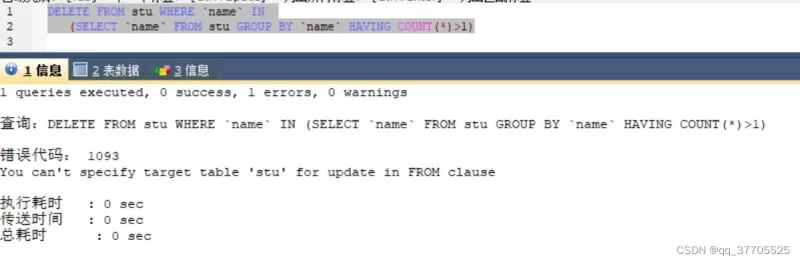
当前位置:网站首页>Design of electronic clock based on 51 single chip microcomputer
Design of electronic clock based on 51 single chip microcomputer
2022-07-05 17:16:00 【Teenagers, sneaking】
be based on 51 Design of electronic clock of single chip microcomputer
0 Function is introduced
1、 from DS1302 Read time display in
2、 altogether 4 A button , Key 1 Press to enter the modify time mode , Press again to switch the modified time variable , This is the time 2 and 3 The first key is the key to modify the time variable , After modification , Click the key 4 Confirm the change
3、 Not in modify mode , Press the button 2, You can switch the display of time and date
4、 In modify mode , The corresponding modified time variable will flash
1 Software platform and open source code
Simulation software :Proteus 8.9
Code writing :Keil5
Baidu network disk link :
link :https://pan.baidu.com/s/1RP_8MkZIqHt7WFPc6na3sQ
Extraction code :y2fn
– From Baidu network disk super member V4 The share of
Gitee link :
2 Simulation hardware selection
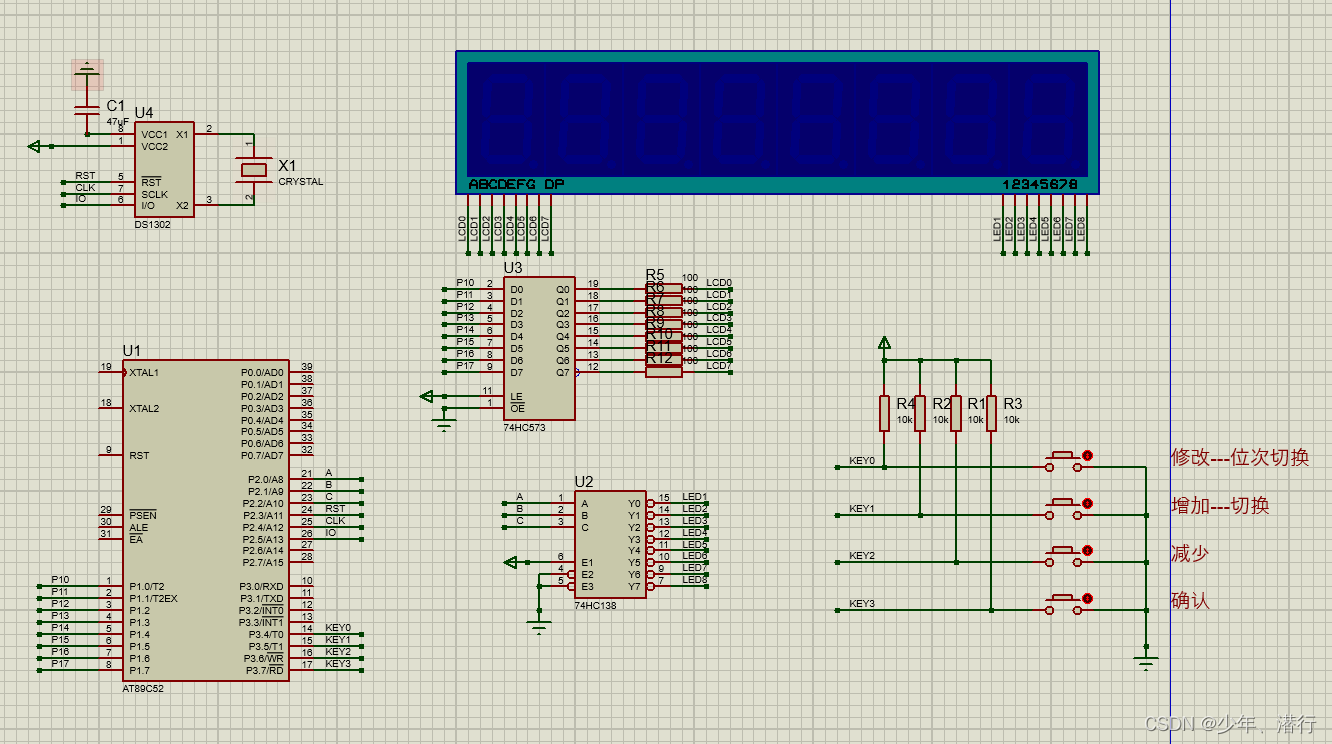
DS1302 Get the current time ,8 Bit common cathode digital tube ,74HC138 Make a choice ,74HC573 Make segment selection ,4 A button .
