当前位置:网站首页>Summary of common algorithms of binary tree
Summary of common algorithms of binary tree
2020-11-06 01:18:00 【Clamhub's blog】
Node definition
1 |
public static class BinaryNode<T> { |
Binary tree nodes include element values and left and right child node references .
Create nodes
1 |
BinaryNode g = new BinaryNode(7); |
Form like :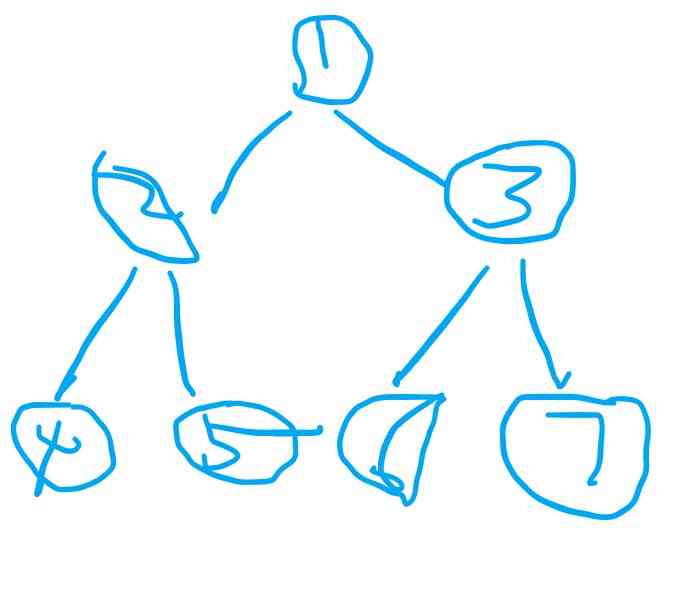
1、 front 、 in 、 After the sequence traversal
In front of the binary tree 、 in 、 Before in postorder traversal 、 in 、 The root node ;
Before the order : Output the root node first , And then the left and right nodes .
Middle preface : First left , Then output the root node , To the right .
In the following order : First left and right , Then output the root node .
1 |
public static void visit(BinaryNode p) { |
1.1、 The former sequence traversal
1 |
root -> Left -> Right |
1.1.1、 Recursive implementation
1 |
public static void recursivePreOrder(BinaryNode p) { |
If the node is null, Go straight back to ;
Print out the root node first , Then recursion left subtree , Then recurs the right subtree .
Just meet : First root , And then around .
1.1.2、 Non recursive implementation
1 |
public static void iterativePreOrder(BinaryNode p) { |
Make full use of the idea of stack , First in, then out .
When the node is not empty , Putting nodes on the stack , Iterate the elements in the stack , Pop up top element , Currently the root element , After that, press the right and left child nodes on the stack respectively . In this way, the order of the child nodes is left first and then right .
1.2、 In the sequence traversal
1 |
Left -> root -> Right |
1.2.1、 Recursive implementation
1 |
public static void recursiveInOrder(BinaryNode p) { |
1.2.2、 Non recursive implementation
1 |
public static void iterativeInOrder(BinaryNode p) { |
1.3、 After the sequence traversal
1 |
Left -> Right -> root |
1.3.1、 Recursive implementation
1 |
public static void recursivePostOrder(BinaryNode p) { |
1.3.2、 Non recursive implementation
1 |
public static void iterativePostOrder(BinaryNode p) { |
2、BFS And DFS
2.1、BFS Breadth first search
1 |
1234567 |
Breadth first traversal is to read node elements by layer , We need to use the data structure of the queue .
1 |
public static void levelOrderTraversal(BinaryNode node) { |
2.2、DFS Depth-first search
1 |
1245367 |
Starting from the root node , Select a branch to read all the elements , We need to use the data structure of the stack .
1 |
public static void depthTraversal(BinaryNode node) { |
3、 The depth of the binary tree
104. The maximum depth of a binary tree
3.1、 recursive
1 |
private static int calcDepth(BinaryNode node) { |
3.2、 Depth first
maxDepth Compare the length of each branch to update , Finally get the deepest branch length .
1 |
public static int maxDepthDFS(BinaryNode node) { |
3.3、 breadth-first
Search by layer , Every step into the floor , depth +1.
1 |
public static int maxDepthBFS(BinaryNode node) { |
4、 Binary tree image
Traverse by depth or breadth , Swap the left and right subtrees of nodes .
1 |
public static void mirror(BinaryNode root) { |
5、 Symmetric binary tree
101. Symmetric binary tree
This problem is a variation of binary tree mirror image , If two binary trees are symmetric , be :
- Two root nodes have the same value
- The left subtree of each tree , Are the same as the right subtree of another tree
Recursive implementation :Iterative implementation :1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public boolean isSymmetric(BinaryNode root) {
return isMirror(root, root);
}
public boolean isMirror(BinaryNode t1, BinaryNode t2) {
if (t1 == null && t2 == null) return true;
if (t1 == null || t2 == null) return false;
return (t1.val == t2.val)
&& isMirror(t1.right, t2.left)
&& isMirror(t1.left, t2.right);
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17public boolean isSymmetric(BinaryNode root) {
LinkedList<BinaryNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
q.add(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
BinaryNode t1 = q.poll();
BinaryNode t2 = q.poll();
if (t1 == null && t2 == null) continue;
if (t1 == null || t2 == null) return false;
if (t1.val != t2.val) return false;
q.add(t1.left);
q.add(t2.right);
q.add(t1.right);
q.add(t2.left);
}
return true;
}
summary
The algorithm of various topics of binary tree will think of recursion in the first consciousness , But when the recursion depth is too large, there will be stack overflow , So iterations will be used to implement accordingly , Accordingly, the data structure of queue or stack is introduced .
It feels like the most important algorithm is DFS And BFS, among DFS Depth first search uses the FIFO feature of the stack , and BFS Breadth first search uses the first in first out feature of the queue .

版权声明
本文为[Clamhub's blog]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

快快使用ModelArts,零基础小白也能玩转AI!
Do not understand UML class diagram? Take a look at this edition of rural love class diagram, a learn!

GUI 引擎评价指标

PN8162 20W PD快充芯片,PD快充充电器方案

直播预告 | 微服务架构学习系列直播第三期

选择站群服务器的有哪些标准呢?

做外包真的很难,身为外包的我也无奈叹息。
This article will introduce you to jest unit test

TRON智能钱包PHP开发包【零TRX归集】
中国提出的AI方法影响越来越大,天大等从大量文献中挖掘AI发展规律
随机推荐
Chainlink将美国选举结果带入区块链 - Everipedia
Elasticsearch 第六篇:聚合統計查詢
Do not understand UML class diagram? Take a look at this edition of rural love class diagram, a learn!
Computer TCP / IP interview 10 even asked, how many can you withstand?
阿里云Q2营收破纪录背后,云的打开方式正在重塑
Sort the array in ascending order according to the frequency
嘘!异步事件这样用真的好么?
直播预告 | 微服务架构学习系列直播第三期
一时技痒,撸了个动态线程池,源码放Github了
《Google軟體測試之道》 第一章google軟體測試介紹
基於MVC的RESTFul風格API實戰
PHPSHE 短信插件说明
Why do private enterprises do party building? ——Special subject study of geek state holding Party branch
Leetcode's ransom letter
Every day we say we need to do performance optimization. What are we optimizing?
Tool class under JUC package, its name is locksupport! Did you make it?
华为云“四个可靠”的方法论
选择站群服务器的有哪些标准呢?
html
Python自动化测试学习哪些知识?