当前位置:网站首页>Fourier series
Fourier series
2022-07-02 03:33:00 【Zeehoy】
Fourier series theory : The period is 2 π 2π 2π The periodic function of f ( x ) f(x) f(x) , You can write a series of linear combinations of trigonometric functions :
f ( x ) = a 0 c o s 0 + b 0 s i n 0 + a 1 c o s x + b 1 s i n x + a 2 c o s 2 x + b 2 s i n 2 x + . . . + a n c o s n x + b n s i n n x f(x)=a_0cos0+b_0sin0+a_1cosx+b_1sinx+a_2cos2x+b_2sin2x+...+a_ncosnx+b_nsinnx f(x)=a0cos0+b0sin0+a1cosx+b1sinx+a2cos2x+b2sin2x+...+ancosnx+bnsinnx
From the two-dimensional plane , Talking about orthogonal basis :
Assume a ⃗ \vec{a} a, b ⃗ \vec{b} b Orthogonal to each other , Their linear combination can represent any vector in the plane v ⃗ \vec{v} v:
v ⃗ = n a ⃗ + m b ⃗ \vec{v}=n\vec{a}+m\vec{b} v=na+mb
For coefficients n , m n,m n,m It can be solved in the following way :
v ⃗ ⋅ a ⃗ = n a ⃗ ⋅ a ⃗ + m b ⃗ ⋅ a ⃗ \vec{v} \cdot \vec{a}=n\vec{a}\cdot\vec{a}+m\vec{b}\cdot\vec{a} v⋅a=na⋅a+mb⋅a
because a ⃗ , b ⃗ \vec{a},\vec{b} a,b Orthogonal to each other , So the result of their dot multiplication is 0:
v ⃗ ⋅ a ⃗ = n a ⃗ ⋅ a ⃗ n = v ⃗ ⋅ a ⃗ a ⃗ ⋅ a ⃗ \vec{v} \cdot \vec{a}=n\vec{a}\cdot\vec{a}\\ n=\frac{\vec{v} \cdot \vec{a}}{\vec{a}\cdot\vec{a}} v⋅a=na⋅an=a⋅av⋅a
Empathy :
m = v ⃗ ⋅ b ⃗ b ⃗ ⋅ b ⃗ m=\frac{\vec{v} \cdot \vec{b}}{\vec{b}\cdot\vec{b}} m=b⋅bv⋅b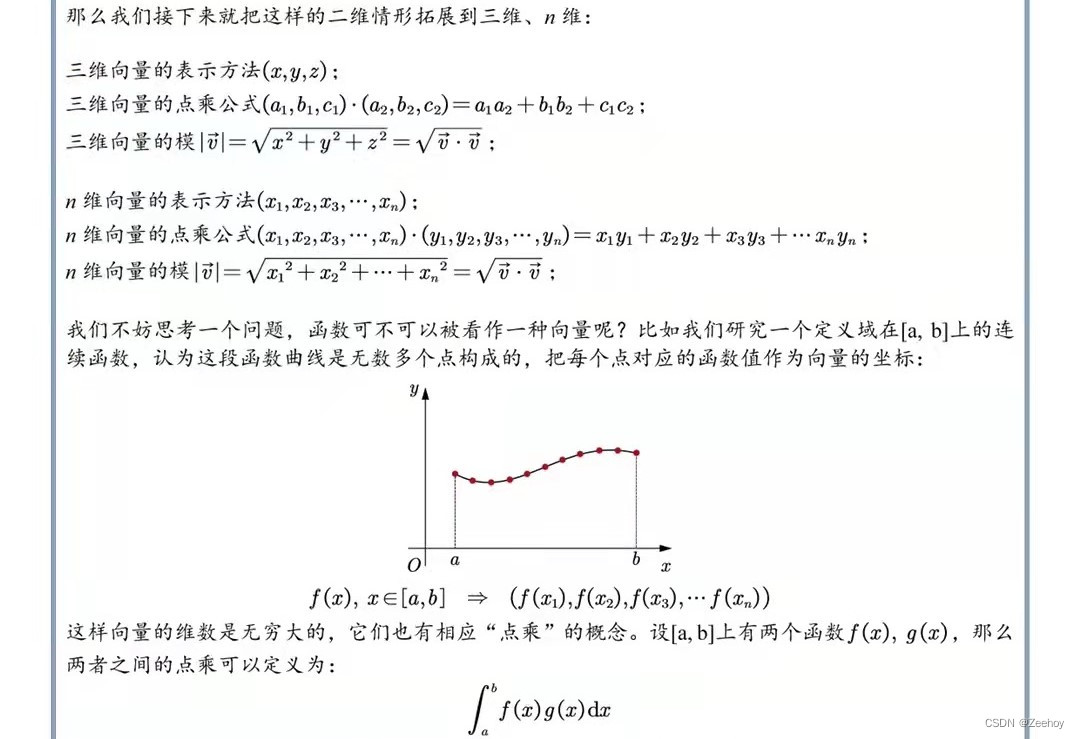