3 Code writing
3.1 The overall design idea
from DS1302 Read out the current time display , When modifying the time , First save the current time into a cache , Then modify the data in the cache , Wait until the modification is completed , Then write the data in the cache DS1302 in .
3.2 Software code design
3.2.1 The nixie tube shows
The display of the nixie tube will be placed in a 5ms In the timer of , every other 5ms, Change the display order , adopt 74HC138 To achieve the change of display bit .segCode It is the stored digital tube segment code , cache ,segBuff What is the actual value of , Is whose segment code , If the value is 10, I set it up. segCode by 0x00, That is, do not show .
void SegShow()
{
static u8 segSelectCount = 0;// Bit select variable
segSelectCount ++;
if(segSelectCount > 7)
segSelectCount = 0;
SEG = 0x00;// Blanking
switch (segSelectCount)
{
case 0: HCC = 0;HCB = 0;HCA = 0;SEG = segCode[segBuff[0]];break;
case 1: HCC = 0;HCB = 0;HCA = 1;SEG = segCode[segBuff[1]];break;
case 2: HCC = 0;HCB = 1;HCA = 0;SEG = 0x40 ;break;
case 3: HCC = 0;HCB = 1;HCA = 1;SEG = segCode[segBuff[2]];break;
case 4: HCC = 1;HCB = 0;HCA = 0;SEG = segCode[segBuff[3]];break;
case 5: HCC = 1;HCB = 0;HCA = 1;SEG = 0x40 ;break;
case 6: HCC = 1;HCB = 1;HCA = 0;SEG = segCode[segBuff[4]];break;
case 7: HCC = 1;HCB = 1;HCA = 1;SEG = segCode[segBuff[5]];break;
default:HCC = 0;HCB = 0;HCA = 0;SEG = segCode[segBuff[0]];break;
}
}
3.2.2 DS1302 Data processing in
Go to DS1302 Write value in register
void ds1302write(u8 addre,u8 dat)
{
u8 i;
RST=0;
_nop_();
SCK=0;
_nop_();
RST=1;
_nop_();
for (i=0;i<8;i++)
{
IO=addre&0x01;
addre>>=1;
SCK=1;
_nop_();
SCK=0;
_nop_();
}
for (i=0;i<8;i++)
{
IO=dat&0x01;
dat>>=1;
SCK=1;
_nop_();
SCK=0;
_nop_();
}
RST=0;
}
from DS1302 Medium reading value
u8 ds1302read(u8 addre)
{
u8 i,dat1,dat;
RST=0;
_nop_();
SCK=0;
_nop_();
RST=1;
_nop_();
for (i=0;i<8;i++)
{
IO=addre&0x01;
addre>>=1;
SCK=1;
_nop_();
SCK=0;
_nop_();
}
_nop_();
for (i=0;i<8;i++)
{
dat1=IO;
dat=(dat>>1)|(dat1<<7);
SCK=1;
_nop_();
SCK=0;
_nop_();
}
RST=0;
_nop_();
SCK=1;
_nop_();
IO=1;
_nop_();
IO=0;
_nop_();
return dat;
}
DS1302 The initialization , If defined at the beginning of the file FIRST_WRITE The value of is 1, Then it will go to DS1302 writes time[] Time set in , You can open this code for the first time , You can close it later .
void ds1302init()
{
#if FIRST_WRITE == 1
u8 i;
ds1302write(0x8e,0x00);
for (i=0;i<7;i++)
{
ds1302write(writeaddre[i],time[i]);
}
ds1302write(0x8e,0x80);
#endif
}
DS1302 Read time , Take data from DS1302 Read it from the register , Then make another one BCD Transcoding 10 Base conversion .
void ds1302readtime()
{
u8 i;
for (i=0;i<7;i++)
{
time[i]=ds1302read(readaddre[i]);
}
second = (time[0]/16)*10+(time[0]&0x0f);
minute = (time[1]/16)*10+(time[1]&0x0f);
hour = (time[2]/16)*10+(time[2]&0x0f);
day = (time[3]/16)*10+(time[3]&0x0f);
month = (time[4]/16)*10+(time[4]&0x0f);
week = (time[5]/16)*10+(time[5]&0x0f);
year = (time[6]/16)*10+(time[6]&0x0f);
}
DS1302 Write time , Do the variable to be written first 10 Turn into the system BCD code , Then write the corresponding register .
