当前位置:网站首页>[hand torn STL] list
[hand torn STL] list
2022-07-07 04:46:00 【The August】
Catalog
list The introduction and use of
- list It is a sequential container that can be inserted and deleted anywhere within the constant range , And the container can iterate back and forth .
- list The bottom layer of is a two-way linked list structure , Each element in a two-way linked list is stored in independent nodes that are not related to each other , In a node, point to its previous element and the next element through a pointer .
- list And forward_list Very similar : The main difference is forward_list It's a single chain table , Can only iterate forward , Has made it simpler and more efficient .
- Compared with other sequential containers (array,vector,deque),list It is usually inserted at any position 、 Removing elements is more efficient .
- Compared with other sequential containers ,list and forward_list The biggest drawback is that random access to any location is not supported , such as : To visit list Of the 6 Elements , Must be from a known location ( Like the head or tail ) Iterate to this location , Iterating at this location requires a linear time overhead ;list Some extra space is needed , To save the associated information of each node ( For large elements with smaller storage types list This may be an important factor )
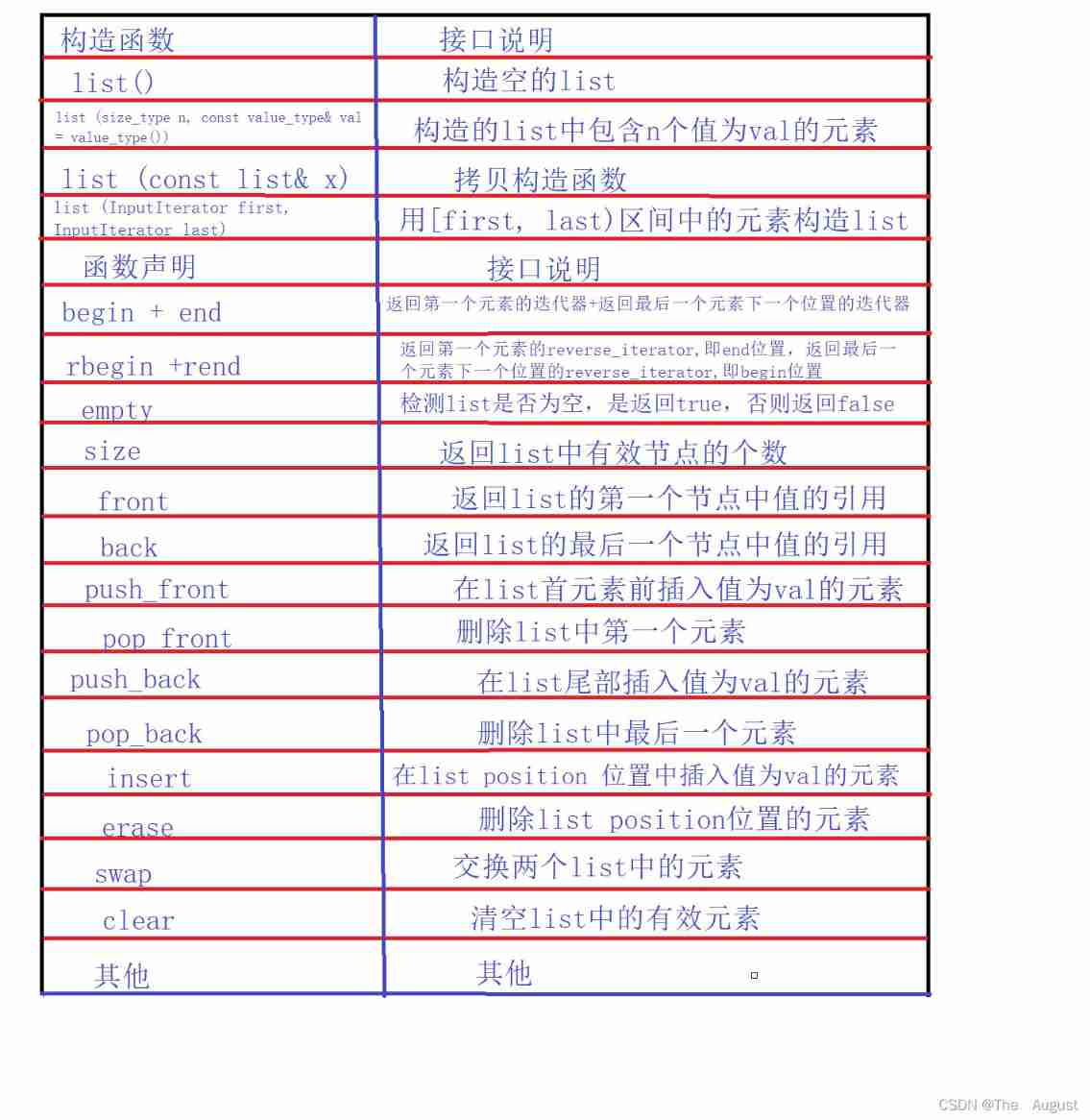
notes :
- begin And end Is a forward iterator , Perform... On iterators ++ operation , The iterator moves backwards
- rbegin(end) And rend(begin) Is a reverse iterator , Perform... On iterators ++ operation , The iterator moves forward
- list In container swap And in the algorithm swap The effect is the same but the efficiency is different ( In the algorithm swap It is done by deep copy , and list Medium swap It is done by exchanging header pointers ),vector、string And other containers are similar
- The two containers should exchange their own swap, Don't use swap
void test_list1()
{
list<int> lt1;
list<int> lt2(10, 5);
list<int> lt3(lt2.begin(), lt2.end());
vector<int> v = {
1,2,3,4,5,6 };
list<int> lt4(v.begin(), v.end());
list<int>::iterator it = lt4.begin();
while (it != lt4.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
for (const auto& e : lt4)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt3.assign(5, 3); // 3 3 3 3 3
for (const auto& e : lt3)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_front(50);
lt.pop_back();
lt.pop_front();
for (const auto& e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_list3()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.sort();
