- object-oriented
- Object oriented definition
- The relationship between classes and objects
- Create and initialize objects
- Create memory analysis objects .
- attribute : Field Field Member variables Default initialization
- class
- encapsulation
- Inherit
- polymorphic
- instanceof
- Reference type conversion
- static
- abstract class
- Interface
- Inner class
object-oriented
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV12J41137hu/?p=60
Object oriented definition
- object-oriented programming OOP Object Oriented Programming
- The essence of object-oriented programming : Organize code as a class , Organize in the form of objects ( encapsulation ) data .
- abstract
- The three major characteristics
- encapsulation
- Inherit
- polymorphic
The relationship between classes and objects
- Class is an abstract data type , It is a general description of a certain kind of things / Definition , But it doesn't represent a specific thing .
- Objects are concrete instances of abstract concepts .
Create and initialize objects
Use new Keyword to create an object .
- Use new When the keyword creates an object , In addition to allocating memory space , It also initializes the created object by default and calls the constructor in the class .
- The constructor in a class also becomes a constructor , It must be called when creating an object . And the constructor has the following two characteristics .
- Must be the same as the class name .
- There must be no return type , You can't write void.
- Use new keyword , The essence is calling the constructor , Initialize the value of the object .
- By default, there will be an implicit parameterless constructor .
- Once the parameter constructor is written , The implicit constructor doesn't exist , Must also write a parameterless constructor , Otherwise, there is no reference new Will report a mistake .
- idea in Alt+insert, Build constructor .
package com.oop.demo01;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
}
package com.oop.demo01;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {
}
}
Create memory analysis objects .
- Objects are manipulated by reference , Stack --> Pile up .
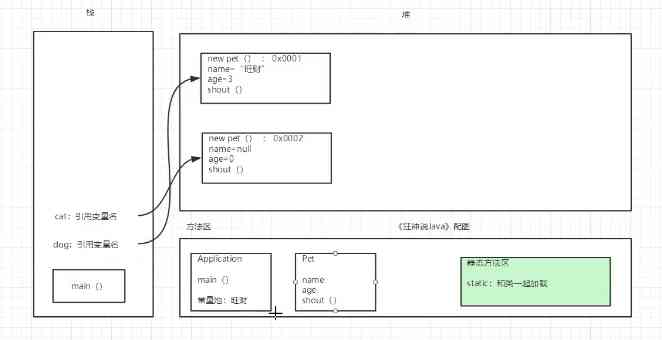
attribute : Field Field Member variables Default initialization
- Numbers : 0 0.0
- char:u0000
- boolean:false
- quote :null
class
- Static properties attribute
- Dynamic behavior Method
encapsulation
High cohesion and low coupling
- High cohesion means that the internal data operation details of a class are completed by themselves , External interference is not allowed .
- Low coupling is exposing only a few methods for external use .
- Property private get/set.
The significance of encapsulation
- Improve the security of the program , Protection data .
- Hide the implementation details of the code .
- Unified interface .
- Improve program maintainability .
Inherit
- Java The middle class has only single inheritance , No more inheritance .
- Inheritance is a relationship between classes .
- Two classes of inheritance relationship , One is a subclass ( Derived class ), One is the parent class ( Base class ).
- Subclass inherits parent , Use keywords extends To express .
- Between the child and the parent , In a sense, it should have "is a" The relationship between .
package com.oop.demo01;
public class Student extends Person {
private int grade;
}
package com.oop.demo01;
public class Student extends Person {
private int grade;
public Student() {
}
}
Object
- stay Java in , All classes inherit from each other by default or indirectly Object.
super
- super Call the properties and methods of the parent class , Can only appear in subclass methods or constructors .
- super() Call the constructor of the parent class , Must be in the first line of the constructor .
- super() and this() Cannot call constructor at the same time .
- this, Reference to the object itself .