void ds1302writetime()
{
u8 i;
ds1302write(0x8e,0x00);
time[0] = (((secondTemp/10)<<4) + (secondTemp%10));
time[1] = (((minuteTemp/10)<<4) + (minuteTemp%10));
time[2] = (((hourTemp/10)<<4) + (hourTemp%10));
time[3] = (((dayTemp/10)<<4) + (dayTemp%10));
time[4] = (((monthTemp/10)<<4) + (monthTemp%10));
time[5] = (((weekTemp/10)<<4) + (weekTemp%10));
time[6] = (((yearTemp/10)<<4) + (yearTemp%10));
for (i=0;i<7;i++)
{
ds1302write(writeaddre[i],time[i]);
}
ds1302write(0x8e,0x80);
}
3.2.3 Key scan
Key scan reference punctual atom writing , But my delay is not according to his use delay Time delay , It is the timer delay used , The advantage of this is that the delay does not occupy CPU resources .
void KeyScan(u8 mode)
{
static int keyCount = 0;
static int keyState = 0;
if(mode == 1) keyState=0;
if (keyState == 0 && (KEY0 == 0||KEY1 == 0||KEY2 == 0||KEY3 == 0))
{
keyCount++;
if(keyCount>2)
{
keyState = 1;
keyCount=0;
if(KEY0 == 0) isKey0 = 1;
else if(KEY1 == 0) isKey1 = 1;
else if(KEY2 == 0) isKey2 = 1;
else if(KEY3 == 0) isKey3 = 1;
}
} else if (KEY0 == 1 && KEY1 == 1 && KEY2 == 1 && KEY3 == 1)
{
keyState = 0;
}
}
3.2.4 Modify the display variables according to the display mode
According to the display status variable , Modify the current display variable
void SegBuffChange()
{
if(showMode == 0)
{
segBuff[5] = second%10;
segBuff[4] = second/10;
segBuff[3] = minute%10;
segBuff[2] = minute/10;
segBuff[1] = hour%10;
segBuff[0] = hour/10;
}else if(showMode == 1)
{
segBuff[5] = day%10;
segBuff[4] = day/10;
segBuff[3] = month%10;
segBuff[2] = month/10;
segBuff[1] = year%10;
segBuff[0] = year/10;
}else if(showMode == 2)
{
segBuff[5] = secondTemp%10;
segBuff[4] = secondTemp/10;
segBuff[3] = minuteTemp%10;
segBuff[2] = minuteTemp/10;
segBuff[1] = hourTemp%10;
segBuff[0] = hourTemp/10;
}else if(showMode == 3)
{
segBuff[5] = dayTemp%10;
segBuff[4] = dayTemp/10;
segBuff[3] = monthTemp%10;
segBuff[2] = monthTemp/10;
segBuff[1] = yearTemp%10;
segBuff[0] = yearTemp/10;
}
}
3.2.5 Flicker function
In the key modification mode , Set the flashing status value 1, Because this function is placed in segBuff After the modification , So before the actual display , What is changed here will be the actual display , You can achieve a flashing effect .
