当前位置:网站首页>Implementation of yolov5 single image detection based on onnxruntime
Implementation of yolov5 single image detection based on onnxruntime
2022-07-02 07:35:00 【wxplol】
Connected to a be based on pytorch Of YOLOv5 Single picture detection implementation , We did pytorch Forward reasoning , But this reasoning process needs to rely on yolov5 Its own model file and the process of structure construction , So it's still troublesome . here , Is there a direct forward reasoning , Then only process the results , Don't need to consider yolov5 Own documents . So now the introduction is based on onnx The reasoning of . The reasoning process is also very simple , Convert the original model into onnx Format , And then use onnxruntime Just do it , See my article for specific operation .
List of articles
One 、pt turn onnx
Here we mainly refer to :https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/issues/251 Content in , Get into yolov5 The installation directory , Perform the following :
python models/export.py --weights yolov5s.pt --img 640 --batch 1
Two 、onnxruntime Forward reasoning
1. Installation dependency
pip install onnxruntime
2. Code implementation
# coding=utf-8
import cv2.cv2 as cv2
import numpy as np
import onnxruntime
import torch
import torchvision
import time
import random
class YOLOV5_ONNX(object):
def __init__(self,onnx_path):
''' initialization onnx'''
self.onnx_session=onnxruntime.InferenceSession(onnx_path)
self.input_name=self.get_input_name()
self.output_name=self.get_output_name()
def get_input_name(self):
''' Get input node name '''
input_name=[]
for node in self.onnx_session.get_inputs():
input_name.append(node.name)
return input_name
def get_output_name(self):
''' Get the output node name '''
output_name=[]
for node in self.onnx_session.get_outputs():
output_name.append(node.name)
return output_name
def get_input_feed(self,image_tensor):
''' Get input tensor'''
input_feed={
}
for name in self.input_name:
input_feed[name]=image_tensor
return input_feed
def letterbox(self,img, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=False, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True,
stride=32):
''' Picture normalization '''
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = img.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better test mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimum rectangle
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, stride), np.mod(dh, stride) # wh padding
elif scaleFill: # stretch
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return img, ratio, (dw, dh)
def xywh2xyxy(self,x):
# Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
y = np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 # top left x
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 # top left y
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
def nms(self,prediction, conf_thres=0.1, iou_thres=0.6, agnostic=False):
if prediction.dtype is torch.float16:
prediction = prediction.float() # to FP32
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
min_wh, max_wh = 2, 4096 # (pixels) minimum and maximum box width and height
max_det = 300 # maximum number of detections per image
output = [None] * prediction.shape[0]
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
box = self.xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4])
conf, j = x[:, 5:].max(1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat((torch.tensor(box), conf, j.float()), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n:
continue
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = torchvision.ops.boxes.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres)
if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detections
i = i[:max_det]
output[xi] = x[i]
return output
def clip_coords(self,boxes, img_shape):
''' Check to see if it's out of bounds '''
# Clip bounding xyxy bounding boxes to image shape (height, width)
boxes[:, 0].clamp_(0, img_shape[1]) # x1
boxes[:, 1].clamp_(0, img_shape[0]) # y1
boxes[:, 2].clamp_(0, img_shape[1]) # x2
boxes[:, 3].clamp_(0, img_shape[0]) # y2
def scale_coords(self,img1_shape, coords, img0_shape, ratio_pad=None):
''' The coordinates correspond to the original image , Reverse operation : subtract pad, Divided by the minimum zoom factor :param img1_shape: Enter dimensions :param coords: Enter coordinates :param img0_shape: Mapped dimensions :param ratio_pad: :return: '''
# Rescale coords (xyxy) from img1_shape to img0_shape
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from img0_shape
gain = min(img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]) # gain = old / new, Calculate the zoom ratio
pad = (img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (
img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh padding , Calculate the expanded size
else:
gain = ratio_pad[0][0]
pad = ratio_pad[1]
coords[:, [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x padding, subtract x Expansion in direction
coords[:, [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y padding, subtract y Expansion in direction
coords[:, :4] /= gain # take box The coordinates correspond to the original image
self.clip_coords(coords, img0_shape) # Boundary check
return coords
def sigmoid(self,x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def infer(self,img_path):
''' Perform the forward operation to predict the output '''
# Super parameter settings
img_size=(640,640) # Picture zoom size
conf_thres=0.25 # Confidence threshold
iou_thres=0.45 #iou threshold
class_num=1 # Number of categories