lt.unique(); // duplicate removal
for (const auto& e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.remove(5); // Delete
lt.remove(3);
for (const auto& e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.clear();
for (const auto& e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.push_back(10);
lt.push_back(20);
lt.push_back(30);
for (const auto& e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int> lt1;
lt1.push_back(1);
lt1.push_back(2);
lt.swap(lt1);
for (const auto& e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//lt.sort(greater<int>()); // Descending
lt.sort(); // Ascending
for (const auto& e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
list The iterator of
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
void TestListIterator1()
{
int array[] = {
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
list<int> l(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]));
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
// erase() After function execution ,it The node pointed to has been deleted , therefore it Invalid , In the next use it when , It must be assigned a value first
l.erase(it);
++it;
}
}
// correct
void TestListIterator()
{
int array[] = {
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
list<int> l(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]));
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
l.erase(it++); // it = l.erase(it);
}
}
void test_list2()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
list<int>::iterator it = find(lt.begin(), lt.end(), 3);
if (it != lt.end())
{
lt.insert(it, 10);
}
cout << *it << endl;
for (const auto& e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
notes :
- vector insert->it It will fail , Because the underlying space is a physically continuous array , Possible expansion , Cause wild pointer problems . Moving data without capacity expansion will also lead to it Meaning changes
- list insert->it It won't fail , because list It is an independent node ,3 The data inserted in front is a new node ,it Or point to the original 3 This node , It doesn't make a wild pointer , The meaning has not changed
summary :
The iterator fails, that is, the node pointed to by the iterator is invalid , That is, the node is deleted . because list The underlying structure of is a two-way circular linked list of leading nodes , So in list When inserting in, it will not lead to list The iterator of is invalid , It will be invalid only when deleted , And the only thing that fails is the iterator pointing to the deleted node , Other iterators will not be affected .