void dataBlink()
{
static u8 blinkCount = 0;
static bit blinkState = 0;
if(changeOrNormalState == 1)// In the key modification mode
{
blinkCount++;
if(blinkCount == 80)// every other 80*5 Flashing state value transition
{
blinkState = !blinkState;
blinkCount = 0;
}
}else
{
blinkState = 0;
}
if(blinkState == 1)// If the flashing status value is 1, The digit variable nixie tube does not display , I am here seg.c There are definitions. ,10 Just don't show
{
segBuff[(2-changeCount%3)*2+1] = 10;
segBuff[(2-changeCount%3)*2] = 10;
}
}
3.2.6 Press the key to execute the function
The execution function after pressing the key , You can see the code comments
void ClockChangeFunction()
{
if(isKey0 == 1)
{
isKey0 = 0;
if(changeCount == 0 && changeOrNormalState == 0)// The modified bit is 0, Seconds , At the same time, the display state is under the normal display state
{
changeOrNormalState = 1;// Change the display status to modify the time mode
DataTempGet();// Get the value of the time variable before modification
showMode = 2;// The display mode is to display the hours, minutes and seconds under the modified time
}else if(changeOrNormalState == 1)// If it is in display mode
{
changeCount++;// Press the next key ++
if(changeCount > 5)
changeCount = 0;
if(changeCount > 2)// Hours, minutes and seconds are 0、1、2, Greater than 2 It is necessary to change the display of year, month and day
showMode = 3;// The display mode is to display the year, month and day under the modified time
else
showMode = 2;
}
}else if(isKey1 == 1)
{
isKey1 = 0;
if(changeOrNormalState == 1)// The display status is modified time mode
{
dataAdd();// The corresponding bit time variable increases
}else // Normal display mode
{
if(showMode == 0)// Switch the display of time and date
showMode = 1;
else if(showMode == 1)
showMode = 0;
}
}else if(isKey2 == 1)
{
isKey2 = 0;
if(changeOrNormalState == 1)// Just like adding
{
dataSub();
}
}else if(isKey3 == 1)
{
isKey3 = 0;
if(changeOrNormalState == 1)// Press... In modify mode
{
changeOrNormalState = 0;// Change to normal display mode
ds1302writetime();// Write the modified time
showMode = 0;// The display mode lasts for minutes and seconds
changeCount = 0;// Change the bit to zero
}
}
}
3.2.7 Time variable increasing function
This part of the code , Execute in the key execution function , But because of This part is too much , So encapsulate the function , Mainly used to change time variables . The main reason is that there is a leap year , Everything else is normal .
void dataAdd()
{
if(changeCount == 0)
{
secondTemp ++;
if(secondTemp > 59)
secondTemp = 0;
}else if(changeCount == 1)
{
minuteTemp ++;
if(minuteTemp > 59)
minuteTemp = 0;
}else if(changeCount == 2)
{
hourTemp ++;
if(hourTemp > 23)
