当前位置:网站首页>Gnawing down the big bone - sorting (II)
Gnawing down the big bone - sorting (II)
2022-07-04 22:39:00 【Let everything burn】
List of articles
2.3 Exchange sort
The basic idea : So called exchange , It is to exchange the positions of the two records in the sequence according to the comparison results of the key values of the two records in the sequence , The characteristics of exchange sorting are : Move the record with large key value to the end of the sequence , Records with smaller key values move to the front of the sequence .
2.3.1 Bubble sort
Find the largest number to the back
Bubble sorted Feature summary :
- Bubble sort is a sort that is very easy to understand
- Time complexity :O(N^2)
- Spatial complexity :O(1)
- stability : Stable
Code
void BubbleSort(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
int exchange = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n - j; ++i)
{
if (a[i - 1]>a[i])
{
Swap(&a[i - 1], &a[i]);
exchange = 1;
}
}
// No exchange
if (exchange == 0)
{
break;
}
}
}
Compared with insert sorting :
Bubbling :N-1 + n-2
Insert :N Near order or partial order, etc ,Insertion can be used better
2.3.2 Quick sort
Quick sort is
HoareOn 1962 A binary tree structure of the exchange sort method
Its The basic idea by :
Take any element in the element sequence to be sorted as the reference value , According to the sorting code, the set to be sorted is divided into two subsequences , All elements in the left subsequence are less than the base value , All elements in the right subsequence are greater than the base value , Then the leftmost and rightmost subsequences repeat the process , Until all the elements are aligned in their respective positions
Single trip :
Choose one key, It is usually the leftmost or the rightmost
Ask for : On the left key smaller , Right ratio key Be big
The above is the main framework for the recursive implementation of quick sorting , It is found that it is very similar to the preorder traversal rule of binary tree , When writing a recursive framework, students can think about the pre order traversal rules of binary tree and write them quickly , In the following sequence, you only need to analyze how to divide the data in the interval according to the benchmark value .
Divide the interval into left and right halves according to the reference value Common ways are :
1. hoare edition
Select the leftmost as key,R Go ahead from behind to find a better place than key Small number ( here L It's not moving , etc. R Find out L To start ), then L Go back and forth to find Bi key Large number , At this time, the two exchange , Then continue to , until R And L meet , Compare the value of this position with key In exchange for
Because not at the same time , therefore R And L Don't miss .
On the left is key Why can't you go first on the left ?
Conclusion : Ensure the value ratio of the encounter position key Be small or key The location of
Two cases :
1.R Go ahead ,R stop ,L To meet R At this time, the meeting position is R Where to stop , and R The condition for stopping is to meet Bi key Small value , So at this time, it meets the meeting position ratio key Small conclusions
2.R Go ahead ,R No better than key Smaller value ,R I met L
1)L Didn't go ,R Direct and L meetkey The location of ( And key equal
2)R And L It's been a round , The meeting place is L Where the last round of stopped , At this time, this position is smaller than key smaller . Because the last round L Already with R Exchanged , So at this time L It's more than key Smaller numberThan key smaller
Conclusions and recommendations :On the left is key, Go first on the right On the right is key, Go first on the left
// [begin, end]
//N*log^N
void QuickSort(int* a, int begin, int end)
{
// The interval does not exist , Or only one value does not need to be processed
if (begin >= end)
{
return;
}
int left = begin, right = end;
int keyi = left;
while (left < right)
{
// Go first on the right , Looking for a small
while (left < right && a[right] >= a[keyi])
{
--right;
}
// Go left , Looking for big
while (left < right && a[left] <= a[keyi])
{
++left;
}
Swap(&a[left], &a[right]);
}
Swap(&a[keyi], &a[left]);
keyi = left;
// recursive
// [begin, keyi-1] keyi [keyi+1, end]
// The left interval is ordered + Right interval order = Overall order
QuickSort(a, begin, keyi - 1);
QuickSort(a, keyi + 1, end);
}
2. Excavation method (hoare improvement )
Choose one first key Take it out to form a pit
// Excavation method
int PartSort2(int* a, int begin, int end)
{
int key = a[begin];
int piti = begin;
while (begin < end)
{
// Look for a small on the right , Fill the hole on the left . This position forms a new pit
while (begin < end && a[end] >= key)
{
--end;
}
a[piti] = a[end];
piti = end;
// Look big on the left , Fill the hole on the right . This position forms a new pit
while (begin < end && a[begin] <= key)
{
++begin;
}
a[piti] = a[begin];
piti = begin;
}
a[piti] = key;
return piti;
}
void QuickSort(int* a, int begin, int end)
{
// The interval does not exist , Or if there is only one value, it does not need to be processed
if (begin >= end)
{
return;
}
int keyi = PartSort2(a, begin, end);
//[begin, keyi-1] keyi [keyi+1, end]
QuickSort(a, begin, keyi-1);
QuickSort(a, keyi + 1, end);
}
3. Front and back pointer method
Select the leftmost as key
cur The pointer looks small ( Than key Small ), Find it and prev In exchange for , if cur Cross the line so perv And key In exchange for
What will affect the efficiency of fast platoon ?