stride=[8,16,32]
anchor_list= [[10,13, 16,30, 33,23],[30,61, 62,45, 59,119], [116,90, 156,198, 373,326]]
anchor = np.array(anchor_list).astype(np.float).reshape(3,-1,2)
area = img_size[0] * img_size[1]
size = [int(area / stride[0] ** 2), int(area / stride[1] ** 2), int(area / stride[2] ** 2)]
feature = [[int(j / stride[i]) for j in img_size] for i in range(3)]
# Read the picture
src_img=cv2.imread(img_path)
src_size=src_img.shape[:2]
# Picture filling and normalization
img=self.letterbox(src_img,img_size,stride=32)[0]
# Convert
img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) # BGR to RGB, to 3x416x416
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
# normalization
img=img.astype(dtype=np.float32)
img/=255.0
# # BGR to RGB
# img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1)
# img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
# Dimension expansion
img=np.expand_dims(img,axis=0)
# Forward reasoning
start=time.time()
input_feed=self.get_input_feed(img)
pred=self.onnx_session.run(output_names=self.output_name,input_feed=input_feed)
# Extract features
y = []
y.append(torch.tensor(pred[0].reshape(-1,size[0]*3,5+class_num)).sigmoid())
y.append(torch.tensor(pred[1].reshape(-1,size[1]*3,5+class_num)).sigmoid())
y.append(torch.tensor(pred[2].reshape(-1,size[2]*3,5+class_num)).sigmoid())
grid = []
for k, f in enumerate(feature):
grid.append([[i, j] for j in range(f[0]) for i in range(f[1])])
z = []
for i in range(3):
src = y[i]
xy = src[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5
wh = (src[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2
dst_xy = []
dst_wh = []
for j in range(3):
dst_xy.append((xy[:, j * size[i]:(j + 1) * size[i], :] + torch.tensor(grid[i])) * stride[i])
dst_wh.append(wh[:, j * size[i]:(j + 1) * size[i], :] * anchor[i][j])
src[..., 0:2] = torch.from_numpy(np.concatenate((dst_xy[0], dst_xy[1], dst_xy[2]), axis=1))
src[..., 2:4] = torch.from_numpy(np.concatenate((dst_wh[0], dst_wh[1], dst_wh[2]), axis=1))
z.append(src.view(1, -1, 5+class_num))
results = torch.cat(z, 1)
results = self.nms(results, conf_thres, iou_thres)
cast=time.time()-start
print("cast time:{}".format(cast))
# Map to the original image
img_shape=img.shape[2:]
print(img_size)
for det in results: # detections per image
if det is not None and len(det):
det[:, :4] = self.scale_coords(img_shape, det[:, :4],src_size).round()
if det is not None and len(det):
self.draw(src_img, det)
def plot_one_box(self,x, img, color=None, label=None, line_thickness=None):
# Plots one bounding box on image img
tl = line_thickness or round(0.002 * (img.shape[0] + img.shape[1]) / 2) + 1 # line/font thickness
color = color or [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)]
c1, c2 = (int(x[0]), int(x[1])), (int(x[2]), int(x[3]))
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
if label:
tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness
t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0]
c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(img, label, (c1[0], c1[1] - 2), 0, tl / 3, [225, 255, 255], thickness=tf, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
def draw(self,img, boxinfo):
colors = [[0, 0, 255]]
for *xyxy, conf, cls in boxinfo:
label = '%s %.2f' % ('image', conf)
print('xyxy: ', xyxy)
self.plot_one_box(xyxy, img, label=label, color=colors[int(cls)], line_thickness=1)
cv2.namedWindow("dst",0)
cv2.imshow("dst", img)
cv2.imwrite("data/res1.jpg",img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.imencode('.jpg', img)[1].tofile(os.path.join(dst, id + ".jpg"))
return 0
if __name__=="__main__":
model=YOLOV5_ONNX(onnx_path="./weights/image_detect.onnx")
model.infer(img_path="data/PMC2663376_00004.jpg")
result :
3、onnxruntime and pytorch Compare
- onnxruntime Reasoning time
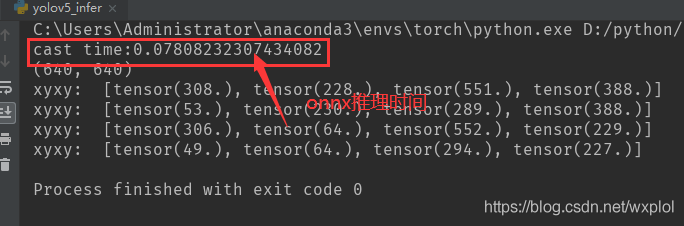
- pytorch Reasoning time

We are normalizing to 640x640 Compare on the image ,onnx Inferential than pure pytorch Time has improved 1 times . explain onnx Reasoning is still possible , Later, it will be tested on other acceleration frameworks , Look forward to the follow-up ...
github link :yolov5 Forward reasoning implementation
Reference link :
onnxruntime-for-yolov5
python3 onnx Reasoning Demo
边栏推荐
- conda常用命令
- Conversion of numerical amount into capital figures in PHP
- Error in running test pyspark in idea2020
- JSP intelligent community property management system
- Using compose to realize visible scrollbar
- 離線數倉和bi開發的實踐和思考
- Determine whether the version number is continuous in PHP
- 【深度学习系列(八)】:Transoform原理及实战之原理篇
- 解决万恶的open failed: ENOENT (No such file or directory)/(Operation not permitted)
- A summary of a middle-aged programmer's study of modern Chinese history
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Faster-ILOD、maskrcnn_benchmark安装过程及遇到问题
SSM学生成绩信息管理系统
parser. parse_ Args boolean type resolves false to true
Practice and thinking of offline data warehouse and Bi development
Typeerror in allenlp: object of type tensor is not JSON serializable error
ARP attack
自然辩证辨析题整理
Conversion of numerical amount into capital figures in PHP
Yaml file of ingress controller 0.47.0
【MEDICAL】Attend to Medical Ontologies: Content Selection for Clinical Abstractive Summarization
spark sql任务性能优化(基础)
Regular expressions in MySQL
Sparksql data skew
读《敏捷整洁之道:回归本源》后感
Implement interface Iterable & lt; T>
【信息检索导论】第二章 词项词典与倒排记录表
如何高效开发一款微信小程序
Record of problems in the construction process of IOD and detectron2
A summary of a middle-aged programmer's study of modern Chinese history
使用Matlab实现:Jacobi、Gauss-Seidel迭代