If ∫ a b f ( x ) g ( x ) d x = 0 \int_a^bf(x)g(x)dx=0 ∫abf(x)g(x)dx=0, That is, the result of dot multiplication is 0, Think of two functions f ( x ) f(x) f(x), g ( x ) g(x) g(x) It is orthogonal. .
Similar to the orthogonal basis of a vector , Linear combination of a set of orthogonal bases in functional form , It can also represent any function of the same interval .
One 、 [ 0 , 2 π ] [0,2π] [0,2π]
And trigonometric function set : { c o s 0 , s i n 0 , c o s x , s i n x , c o s 2 x , s i n 2 x , . . . . . . , c o s n x , s i n n x } \{ {cos0,sin0,cosx,sinx,cos2x,sin2x,......,cosnx,sinnx\}} { cos0,sin0,cosx,sinx,cos2x,sin2x,......,cosnx,sinnx} in , Because any two different functions are in the interval [ 0 , 2 π ] [0,2π] [0,2π] The result of dot multiplication in is 0, The result of each function multiplied by its own point is π π π, So it can be considered as interval [ 0 , 2 π ] [0,2π] [0,2π] A set of orthogonal bases in .
therefore , Section [ 0 , 2 π ] [0,2π] [0,2π] Any function in can be represented by a linear combination of these bases :
f ( x ) = a 0 c o s 0 + b 0 s i n 0 + a 1 c o s x + b 1 s i n x . . . + a n c o s n x + b n s i n n x f(x)=a_0cos0+b_0sin0+a_1cosx+b_1sinx...+a_ncosnx+b_nsinnx f(x)=a0cos0+b0sin0+a1cosx+b1sinx...+ancosnx+bnsinnx
That is, the Fourier series theory mentioned at the beginning of the article .
