当前位置:网站首页>Codeforces Round #605 (Div. 3)
Codeforces Round #605 (Div. 3)
2022-08-02 15:31:00 【Stubborn and cute】
Codeforces Round #605 (Div. 3)
B. Snow Walking Robot
Recently you have bought a snow walking robot and brought it home. Suppose your home is a cell (0,0)on an infinite grid.
You also have the sequence of instructions of this robot. It is written as the string s consisting of characters ‘L’, ‘R’, ‘U’ and ‘D’. If the robot is in the cell (x,y) right now, he can move to one of the adjacent cells (depending on the current instruction).
| 操作 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| If the current instruction is ‘L’, | then the robot can move to the left to (x−1,y); |
| if the current instruction is ‘R’, | then the robot can move to the right to (x+1,y); |
| if the current instruction is ‘U’, | then the robot can move to the top to (x,y+1); |
| if the current instruction is ‘D’, | then the robot can move to the bottom to (x,y−1) |
You’ve noticed the warning on the last page of the manual: if the robot visits some cell (except (0,0)) twice then it breaks.
So the sequence of instructions is valid if the robot starts in the cell (0,0), performs the given instructions, visits no cell other than (0,0) two or more times and ends the path in the cell (0,0). Also cell (0,0) should be visited at most two times: at the beginning and at the end (if the path is empty then it is visited only once). For example, the following sequences of instructions are considered valid: “UD”, “RL”, “UUURULLDDDDLDDRRUU”, and the following are considered invalid: “U” (the endpoint is not (0,0)) and “UUDD” (the cell (0,1) is visited twice).
The initial sequence of instructions, however, might be not valid. You don’t want your robot to break so you decided to reprogram it in the following way: you will remove some (possibly, all or none) instructions from the initial sequence of instructions, then rearrange the remaining instructions as you wish and turn on your robot to move.
Your task is to remove as few instructions from the initial sequence as possible and rearrange the remaining ones so that the sequence is valid. Report the valid sequence of the maximum length you can obtain.
Note that you can choose any order of remaining instructions (you don’t need to minimize the number of swaps or any other similar metric).
You have to answer q independent test cases.
Input
The first line of the input contains one integer q
(1≤q≤2⋅10^4) — the number of test cases.
The next q lines contain test cases. The i-th test case is given as the string s consisting of at least 1 and no more than 10^5 characters ‘L’, ‘R’, ‘U’ and ‘D’ — the initial sequence of instructions.
It is guaranteed that the sum of |s| (where |s| is the length of s) does not exceed 105 over all test cases (∑|s|≤105).
Output
For each test case print the answer on it. In the first line print the maximum number of remaining instructions. In the second line print the valid sequence of remaining instructions t the robot has to perform. The moves are performed from left to right in the order of the printed sequence. If there are several answers, you can print any. If the answer is 0, you are allowed to print an empty line (but you can don’t print it).
Example
Input
6
LRU
DURLDRUDRULRDURDDL
LRUDDLRUDRUL
LLLLRRRR
URDUR LLL
Output
2
LR
14
RUURDDDDLLLUUR
12
ULDDDRRRUULL
2
LR
2
UD
0
Note
There are only two possible answers in the first test case: “LR” and “RL”.
The picture corresponding to the second test case: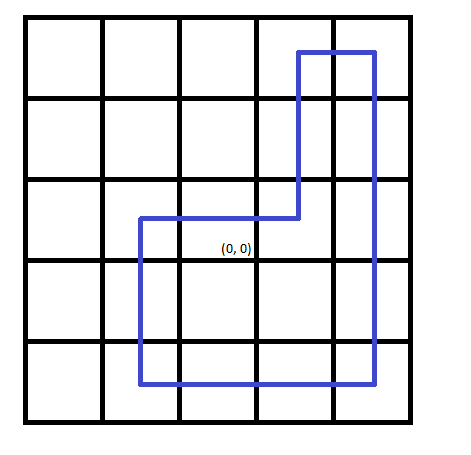
Note that the direction of traverse does not matter.
Another correct answer to the third test case: “URDDLLLUURDR”.
解析
题目很长,但是并不难,It's easy to do when you understand it.大概意思就是说,The given path that you want to modify the least number of times,The realization of returning to the origin after one round of operations(0,0),And the same point is not passed twice in the middle,Except for the origin of course.The implementation method is also easy to think of,Just around a rectangle,Output up, down, left and right.
ac代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long l,u,r,d;
string s;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
while(n--){
cin>>s;
l=r=u=d=0;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){
if(s[i]=='L')l++;
if(s[i]=='D')d++;
if(s[i]=='U')u++;
if(s[i]=='R')r++;
}
l=r=min(l,r);
u=d=min(u,d);
if(u==0)l=r=min(1ll,l);
/*其中用了1LL.LL其实代表long long, 1LL是为了在计算时,把int类型的变量转化为long long, 然后再赋值给long long类型的变量.*/
if(l==0)u=d=min(1ll,u);
cout<<l+d+u+r<<"\n";
for(int i=0;i<l;i++)cout<<"L";
for(int i=0;i<u;i++)cout<<"U";
for(int i=0;i<r;i++)cout<<"R";
for(int i=0;i<d;i++)cout<<"D";
cout<<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
D. Remove One Element
You are given an array a consisting of n integers.
You can remove at most one element from this array. Thus, the final length of the array is n−1 or n.
Your task is to calculate the maximum possible length of the strictly increasing contiguous subarray of the remaining array.
Recall that the contiguous subarray a with indices from l to r is a[l…r]=al,al+1,…,ar. The subarray a[l… r] is called strictly increasing if al<al+1<⋯<ar.
Input
The first line of the input contains one integer n
(2≤n≤2⋅105) — the number of elements in a.
The second line of the input contains n integers a1,a2,…,an (1≤ai≤109), where ai is the i-th element of a.
Output
Print one integer — the maximum possible length of the strictly increasing contiguous subarray of the array a after removing at most one element.
Examples
Input
5
1 2 5 3 4
Output
4
Input
2
1 2
Output
2
Input
7
6 5 4 3 2 4 3
Output
2
Note
In the first example, you can delete a3=5. Then the resulting array will be equal to [1,2,3,4] and the length of its largest increasing subarray will be equal to 4.
解析
The topic is probably about,Choose whether to delete a number,and find the longest consecutive increasing subsequence.
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+5;
int a[N],pre[N];
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
cin>>a[i];
if(a[i]>a[i-1])
pre[i]+=pre[i-1]+1;
else pre[i]=1;
}
for(int i=n;i>1;i--)
{
if(pre[i]<=pre[i-2]&&a[i]>a[i-2])
{
pre[i]=pre[i-2]+1;
for(int j=i;j<n;++j)
{
if(a[j+1]<=a[j])break;
pre[j+1]=pre[j]+1;
}
}
}
int *k=max_element(pre+1,pre+n+1);
cout<<*k;
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- Open the door of power and electricity "Circuit" (2): Power Calculation and Judgment
- MATLAB制作简易小动画入门详解
- SQL的通用语法和使用说明(图文)
- 软件测试基础知识(背)
- 编译error D8021 :无效的数值参数“/Wextra” cl command line error d8021 invalid numeric argument ‘/wextra‘
- What are IPV4 and IPV6?
- Publish module to NPM should be how to operate?Solutions to problems and mistake
- In-depth understanding of Golang's Map
- Fast advanced TypeScript
- MATLAB绘图函数ezplot入门详解
猜你喜欢
Summarize computer network super comprehensive test questions
二叉树遍历之后序遍历(非递归、递归)入门详解
Detailed introduction to drawing complex surfaces using the plot_surface command
How to reinstall Win7 system with U disk?How to reinstall win7 using u disk?