hourTemp = 0;
}else if(changeCount == 3)
{
dayTemp ++;
if(monthTemp == 1 || monthTemp == 3 || monthTemp == 5 || monthTemp == 7 || monthTemp == 8 || monthTemp == 10 || monthTemp == 12)
{
if(dayTemp > 31)
dayTemp = 1;
}else if(monthTemp == 3 || monthTemp == 6 || monthTemp == 9 || monthTemp == 11)
{
if(dayTemp > 30)
dayTemp = 1;
}else if(monthTemp == 2)
{
if((2000+year)%400==0)
{
if(dayTemp > 29)
dayTemp = 1;
}
else
{
if((2000+year)%4==0&&(2000+year)%100!=0)
{
if(dayTemp > 29)
dayTemp = 1;
}else
{
if(dayTemp > 28)
dayTemp = 1;
}
}
}
}else if(changeCount == 4)
{
monthTemp ++;
if(monthTemp > 12)
monthTemp = 1;
}else if(changeCount == 5)
{
yearTemp ++;
if(yearTemp > 99)
yearTemp = 0;
}
}
4 summary
This design function is relatively simple , Maybe some places also have some small BUG, But I haven't found it yet , If anyone finds out , Welcome to exchange .
边栏推荐
- 启牛商学院股票开户安全吗?靠谱吗?
- The first lesson of EasyX learning
- Understand the usage of functions and methods in go language
- Machine learning compilation lesson 2: tensor program abstraction
- 浏览器渲染原理以及重排与重绘
- American chips are no longer proud, and Chinese chips have successfully won the first place in emerging fields
- dried food! Semi supervised pre training dialogue model space
- Application of threshold homomorphic encryption in privacy Computing: Interpretation
- goto Statement
- MySQL queries the latest qualified data rows
猜你喜欢
Example tutorial of SQL deduplication
![[729. My schedule I]](/img/e3/32914227d00cf7595ee850e60f2b72.png)
[729. My schedule I]
Judge whether a string is a full letter sentence
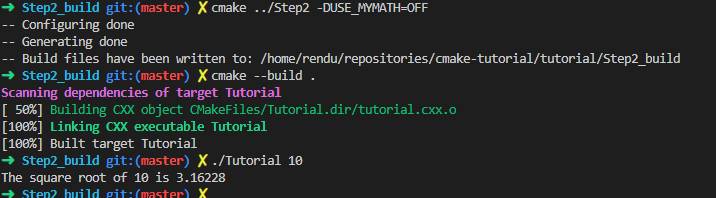
CMake教程Step2(添加库)
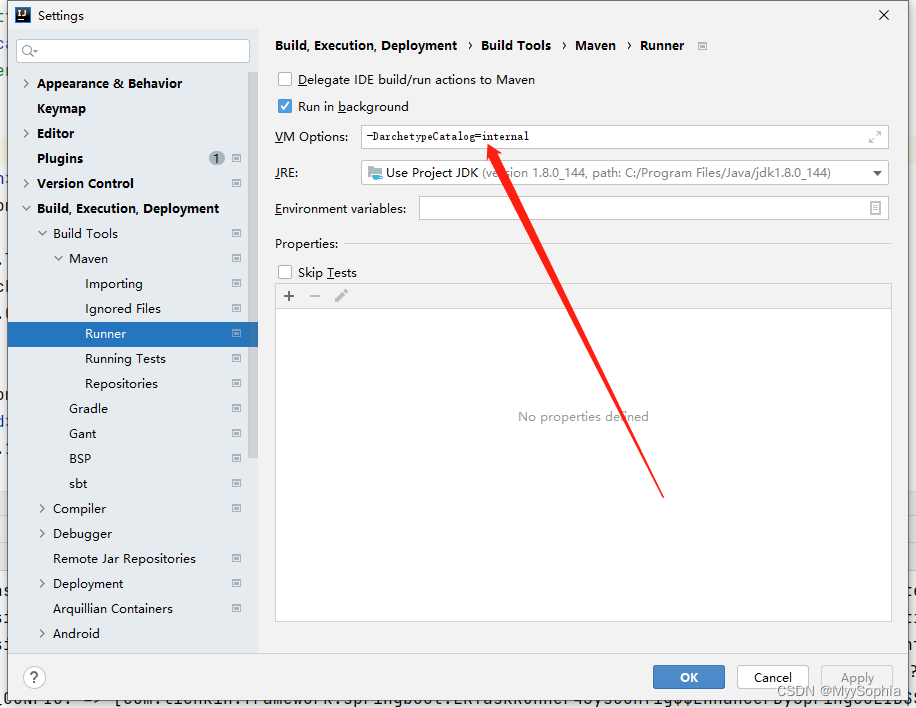
项目引入jar从私服Nexus 拉去遇到的一个问题
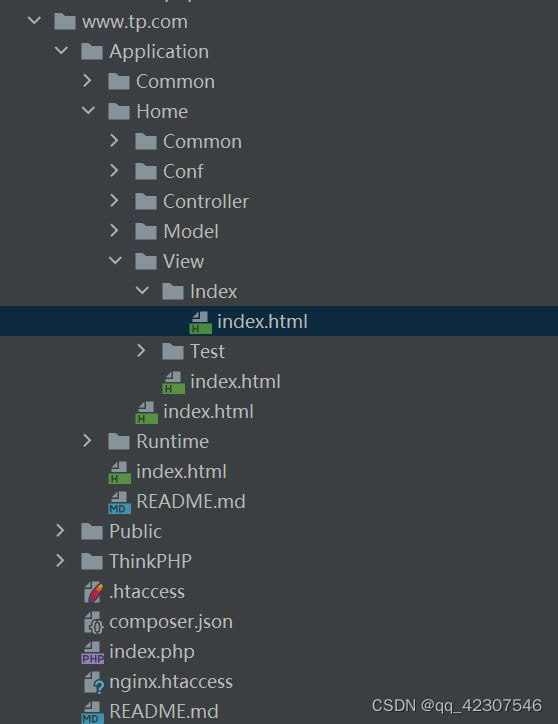
thinkphp模板的使用
Learnopongl notes (II) - Lighting
SQL删除重复数据的实例教程
PHP talent recruitment system development source code recruitment website source code secondary development
thinkphp3.2.3
随机推荐
CMake教程Step5(添加系统自检)
国内首家 EMQ 加入亚马逊云科技「初创加速-全球合作伙伴网络计划」
C how TCP restricts the access traffic of a single client
Zhang Ping'an: accélérer l'innovation numérique dans le cloud et construire conjointement un écosystème industriel intelligent
thinkphp3.2.3
齐宣王典故
Example tutorial of SQL deduplication
Embedded UC (UNIX System Advanced Programming) -3
项目引入jar从私服Nexus 拉去遇到的一个问题
Zhang Ping'an: accelerate cloud digital innovation and jointly build an industrial smart ecosystem
Three traversal methods of binary tree
CMake教程Step3(添加库的使用要求)
Judge whether a number is a prime number (prime number)
【Web攻防】WAF检测技术图谱
飞桨EasyDL实操范例:工业零件划痕自动识别
The third lesson of EasyX learning
【二叉树】根到叶路径上的不足节点
菜刀,蚁剑,冰蝎,哥斯拉的流量特征
Rider 设置选中单词侧边高亮,去除警告建议高亮
How to write a full score project document | acquisition technology