It is similar to the coefficient solution method of the two-dimensional plane part in the above , The coefficients here can also be solved in a similar way :
a n = ∫ 0 2 π f ( x ) c o s n x d x ∫ 0 2 π c o s n x c o s n x d x = 1 π ∫ 0 2 π f ( x ) c o s n x d x , n ∈ N a_n=\frac{\int_0^{2π}f(x)\,cosnx\,dx}{\int_0^{2π}cosnx\,cosnx\,dx}=\frac{1}{π}\int_0^{2π}f(x)cosnx\,dx,n\in N an=∫02πcosnxcosnxdx∫02πf(x)cosnxdx=π1∫02πf(x)cosnxdx,n∈N
b n = ∫ 0 2 π f ( x ) s i n n x d x ∫ 0 2 π s i n n x s i n n x d x = 1 π ∫ 0 2 π f ( x ) s i n n x d x , n ∈ N b_n=\frac{\int_0^{2π}f(x)\,sinnx\,dx}{\int_0^{2π}sinnx\,sinnx\,dx}=\frac{1}{π}\int_0^{2π}f(x)sinnx\,dx,n\in N bn=∫02πsinnxsinnxdx∫02πf(x)sinnxdx=π1∫02πf(x)sinnxdx,n∈N
The first two terms of the formula :
a 0 c o s 0 + b 0 s i n 0 = a 0 c o s 0 + 0 = a 0 = ∫ 0 2 π f ( x ) c o s 0 d x ∫ 0 2 π c o s 0 c o s 0 d x = ∫ 0 2 π f ( x ) d x ∫ 0 2 π 1 d x = 1 2 π ∫ 0 2 π f ( x ) d x a_0cos0+b_0sin0=a_0cos0+0=a_0=\frac{\int_0^{2π}f(x)\,cos0\,dx}{\int_0^{2π}cos0\,cos0\,dx}=\frac{\int_0^{2π}f(x)\,dx}{\int_0^{2π}1dx}=\frac{1}{2π}\int_0^{2π}f(x)\,dx a0cos0+b0sin0=a0cos0+0=a0=∫02πcos0cos0dx∫02πf(x)cos0dx=∫02π1dx∫02πf(x)dx=2π1∫02πf(x)dx
The latter part is written in the form of accumulation :
f ( x ) = a 0 + ∑ n = 1 + ∞ ( a n c o s n x + b n s i n n x ) f(x)=a_0+\sum_{n=1}^{+∞}(a_n\,cosnx+b_n\,sinnx) f(x)=a0+n=1∑+∞(ancosnx+bnsinnx)
Two 、 [ 0 , 2 l ] [0,2l] [0,2l]
The interval of one is limited to [ 0 , 2 π ] [0,2π] [0,2π], The interval can be extended to [ 0 , 2 l ] [0,2l] [0,2l] :
Such as c o s x cosx cosx The period of is T = 2 π w = 2 π 1 = 2 π T=\frac{2π}{w}=\frac{2π}{1}=2π T=w2π=12π=2π stay 2 π 2π 2π It will begin to repeat , Want its cycle to become 2 l 2l 2l, That is to say 2 l 2l 2l Enter repeat , namely T = 2 π w = 2 l T=\frac{2π}{w}=2l T=w2π=2l, have to : w = 2 π 2 l = π l w=\frac{2π}{2l}=\frac{π}{l} w=2l2π=lπ
c o s x cosx cosx Turn into c o s π l x cos \frac{π}{l}x coslπx To meet the requirements
On the other hand , although c o s 2 x cos2x cos2x The period of is π π π, But it will still be 2 π 2π 2π Start repeating at , namely 2 π 2π 2π Is still c o s 2 x cos2x cos2x A cycle of , other c o s n x cosnx cosnx Empathy
After all expansion :
{ c o s π l n x , s i n π l n x ∣ n ∈ N } \{ {cos\frac{π}{l}nx,sin\frac{π}{l}nx\,| \,n\in N\}} { coslπnx,sinlπnx∣n∈N} There is also a minimum public period 2 l 2l 2l, And because they still maintain an orthogonal relationship , The result of dot multiplication with itself is l l l, Therefore, the set is still a set of bases , At this time, its linear combination can represent [ 0 , 2 l ] [0,2l] [0,2l] Any function in .