- super, Reference to parent object .
public class Student extends Person {
private int grade;
public Student() {}
public Student(int grade) {
super();
this.grade = grade;
}
public Student(String name, int age, int grade) {
super(name, age);
this.grade = grade;
}
}
Method rewriting
- There needs to be an inheritance relationship , Subclasses override methods of the parent class .
- An override cannot be a static method , Static methods are loaded with the class .
- The method name must be the same and the parameter list must be the same .
- Modifiers can expand , Can't shrink .public>protected>default>private
- The exception thrown can be narrowed down , Can't expand .
package com.oop.demo01;
public class A {
public void test() {
System.out.println("A=>test");
}
}
package com.oop.demo01;
public class B extends A {
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println("B=>test");
}
}
B=>test
B=>test
polymorphic
- Polymorphism means that the same method can adopt many different behaviors according to different calling objects .
- The actual type of an object is certain , But there are many reference types that can point to objects ( In itself , Parent class , The parent of the parent ...).
- A reference to a parent class points to a child class .
- Objects can execute those methods , Look at the reference type of the object .
- After subclasses override methods , Both parent and child references execute subclass methods .
// Objects can execute those methods , Look at the reference type of the object .
// Parent class reference a Only the parent class can be called A Methods , Subclass reference b You can call the parent class A And subclasses B Methods , Subclass reference c You can call the parent class A And subclasses C Methods .
// If the subclass overrides the parent method , All execute subclass methods .
A a = new B();
B b = new B();
A c = new C();
The condition of polymorphism
- There is an inheritance relationship .
- Subclasses override methods of the parent class .
- The parent class reference points to the subclass object .
Methods that can't be polymorphic
- static Method , Belong to category , He doesn't belong to the example .
- final
- private Method .
instanceof
- Judge object type .
- Whether an object is an instance of a class or an instance of a subclass of a class or a subclass of a subclass of a class ... Example .
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Object > String
//Object > Person > Student
//Object > Person > Teacher
Object object = new Student();
System.out.println(object instanceof Student);//true
System.out.println(object instanceof Person);//true
System.out.println(object instanceof Object);//true
System.out.println(object instanceof Teacher);//false
System.out.println(object instanceof String);//false
System.out.println("=============================");
Person person = new Student();
System.out.println(person instanceof Student);//true
System.out.println(person instanceof Person);//true
System.out.println(person instanceof Object);//true
System.out.println(person instanceof Teacher);//false
// System.out.println(person instanceof String);// Compiler error
System.out.println("=============================");
Student student = new Student();
System.out.println(student instanceof Student);//true
System.out.println(student instanceof Person);//true
System.out.println(student instanceof Object);//true
// System.out.println(student instanceof Teacher);// Compiler error
// System.out.println(student instanceof String);// Compiler error
}
Reference type conversion
- Conversion between reference types : Parent class Subclass
- Automatic conversion from subclass to parent class .Object object = person;
- Parent class rotor class cast .Student b = (Student) person;
- The subclass becomes the parent class , Can only call methods of the parent class .
Person person = new Student();
Object object = person;
Student b = (Student) person;
static
- Static variables :static Decorated variable , Also called class variables .
static int age;
// Static variable call
System.out.println(Person.age);
- Static methods :static The method of decoration .
- Static methods cannot call non static methods , Because static methods load with the class , When static methods are loaded, non static methods are not loaded yet .
- Non static methods can call static methods .
- Static methods cannot call non static variables .
- Non static methods can call static variables .
public static void test(){}
- Static code block : Class is loaded once .
package com.oop.demo01;
public class Demo {
// Execution order :2 It is usually used to assign initial values
{
System.out.println(" Anonymous code block ");
}
// Execution order :1 Only once
static {
System.out.println(" Static code block ");
}
// Execution order :3
public Demo() {
System.out.println(" Nonparametric construction method ");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo demo1 = new Demo();
System.out.println("=======================");
Demo demo2 = new Demo();
}
}
Static code block
Anonymous code block
Nonparametric construction method
=======================
Anonymous code block
Nonparametric construction method
- Static import package
import static java.lang.Math.random;
abstract class
- abstract Modification methods , This method is an abstract method .
