当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode203. Remove linked list elements
LeetCode203. Remove linked list elements
2022-07-07 22:49:00 【Qingshan's green shirt】
LeetCode203. Remove linked list elements
List of articles
1. subject
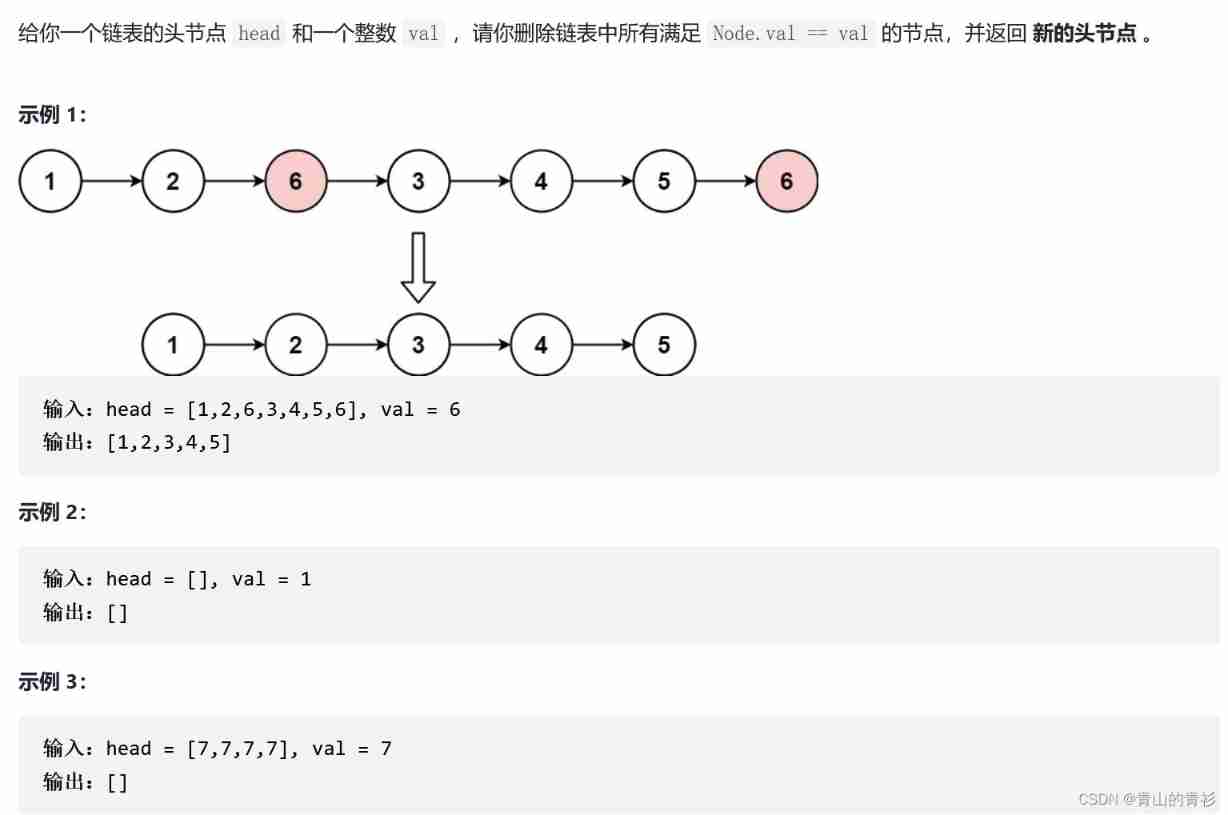
2. Ideas
The overall idea is to delete nodes , But there are two ways to realize it .
(1) Do not use sentinel nodes
Relatively speaking, it is more complicated , Because it's not good to manage header nodes , There are two ways of thinking .
a. At the beginning, the special judgment head node , Time complexity is high .
b. Finally, determine the head node .(2) Use the header node
3. Specific code implementation
Create linked lists and function interfaces
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {
}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {
}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {
}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
} };
Do not use sentinel nodes
(1) First special judgment header node
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode* p =head; // Point to the head node
// Special judgment head node
while(p!= NULL && p->val == val)
{
ListNode* m =p;
head = head->next;
p = p->next;
delete m;
}
if(head == NULL) return nullptr;//1.NULL still nullptr? All the
ListNode* q =head; // Point to the head node Fixed ! And certainly not to be deleted
while(q != NULL && q->next != NULL)//2.q!=NULL Don't write it ? Sure
{
if(q->next->val == val)
{
ListNode* n = q->next;
q->next = n->next; // Connect the linked lists
delete n;
}
else// This can't be lost
q = q->next;
}
return head;
}
};
matters needing attention
1.return NULL/nullptr/head It's all right .
2. When q When the position pointed to is not sure whether it really exists, you can't just write q->next != NULL , Must be right q There is also judgment in the direction of .
3. When deleting nodes, you should not forget to connect the linked lists
(2) Finally, determine the head node
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode* p =head; // Point to the head node
ListNode* m =head; // Point to the head node
while(p!= NULL && p->next != NULL)//1. Can't be without p!=NULL It doesn't judge whether the current pointer is meaningful !
{
if(p->next->val == val){
ListNode* q =p->next;
p->next = q->next;
delete q;}
else
{
p = p->next;}
}
Special judgment head node
if(head != NULL && head->val == val)// Finally, determine the head node It is not empty and the value is val
{
if(head->next != NULL)// There are elements after the header node
{
head = head->next;
delete m;
return head;
}
else// There is no element after the header node
{
delete head;
return head;//2. Here it's changed to NULL also nullptr Fine
}
}
else// The head node is empty
return head;
}
};
matters needing attention
1. Be sure to judge whether the current pointer is meaningful !
2.return head Here it's changed to NULL also nullptr Fine
Use sentinel nodes
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
// Set up a sentinel node
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;// Point to the head node
ListNode *p = dummyHead;
while(p->next!= NULL)
{
if(p->next->val == val)
{
ListNode *q = p->next;
p->next = q->next;
delete q;
}else
p = p->next;
}
head = dummyHead->next;// I don't know
delete dummyHead;// No delete It's OK Habit should delete
return head;
}
};
matters needing attention
1. Using sentinel nodes should release ! This habit is better !
2.dummyHead The creation of :( according to struct The function in )//1. ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0); dummyHead->next = head;// Point to the head node //2. ListNode *dummyHead = new ListNode(0,head);// At the same time, specify its value and pointer to //3. You can also specify the direction first and then the value .
边栏推荐
- Ueeditor custom display insert code
- Microservice Remote debug, nocalhost + rainbond microservice Development second Bomb
- Dayu200 experience officer MPPT photovoltaic power generation project dayu200, hi3861, Huawei cloud iotda
- Gazebo import the mapping model created by blender
- 行测-图形推理-8-图群类
- Relationship between URL and URI
- Redis official ORM framework is more elegant than redistemplate
- Firefox browser installation impression notes clipping
- Anti climbing killer
- Record layoutrebuild Forcerebuildlayoutimmediate does not take effect
猜你喜欢
C # realizes the communication between Modbus protocol and PLC
Redis cluster installation
如何选择合适的自动化测试工具?