Win11系统找不到dll文件怎么修复
TCP三次握手、四次挥手
将SSE指令转换为ARM NEON指令

基于最小二乘法的线性回归分析方程中系数的估计

Win11 system cannot find dll file how to fix
MATLAB绘图命令fimplicit绘制隐函数图形入门详解
随机推荐
2.4G无线小模块CI24R1超低成本
奇技淫巧-位运算
推开机电的大门《电路》(三):说说不一样的电阻与电导
pygame图像连续旋转
Compilation error D8021: Invalid numeric argument '/Wextra' cl command line error d8021 invalid numeric argument '/Wextra'
实战美团Nuxt +Vue全家桶,服务端渲染,邮箱验证,passport鉴权服务,地图API引用,mongodb,redis等技术点
Article pygame drag the implementation of the method
Introduction to in-order traversal (non-recursive, recursive) after binary tree traversal
Failed to install using npx -p @storybook/cli sb init, build a dedicated storybook by hand
推开机电的大门《电路》(二):功率计算与判断
2021-10-14
Mapreduce环境详细搭建和案例实现
CS4398音频解码替代芯片DP4398完全兼容DAC解码
PHY6222蓝牙5.2支持MESH组网M0内核超低功耗
How to simulate 1/3 probability with coins, and arbitrary probability?
GMP scheduling model of golang
Win11没有本地用户和组怎么解决
Introduction to MATLAB drawing functions ezplot explanation
MATLAB图形加标注的基本方法入门简介
Golang 垃圾回收机制详解