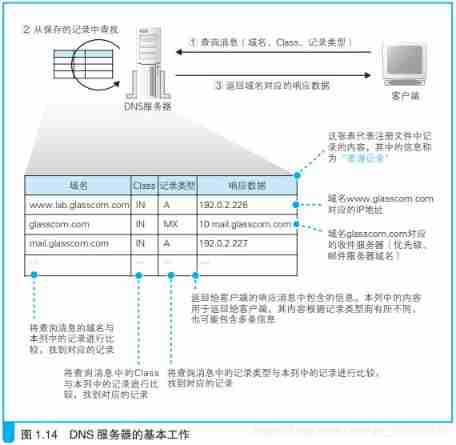
DNS The server will from the domain name and IP Find the corresponding record in the cross reference table of address , And back to IP Address .
domain name
for example :www.baidu.com
The server 、 Mail server ( In the email address @ Back section ) The name of
Class
In the earliest design DNS Scenario time , DNS Applications in networks other than the Internet are also considered , and Class It's information used to identify the network . however , Now there is no other network except the Internet , therefore Class The value of is always on behalf of the Internet IN
Record type
for example :A = IP Address
MX = Mail server
CNAME = Domain name related alias
Indicates what type of record the domain name corresponds to . for example , When the type is A when , The domain name corresponds to IP Address ; When the type is MX when , Indicates that the domain name corresponds to the mail server . For different record types , The information that the server returns to the client will also be different
2.8、 How in tens of thousands DNS Target found in server DNS The server
Domain name hierarchy
DNS The domain names in are separated by periods , such as www.lab.glasscom.com, The period here represents the boundary between different levels , It is equivalent to the organizational structure of the company without the Department 、 Families and so on , It's just separated by periods .
In the domain name , The more right the position is, the higher the level is , such as www. lab. glasscom. com This domain name, according to the organizational structure of the company , Is probably “ com Business groups glasscom Ministry lab Coed www” such . among , The part equivalent to one level is called domain . therefore , com The next level of the domain is glasscom Domain , The next level is lab Domain , Next is www The name .
Root region
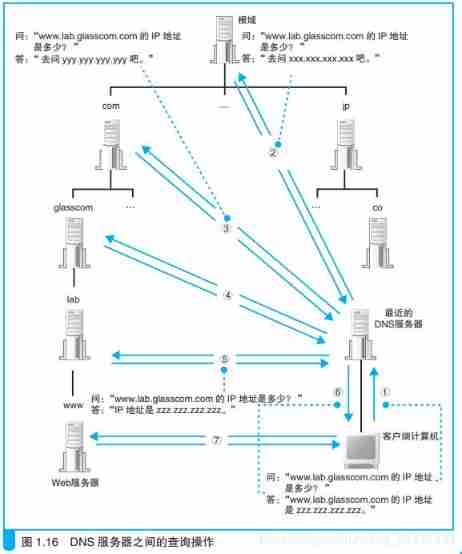
com、jp、cn These domains ( It's called the top level domain ) It's the top floor , Each of them is responsible for keeping the records of its subordinates DNS Server information , But it's not . On the Internet ,com and jp There is also a level of domain above , This is called the root domain . The root domain is not like com、 jp It has its own name , Therefore, it is often omitted when writing domain names , If you want to explicitly represent the root domain , It should be like www. lab. glasscom. com. So add a period at the end of the domain name , And this last period represents the root field . however , Usually don't write the last period , Therefore, the existence of root domain is often ignored , But the root domain is real after all , Root domain DNS In the server com、 jp Waiting DNS Server information . Because the superior DNS The server keeps all its subordinates DNS Server information , So we can start from the root domain and find the of any domain all the way down DNS The server .
Find the target through the root domain DNS The server
There is another work to be done , That is to put the root domain DNS The server information is stored in the Internet DNS Server . thus , whatever DNS The server can find and access the root domain DNS The server . therefore , As long as the client can find any one DNS The server , You can find the root domain through it DNS The server , And then follow the trail to find a target at the bottom DNS The server . Assigned to the root domain DNS Server's IP There are only... Addresses in the world 13 individual , And the addresses hardly change , So keep these addresses in all DNS It's not hard to be on the server . actually , Root region DNS Information about the server has been included in DNS In the configuration file of the server program , So just install DNS Server program , This information is automatically configured .
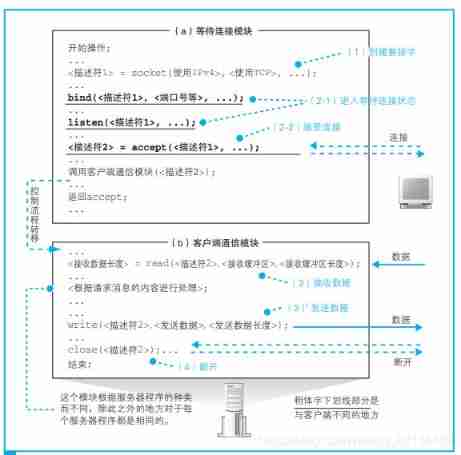
3、 ... and 、 Browser entrusts protocol stack to send message
Overall flow chart
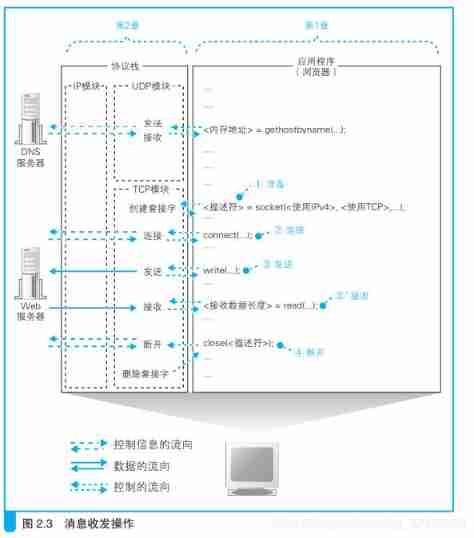
Create socket
< The descriptor > = socket(< Use IPv4>,< Use TCP>,…)
Browser call Socket In the library socket Program components , Just like calling the parser , call socket after , The control process will be transferred to socket Internal and execute the operation of creating socket , After completion, the control process will be handed back to the application .
Application calls socket Request to create socket , The protocol stack performs the operation of creating sockets according to the application of the application . In the process , The protocol stack will first allocate the memory space required to store a socket , Then write the initial state . This memory space is used to record the control information of the socket .
Socket Once created , The protocol stack will return a The descriptor , The application will store the received descriptor in memory .
The descriptor
The application is through “ The descriptor ” This kind of Something like a number plate to identify the socket .
Descriptors are used to identify different sockets , You can make the following understanding . We are now only concerned with browser access Web The process of the server , But in fact, the computer will communicate multiple data at the same time , For example, you can open two browser windows , Visit two stations at the same time Web The server . At this time , There are two data sending and receiving operations at the same time , You need to create two different sockets . This is an example , Multiple sockets may exist on the same computer at the same time , In this case , We need a way to identify a particular socket , This method is called descriptor . We can understand the descriptor as the number assigned to a socket . Maybe just saying the number is not enough , You can imagine the scene when you check in your luggage in the hotel , The hotel staff will give you a number plate , Show the number plate to the service personnel , You can retrieve your checked baggage , The principle of descriptor is similar to this . When the socket is created , We can use this socket to send and receive data . At this time , As long as we show the descriptor , The protocol stack can determine which socket we want to use to connect or send and receive data .
Because the socket records the information of both sides of communication and the state of communication , So as long as the corresponding socket is determined through the descriptor , The protocol stack can get all the relevant information , thus , The application does not need to tell the protocol stack who to communicate with every time .
Socket
socket The essence is programming interface (API), Yes TCP/IP Encapsulation ,TCP/IP It is also necessary to provide an interface for programmers to do network development , This is it. Socket Programming interface (API) .
Socket is an abstract representation of endpoint in the process of network communication , Contains five kinds of information necessary for network communication : The protocol used for the connection , localhost IP Address , Protocol port of local process , Remote host's IP Address , Protocol port of remote process .
socket = IP address + TCP/UDP + port.
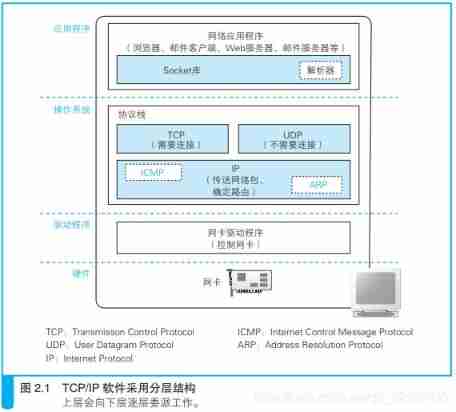
Protocol stack
The network control software in the operating system is the protocol stack , Network hardware is network card .
The relationship between socket and protocol stack
All kinds of control information used to control communication operation are recorded in socket , The protocol stack needs to judge the next action based on this information , That's what sockets do .
The protocol stack works according to the control information recorded in the socket .