iterator

Iterator classification :
- From the perspective of function :( positive 、 reverse )+const
- The angle of the container substructure : A one-way 、 two-way 、 Random
- One way linked list iterator 、 Hash table iterator : A one-way ++
- Bidirectional linked list iterator 、map iterator : two-way ++、–
- string、vector、deque iterator 、map iterator : Random ++、–、+、-
notes :
- Iterators do not expose the underlying implementation details , Provide a unified way to access and modify the data stored in the container
- Iterators are the glue between containers and algorithms
- Without destroying the container packaging , Shield underlying structure differences , Provide a unified way to access containers
The implementation of iterators :
- Native pointers ( Natural iterators ), Because the space pointed by the native pointer is physically continuous
- Native pointers ( Use a class to encapsulate the native pointer , Overloading the correlation operator makes the object of this class , It works like a pointer ), Because the physical structure pointed by the native pointer is discontinuous
list Simulation Implementation of
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
namespace lc
{
template<class T>
struct _list_node
{
_list_node(const T& x=T())
:_next(nullptr)
,_prev(nullptr)
,_data(x)
{
}
_list_node<T>* _next;
_list_node<T>* _prev;
T _data;
};
/* List The iterator Iterators can be implemented in two ways , It shall be implemented according to the underlying data structure of the container : 1. Original ecological pointer , such as :vector 2. Encapsulate the original ecological pointer , Because iterators use exactly the same form as pointers , Therefore, the following... Must be implemented in the custom class Method : 1. Pointers can dereference , Iterator must be overloaded in its class operator*() 2. The pointer can pass through -> Access the space member it refers to , Iterator class must be overloaded oprator->() 3. The pointer can ++ Move backward , Iterator class must be overloaded operator++() And operator++(int) as for operator--()/operator--(int) Reloading is required for release , Choose according to the specific structure , A two-way linked list can Move forward Move , So you need to overload , If it is forward_list There's no need to overload -- 4. Iterators need to compare whether they are equal , Therefore, you also need to overload operator==() And operator!=() */
// iterator - Encapsulate the pointer of the node with a class
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct _list_iterator
{
typedef _list_node<T> Node;
typedef _list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;
_list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{
}
// Copy construction of iterators 、 Assignment overload 、 Destructors can be generated by default , You don't have to do it yourself
// Be careful : The nodes used by iterators are list Instead of iterators
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
// When the content of the access node is a custom type , It can be used -> To visit . Originally call this code it->->val
// But the readability of this writing is too poor , Therefore, the compiler makes special treatment , Omitted a ->, Keep readability it->val
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const self& it)const
{
return _node != it._node;
}