f ( x ) = a 0 + ∑ n = 1 + ∞ ( a n c o s π l n x + b n s i n π l n x ) f(x)=a_0+\sum_{n=1}^{+∞}(a_n\,cos\frac{π}{l}nx+b_n\,sin\frac{π}{l}nx) f(x)=a0+n=1∑+∞(ancoslπnx+bnsinlπnx)
The same is true of No. 1 middle school , a 0 a_0 a0 Are the first two terms of linear combination :
a 0 c o s π l 0 + b 0 s i n π l 0 = a 0 c o s 0 + b 0 s i n 0 = a 0 = ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) c o s π l 0 d x ∫ 0 2 l c o s π l 0 c o s π l 0 d x = ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) c o s 0 d x ∫ 0 2 l c o s 0 c o s 0 d x = 1 2 l ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) d x a_0cos\frac{π}{l}0+b_0sin\frac{π}{l}0\\ =a_0cos0+b_0sin0\\ =a_0\\ =\frac{\int_0^{2l}f(x)\,cos\frac{π}{l}0\,dx}{\int_0^{2l}cos\frac{π}{l}0\,cos\frac{π}{l}0\,dx}\\ =\frac{\int_0^{2l}f(x)\,cos0\,dx}{\int_0^{2l}cos0\,cos0\,dx}\\ =\frac{1}{2l}\int_0^{2l}f(x)dx a0coslπ0+b0sinlπ0=a0cos0+b0sin0=a0=∫02lcoslπ0coslπ0dx∫02lf(x)coslπ0dx=∫02lcos0cos0dx∫02lf(x)cos0dx=2l1∫02lf(x)dx
The other two coefficients :
a n = ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) c o s π l n x d x ∫ 0 2 l c o s π l n x c o s π l n x d x = 1 l ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) c o s π l n x d x , n ∈ N a_n=\frac{\int_0^{2l}f(x)cos\frac{π}{l}nx\,dx}{\int_0^{2l}cos\frac{π}{l}nx\,cos\frac{π}{l}nx\,dx}=\frac{1}{l}\int_0^{2l}f(x)cos\frac{π}{l}nx\,dx,n\in N an=∫02lcoslπnxcoslπnxdx∫02lf(x)coslπnxdx=l1∫02lf(x)coslπnxdx,n∈N
b n = ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) s i n π l n x d x ∫ 0 2 l s i n π l n x s i n π l n x d x = 1 l ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) s i n π l n x d x , n ∈ N b_n=\frac{\int_0^{2l}f(x)sin\frac{π}{l}nx\,dx}{\int_0^{2l}sin\frac{π}{l}nx\,sin\frac{π}{l}nx\,dx}=\frac{1}{l}\int_0^{2l}f(x)sin\frac{π}{l}nx\,dx,n\in N bn=∫02lsinlπnxsinlπnxdx∫02lf(x)sinlπnxdx=l1∫02lf(x)sinlπnxdx,n∈N
3、 ... and 、 Further simplification with the help of Euler formula ( Another group of bases )
Make π l = w \frac{π}{l}=w lπ=w, The interval is still [ 0 , 2 l ] [0,2l] [0,2l] :
f ( x ) = a 0 + ∑ n = 1 + ∞ ( a n c o s ( n w x ) + b n s i n ( n w x ) ) (1) f(x)=a_0+\sum_{n=1}^{+∞}(a_n\,cos(nwx)+b_n\,sin(nwx))\tag{1} f(x)=a0+n=1∑+∞(ancos(nwx)+bnsin(nwx))(1)
Euler formula :
e i θ = c o s θ + i s i n θ e − i θ = c o s θ − i s i n θ e^{i\theta}=cos\theta+i\,sin\theta\\ e^{-i\theta}=cos\theta-i\,sin\theta eiθ=cosθ+isinθe−iθ=cosθ−isinθ
namely :
e i n w x = c o s ( n w x ) + i s i n ( n w x ) e − i n w x = c o s ( n w x ) − i s i n ( n w x ) e^{inwx}=cos(nwx)+i\,sin(nwx)\\ e^{-inwx}=cos(nwx)-i\,sin(nwx) einwx=cos(nwx)+isin(nwx)e−inwx=cos(nwx)−isin(nwx)
therefore :