Network protocol
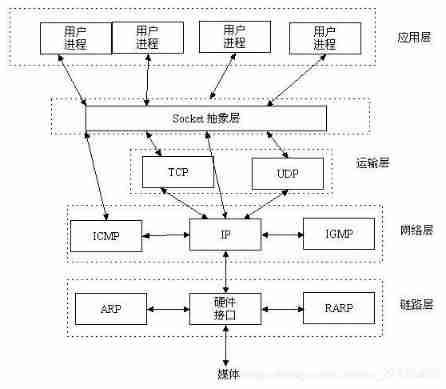
| OSI Seven layer network model (Open System Interconnect) | TCP/IP A network model | Corresponding network protocol |
|---|---|---|
| application layer (Application) | HTTP、FTP、TFTP、SMTP、NFS | |
| The presentation layer (Presentation) | application layer | |
| The session layer (Session) | SMTP、DNS | |
| Transport layer (Transport) | Transport layer | TCP、UDP |
| The network layer (Network) | The network layer | IP、ARP、ICMP |
| Data link layer (Data Link) | Data link layer | |
| The physical layer (Physical) | The physical layer |
3.2、 Connect to server
#include <sys/socket.h>
int connect(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr* servaddr, socklen_t addrlen); // return : Success for 0, error -1
The application calls Socket The name in the library is connect Program components to complete this operation .
The first parameter : namely The descriptor ,connect The protocol stack will be informed of the descriptor specified by the application , Then the protocol stack determines which socket to use to connect to the server socket according to this descriptor , And perform the operation of connection
The second parameter , namely The server IP Address , It is through DNS The information of the server we want to access obtained from the server query IP Address .
The third parameter , namely Port number ,IP An address is a number assigned to distinguish between computers in a network . therefore , Just know IP Address , We can identify a computer on the network . however , The object of connection operation is a specific socket , Therefore, the specific socket must be recognized , And just by IP Address can't do this .
If descriptors are the mechanism used to identify sockets inside a computer , Then the port number is the mechanism used to make the other party of communication recognize the socket .
The port number used on the server is specified in advance according to the type of application , That's it .
Web yes 80 Port no. , E-mail is 25 Port no. 65
problem : We know the port number of the server , But the server does not know the port number of the client ?
Since it is determined that the socket of the connection object needs to use the port number , Then the server also needs to know the socket number of the client , How to solve this problem ?
Here's the thing , First , When the client creates the socket , The protocol stack will randomly assign a port number to this socket . Next , When the protocol stack performs a connection operation , The randomly assigned port number will be notified to the server .
Connection server essence
Connection is actually the exchange of control information between the two sides of communication
Control information
There are two types of control information used in communication operations .
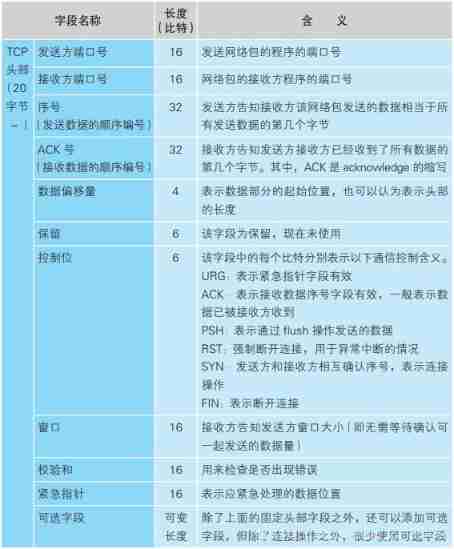
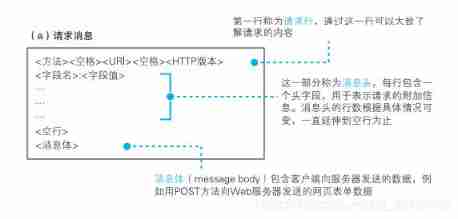
(1) The information recorded in the header
(2) Socket ( Memory space in the protocol stack ) Information recorded in
Control information I : The information recorded in the header
They are the control information exchanged when the client and server communicate with each other . These fields are fixed , In connection 、 Send and receive 、 Disconnection and other stages , Every time a client communicates with a server , All need to provide these control information . say concretely , This information will be added at the beginning of the network package passed between the client and the server . In the connection phase , Because data sending and receiving has not started yet , There is no actual data in the network packet , Only control information . This control information is located at the beginning of the network packet , So it's called the head . Besides , Ethernet and IP The protocol also has its own control information , This information is also called Head , To avoid confusion between different heads , We usually write it down as TCP Head 、 Ethernet head 、 IP Head .
Control information II : Socket ( Memory space in the protocol stack ) Information recorded in
That is to save in the socket , Information used to control the operation of the protocol stack . The information passed by the application and received from the communication object will be saved here , Information such as the execution status of sending and receiving data operations will also be saved here , The protocol stack will perform each step of operation according to this information .
3.2.1、 The actual process of connection operation
This process is called from the application Socket Library connect At the beginning ( Look at the picture above 『 Overall flow chart 』 in ②). >
connect(< The descriptor >,< The server IP Address and port number >, …)
The first step in the connection operation is TCP A header representing the connection control information is created at the module .
adopt TCP The sender and receiver in the header can find the socket to be connected .
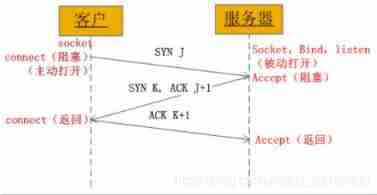
TCP To establish a connection “ Three handshakes ”
- The client sends a... To the server SYN J
- The server responds to the client with a SYN K, Also on SYN J Confirm ACK J+1
- The client sends a confirmation to the server ACK K+1
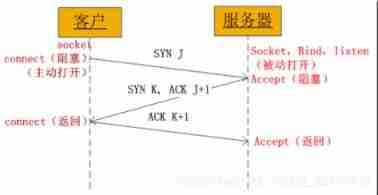
As you can see from the diagram , When the client calls connect when , Connection request triggered , Sent... To the server SYN J package , At this time connect Go into blocking mode ; The server listens for connection requests , I will receive SYN J package , call accept Function to receive the request and send it to the client SYN K ,ACK J+1, At this time accept Go into blocking mode ; Client receives server's SYN K ,ACK J+1 after , At this time connect return , Also on SYN K Confirm ; Server received ACK K+1 when ,accept return , Now the three handshakes are over , Connection is established .
Once the connection is established , The connection operation of the protocol stack is over , in other words connect Execution completed , The control flow is handed back to the application .
3.3、 Sending and receiving data
3.3.1、 take HTTP The request message is delivered to the protocol stack
Next, we will enter the data sending and receiving stage . The data sending and receiving operation is called from the application write Give the data to be sent to the beginning of the protocol stack ( Look at the picture above 『 Overall flow chart 』 in ③), After receiving the data, the protocol stack performs the sending operation .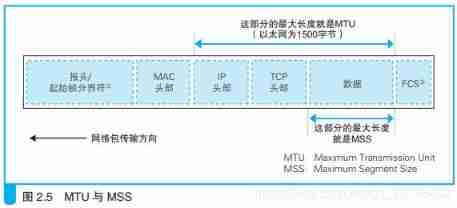
MTU/MSS
MTU: Maximum Transmission Unit, Maximum transmission unit . The maximum length of a network packet , Ethernet is generally 1500 byte .
MSS: Maximum Segment Size, Maximum segment size . After removing the head , What a network packet can hold TCP Maximum length of data .TCP and IP The head of usually adds up to 40 byte , therefore MTU Subtracting this length is MSS. for example , In Ethernet , MTU by 1500, therefore MSS Namely 1460. TCP/ IP Some optional parameters can be used ( protocol option), Such as encryption , At this time, the length of the head will increase , that MSS It will shorten as the length of the head increases .
3.3.2、 Split large data
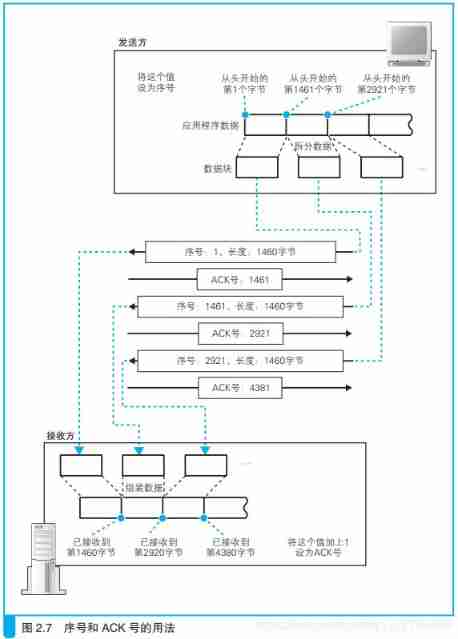
The data of an application is generally large , therefore TCP The data will be split according to the size of the network packet .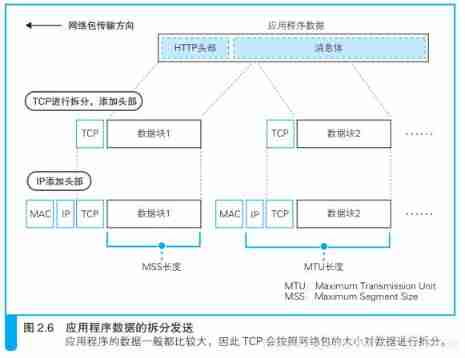
3.3.3、TCP adopt ACK No. ensure whether the network packet is received
adopt “ Serial number ” and “ ACK Number ” You can confirm whether the receiver has received the network packet .