bool operator == (const self& it)const
{
return _node == it._node;
}
Node* _node;
};
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef _list_node<T> Node;
public:
typedef _list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef _list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
list()
:_head(nullptr)
{
// Lead two-way cycle list
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
}
template<class InputIterator>
list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
// The traditional way of writing
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
for (const auto& e : lt)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
Modern writing
//list(const list<T>& lt)
//{
// _head = new Node;
// _head->_next = _head;
// _head->_prev = _head;
// list<T> tmp(lt.begin(), lt.end());
// ::swap(_head, tmp._head);
//}
The traditional way of writing
//list<T>& operator=(const list<T>& lt)
//{
// if (this != <)
// {
// clear();
// for (const auto& e : lt)
// {
// push_back(e);
// }
// }
// return *this;
//}
// Modern writing
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
{
::swap(_head, lt._head);
return *this;
}
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_head);
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return const_iterator(_head);
}
/*void push_back(const T& x) { Node* newnode = new Node(x); Node* tail = _head->_prev; tail->_next = newnode; newnode->_prev = tail; newnode->_next = _head; _head->_prev = newnode; }*/
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
return iterator(newnode);
// return newnode; One parameter implicit type conversion
// iterator ret(newnode);
//return ret ;
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
insert(end(), x);
}
void push_front(const T& x)
{
insert(begin(), x);
}
// The member functions in the template are instantiated on demand , Which member function was called , Instantiate which
// Function templates
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* next = cur->_next;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
delete cur;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
return iterator(next);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(end()--);
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
size_t size()
{
size_t n = 0;
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it++;
n++;
}
return n;
}
bool empty()
{
return begin() == end();
}
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it); //erase Automatically point the header node to itself
}
}
private:
Node* _head;
};
}
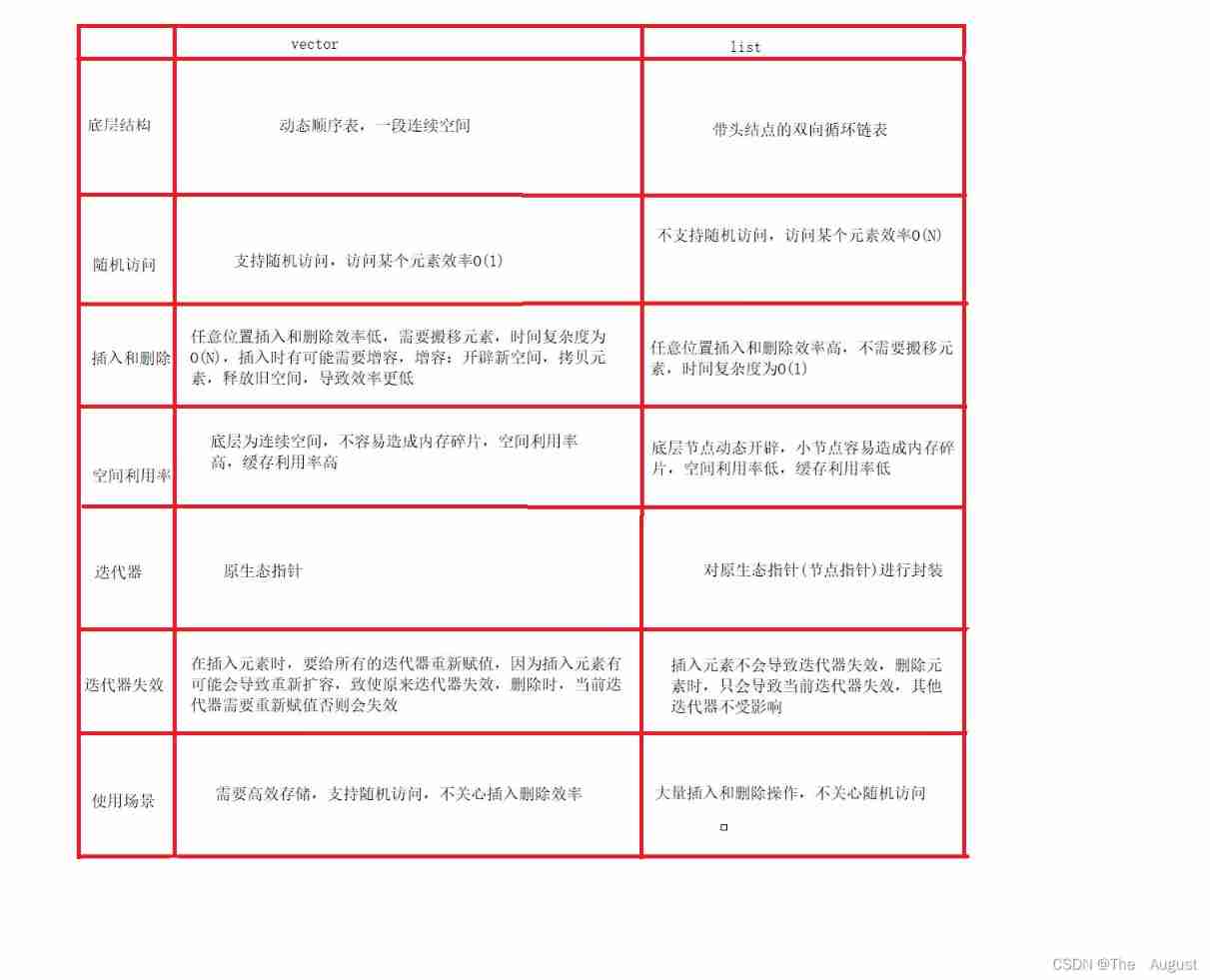
list And vector Comparison of
边栏推荐
- A picture to understand! Why did the school teach you coding but still not
- Win11控制面板快捷键 Win11打开控制面板的多种方法
- JS form get form & get form elements
- Jetson nano configures pytorch deep learning environment / / to be improved
- System framework of PureMVC
- What if the win11 screenshot key cannot be used? Solution to the failure of win11 screenshot key
- C # use Siemens S7 protocol to read and write PLC DB block
- 《原动力 x 云原生正发声 降本增效大讲堂》第三讲——Kubernetes 集群利用率提升实践
- NTU notes 6422quiz review (1-3 sections)
- Web3 社区中使用的术语
猜你喜欢
Win11 control panel shortcut key win11 multiple methods to open the control panel

The easycvr platform is connected to the RTMP protocol, and the interface call prompts how to solve the error of obtaining video recording?