Orderly or near orderly ,key Value ( Choose the maximum or minimum )
N + N-1 + N-2 + …
O(N^2)
Stack overflow occurs when there is too much data
Method :
1. Choose... At random key
2. Select three numbers At the first , middle , Choose the last one , Choose not the largest nor the smallest
// Choose a value that is neither the maximum nor the minimum
int GetMidIndex(int* a, int begin, int end)
{
int mid = (begin + end) / 2;
if (a[begin] < a[mid])
{
if (a[mid] < a[end])
{
return mid;
}
else if (a[begin] < a[end])
{
return end;
}
else
{
return begin;
}
}
else // (a[begin] >= a[mid])
{
if (a[mid] > a[end])
{
return mid;
}
else if (a[begin] < a[end])
{
return begin;
}
else
{
return end;
}
}
}
// Front and back pointer method
int PartSort3(int* a, int begin, int end)
{
int prev = begin;
int cur = begin + 1;
int keyi = begin;
// Join the optimization of triple data extraction
int midi = GetMidIndex(a, begin, end);
Swap(&a[keyi], &a[midi]);
// It's bigger than , It's equivalent to crossing the border before it ends
while (cur <= end)
{
// cur The value of the position is less than keyi Position value —— Looking for a small
if (a[cur] < a[keyi] && ++prev != cur)
// In exchange for
Swap(&a[prev], &a[cur]);
++cur;// No matter what cur Must be walking backwards
}
Swap(&a[prev], &a[keyi]);
keyi = prev;
return keyi;
}
void QuickSort(int* a, int begin, int end)
{
// The interval does not exist , Or if there is only one value, it does not need to be processed
if (begin >= end)
{
return;
}
int keyi = PartSort3(a, begin, end);
//[begin, keyi-1] keyi [keyi+1, end]
QuickSort(a, begin, keyi-1);
QuickSort(a, keyi + 1, end);
}
2.3.2 Quicksort optimization
- The middle of three numbers key
- Recursion to a small subinterval , Consider using insert sort
Total recursive calls :2^h-1
Reduce the number of recursions
When recursively dividing cells , When the interval is relatively small, it is no longer recursive to divide and sort the cells . You can consider directly using other sorting methods to sort cells ( Insertion sort )
Suppose the interval is less than 10 when , No longer recursively sort cells . It can almost reduce 80% Number of recursions
void QuickSort(int* a, int begin, int end)
{
if (begin >= end)
{
return;
}
// The interval is less than 10 when , No longer recursively sort cells
if (end - begin > 10)
{
int keyi = PartSort3(a, begin, end);
// [begin, keyi-1] keyi [keyi+1, end]
QuickSort(a, begin, keyi - 1);
QuickSort(a, keyi + 1, end);
}
else
{
InsertSort(a + begin, end - begin + 1);
}
}
2.3.2 Quick sort non recursive
Because you want to use the stack
So remember to quote Stack.h Stack.c
// Requirements , Change recursion to non recursion
// Recursive big problem , Under extreme scenes , If the depth is too deep , There will be stack overflow
// 1、 Directly change the cycle -- Like Fibonacci series 、 Merge sort
// 2、 Use data structure stack to simulate recursive process
void QuickSortNonR(int* a, int begin, int end)
{
ST st;
StackInit(&st);
StackPush(&st, end);
StackPush(&st, begin);
while (!StackEmpty(&st))
{
int left = StackTop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
int right = StackTop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
int keyi = PartSort3(a, left, right);
// [left, keyi-1] keyi[keyi+1, right]
if (keyi + 1 < right)
{
StackPush(&st, right);
StackPush(&st, keyi + 1);
}
if (left < keyi - 1)
{
StackPush(&st, keyi - 1);
StackPush(&st, left);
}
}
StackDestroy(&st);
}
In quick order Feature summary :
- The overall performance and usage scenarios of quick sort are quite good , That's why we call it quick sort
- Time complexity :O(N*logN)
- Spatial complexity :O(logN)
- stability : unstable
2.4 Merge sort
The basic idea :
Merge sort (MERGE-SORT) It is an effective sorting algorithm based on merge operation , The algorithm is a divide-and-conquer method (Divide andConquer) A very typical application . Merges ordered subsequences , You get a perfectly ordered sequence ; So let's make each subsequence in order , Then make the subsequence segments in order . If two ordered tables are merged into one ordered table , be called Merge two ways .