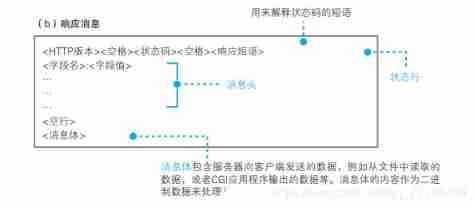
3.3.4、 Accept HTTP The response message
First , After the browser sends the request message to the delegation protocol stack , Would call read Program ( Look at the picture above 『 Overall flow chart 』 in ④) To get the response message . then , The control process will pass read Transfer to protocol stack , Then the protocol stack will execute the following
The operation of . Just like sending data , Receiving data also needs to be temporarily stored in the receiving buffer , The operation process here is as follows . First , The protocol stack attempts to fetch data from the receive buffer and pass it to the application , But at this time, the request message has just been sent , The response message may not have returned . The return of the response message needs to wait for some time , Therefore, there is no data in the receiving buffer , Then the operation of receiving data cannot continue . At this time , The protocol stack will delegate the application , That is, the work of fetching data from the receive buffer and passing it to the application is temporarily suspended , Wait until the response message returned by the server arrives, and then continue to perform the receiving operation .
The protocol stack checks the received data blocks and TCP The content of the head , Determine whether there is data loss , If there is no problem, return ACK Number . then , The protocol stack temporarily stores data blocks in the receive buffer , And connect the data blocks in order to restore the original data , Finally, give the data to the application . say concretely , The protocol stack will copy the received data to the memory address specified by the application , Then return the control process to the application . After the data is handed over to the application , The protocol stack also needs to find an appropriate time to send window updates to the sender .
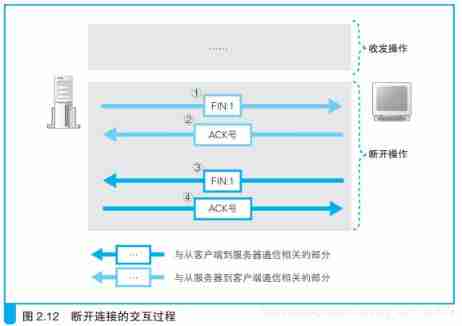
3.4、 disconnect , And delete the socket
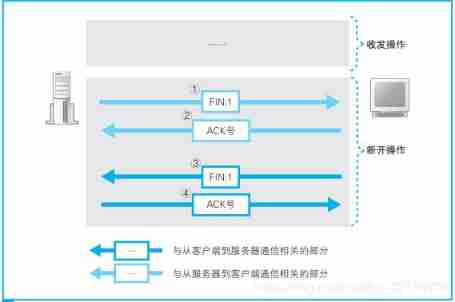
3.4.1、 Disconnect from the server
Here we take the disconnection process initiated by the server as an example to explain .
First , The application on the server side will call Socket Library close Program . then , The protocol stack of the server will generate a message containing disconnection information TCP Head , Specifically, it is to put the... In the control bit FIN Bit set to 1. Next , The protocol stack will delegate IP The module sends data to the client . meanwhile , The socket of the server will also record the information related to the disconnection operation .
3.4.2、 Disconnect from the client
- The application process first calls close Active close connection , At this time TCP Send a FIN M;
- The other end receives FIN M after , Perform passive shutdown , For this FIN Confirm . Its reception is also passed to the application process as a file Terminator , because FIN It means that the application process can no longer receive additional data on the corresponding connection ;
- After a while , Receive the application process call of the end of file close Turn it off socket. This leads to its TCP Also send a FIN N;
- Received this FIN Source sender of TCP Confirm it .
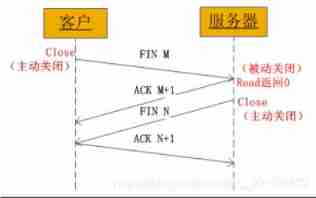
3.4.3、 Delete socket
After the communication with the server ends , The socket used for communication will no longer be used , Then we can delete the socket . however , The socket will not be deleted immediately , Instead, it will wait for a period of time before being deleted . Waiting for this time is to prevent misoperation .
Examples of misoperation : If the last client returns ACK The number is lost , What will happen ? At this time , Server did not receive ACK Number , It may be resend FIN. If the socket of the client has been deleted , What will happen ? Socket deleted , Then the control information stored in the socket disappears , The port number corresponding to the socket will be released . At this time , If another application wants to create a socket , The new socket happens to be assigned the same port number again , And the server retransmits FIN Just arrived at , What will happen ? Originally this FIN It is sent to the socket just deleted , But the new socket has the same port number , So this FIN It will run into the new socket by mistake , The new socket begins to perform the disconnect operation . Why not delete the socket immediately , Is to prevent such misoperation .
TCP Overview of the whole process 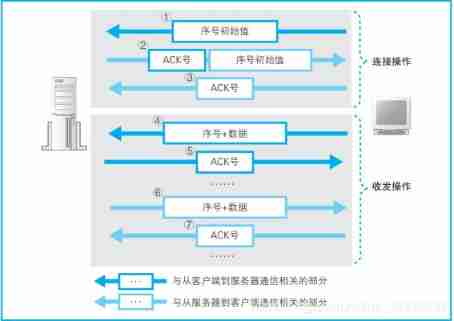
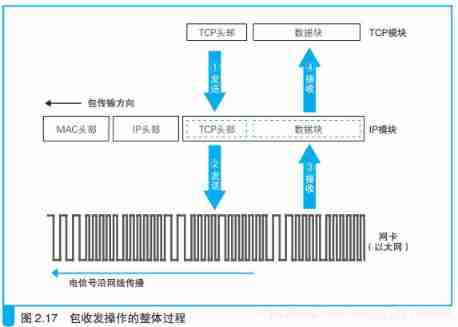
Four 、IP Packet sending and receiving operation with Ethernet
4.1、 Basic knowledge of package
TCP The module is performing the connection 、 Send and receive 、 Disconnect and other stages of operation , You have to delegate IP The module packages the data and sends it to the communication object . We are TCP It is often mentioned in the explanation of IP, Let's talk about IP How the module sends packets to the other side .
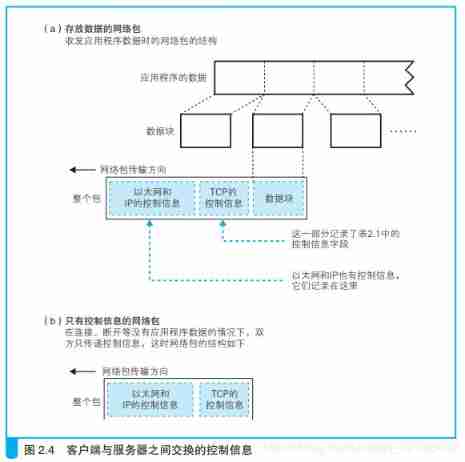
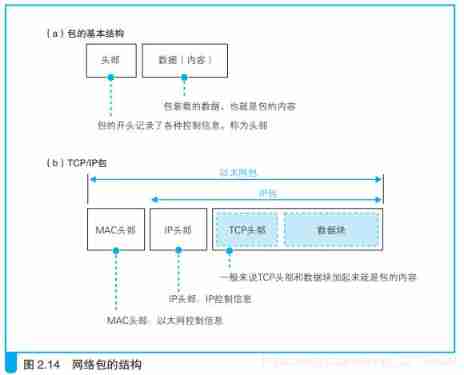
Before starting this topic , Let's first introduce some basic knowledge about network packets . First , The package is composed of header and data ( The figure below (a)). The header contains the destination address and other control information , You can understand it as the face list of express packages ; Behind the header is the data to be sent by the entrusting party to the other party , It is equivalent to the goods in the express package . The process of sending a package to the destination is shown in the figure 2. 15 Shown .
4.2、IP Role of module
4.2.1、 When sending the packet ,IP Modules work
After receiving the entrustment , IP The module treats the contents of the package as a whole piece of data , Add a header containing control information to the front .
IP The module is responsible for adding the following two headers :
(1)IP Head : IP With the head , contain IP Address .IP The head contains IP Under the agreement 、 according to IP Address the control information required to send the packet to the destination ;
(2)MAC Head : Ethernet head , contain MAC Address .MAC The header contains the control information needed to transmit the packet to the nearest router through the Ethernet LAN .
All in all , Add these two heads , One package is sealed , These are the IP The module is responsible for .
4.2.2、 When receiving packets ,IP Modules work
The returned packet will also be sent back through the forwarding device , Then we need to receive this package . The process of receiving is opposite to that of sending , Information is first transmitted from the network cable in the form of electrical signals , Then the network card converts it into digital information and transmits it to IP modular ( Image below “ ③ receive ”). Next , IP The module will MAC Head and IP What's behind the head , That is to say TCP Header plus data block , Pass to TCP modular . The next operation is what we talked about before TCP The module is responsible for .