c o s ( n w x ) = e i n w x + e − i n w x 2 s i n ( n w x ) = e i n w x − e − i n w x 2 i cos(nwx)=\frac{e^{inwx}+e^{-inwx}}{2}\\ sin(nwx)=\frac{e^{inwx}-e^{-inwx}}{2i} cos(nwx)=2einwx+e−inwxsin(nwx)=2ieinwx−e−inwx
Substitute the above two formulas into the formula (1), have to :
f ( x ) = a 0 + ∑ n = 1 + ∞ ( a n e i n w x + e − i n w x 2 + b n e i n w x − e − i n w x 2 i ) f(x)=a_0+\sum_{n=1}^{+∞}(a_n\,\frac{e^{inwx}+e^{-inwx}}{2}+b_n\,\frac{e^{inwx}-e^{-inwx}}{2i}) f(x)=a0+n=1∑+∞(an2einwx+e−inwx+bn2ieinwx−e−inwx)
Let's simplify :
f ( x ) = a 0 + ∑ n = 1 + ∞ ( a n e i n w x + e − i n w x 2 + i b n e i n w x − e − i n w x 2 i 2 ) f(x)=a_0+\sum_{n=1}^{+∞}(a_n\,\frac{e^{inwx}+e^{-inwx}}{2}+ib_n\,\frac{e^{inwx}-e^{-inwx}}{2i^2}) f(x)=a0+n=1∑+∞(an2einwx+e−inwx+ibn2i2einwx−e−inwx)
because i 2 = − 1 i^2=-1 i2=−1:
f ( x ) = a 0 + ∑ n = 1 + ∞ ( a n e i n w x + e − i n w x 2 − i b n e i n w x − e − i n w x 2 ) f(x)=a_0+\sum_{n=1}^{+∞}(a_n\,\frac{e^{inwx}+e^{-inwx}}{2}-ib_n\,\frac{e^{inwx}-e^{-inwx}}{2}) f(x)=a0+n=1∑+∞(an2einwx+e−inwx−ibn2einwx−e−inwx)
f ( x ) = a 0 + ∑ n = 1 + ∞ ( a n e i n w x − i b n e i n w x 2 + a n e − i n w x + i b n e − i n w x 2 ) f(x)=a_0+\sum_{n=1}^{+∞}(\frac{a_ne^{inwx}-ib_ne^{inwx}}{2}+\frac{a_ne^{-inwx}+ib_ne^{-inwx}}{2}) f(x)=a0+n=1∑+∞(2aneinwx−ibneinwx+2ane−inwx+ibne−inwx)
f ( x ) = a 0 + ∑ n = 1 + ∞ ( a n − i b n 2 e i n w x + a n + i b n 2 e − i n w x ) (2) f(x)=a_0+\sum_{n=1}^{+∞}(\frac{a_n-ib_n}{2}e^{inwx}+\frac{a_n+ib_n}{2}e^{-inwx})\tag{2} f(x)=a0+n=1∑+∞(2an−ibneinwx+2an+ibne−inwx)(2)
because :
a n = 1 l ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) c o s ( n w x ) d x b n = 1 l ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) s i n ( n w x ) d x a_n=\frac{1}{l}\int_0^{2l}f(x)cos(nwx)\,dx\\ b_n=\frac{1}{l}\int_0^{2l}f(x)sin(nwx)\,dx an=l1∫02lf(x)cos(nwx)dxbn=l1∫02lf(x)sin(nwx)dx
a − n = 1 l ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) c o s ( − n w x ) d x = a n a_{-n}=\frac{1}{l}\int_0^{2l}f(x)cos(-nwx)\,dx\\ =a_n a−n=l1∫02lf(x)cos(−nwx)dx=an
b − n = 1 l ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) s i n ( − n w x ) d x = − b n b_{-n}=\frac{1}{l}\int_0^{2l}f(x)sin(-nwx)\,dx\\ =-b_n b−n=l1∫02lf(x)sin(−nwx)dx=−bn
So the formula (2) Can integrate :
f ( x ) = a 0 + ∑ n = 1 + ∞ ( a n − i b n 2 e i n w x + a n + i b n 2 e − i n w x ) f(x)=a_0+\sum_{n=1}^{+∞}(\frac{a_n-ib_n}{2}e^{inwx}+\frac{a_n+ib_n}{2}e^{-inwx}) f(x)=a0+n=1∑+∞(2an−ibneinwx+2an+ibne−inwx)
f ( x ) = a 0 + ∑ n = 1 + ∞ a n − i b n 2 e i n w x + ∑ n = 1 + ∞ a − n − i b − n 2 e − i n w x f(x)=a_0+\sum_{n=1}^{+∞}\frac{a_n-ib_n}{2}e^{inwx}+\sum_{n=1}^{+∞}\frac{a_{-n}-ib_{-n}}{2}e^{-inwx} f(x)=a0+n=1∑+∞2an−ibneinwx+n=1∑+∞2a−n−ib−ne−inwx