0-5vac to 4-20mA AC current isolated transmitter / conversion module
Micro service remote debug, nocalhost + rainbow micro service development second bullet
“拧巴”的早教行业:万亿市场,难出巨头

Redis集群安装
Visual studio 2019 installation

Remember an experience of using selectmany
![VTOL in Px4_ att_ Control source code analysis [supplement]](/img/7a/4ce0c939b9259faf59c52da2587693.jpg)
VTOL in Px4_ att_ Control source code analysis [supplement]
随机推荐
7-18 simple simulation of banking business queue
The PHP source code of the new website + remove authorization / support burning goose instead of pumping
行测-图形推理-3-对称图形类
Digital transformation: five steps to promote enterprise progress
Visual studio 2019 installation
C # realizes the communication between Modbus protocol and PLC
OpenGL configuration vs2019
Matplotlib快速入门
Leetcode206. Reverse linked list
客户案例|华律网,通过观测云大幅缩短故障定位时间
ASP.NET Core入门五
Robot autonomous exploration DSVP: code parsing
Kaggle-Titanic
Remember that a development is encountered in the pit of origin string sorting
Revit secondary development - Hide occlusion elements
php 获取图片信息的方法
Revit secondary development - shielding warning prompt window
Unity technical notes (I) inspector extension
UWA Q & a collection
Revit secondary development - link file collision detection