4.3、 The generation contains the receiver IP Address of the IP Head
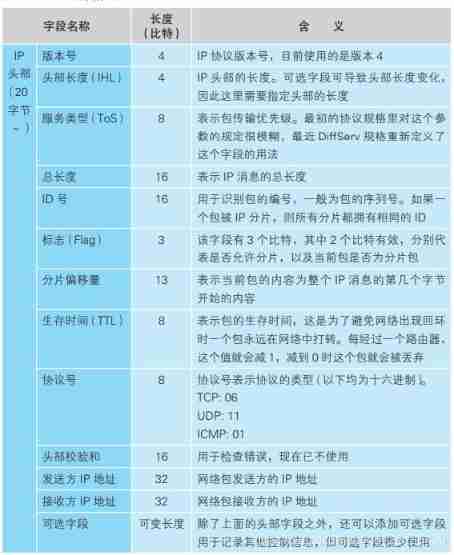
IP The head of the “ The receiving party IP Address ” Fill in the IP Address .
The sender IP The address needs to determine the network card used for sending , And fill in the name of the network card IP Address .
The problem is coming. : One computer has multiple network cards , How to set the sender IP Address ?
Many servers will install multiple network cards , At this time, a computer has multiple IP Address , Fill in the sender IP You need to decide which address to fill in when you write the address . This judgment is equivalent to judging which network card should be used to send this packet among multiple network cards , It is equivalent to judging which router the packet should be sent to , So as long as the target router is determined , This determines which network card should be used , This determines the sender's IP Address .
that , How should we decide which network card to give the package to ? In fact, it is used with routers IP surface ( Also called Routing table ) The operation of determining the location of the next router is the same . Because the protocol stack IP The module and the part of the router responsible for sending and receiving packets are based on IP Protocol rules to send and receive packets , So they all use the same method to determine who to send the package to .
( The next chapter of router sending and receiving is about )
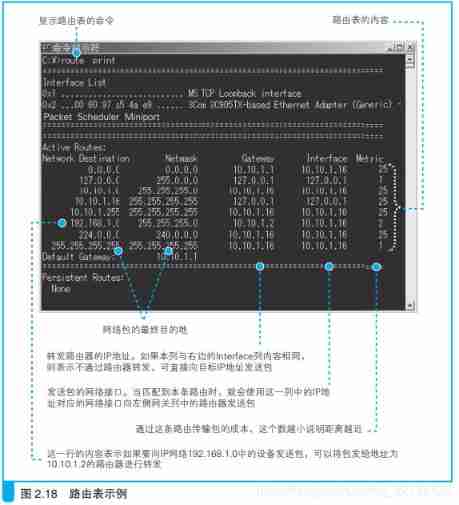
see Windows The routing table of this machine Route Table
4.4、 For generating Ethernet MAC Head
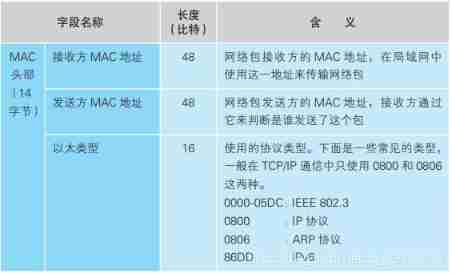
The sender MAC Address
The sender MAC Address , Fill in the name of the network card itself here MAC Address . MAC The address is written when the network card is produced ROM Inside , Just read out this value and write it to MAC Just the head . For the case of multiple network cards , Please recall setting the sender IP Address method . Set sender IP Address time , We have determined from which network card to send this packet , So now just put the corresponding network card MAC Just fill in the address .
The receiving party MAC Address
Just tell Ethernet the other side MAC The address of , Ethernet will help us send the packets to , So it's clear that you should fill in each other's MAC Address . However , At this point in time , We haven't sent the package yet , So first we have to find out who should send the bag to , Just look up the routing table . Find a matching entry in the routing table , Then send the bag to Gateway In column IP The address will do . Now that we know who the bag should be sent to , Then just put the other party's MAC Just fill in the address , But so far, there has been no other party's MAC Address , In other words, we don't know each other's MAC What's the address . therefore , We also need to implement according to IP Address the query MAC Address operation . For details, see 4.4.1、 adopt ARP Query the destination router's MAC Address
IP Module according to routing table Gateway The contents of the column determine who should send the package to .
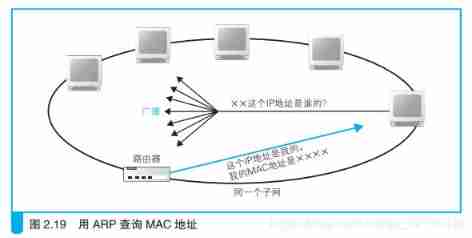
4.4.1、 adopt ARP Query the destination router's MAC Address
Here we need to use ARP agreement ( Network layer protocol ), It's very simple . In Ethernet , There is a method called broadcasting , Packets can be sent to all devices connected to the same Ethernet . ARP It's using the radio to ask questions about all the devices :“ × × This IP Whose address is ? Please take your MAC Tell me the address .” Then someone will answer :“ This IP The address is mine , my MAC The address is × × × ×.” ( The figure below )
ARP: Address Resolution Protocol, Address resolution protocol .
adopt ARP Caching improves efficiency , Avoid sending... Every time
Windows see ARP cache 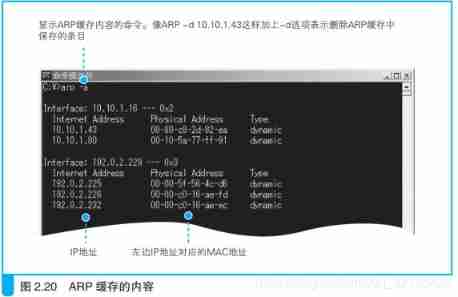
MAC Address 
MAC: Media Access Control Abbreviation . MAC Head 、 MAC The address of the MAC That's what it means . in other words , adopt MAC The header and address used in the module control packet sending and receiving operation are called MAC Head and MAC Address .
4.5、 network card - take IP Packets are converted into electrical or optical signals and sent out
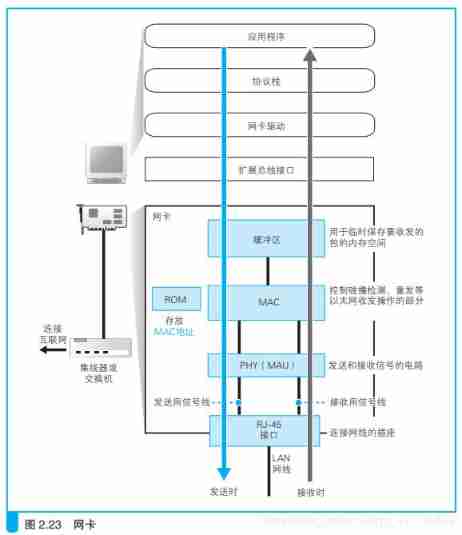
IP The generated network packet is simply a string of numeric information stored in memory , There's no way to send it directly . therefore , We need to convert digital information into electrical or optical signals , To transmit over the Internet , in other words , This is the real data sending process . It is the network card that is responsible for this operation , But the network card can't work alone , To control the network card, you also need the network card driver . Drivers are not only available for network cards , keyboard 、 mouse 、 The graphics card 、 Sound card and other hardware devices . Of course , Different manufacturers and models of network cards have different structures , Therefore, the network card driver is also a special program developed by the manufacturer .
NIC ROM The world's only MAC Address , This is written when the network card is produced .
How does the network card convert packets into electrical signals and send them to the network cable
Network card driver from IP After the module obtains the package , It will be copied to the buffer in the network card , And then to MAC The module sends the command to send the packet . Then it's the turn MAC The module works . First , MAC The module takes the package out of the buffer , And add the header and start frame delimiter at the beginning , Add a frame check sequence for error detection at the end
Add... To the network packet 3 Two control data
network card MAC The module takes the package out of the buffer , And add at the beginning Headlines and Start frame delimiter , Add at the end the... For error detection Frame check sequence .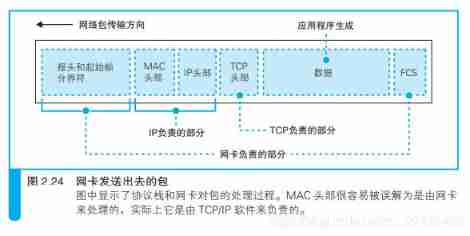
4.5.1、 Headlines
Header function
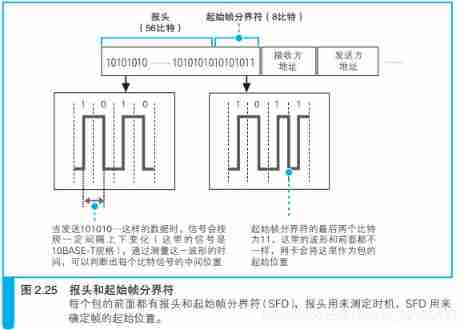
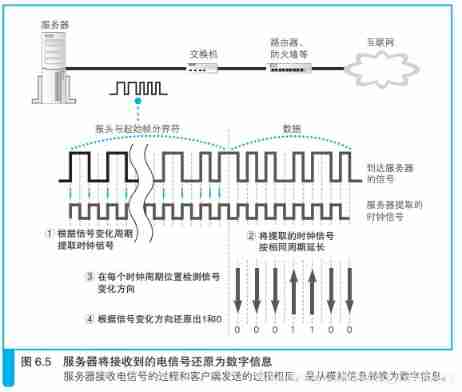
The header is a string like 10101010… such 1 and 0 Alternating bit sequences , The length is 56 The bit , Its function is to determine the reading time of the package . When these 1010 After the bit sequence of is converted into an electrical signal , It will form a waveform like the one shown in the figure . When the receiver receives the signal , When encountering such waveform, we can judge the time of reading data .