![[team learning] [34 issues] scratch (Level 2)](/img/29/8383d753eedcffd874bc3f0194152a.jpg)
[team learning] [34 issues] scratch (Level 2)
Lessons and thoughts of the first SQL injection

窗口可不是什么便宜的东西
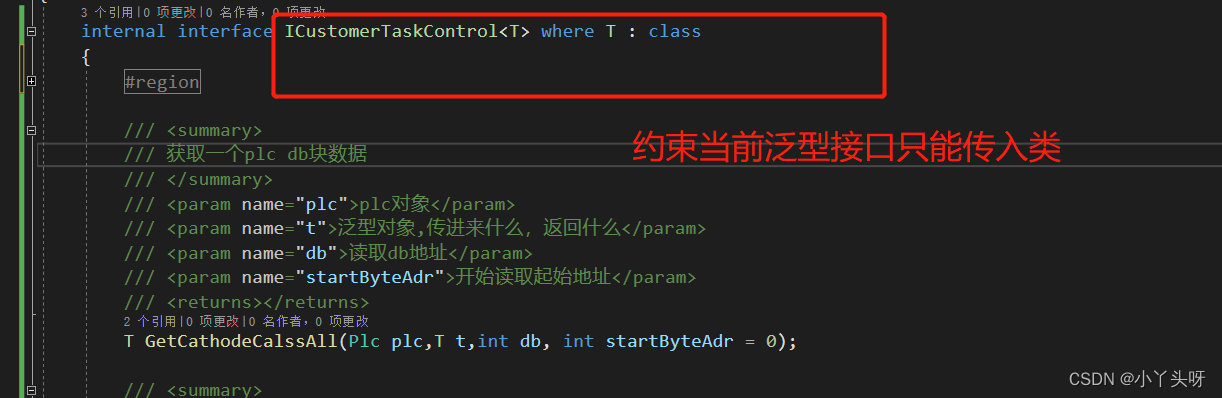
C#使用西门子S7 协议读写PLC DB块
What if the win11 screenshot key cannot be used? Solution to the failure of win11 screenshot key
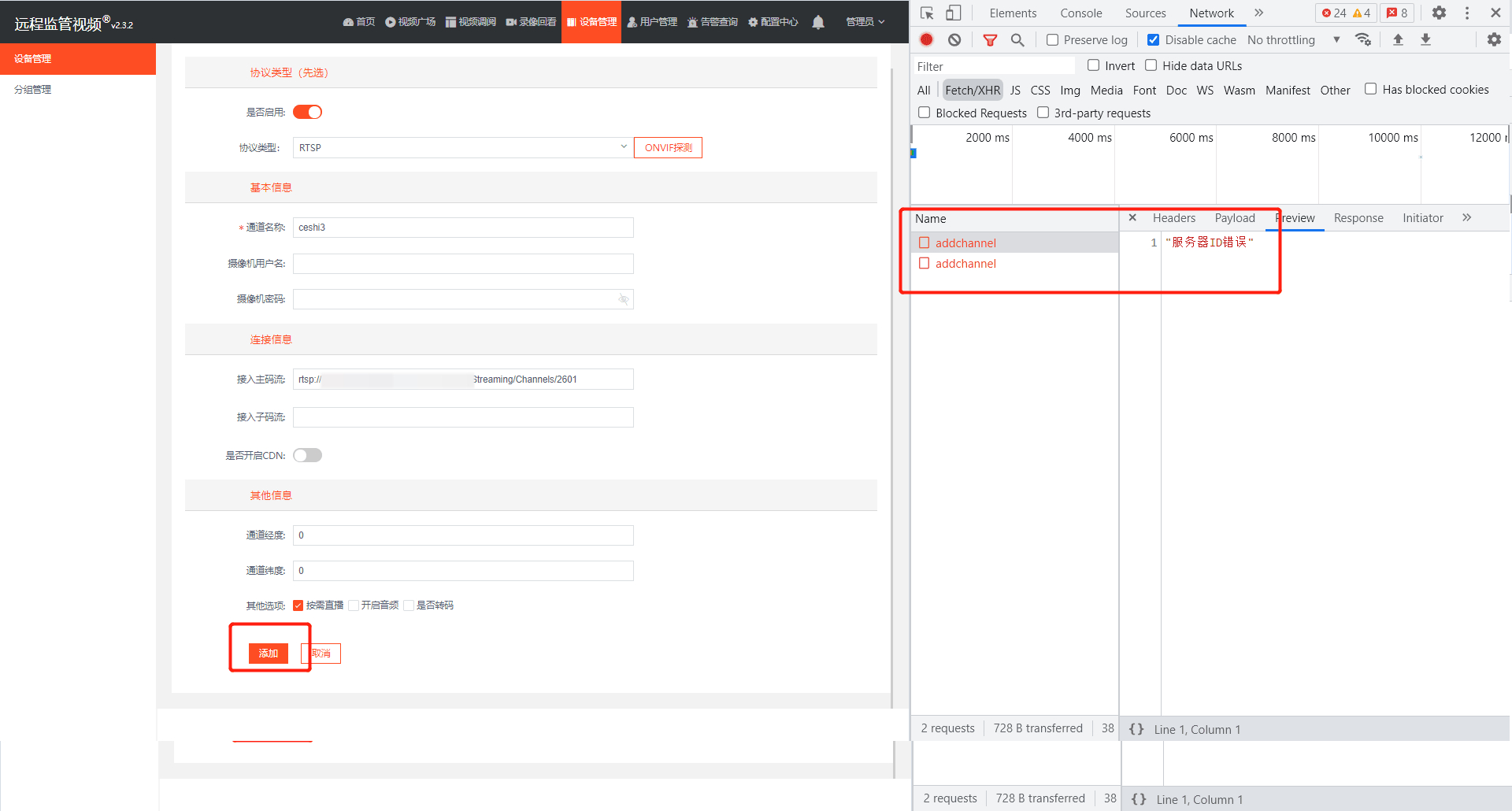
EasyCVR集群版本添加RTSP设备提示服务器ID错误,该如何解决?
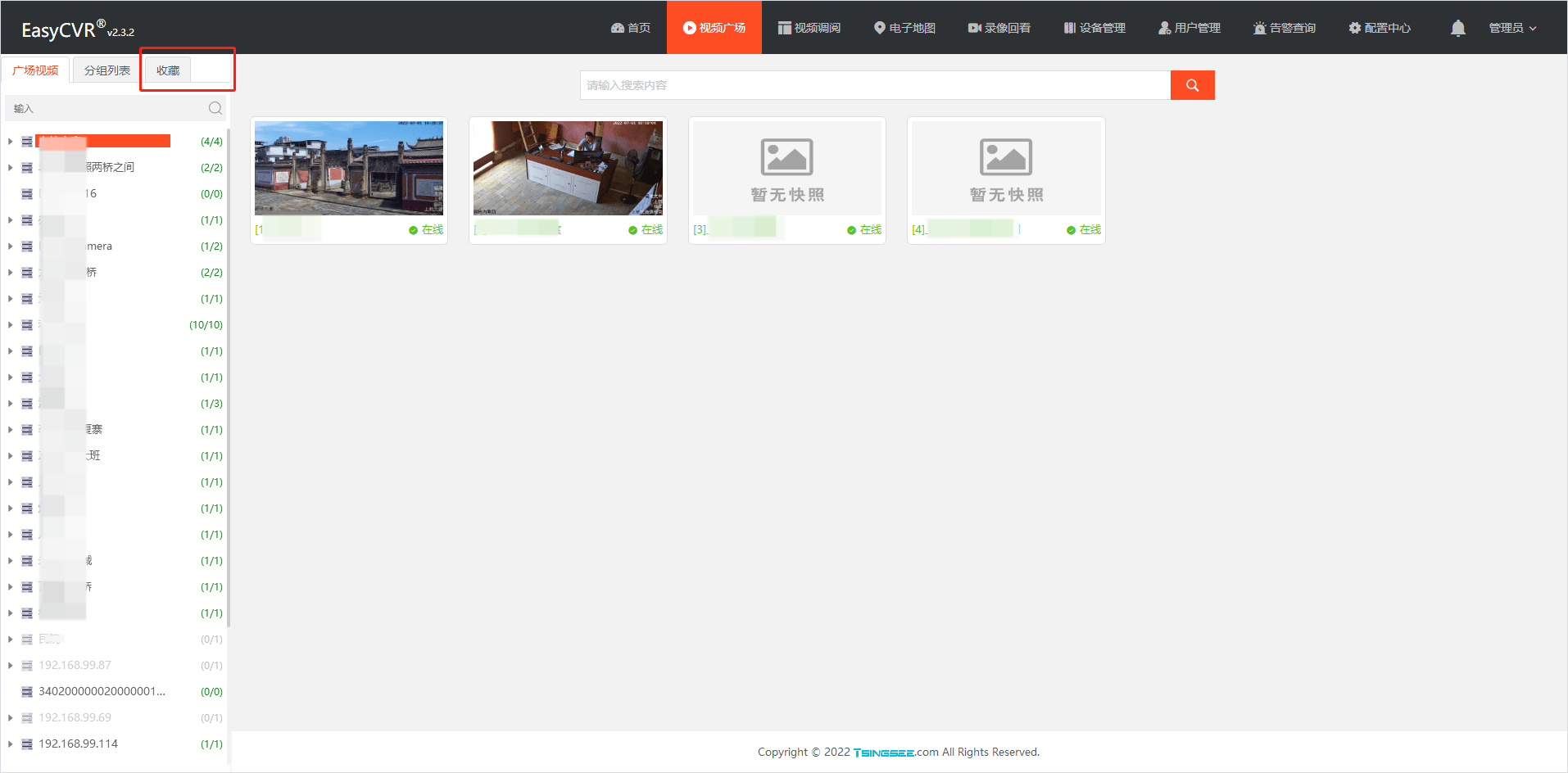
视频融合云平台EasyCVR视频广场左侧栏列表样式优化
