xml
One 、XML brief introduction
What is? xml?
xml It's an extensible markup language .
xml The role of ?
1. To hold data , And the data are self descriptive ;
2. It can be used as a configuration file for a project or module ;
3. It can also be used as a network transmission data format ( Now in order to JSON Mainly ).
Two 、xml grammar
1、 The document statement
① Create a XML file
Input file name :
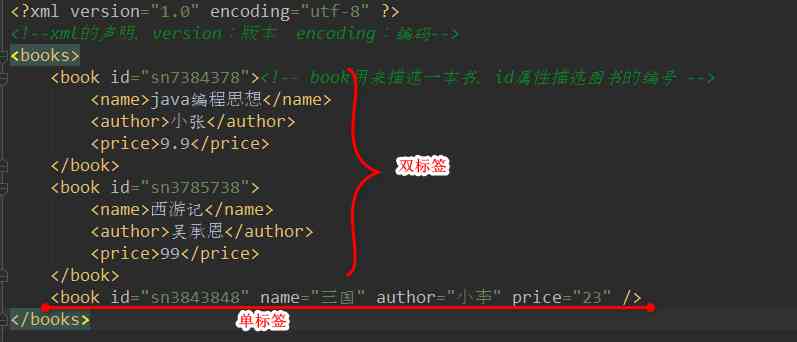
②books.xml Files store books and information .( Books have id attribute It means only identification , Title , There are authors , Price information )
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <!--xml Statement of ,version: edition encoding: code --> <books> <book id="sn7384378"><!-- book Used to describe a book ,id Property describes the number of the book --> <name>java Programming idea </name> <author> Xiao Zhang </author> <price>9.9</price> </book> <book id="sn3785738"> <name> Journey to the west </name> <author> Wu chengen </author> <price>99</price> </book> </books>
You can view the document in the browser :

2、xml notes
xml And HTML It's the same :<!-- The comment -->
3、 Elements ( label )
xml The element refers to the part from the start tag to the end tag . Elements can contain other elements 、 Text or a mixture of the two . Elements can also have attributes .
① Name can contain letters 、 Numbers and other characters ;
② Names cannot begin with Numbers or punctuation marks ;
③ The name cannot contain spaces ;
Single label : < Tag name Property name =" Property value " /> Double label : < Tag name Property name =" Property value "> Encapsulated data </ Tag name >
4、xml attribute
xml Tag properties and html The tag properties of are very similar , Attributes can provide additional information about the element .
5、 Rule of grammar
① be-all xml label , Whether single label or double label , Must be closed .
②xml Tags are case sensitive .
③xml Tags must be nested correctly .
④XML The document must have a root element
The root element is the top element ,
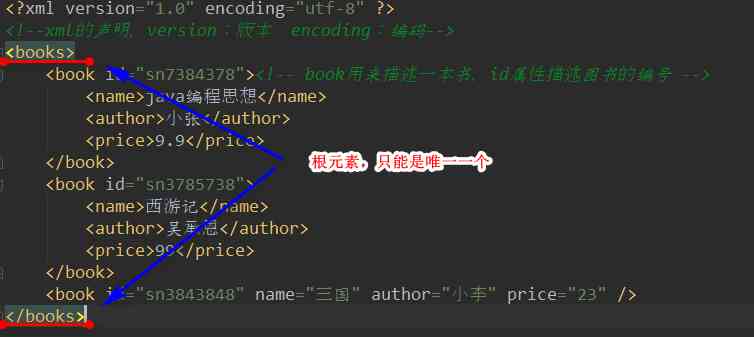
⑤xml Property values of must be quoted .
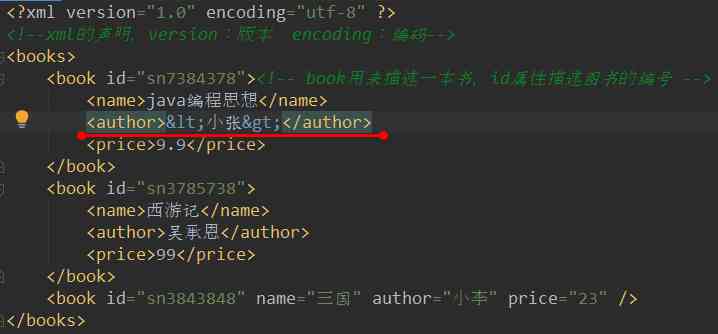
⑥xml Special character in :
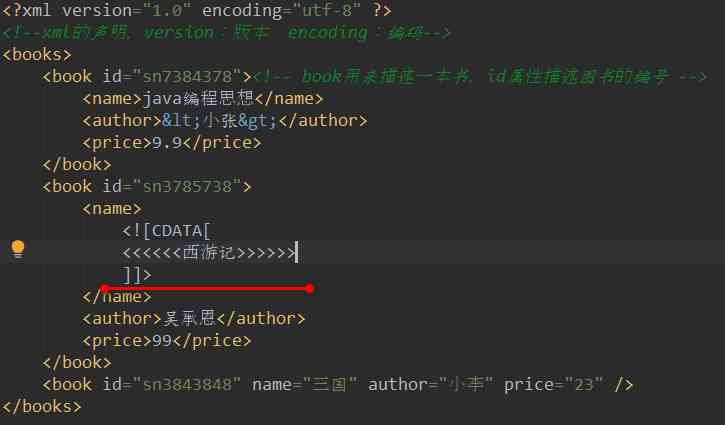
⑦ Text area (CDATA District )
CDATA Grammar can tell xml Parser , I CDATA The text in , It's just plain text , Unwanted xml Syntax parsing .
CDATA Format :
3、 ... and 、xml Introduction to parsing technology