How to read data through electrical signals
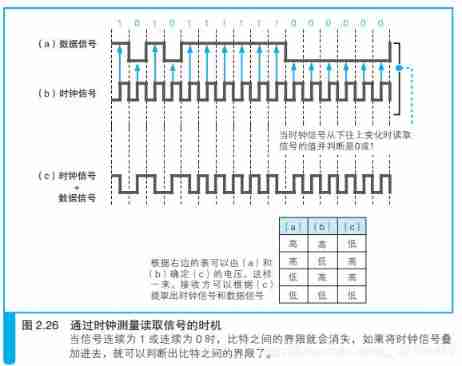
When using electrical signals to express digital information , We need to get 0 and 1 The two bits correspond to specific voltage and current respectively , Such as below ( a) Such electrical signals can express digital information . The process of reading data through electrical signals is to reverse this correspondence . in other words , By measuring the voltage and current changes in the signal , Revert out 0 and 1 Two bit values . However , The actual signal does not have auxiliary lines separating each bit as shown in the figure below , Therefore, when measuring voltage and current, we must first determine where the limit of each bit is . however , Like the picture below ( a) The one on the right 1 and 0 Continuous signals , Because the voltage and current do not change , We can't tell where each bit should be segmented .
The timing of reading the signal is measured by the clock
How to determine where each bit should be segmented ?
To solve this problem , The simplest way is to send a group of clock signals to distinguish bit intervals in addition to the data signals . Pictured ( b) Shown , When the clock signal changes from bottom to top, read the value of voltage and current , And then 0 or 1 Just make a corresponding . But there are problems with this method . When the distance is far , When the network cable is long , The length of the two lines will vary , The transmission of data signal and clock signal will cause time difference , The clock will shift .
The transmission of data signal and clock signal will cause time difference , The clock will shift .
Another method is to read when the clock signal changes from top to bottom . To solve this problem , The method of superimposing data signal and clock signal can be adopted . Such signals are shown in the figure ( c) Shown , The sender sends such a signal to the receiver . Because the clock signal is like the picture ( b) This changes at a fixed frequency , As long as we can find the cycle of this change , From the received signal ( c) Extract the clock signal ( b), Then by receiving the signal ( c) And clock signals ( b) Calculate the data signal ( a), This is the opposite of the process that the sender superimposes the data signal and the clock signal . then , Just according to the clock signal ( b) The change cycle of , We can get the signal from the data ( a) Read the corresponding voltage and current values , And restore it to 0 or 1 Bit of .
4.5.2、 Start frame delimiter
Start frame delimiter , There is a slight change in the bit arrangement at the end of it . The receiver marks this change , Start here to extract network packet data . in other words , The start frame delimiter is a marker used to indicate the start position of a packet .
4.5.3、 Frame check sequence
Last FCS( Frame check sequence ) It is used to check the waveform disorder caused by noise during packet transmission 、 Data error , It's a string 32 A sequence of bits , It is calculated from the beginning to the end of the package through a formula . The specific calculation formula is omitted here , It is similar to that used in devices such as disks CRC Error check codes are the same thing , When a bit in the original data changes , The result of calculation will change . During packet transmission , If the data changes due to the interference of noise , Then the receiver calculates FCS And calculated by the sender FCS It will be different , In this way, we can judge whether the data is wrong .
4.5.4、 Send network packets to the hub
NIC MAC The module generates general signals , Then from PHY( MAU) The module is converted into a format that can be transmitted in the network cable , And send it out through the cable .
4.6、 Receive return packet
The network card receives network packets
The first step of receiving operation is to receive all these signals no matter what happens . The beginning of the signal is the header , Synchronize the clock with the waveform of the header , Then, when encountering the starting frame delimiter, start to convert the following signal into digital information . This operation is the opposite of sending , namely PHY( MAU) The module works first , Then it's MAC modular . First , PHY( MAU) The module will convert the signal into a common format and send it to MAC modular , MAC The module converts the signal into digital information from scratch , And store it in the buffer . When the end of the signal is reached , We need to check FCS. say concretely , Is to apply all bits from the beginning to the end of the packet to the formula to calculate FCS, And then with the... At the end of the package FCS Contrast , Under normal circumstances, the two should be consistent , If the waveform is disordered due to noise interference in the middle , Then the values of the two will be different , At this time, the packet will be discarded as the wrong packet . If FCS There is no problem with the verification , Next, let's take a look MAC Receiver in the head MAC The address and network card are assigned to their own when initializing MAC Is the address consistent , To determine if the bag was sent to yourself . We don't have to receive bags sent to others , So if it's not your own bag, just throw it away , If the receiver MAC Address and yourself MAC The address is consistent , Put the package in the buffer . Come here , MAC The work of the module is completed , Next, the network card will inform the computer that a package has been received .
The network card interrupts the computer , The network card driver reads data from the network card cache
The operation of notifying the computer will use a mechanism called interrupt . When the network card performs the operation of receiving packets , The computer does not always monitor the activity of the network card , But to continue to perform other tasks . therefore , If the network card does not notify the computer , The computer doesn't know that the package has received this . The network card driver is also a program running in the computer , So it doesn't know the arrival status of the packet . under these circumstances , We need a mechanism that can interrupt the task that the computer is performing , Let the computer notice what happens in the network card , This mechanism is interrupt . say concretely , The interrupted working process is like this . First , The network card sends signals to the interrupt signal line in the expansion bus , The signal line is connected to... By an interrupt controller in the computer CPU. When an interrupt signal is generated , CPU Will temporarily suspend the task being processed , Switch to the interrupt handler in the operating system . then , The interrupt handler will call the network card driver , Control the network card to perform the corresponding receiving operation .
After the network card driver is called by the interrupt handler , The received packet will be extracted from the buffer of the network card , And pass MAC The Ethernet type field in the header determines the type of protocol . Now we use... In most cases TCP/ IP agreement , But in addition to TCP/ IP There are many other types of agreements , for example NetWare Used in IPX/ SPX, as well as Mac Used in computers AppleTalk Such agreement . These protocols are assigned different Ethernet types , Such as 0080( Hexadecimal ) representative IP agreement , The network card driver will give such a package to TCP/ IP Protocol stack ; If it is 809B said AppleTalk agreement , Just give the bag to AppleTalk Protocol stack , And so on .
4.7、 Send the response package of the server from IP Pass to TCP
Let's assume that Web The server returned a network packet , So what will the protocol stack do 100? The Ethernet type of the package returned by the server should be 0800, Therefore, the network card driver will give it to TCP/ IP Protocol stack for processing . Then it's the turn IP The module starts working first , The first step is to check IP Head , Confirm whether the format is correct . If the format is OK , The next step is to view the receiver IP Address . If the device receiving the network packet is a Windows Client computers , Then the receiver of the package returned by the server IP The address should be consistent with the address of the client network card , After checking and confirming, we can receive the package .
IP Module check IP Head , If the receiver IP The address is not your own address , adopt ICMP Feedback back
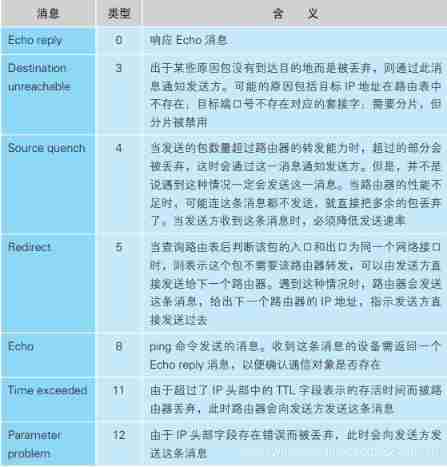
If the receiver IP The address is not your own address , Then something must have gone wrong . The client computer is not responsible for forwarding packets , Therefore, you should not receive a package that is not sent to you 101. When such a mistake occurs , IP The module will go through ICMP The message informs the sender of the error ( chart 2. 1). ICMP Specifies various types of messages , As shown in the table . When we encounter this error , IP The module will pass the Destination unreachable Inform the other party of the news . From the contents of this table, we can see all kinds of errors that can be encountered in the process of receiving and forwarding packets , So I hope you have a look at this table .