f ( x ) = a 0 + ∑ n = 1 + ∞ a n − i b n 2 e i n w x + ∑ n = − ∞ − 1 a n − i b n 2 e i n w x f(x)=a_0+\sum_{n=1}^{+∞}\frac{a_n-ib_n}{2}e^{inwx}+\sum_{n=-∞}^{-1}\frac{a_{n}-ib_{n}}{2}e^{inwx} f(x)=a0+n=1∑+∞2an−ibneinwx+n=−∞∑−12an−ibneinwx
f ( x ) = ∑ n = 0 0 a n e i n w x + ∑ n = 1 + ∞ a n − i b n 2 e i n w x + ∑ n = − ∞ − 1 a n − i b n 2 e i n w x f(x)=\sum_{n=0}^{0}a_ne^{inwx}+\sum_{n=1}^{+∞}\frac{a_n-ib_n}{2}e^{inwx}+\sum_{n=-∞}^{-1}\frac{a_{n}-ib_{n}}{2}e^{inwx} f(x)=n=0∑0aneinwx+n=1∑+∞2an−ibneinwx+n=−∞∑−12an−ibneinwx
Finally, it is integrated into an accumulation symbol :
f ( x ) = ∑ n = − ∞ + ∞ c n e i n w x (3) f(x)=\sum_{n=-∞}^{+∞}c_ne^{inwx}\tag{3} f(x)=n=−∞∑+∞cneinwx(3)
When n = 0 n=0 n=0 when ,
c n = a 0 c_n=a_0 cn=a0
When n ≠ 0 n≠0 n=0 when ,
c n = a n − i b n 2 c_n=\frac{a_n-ib_n}{2} cn=2an−ibn
= 1 l ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) c o s ( n w x ) d x − i 1 l ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) s i n ( n w x ) d x 2 =\frac{\frac{1}{l}\int_0^{2l}f(x)cos(nwx)\,dx-i\frac{1}{l}\int_0^{2l}f(x)sin(nwx)\,dx}{2} =2l1∫02lf(x)cos(nwx)dx−il1∫02lf(x)sin(nwx)dx
= 1 l ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) c o s ( n w x ) d x − 1 l ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) i s i n ( n w x ) d x 2 =\frac{\frac{1}{l}\int_0^{2l}f(x)cos(nwx)\,dx-\frac{1}{l}\int_0^{2l}f(x)\,i\,sin(nwx)\,dx}{2} =2l1∫02lf(x)cos(nwx)dx−l1∫02lf(x)isin(nwx)dx
= 1 2 l ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) [ c o s ( n w x ) − i s i n ( n w x ) ] d x =\frac{1}{2l}\int_0^{2l}f(x)[cos(nwx)-i\,sin(nwx)]dx =2l1∫02lf(x)[cos(nwx)−isin(nwx)]dx
= 1 2 l ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) e − i n w x d x =\frac{1}{2l}\int_0^{2l}f(x)\,e^{-inwx}dx =2l1∫02lf(x)e−inwxdx
f ( x ) = ∑ n = − ∞ + ∞ c n e i n w x (3) f(x)=\sum_{n=-∞}^{+∞}c_ne^{inwx}\tag{3} f(x)=n=−∞∑+∞cneinwx(3)
type (3) signify f ( x ) f(x) f(x) It can also be represented by a linear combination of another set of bases , This set of bases is a set of complex exponential functions :
{ . . . , e − i 2 w x , e − i w x , e 0 , e i w x , e i 2 w x , . . . } \{ {...\,,e^{-i2wx}\,,e^{-iwx}\,,e^{0}\,,e^{iwx}\,,e^{i2wx}\,,...\}} { ...,e−i2wx,e−iwx,e0,eiwx,ei2wx,...}
{ e i n w x ∣ n ∈ Z } \{ {e^{inwx}\,|\,n\in Z\}} { einwx∣n∈Z}
To sum up , Fourier series can finally be written as another set of bases { e i n w x ∣ n ∈ Z } \{ {e^{inwx}\,|\,n\in Z\}} { einwx∣n∈Z} The linear combination of :
f ( x ) = ∑ n = − ∞ + ∞ c n e i n w x f(x)=\sum_{n=-∞}^{+∞}c_ne^{inwx} f(x)=n=−∞∑+∞cneinwx