Merge sort The core step :
First, it is divided into left and right sub intervals , If the two subintervals are ordered, merge
( Two hands go at the same time , Compare , The younger one goes to the new area first )
If the left and right intervals are disordered , It is divided into single numbers from the left and right intervals , Recursion
Go aside first
The ordered left and right intervals with two numbers are merged into an ordered interval with four numbers , Then the ordered left and right intervals with four numbers are merged into the ordered interval of the last eight digits
1 2 4 8( Yes, not necessarily 2 Multiple )
Merge and rank Feature summary :
- The disadvantage of merging is that it requires O(N) Spatial complexity of , The thinking of merge sort is more about solving the problem of external sort in disk .
- Time complexity :O(N*logN)
- Spatial complexity :O(N)
- stability : Stable
Recursive version :
void _MergeSort(int* a, int begin, int end, int* tmp)
{
if (begin >= end)
return;
int mid = (begin + end) / 2;
// [begin, mid] [mid+1, end] Divide and conquer recursion , Let the subinterval be orderly
_MergeSort(a, begin, mid, tmp);// Left
_MergeSort(a, mid + 1, end, tmp);// Right
// Merger [begin, mid] [mid+1, end]
int begin1 = begin, end1 = mid;// Left
int begin2 = mid + 1, end2 = end;// Right
int i = begin1;// The starting position
while (begin1 <= end1 && begin2 <= end2)
{
// Whoever is younger will go first
if (a[begin1] < a[begin2])
{
tmp[i++] = a[begin1++];
}
else
{
tmp[i++] = a[begin2++];
}
}
// Logically speaking , Here are two while Only one can go in
while (begin1 <= end1)
{
tmp[i++] = a[begin1++];
}
while (begin2 <= end2)
{
tmp[i++] = a[begin2++];
}
// Copy the merged data back to the original array
memcpy(a + begin, tmp + begin, (end - begin + 1)*sizeof(int));
}
void MergeSort(int* a, int n)
{
// The third new interval
int* tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
_MergeSort(a, 0, n - 1, tmp);
// Release the third-party interval
free(tmp);
}
Non recursive version :
//void MergeSortNonR(int* a, int n)
//{
// int* tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);
// if (tmp == NULL)
// {
// printf("malloc fail\n");
// exit(-1);
// }
//
// int gap = 1;
// while (gap < n)
// {
// printf("gap=%d->", gap);
// for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 2 * gap)
// {
// // [i,i+gap-1][i+gap, i+2*gap-1]
// int begin1 = i, end1 = i + gap - 1;
// int begin2 = i + gap, end2 = i + 2 * gap - 1;
//
// // Transboundary - Fix the boundary
// if (end1 >= n)
// {
// end1 = n - 1;
// // [begin2, end2] Corrected to no interval
// begin2 = n;
// end2 = n - 1;
// }
// else if (begin2 >= n)
// {
// // [begin2, end2] Corrected to no interval
// begin2 = n;
// end2 = n - 1;
// }
// else if(end2 >= n)
// {
// end2 = n - 1;
// }
//
// printf("[%d,%d] [%d, %d]--", begin1, end1, begin2, end2);
//
// int j = begin1;
// while (begin1 <= end1 && begin2 <= end2)
// {
// if (a[begin1] < a[begin2])
// {
// tmp[j++] = a[begin1++];
// }
// else
// {
// tmp[j++] = a[begin2++];
// }
// }
//
// while (begin1 <= end1)
// {
// tmp[j++] = a[begin1++];
// }
//
// while (begin2 <= end2)
// {
// tmp[j++] = a[begin2++];
// }
