当前位置:网站首页>[factorial inverse], [linear inverse], [combinatorial counting] Niu Mei's mathematical problems
[factorial inverse], [linear inverse], [combinatorial counting] Niu Mei's mathematical problems
2022-07-06 07:39:00 【Code chess】
️ Pre knowledge ️
1️⃣ Introduction to inverse element
a × b ≡ 1 ( m o d p ) a \times b \equiv 1 ( mod\,\,p) a×b≡1(modp), It can be said that a yes b In the mold p Inverse element in case .
In fact, the inverse element can be regarded as the reciprocal
2️⃣ Factorial inverse
Mode one :
Find the inverse element through Fermat's theorem :
When p As a prime number , also gcd(a,p)=1 when , We have a p − 1 ≡ 1 ( m o d p ) a^{p−1}≡1(mod\ p) ap−1≡1(mod p). Then there is a p − 2 × a ≡ 1 ( m o d p ) a^{p−2}×a≡1(mod\ p) ap−2×a≡1(mod p), be a The inverse of is a p − 2 a^{p−2} ap−2
below ksm The function is a fast power
fact[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i % mod;
inv[i] = ksm(fact[i], mod - 2);
}
Mode two :
Pass formula 1 ( n + 1 ) ! × ( n + 1 ) = 1 n ! \frac{1}{(n+1)!}\times (n+1)=\frac{1}{n!} (n+1)!1×(n+1)=n!1 The inverse element of factorial is deduced from the approximate linearity
1 ( n + 1 ) ! \frac{1}{(n+1)!} (n+1)!1 In fact, it can be seen as ( n + 1 ) ! {(n+1)!} (n+1)! Inverse element
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i % mod;
inv[n] = ksm(fact[n], mod - 2);
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--)
inv[i] = inv[i + 1] * (i + 1) % mod;
3️⃣ Linear inverse element
seek [ 1 , N − 1 ] [1,N-1] [1,N−1] About mod Inverse element time of , It can be done in O ( N ) O(N) O(N) Solve in time
Let the modulus be p
For the present i, set up p = k × i + r p=k×i+r p=k×i+r, be
k × i + r ≡ 0 ( m o d p ) k × i × ( i − 1 × r − 1 ) + r × ( i − 1 × r − 1 ) ≡ 0 ( m o d p ) k × r − 1 + i − 1 ≡ 0 ( m o d p ) i − 1 ≡ − k × r − 1 ( m o d p ) i − 1 ≡ − ⌊ p i ⌋ × r − 1 ( m o d p ) \begin{aligned} k \times i + r & \equiv 0 &\,\,(mod \,\, p) \\ k \times i \times ( i^{-1} \times r ^{-1}) + r \times (i^{-1} \times r^{-1}) &\equiv 0 &\,\,( mod \,\, p) \\ k \times r^{-1} + i ^ {-1} & \equiv 0 &\,\, (mod \,\, p)\\ i^{-1} & \equiv -k \times r^{-1} &\,\, (mod \,\, p) \\ i^{-1} & \equiv - \left \lfloor \frac{p}{i}\right \rfloor \times r^{-1} &\,\,(mod\,\,p) \end{aligned} k×i+rk×i×(i−1×r−1)+r×(i−1×r−1)k×r−1+i−1i−1i−1≡0≡0≡0≡−k×r−1≡−⌊ip⌋×r−1(modp)(modp)(modp)(modp)(modp)
Be careful :
i n v [ 1 ] inv[1] inv[1] Be sure to initialize to 1, Need from 2 Start tweeting , Cannot from 1 Start tweeting
inv[0] = inv[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < N; i++)
inv[i] = inv[mod % i] * (mod - mod / i) % mod;
At the same time, we can find Factorial inverse :
Just multiply the inverse element in a form similar to factorial , Obtained inv[i] That is to say i ! i! i! Inverse element
for(int i = 2; i < N; i++)
inv[i] = inv[i - 1] * inv[i] % mod;
4️⃣ Combination number calculation
C n m C_n^m Cnm Calculation
️ Mode one : Formula calculation
Calculations are based on inverse elements or factorials
C n m = n ! m ! ∗ ( n − m ) ! C_n^m = \frac{n!}{m!*(n-m)!} Cnm=m!∗(n−m)!n!
ll C(ll n, ll m)
{
if(n < m) return 0;
return fact[n] * inv[m] % mod * inv[n - m] % mod;
}
️ Mode two : Recursive method
Table creation required , Therefore, if the calculation range is relatively large, the space required is also large
The recursive formula : C n m = C n − 1 m + C n − 1 m − 1 C_n^m = C_{n-1}^{m} + C_{n-1}^{m-1} Cnm=Cn−1m+Cn−1m−1
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
{
if(i == j || j == 0) c[i][j] = 1;
else c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j - 1] + c[i - 1][j];
}
5️⃣ subject
link :
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/23481/J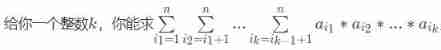
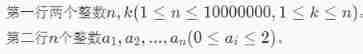
Is to select k Multiply values , Finally, add the results
Because there are only three cases of the number size in the array . So you can cut the entrance according to this .
First 0 0 0 You don't have to think about , Next, consider n n n individual 1 1 1 and m m m individual 2 2 2, If the sum above 1 1 1 There is i i i individual , that 2 2 2 There needs to be k − i k-i k−i individual , So the answer is ∑ i = 0 k C ( n , i ) ∗ C ( m , k − i ) ∗ 2 k − i \sum_{i=0}^kC(n,i)*C(m,k-i)*2^{k-i} ∑i=0kC(n,i)∗C(m,k−i)∗2k−i
Pay attention to various initializations in the code
Initialization in linear inverse :inv[1] = 1fac[i]: 2 i 2^i 2ifact[i]: i ! i! i!
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const int N = 1e7 + 5, mod = 998244353;
ll fac[N], fact[N], inv[N];
ll C(ll n, ll m)
{
if(n < m) return 0;
return fact[n] * inv[m] % mod * inv[n - m] % mod;
}
void solve()
{
fac[1] = 2;
fac[0] = fact[0] = fact[1] = inv[0] = inv[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < N; i++)
{
fac[i] = fac[i - 1] * 2 % mod;
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i % mod;
inv[i] = inv[mod % i] * (mod - mod / i) % mod;
}
for(int i = 2; i < N; i++)
inv[i] = inv[i - 1] * inv[i] % mod;
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
vector<int> a(n);
int o = 0, t = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
if(a[i] == 1) o ++;
else if(a[i] == 2) t ++;
}
ll res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= k; i++)
{
res += C(o, i) * C(t, k - i) % mod * fac[k - i] % mod;
res %= mod;
}
cout << res << "\n";
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t;
// cin >> t;
t = 1;
while(t--) solve();
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- Launch APS system to break the problem of decoupling material procurement plan from production practice
- Ble of Jerry [chapter]
- word中如何删除某符号前面或后面所有的文字
- Wonderful use of TS type gymnastics string
- Three no resumes in the software testing industry. What does the enterprise use to recruit you? Shichendahai's resume
- Typescript void base type
- leecode-C语言实现-15. 三数之和------思路待改进版
- Word delete the contents in brackets
- Memory error during variable parameter overload
- Typescript indexable type
猜你喜欢
学go之路(一)go的基本介绍到第一个helloworld
Solution: système de surveillance vidéo intelligent de patrouille sur le chantier