among , c n c_n cn It's the plural ,
When n = 0 n=0 n=0 when , c n = a 0 c_n=a_0 cn=a0
When n ≠ 0 n≠0 n=0 when , c n = a n − i b n 2 = 1 2 l ∫ 0 2 l f ( x ) e − i n w x d x c_n=\frac{a_n-ib_n}{2}=\frac{1}{2l}\int_0^{2l}f(x)\,e^{-inwx}dx cn=2an−ibn=2l1∫02lf(x)e−inwxdx
Reference resources :
1. Detailed derivation of Fourier transform
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/77345128
2. Fourier series and Fourier transform
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/366974965
3. I understand the Fourier transform
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/23739221
4. If you don't understand Fourier transform after reading this article , Then come and strangle me
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/19759362
边栏推荐
- Download and use of the super perfect screenshot tool snipaste
- Continuous assignment of Verilog procedure
- Unity脚本的基础语法(7)-成员变量和实例化
- VS2010插件NuGet
- Basic syntax of unity script (8) - collaborative program and destruction method
- PY3 link MySQL
- 蓝桥杯单片机省赛第十届
- Eight steps of agile development process
- [designmode] Prototype Pattern
- Kotlin basic learning 17
猜你喜欢

MSI announced that its motherboard products will cancel all paper accessories
蓝桥杯单片机第四届省赛
蓝桥杯单片机省赛第十届

halcon图像矫正
Introduction to Robotics II. Forward kinematics, MDH method

Analyse de 43 cas de réseaux neuronaux MATLAB: Chapitre 42 opérations parallèles et réseaux neuronaux - - opérations parallèles de réseaux neuronaux basées sur CPU / GPU
Kubernetes cluster storageclass persistent storage resource core concept and use

Download and use of the super perfect screenshot tool snipaste

蓝桥杯单片机省赛第十二届第二场
《MATLAB 神经网络43个案例分析》:第41章 定制神经网络的实现——神经网络的个性化建模与仿真
随机推荐
[database]jdbc
Use blocking or non blocking for streamline
Pointer array & array pointer
Introduction to Robotics II. Forward kinematics, MDH method
MySQL connection query and subquery
Merge interval, linked list, array
C#联合halcon脱离halcon环境以及各种报错解决经历
《MATLAB 神經網絡43個案例分析》:第42章 並行運算與神經網絡——基於CPU/GPU的並行神經網絡運算
SAML2.0 notes (I)
Exchange rate query interface
Generate random numbers that obey normal distribution
Analyse de 43 cas de réseaux neuronaux MATLAB: Chapitre 42 opérations parallèles et réseaux neuronaux - - opérations parallèles de réseaux neuronaux basées sur CPU / GPU
/silicosis/geo/GSE184854_scRNA-seq_mouse_lung_ccr2/GSE184854_RAW/GSM5598265_matrix_inflection_demult
Verilog wire type
Kotlin basic learning 14
蓝桥杯单片机省赛第十二届第二场
ORA-01547、ORA-01194、ORA-01110
Grpc快速实践
Apple added the first iPad with lightning interface to the list of retro products
[HCIA continuous update] working principle of OSPF Protocol