树与图的深度优先遍历模版原理
随机推荐
leetcode 53. Maximum Subarray 最大子数组和(中等)
JS form get form & get form elements
EasyCVR集群重启导致其他服务器设备通道状态离线情况的优化
Jetson nano配置pytorch深度学习环境//待完善
R语言主成分pca、因子分析、聚类对地区经济研究分析重庆市经济指标
抖音或将推出独立种草社区平台:会不会成为第二个小红书
九章云极DataCanvas公司摘获「第五届数字金融创新大赛」最高荣誉!
广告归因:买量如何做价值衡量?
英特尔David Tuhy:英特尔傲腾技术成功的原因
C#使用西门子S7 协议读写PLC DB块
这项15年前的「超前」技术设计,让CPU在AI推理中大放光彩
Zhou Yajin, a top safety scholar of Zhejiang University, is a curiosity driven activist
论文上岸攻略 | 如何快速入门学术论文写作
组织实战攻防演练的5个阶段
Chapter 9 Yunji datacanvas was rated as 36 krypton "the hard core technology enterprise most concerned by investors"
Is there any way to bookmark the code in the visual studio project- Is there a way to bookmark code in a Visual Studio project?
Depth first traversal template principle of tree and graph
DFS and BFS concepts and practices +acwing 842 arranged numbers (DFS) +acwing 844 Maze walking (BFS)
NTU notes 6422quiz review (1-3 sections)
NFT meta universe chain diversified ecosystem development case