Google可能在春节后回归中国市场。
杰理之BLE【篇】

Force buckle day31
![[MySQL learning notes 32] mvcc](/img/0d/2df82b63d1eb3283a84e27f67c1523.png)
[MySQL learning notes 32] mvcc

The way to learn go (I) the basic introduction of go to the first HelloWorld

JMeter performance test steps practical tutorial

Simulation of Teman green interferometer based on MATLAB
![[MySQL learning notes 30] lock (non tutorial)](/img/9b/1e27575d83ff40bebde118b925f609.png)
[MySQL learning notes 30] lock (non tutorial)
随机推荐
Helm install Minio
The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
word中把帶有某個符號的行全部選中,更改為標題
Generator Foundation
Database addition, deletion, modification and query
The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
Compliance and efficiency, accelerate the digital transformation of pharmaceutical enterprises, and create a new document resource center for pharmaceutical enterprises
Select all the lines with a symbol in word and change them to titles
Jerry's ad series MIDI function description [chapter]
Leecode-c language implementation -15 Sum of three ----- ideas to be improved
Scala language learning-08-abstract classes
[cf gym101196-i] waif until dark network maximum flow
Ble of Jerry [chapter]
Typescript void base type
MES, APS and ERP are essential to realize fine production
Jerry needs to modify the profile definition of GATT [chapter]
Ali's redis interview question is too difficult, isn't it? I was pressed on the ground and rubbed
TS 体操 &(交叉运算) 和 接口的继承的区别
TypeScript void 基础类型
Significance and measures of encryption protection for intelligent terminal equipment