IP Module check IP Head , If the receiver IP The address is your own address , Regroup in pieces
If the receiver IP The address is correct , Then this packet will be received , At this time, another work needs to be completed . IP The protocol has a function called sharding . Simply speaking , Only small packets can be transmitted in the network cable and LAN , Therefore, the large package needs to be cut into multiple small packages . If the received packet is segmented , that IP The module will restore them to the original package . The split bag will be in IP Mark in the flag field of the header , When a segmented package is received , IP The module will temporarily store it in the internal memory space , And then wait IP Have the same... In the head ID All the bags have arrived , This is because all slices of the same package have the same ID. Besides , IP The head also has a slice offset ( fragment offset) Field , It indicates the position of the current partition in the whole package . Based on this information , After all the pieces are received , You can restore them to the original package , This operation is called fragment reorganization .
TCP Module receives packets
Next, the bag will be handed over to TCP modular . TCP The module will be based on IP Receiver and sender in the header IP Address , as well as TCP The receiver and sender port numbers in the header are used to find the corresponding socket . After finding the corresponding socket , According to the communication status recorded in the socket , Perform the corresponding operation . for example , If the content of the package is application data , Then return to confirm the received packet , And put the data in the buffer , Wait for the application
5、 ... and 、 A hub 、 Switch 、 Router
(1) The router judges the location of the next router according to the target address
(2) The hub transmits network packets to the next route in the subnet
actually , A hub is a device that transmits packets according to Ethernet rules , The router is based on IP The device that rules the transmission of packets , Therefore, we can also make the following understanding .
(1)IP The protocol judges the next according to the target address IP Location of forwarding device
(2) The Ethernet protocol in the subnet transmits the packet to the next forwarding device
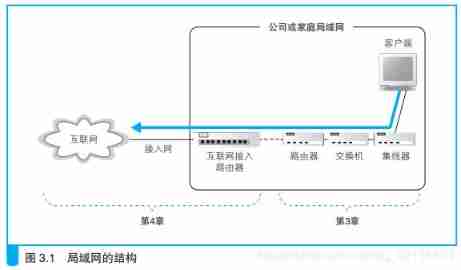
Scene settings : The transmission process of network packets before entering the Internet . Here we assume that the LAN structure connected by the client computer is like the following figure . in other words , After the client sends the package from the network , Going through the hub 、 Switches and routers eventually enter the Internet . actually , The router used in our home has integrated the functions of hub and switch , It's rare to use a stand-alone device like this .
5.1、 The signal propagates in the network cable
network card -> Ethernet cable -> A hub
Start from the signal flowing out of the network card into the network cable . In the network card PHY( MAU) 2 The module is responsible for converting packets into electrical signals , The signal goes through RJ-45 The interface enters the twisted pair cable , The enlarged view of this part is shown in the right part of the figure below . The essence of Ethernet signal is positive and negative voltage , You can think of the network card PHY( MAU) A module is a circuit that outputs signals from positive and negative signal terminals .
Form of twisted pair connection between network card and hub 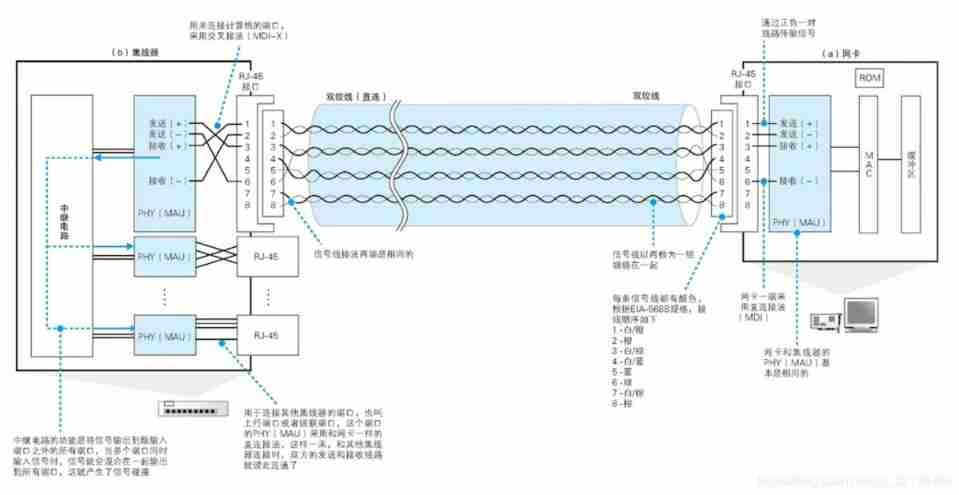
The problem is coming. : Signal attenuation
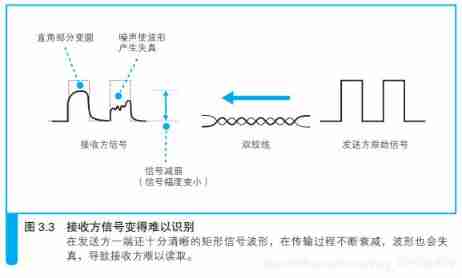
The signal is transmitted through the network cable , Energy will gradually lose . The longer the cable , The more serious the signal attenuation . The signal received by the hub sometimes decays . Here's the picture .
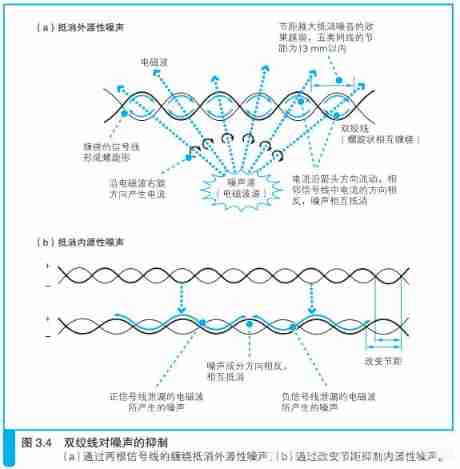
“ Twisted pair ” To suppress noise
The LAN cable is twisted pair , among “ Twisted pair ” It means that two signal wires are wound together as a group , This twist fried dough twist is designed to suppress noise. .
How noise is produced
First , Let's see how noise is produced . The cause of noise is the electromagnetic wave around the network cable , When electromagnetic waves come into contact with conductors such as metals , There will be an electric current . therefore , If there are electromagnetic waves around the network cable , It will generate a current different from the original signal in the network cable . Because the signal itself is also a current with voltage change , Its essence is the same as the current generated by noise , So the current of signal and noise will be mixed together , The waveform of the signal is distorted , This is the effect of noise .
There are two sources of electromagnetic waves : Outside and inside
There are two kinds of electromagnetic waves that affect the network cable :
One is by motor 、 Fluorescent lamp 、 CRT Electromagnetic wave leaked from display and other equipment , This electromagnetic wave comes from other equipment outside the network cable ,
Another kind of electromagnetic wave is leaked from the adjacent signal lines in the network cable . Because the transmitted signal itself is a kind of current , When the current flows through, it will send electromagnetic waves to the surroundings , These electromagnetic waves become noise for other signal lines . This internal noise is called crosstalk ( crosstalk).
Noise suppression of twisted pair
a) The external noise is offset by the winding of two signal wires ;
b) Suppress endogenous noise by changing pitch .
5.2、 The hub sends signals to all devices
The function of hub ?
The hub sends signals to all lines connected to it .
The signal reaches the hub PHY( MAU) After module , Will enter the relay circuit . The basic function of the relay circuit is to broadcast the input signal to all ports of the hub . Of course , There are also some products with signal shaping 、 Error suppression and other functions , But basically, the input signal is output to the network cable interface intact . Next , Signals flow from all interfaces , Reach all devices connected to the hub . then , These devices will pass... After receiving the signal MAC Receiver in header MAC Whether the address judgment is sent to yourself , If it is sent to yourself, accept , Otherwise, ignore . such , The network packet can reach the specified MAC The recipient of the address .
Because the hub just broadcasts the signal intact , So even if the signal is disturbed by noise and distorted , It will also be sent to the destination as is . At this time , A device that receives signals , That is, the switch 、 Router 、 The server etc. , The information will be converted into a digital signal after FCS8 Verification found an error , And discard the wrong packet . Of course , Discarding packets does not affect data transmission , Because discarded packets do not trigger an acknowledgement response . So the of the protocol stack TCP The module will detect packet loss , And retransmit the packet .
5.3、 Packet forwarding operation of switch
Switch (Switch) Meaning for “ switch ” It's used for electricity ( light ) Network equipment for signal forwarding . It can provide exclusive electrical signal path for any two network nodes of access switch . The most common switch is the Ethernet switch . Other common ones are telephone voice switches 、 Optical switch, etc
5.4、 Packet forwarding operation of router
5.4.1、 Router internal structure
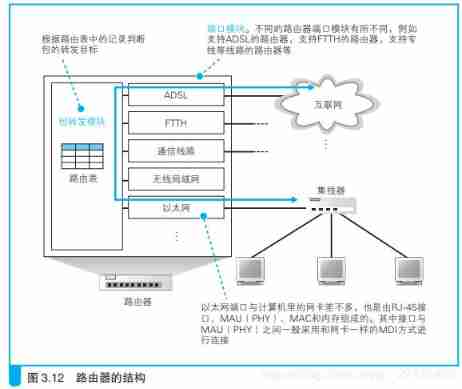
You just need to understand that the router includes two parts: forwarding module and port module . The forwarding module is responsible for determining the forwarding destination of the packet , The port module is responsible for sending and receiving packets . let me put it another way , The relationship between router forwarding module and port module , It is equivalent to the protocol stack IP Relationship between module and network card .