// }
//
// printf("\n");
// memcpy(a, tmp, sizeof(int)*n);
//
// gap *= 2;//1 2 4
// }
//
// free(tmp);
//}
void MergeSortNonR(int* a, int n)
{
int* tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
int gap = 1;
while (gap < n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 2 * gap)
{
// [i,i+gap-1][i+gap, i+2*gap-1]
int begin1 = i, end1 = i + gap - 1;
int begin2 = i + gap, end2 = i + 2 * gap - 1;
// end1 Cross the border or begin2 Transboundary , Then you can not merge
if (end1 >= n || begin2 >= n)
{
break;
}
else if (end2 >= n)
{
end2 = n - 1;
}
int m = end2 - begin1 + 1;
int j = begin1;
while (begin1 <= end1 && begin2 <= end2)
{
if (a[begin1] < a[begin2])
{
tmp[j++] = a[begin1++];
}
else
{
tmp[j++] = a[begin2++];
}
}
while (begin1 <= end1)
{
tmp[j++] = a[begin1++];
}
while (begin2 <= end2)
{
tmp[j++] = a[begin2++];
}
memcpy(a + i, tmp + i, sizeof(int)* m);
}
gap *= 2;
}
free(tmp);
}
besides , There are also some sort :
Bucket sort
Radix sorting
Count sorting
Understanding is good. , There is no need to master .
2.5 Non comparative ordering
For integers ( Negative numbers are OK )
thought : Counting sorting is also called pigeon nest principle , It is a variant application of hash direct addressing method . Operation steps :
- Count the number of occurrences of the same element
- According to the statistical results, the sequence is recycled into the original sequence
limitations :
1. If it's a floating point number 、 String cannot use high
2. If the data range is large , The space complexity will be very , Not suitable for
3. It is suitable for many duplicate data in the scope
Count ordered Feature summary :
- When the count sort is in the data range set , It's very efficient , However, the scope of application and scenarios are limited .
- Time complexity :O(MAX(N, Range ))
- Spatial complexity :O( Range )
4. stability : Stable
// Time complexity :O(max(range, N))
// Spatial complexity :O(range)
void CountSort(int* a, int n)
{
int min = a[0], max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
if (a[i] < min)
min = a[i];
if (a[i] > max)
max = a[i];
}
// An array of statistical times
int range = max - min + 1;
int* count = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*range);
if (count == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
memset(count, 0, sizeof(int)*range);
// Count the times
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
count[a[i] - min]++;
}
// Write back - Sort
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < range; ++i)
{
// A few times will be written back i+min
while (count[i]--)
{
a[j++] = i + min;
}
}
}
边栏推荐
- 醒悟的日子,我是怎么一步一步走向软件测试的道路
- 攻防世界 misc 高手进阶区 a_good_idea
- Recommendation of mobile app for making barcode
- ACM multimedia 2022 | counterfactual measurement and elimination of social prejudice in visual language pre training model
- Tla+ introductory tutorial (1): introduction to formal methods
- Challenges faced by virtual human industry
- BigFilter全局交易防重组件的介绍与应用
- The table is backed up in ODPs. Why check m in the metabase_ Table, the logical sizes of the two tables are inconsistent, but the number of
- Why is Dameng data called the "first share" of domestic databases?