Four 、dom4j Parsing Technology ( a key *****)
because dom4j It is not sun Company technology , And technology that belongs to a third party company , We need to use dom4j You need to get to dom4j Download from the official website dom4j
1、Dom4j Use of class library

After decompressing :
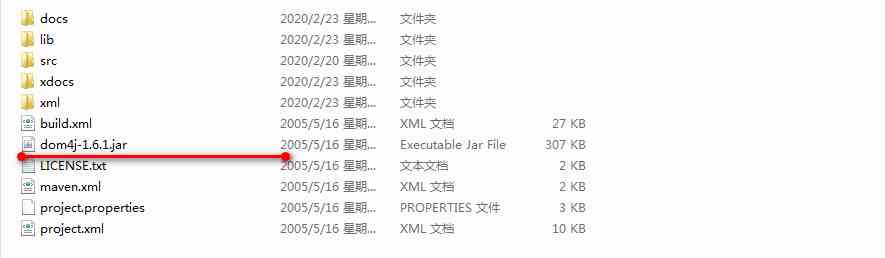
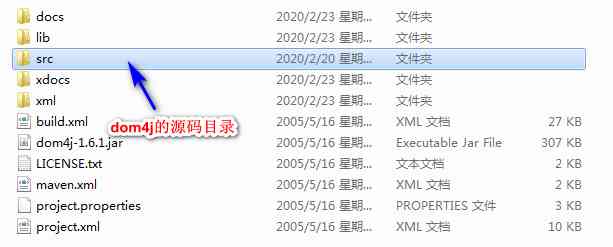
2、dom4j Introduction to the catalogue
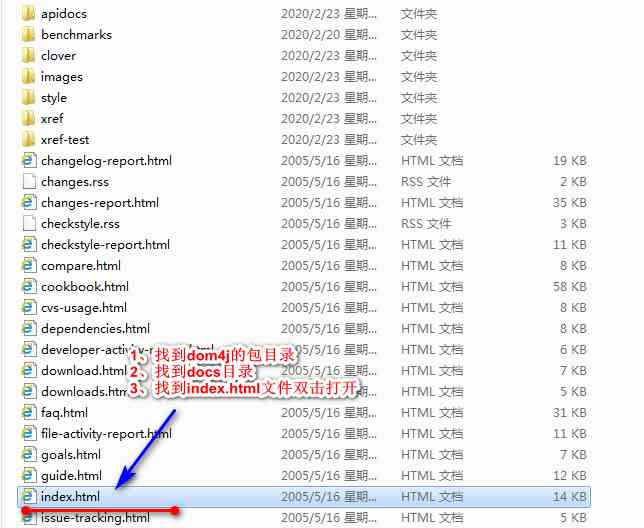
src Directory is dom4j Source directory
3、dom4j Programming steps :

4、 obtain document object
Prepare the books.xml file ( This file is in src Next ):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <!--xml Statement of ,version: edition encoding: code --> <books> <book id="sn7384378"><!-- book Used to describe a book ,id Property describes the number of the book --> <name>java Programming idea </name> <author> Xiao Zhang </author> <price>9.9</price> </book> <book id="sn3785738"> <name> Journey to the west </name> <author> Wu chengen </author> <price>99</price> </book> </books>
obtain document object :
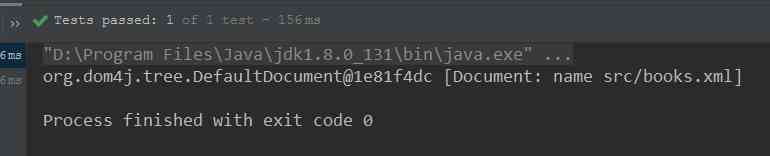
public class dom4jTest { @Test public void getDocument() throws DocumentException { //1. Create a SAXReader object SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); //2. This object is used to read xml file , return Document Document document = reader.read("src/books.xml"); //3. Print , See if it was created successfully System.out.println(document); } }
The effect is as follows :
5、 Traverse label Get the content of all tags (***** a key )
Book.java file :
public class Book { private String id; private String name; private String author; private Double price; public Book() { } public Book(String id, String name, String author, Double price) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.author = author; this.price = price; } public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public Double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(Double price) { this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return "Book{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", author='" + author + '\'' + ", price=" + price + '}'; } }
dom4j Parse test class :
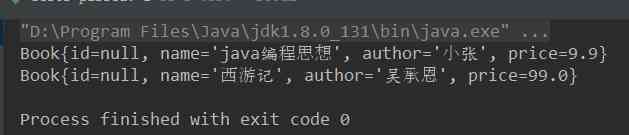
public class dom4jTest { @Test public void readXml() throws DocumentException { //1. Create a SAXReader object SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); Document document = reader.read("src/books.xml"); //2. adopt document object , Get xml The root element object of Element rootElement = document.getRootElement(); // Print test // System.out.println(rootElement.asXML()); //3. Through the root element object , Get all book A collection of tag objects List<Element> books = rootElement.elements("book"); //4. Traverse books, Get every book object for (Element book : books){ // Get book The attribute value String sn = book.attributeValue("sn"); // Get book Below name Content in the element Element name = book.element("name"); String nameText = name.getText(); // Get book Below author Content in the element Element author = book.element("author"); String authorText = author.getText(); // Get book Below price Content in the element Element price = book.element("price"); String priceText = price.getText(); // Encapsulate the acquired data into a Book object Book b = new Book(sn, nameText, authorText, Double.parseDouble(priceText)); System.out.println(b); } } }
The effect is as follows :

![[stm32f429] Chapter 6: stm32f429 dma2d acceleration of ThreadX guix](/img/06/94a66b6072d24e3d69b3a54ab77d28.jpg)