- abstract decorator , This class is an abstract class .
- There can be no abstract methods in an abstract class , But a class with an abstract method must be an abstract class .
- There can be ordinary methods in abstract classes .
- Abstract classes have default parameterless constructors .
- abstract class , Out of commission new Keyword to create the object , It is used to let subclasses inherit .
- Abstract method , Only method declaration , There is no way to achieve , It's used for subclasses to implement .
- Subclass inherits abstract class , You must implement abstract methods that the abstract class does not implement , Otherwise, the subclass should also be declared as an abstract class .
package com.oop.demo02;
// abstract class
public abstract class Action {
// Abstract method
public abstract void test();
}
package com.oop.demo02;
// Normal classes that inherit abstract classes , All non implemented abstract methods of abstract classes must be implemented
// Abstract classes that inherit abstract classes , You can not implement abstract methods of abstract classes
public class ActionA extends Action {
@Override
public void test() {
}
}
Interface
- General class : Only concrete implementation .
- abstract class : Specific implementation and specification ( Abstract method ) There are .
- Interface : Only norms .
- Interface cannot be instantiated , Because there is no constructor in the interface .
- All properties in the interface are constants , Default public static final
- All the methods in the interface are abstract , Default public abstract
- Single inheritance , Multiple implementation : Multiple interfaces can be implemented , You can only inherit one parent class .
- The class that implements the interface , You have to override all methods in the interface .
package com.oop.demo03;
// Interface , Interfaces need to have implementation classes
public interface UserService {
// All properties in the interface are constants , Default public static final
int age = 9999;
// All the methods in the interface are abstract , Default public abstract
void add(String name);
void delete(String name);
void update(String name);
void query(String name);
}
package com.oop.demo03;
public interface TimerService {
}
package com.oop.demo03;
// Single inheritance , Multiple implementation
// Multiple interfaces can be implemented , You can only inherit one parent class
// The class that implements the interface , You have to override all methods in the interface
// Implementation class
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService,TimerService{
@Override
public void add(String name) {
}
@Override
public void delete(String name) {
}
@Override
public void update(String name) {
}
@Override
public void query(String name) {
}
}
Inner class
Inner class is to define a class within a class , such as ,A Class is defining a B class , that B Class relative A Class is an inner class , and A Class relative B A class is an outer class .
Member inner class
- The member inner class can use all the non static properties and methods of the outer class , Including private .
package com.oop.demo04;
public class Outer {
private int id = 10;
private void out() {
System.out.println(" This is the method of the outer class ");
}
// Member inner class
public class Inner {
public void in() {
System.out.println(" This is the method of the inner class ");
}
// Internal classes can use private properties and methods of external classes
public void getId() {
System.out.println(" The inner class outputs the private properties of the outer class :" + id);
out();
}
}
}
package com.oop;
import com.oop.demo04.Outer;
// There should be only one project main Method
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Outer outer = new Outer();
// outer.out();
// Instantiate the inner class through the outer class instance , The inner class must be public
Outer.Inner inner = outer.new Inner();
inner.in();
inner.getId();
}
}
Static inner class
- Static inner classes can use static properties and methods of external classes , You cannot use non static properties and methods .
package com.oop.demo04;
public class Outer {
private static int id = 10;
private static void out() {
System.out.println(" This is the method of the outer class ");
}
// Static inner class
public static class Inner {
public void in() {
System.out.println(" This is the method of the inner class ");
}
// Internal classes can use private properties and methods of external classes
public void getId() {
System.out.println(" The inner class outputs the private properties of the outer class :" + id);
out();
}
}
}
Local inner classes
package com.oop.demo04;
public class Outer {
public void out() {
// Local inner classes
class Inner {
}
System.out.println(" This is the method of the outer class ");
}
}