- The proofreading activity of data science on the command line second edition was restarted
猜你喜欢
质量体系建设之路的分分合合

Unity-VScode-Emmylua配置报错解决
Concurrent optimization summary
How to transfer to software testing, one of the high paying jobs in the Internet? (software testing learning roadmap attached)
PMO: compare the sample efficiency of 25 molecular optimization methods

The Sandbox 和数字好莱坞达成合作,通过人力资源开发加速创作者经济的发展

LOGO特訓營 第一節 鑒別Logo與Logo設計思路
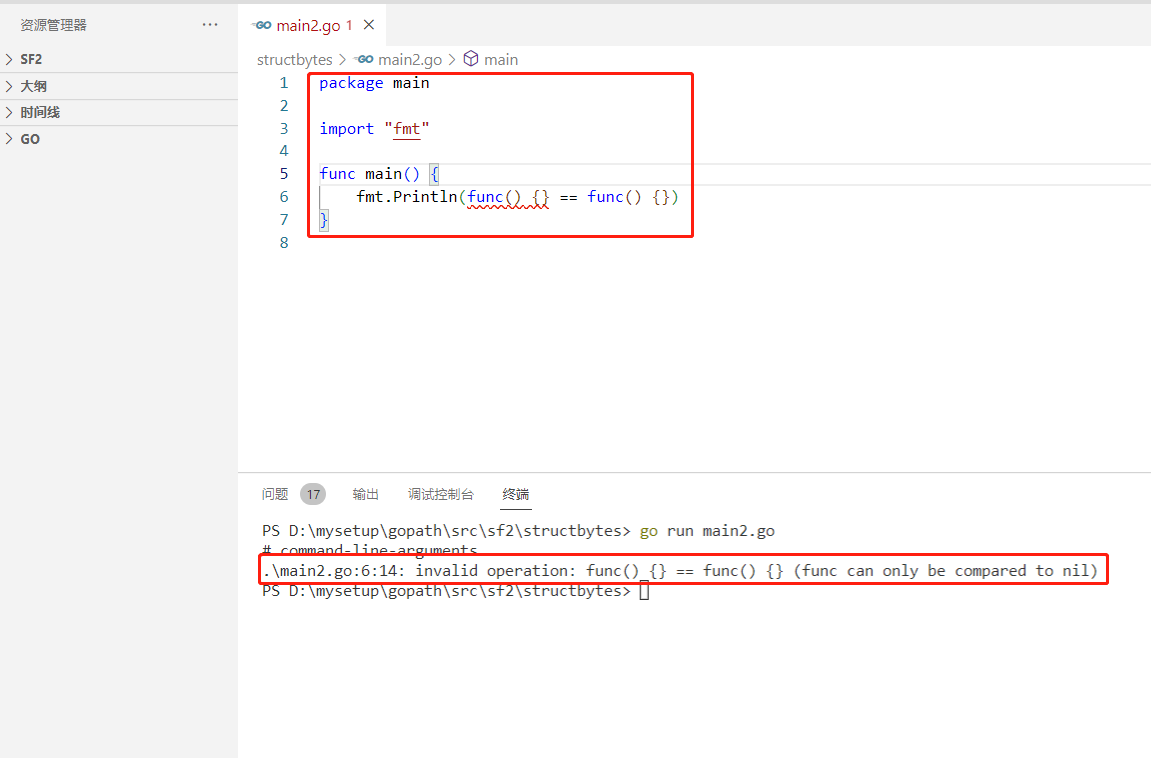
2022-07-04: what is the output of the following go language code? A:true; B:false; C: Compilation error. package main import “fmt“ func main() { fmt.Pri

LOGO特训营 第一节 鉴别Logo与Logo设计思路

Naacl-22 | introduce the setting of migration learning on the prompt based text generation task
随机推荐
阿里推出新品牌“瓴羊”,致力成为“数字化领头羊”
sobel过滤器
MySQL storage data encryption
BigFilter全局交易防重组件的介绍与应用
Logo special training camp section III initial creative techniques
Éducation à la transmission du savoir | Comment passer à un test logiciel pour l'un des postes les mieux rémunérés sur Internet? (joindre la Feuille de route pour l'apprentissage des tests logiciels)
Sqlserver encrypts and decrypts data
繁華落盡、物是人非:個人站長該何去何從
攻防世界 MISC 进阶区 hong
30余家机构联合发起数字藏品行业倡议,未来会如何前进?
Domestic database chaos
通过Go语言创建CA与签发证书
高中物理:直线运动
2022-07-04: what is the output of the following go language code? A:true; B:false; C: Compilation error. package main import “fmt“ func main() { fmt.Pri
Flask 上下文详解
The sandbox has reached a cooperation with digital Hollywood to accelerate the economic development of creators through human resource development
The table is backed up in ODPs. Why check m in the metabase_ Table, the logical sizes of the two tables are inconsistent, but the number of
Concurrent optimization summary
Tiktok actual combat ~ the number of comments is updated synchronously
质量体系建设之路的分分合合