Router internal structure
Each port of the router has one MAC Address and IP Address .
5.4.2、 How routers work
When the router forwards packets , First, the packet sent will be received through the port , The working process of this step depends on the communication technology corresponding to the port . For Ethernet ports , Is to work according to the Ethernet specification , The WLAN port works according to the specification of WLAN , In short, the hardware of the delegate port receives the packet . Next , The forwarding module will be based on the received packet IP The receiver of the record in the header IP Address , Query in the routing table , To determine the forwarding target . then , The forwarding module transfers the packet to the port corresponding to the forwarding target , The port then sends the packet out according to the rules of the hardware , That is, the forwarding module entrusts the port module to send packets .
5.4.3、 The router forwards the packet according to the routing table
The switch is through MAC Receiver in header MAC Address to determine the forwarding target , The router is based on IP The head of the IP Judging by the address .
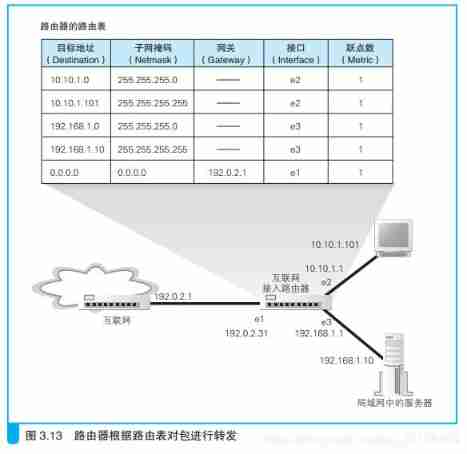
The switch matches only exactly the same records in the address table , and The router will ignore the host number part , Matches only the network part . For example , When forwarding packets, the router only depends on which area the receiver's address belongs to , × × The area goes to this side , × × The area goes that way .
5.4.4、 Packet receiving operation of router
The whole working process of the router . First , The router will receive network packets . There are different types of router ports , Here we only introduce how the Ethernet port receives packets . The structure of Ethernet port is basically the same as that of computer network card , The process of receiving packets and storing them in the buffer is almost the same as that of a network card . First , The signal reaches the network cable interface , Among them PHY( MAU) Module and MAC The module converts the signal into digital information , Then pass through the end of the package FCS Error checking , If there is no problem, check MAC Receiver in header MAC Address , Let's see if it's a bag for you , If so, put it in the receive buffer , Otherwise, discard the package . If the recipient of the package MAC The address is not myself , Explain that this package is sent to other devices , If you receive this packet, you violate the rules of Ethernet .
The router's ports all have them MAC Address , Accept only packets that match its address , Mismatched packages are discarded .
5.4.5、 Query the routing table to determine the output port
MAC Head action
After the packet receive operation is completed , The router drops the beginning of the packet MAC Head . MAC The function of the header is to deliver the packet to the router , The recipient MAC The address is the router port MAC Address . therefore , After the packet arrives at the router , MAC The head job is done , therefore MAC The head is discarded .
Network packets forwarded through routers , Its receiver MAC The address is the address of the router port MAC Address .
The router will IP The contents in the header are forwarded to the packet
- a) Query the routing table to determine the forwarding destination
About the specific work process , Let's take a practical example , As shown in the figure above , Suppose the address is 10. 10. 1. 101 To address 192. 168. 1. 10 The server sends a packet , This packet first reaches the router in the figure . The first step in determining the forwarding target , According to the receiver of the package IP Address query the destination address column in the routing table , To find a matching record . As I said before , This match does not match all 32 A bit , Instead, determine the number of bits of the network number according to the value in the subnet mask column , And match the corresponding number of bits 33. for example , No. in the picture above 3 That's ok , The subnet mask is listed as 255. 255. 255. 0, It means you need to match from the left 24 A bit . Receiver of network package IP The address and the destination address in the routing table start from the left 24 The content of bits is 192. 168. 1, So the two are matched , This row record is one of the candidate forwarding targets .
- b) The validity of the router modification packet
- c) The router splits large network packets through fragmentation function
- d) Router send operation
This step depends on the type of output port . If it's an Ethernet port , Then the packet is converted into an electrical signal and sent out according to the rules of Ethernet ; If it is ADSL According to ADSL To transform , And so on . In the home network , The back of the router is usually connected ADSL Wait for the line to access the Internet , Therefore, the router will send packets according to the rules of the access network . however , To understand the specific operation process , You need to understand the corresponding communication lines first , More complicated , So we'll leave it for the next chapter when we explore the interior of the Internet . here , Let's assume that the router is located inside a local area network such as a company , That is, the output port is also Ethernet , See how this works .
The packet sending operation of Ethernet is carried out according to the Ethernet rules , Even if the type of equipment is different , The rules are the same . in other words , Its basic process and protocol stack IP The process of sending packets by the module is the same , That is, add... In front of the bag MAC Head ,
Set some of these fields , Convert the packet into an electrical signal and send it . Let's briefly review this process . First , To judge MAC The head of the MAC What value should the address fill in , We need to determine the address of the other party according to the gateway column of the routing table . If the gateway is a IP Address , Then this IP Address is the destination address we want to forward to ; If the gateway is empty , be IP Receiver in header IP Address is the destination address to be forwarded . Know each other's IP After the address , Next we need to go through ARP according to IP Address the query MAC Address , And take the result of the query as the receiver MAC Address . Routers also have ARP cache , So first of all ARP Query in cache , Send if not found ARP Query request .
The router judges the next forwarding target as follows .
If the gateway column of the routing table is IP Address , Then this address is the next forwarding destination .
If the gateway column of the routing table is empty , be IP Receiver in header IP The address is the next forwarding destination .
Routers also use ARP To query the next forwarding target MAC Address .
When the network package is complete , It will then be converted into an electrical signal and sent through the port . The working process of this step is the same as that of the computer . for example , When Ethernet works in half duplex mode , It is necessary to confirm that there are no other signals in the line before sending , If a collision is detected , You need to wait for a period of time and resend . If Ethernet works in full duplex mode , Then there is no need to confirm the signal in the line , It can be sent directly . If the output port is Ethernet , Then the sent network packet will reach the next router through the switch . Because the receiver MAC The address is the address of the next router , So the switch will transmit the packet to the next router according to this address . Next , The next router will forward the packet to the next router , After layers of forwarding , The network package reaches the final destination .
5.5、 The relationship between router and switch
IP The protocol itself has no function of transmitting packets , Therefore, the actual transmission of packets should be entrusted to Ethernet .
The router is based on IP The design of the , The switch is designed based on Ethernet , therefore IP The relationship with Ethernet is the relationship between router and switch . let me put it another way , The router entrusts the transmission of packets to the switch
IP( Router ) Responsible for the overall process of delivering the package to the communication object , The process of transferring the packet to the next router is carried by Ethernet ( Switch ) To be responsible for the .
6、 ... and 、 What's the mystery of the LAN on the server side
6.1、 A firewall
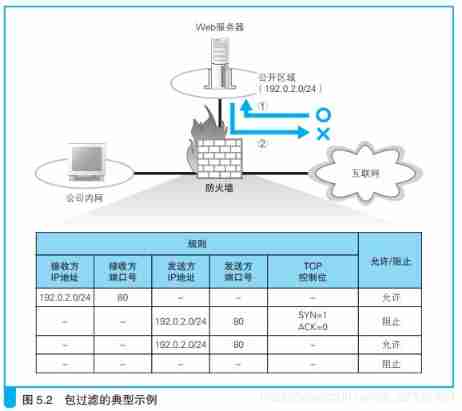
The basic idea of firewall
The basic idea of firewall , That is, only packages sent to specific applications in specific servers are allowed to pass , Then shield other packages .
The mainstream is the packet filtering firewall
The firewall of packet filtering can be based on the receiver IP Address 、 The sender IP Address 、 Slogan of receiver 、 Sender's slogan 、 Control bits and other information to determine whether a packet is allowed to pass .
Deficiencies of firewall
Attacks that firewall can't resist
The firewall can judge whether to allow the packet to pass through according to the starting point and ending point of the packet , But starting point and ending point alone can't screen out all risky packages .
such as , hypothesis Web The server will cause downtime when receiving a package with specific data . But the firewall only cares about the beginning and end of the package , So even if the package contains specific data , The firewall can't find , So the bag was released . then , When the bag arrives Web Server time , It will cause server downtime . Through this example, you can see , This risk can only be identified by checking the contents of the package , Therefore, the firewall can do nothing about this situation .
How to deal with the attack that the firewall cannot resist
a) Method 1 : The root of the problem lies in Web Of the server program Bug, So fix Bug Preventing downtime is one way . This kind of Bug in , Those with high risk will be published as security vulnerabilities , Developers will soon release fixes Bug A new version of the , Therefore, it is very important to continuously pay attention to the security vulnerability information and update the version of the software .
b) Another way is to deploy devices or software outside the firewall to check the contents of packages and prevent harmful packages .
6.2、 Load balancing
6.2.1、 Multiple servers – Distributed architecture
Using multiple servers to share the load is more effective . This architecture is collectively referred to as distributed architecture .
DNS Poll the distribution server IP Address
The simplest one is through DNS Server to assign . When accessing the server , The client needs to report to DNS The server queries the server IP Address , If in DNS Fill in multiple records with the same name in the server , Then every time you query DNS The server will return different IP Address .
DNS Polling deficiencies
for example : If more than one Web One of the servers has failed , At this time, we hope to return IP Address can skip the fault Web The server , But ordinary DNS The server cannot confirm Web Whether the server is working properly , So even if Web Server down , It may still return to this server IP Address .
Use load balancer to allocate access 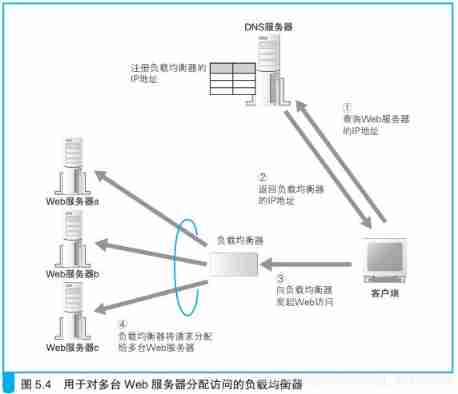
6.2.2、 Cache server
Save the content temporarily and replace Web The server returns the cache server of the content 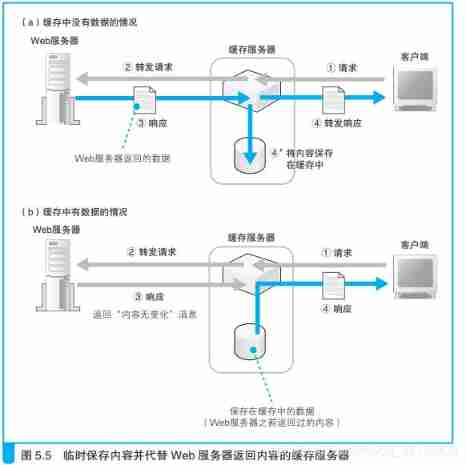
There are three kinds of deployment of cache server 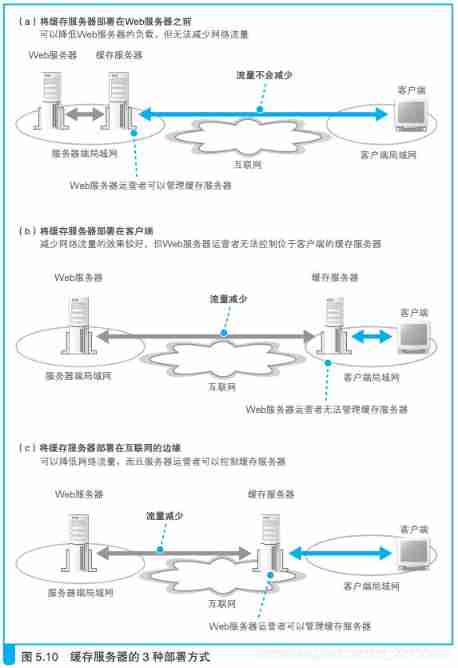
6.3、 Content distribution service
The third way is to distribute the cache servers , Make a layout .
7、 ... and 、 Request arrival Web The server , Response back to browser
7.1、 Server Overview
7.2、 Receive operation of server
7.2.1、 The network card converts the received signal into digital information
The server will restore the received electrical signal to digital information
Digital information restored according to the signal 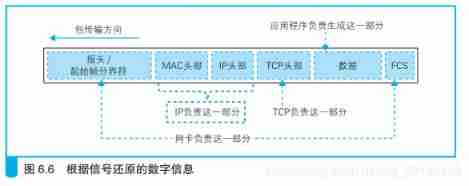
NIC MAC The module restores network packets from signals to digital information , check FCS And store it in the buffer .
In the process , Server's CPU Not always monitoring the arrival of network packets , It's doing other tasks , therefore CPU I don't know that the network packet has arrived at this time . But the next receiving operation needs CPU To participate in , Therefore, the network card needs to pass interrupt Notify the event of network packet arrival to CPU. Next , CPU Will suspend the current work , And switch to the network card task . then , The network card driver will start running , Read the received packets from the network card buffer , according to MAC The Ethernet type field in the header determines the type of protocol , And invoke the software that handles the protocol . here , The value of the etheric type should be the representation IP agreement , So it will call TCP/ IP Protocol stack , And forward the package to it .
The network card driver will MAC Header judgment protocol type , And give the package to the corresponding protocol stack .
7.2.2、IP Module receive operation
( 1)IP The module checks first IP Whether the format of the header conforms to the specification , Then check the receiver IP Address , See if the bag is for yourself ;
( 2) Determine whether network packets have been shard ;
( 3) Need to check IP Protocol number field in the header , And forward the package to the corresponding module . for example , If the protocol number is 06( Hexadecimal ), Forward the package to TCP modular ; If it is 11( Hexadecimal ), Is passed on to UDP modular .
7.2.3、TCP How modules handle connection packages
First step : When TCP Control bit in head SYN by 1 when , Means that this is a package that initiated the connection . At this time , TCP The module performs the operation to accept the connection , But before that , You need to check the recipient side of the packet first , And verify that there is no socket on the port that is the same as the receiver's port number and is waiting for a connection . If the specified port number does not have a socket waiting for a connection , Returns an error notification package to the client . Return a message to the client indicating that there is no socket waiting for connection on the receiver port ICMP news .
The second step : If there is a socket waiting for a connection , Makes a new copy of the socket , And send the sender IP Address 、 Port number 、 Initial value of serial number 、 Necessary parameters such as window size are written to the socket , Memory space is allocated for both the send and receive buffers . Then generate the ACK Number , The initial value of the sequence number used to send data from the server to the client , Represents the window size of the remaining capacity of the receive buffer , And use that information to generate TCP Head , entrust IP Module to client .
The third step : Once the package reaches the client , The client will return a message indicating the receipt of the confirmation ACK Number , When this ACK After No. is returned to the server , The connection is done . At this time , The server-side program should enter the call accept The pause state of , After passing the descriptor of the new socket to the server program , The server program will resume .
7.2.4、TCP How the module processes packets
( 1) When the packet is received , TCP According to the sender of the received packet IP Address 、 Sender's slogan 、 The receiving party IP Address 、 The receiver finds the corresponding socket ;
( 2) Put the blocks together and save them in the receive buffer ;
( 3) Returns to the client ACK.
7.2.5、TCP Disconnect operation of module
stay TCP In the rules of the agreement , The disconnection operation can be initiated by either the client or the server , The specific order is determined by the application layer protocol .Web in , This order follows HTTP The protocol version varies , stay HTTP1.0 in , It is the server that initiates the disconnection operation first .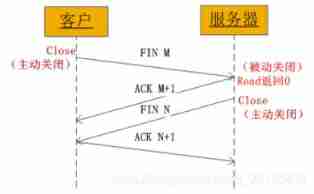
(1) The server will call Socket Library socket,TCP The module will generate a FIN by 1 Of TCP Head , And entrust IP Module to client
(2) When the client receives the package , Will return a ACK Number ,
(3) Next, the client will call close, Generate a FIN by 1 Of TCP Header to server ,
(4) The server returns another ACK Number .
边栏推荐
- LeetCode 1545. Find the k-th bit in the nth binary string
- ~69 other ways to use icon fonts
- 7-8 likes (need to continue to improve)
- How to generate six digit verification code
- Use JQ to realize the reverse selection of all and no selection at all - Feng Hao's blog
- When it comes to Google i/o, this is how ByteDance is applied to flutter
- 我在字节跳动「修电影」
- 字节跳动春招攻略:学长学姐笔经面经,还有出题人「锦囊」
- ~76 sprite map
- Redis standalone startup
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
我走过最迷的路,是字节跳动程序员的脑回路
DOS 功能调用
~69 other ways to use icon fonts
Introduction to microservices
Solr word segmentation analysis
Full record of ByteDance technology newcomer training: a guide to the new growth of school recruitment
7-12 inventory code base
The "advertising maniacs" in this group of programmers turned Tiktok advertisements into ar games
面试集锦库
MySQL日期函数
7-6 sum of combinatorial numbers
汇编语言寻址方式
「博士毕业一年,我拿下 ACL Best Paper」
LeetCode 1552. Magnetic force between two balls
Eureka single machine construction
~76 sprite map
LeetCode 1550. There are three consecutive arrays of odd numbers
Conception du système de thermomètre numérique DS18B20
Li Kou leetcode 280 weekly match
After the subscript is used to assign a value to the string type, the cout output variable is empty.