当前位置:网站首页>Summary of Digital IC design written examination questions (I)
Summary of Digital IC design written examination questions (I)
2022-07-06 07:19:00 【Leather width】
Numbers IC Design a summary of written examination questions ( One )
It's almost autumn , This blog records some recently seen figures IC Design relevant written examination questions , My answer may not be right , For reference only
1. use 100MHz The clock of A To sample 200MHz The clock of B( And A irrelevant ) Produced 8bit Is the signal sampled synchronously or asynchronously ? What problems should be paid attention to when sampling ? How to solve ?
The sampling of slow clock signal to fast clock signal shall be asynchronous sampling .200MHz The length of the generated signal is 5ns, and 100MHz The period of the clock is 10ns(10ns Take a sample ), So if only synchronous sampling is used , It may be difficult to capture the signal ;
Something to be aware of : Even asynchronous sampling , If A Continue to produce 8bit Information , May lead to B These information cannot be sampled in time ( The clock A Output a message as 5ns,B by 10ns);
How to solve : According to the specific circuit characteristics , The introduction of a FIFO Storage is too late to be B Sampling information .
2. use 100MHz The clock of A To sample 50MHz The clock of B( And A irrelevant ) Produced 1bit Is the signal sampled synchronously or asynchronously ? What problems should be paid attention to when sampling ? How to solve ?
The sampling of fast clock signal to slow clock signal should be synchronous sampling .50MHz The length of the generated signal is 20ns, and 100MHz The period of the clock is 10ns(10ns Take a sample ), Therefore, using synchronous sampling can completely capture 50Mhz The generated signal ;
Something to be aware of , How to solve : I can't think of anything to pay attention to for the time being , Think of it and then add ;
3. Please draw CMOS Circuit diagram of inverter , Whether it can be or not? PMOS and NMOS Position exchange ? as a result of ?
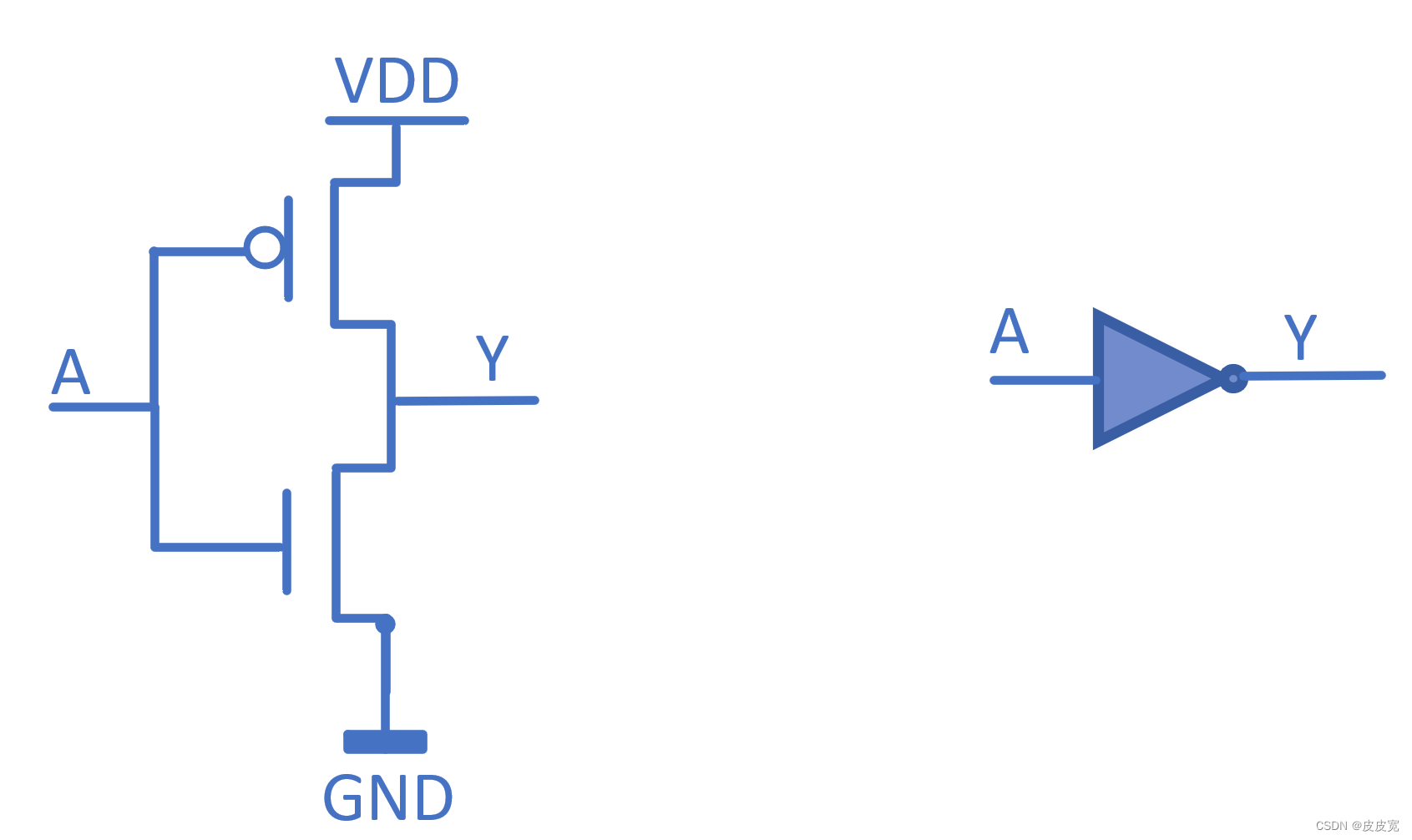
Not interchangeable ; MOS Tubes usually act as switches in circuits , Other conditions remain unchanged , The voltage of the grid , Determines the current between the drain and the drain ; about NMOS( below MOS tube ), When the grid (A) If the voltage of is greater than a certain value, it will turn on , And for PMOS( upper MOS tube ), Grid (A) If the voltage of is less than a certain value, it will turn on . When A For high voltage ,NMOS The pipe is open ,PMOS Pipe cut off ,Y Low level ; When A For high voltage ,NMOS end ,PMOS Conduction ,Y High level ; So as to realize the function of inverter . if NMOS and PMOS swap , be A For high voltage ,Y Also high level ,A Low power level ,Y Also low level , It cannot function as an inverter .
4. Do you understand ( Lidar ) Basic principle of ranging , Examples: simple speed ;
Calculate the distance according to the time difference between sending and receiving signals . The sender A stay t 1 t_{1} t1 It always emits a light or sound signal , encounter B Then it is reflected back ,A The time of receiving the reflected signal is t 2 t_{2} t2, Suppose the speed of the transmitted signal is c c c, be A And B The distance between is s = c ∗ ( t 2 − t 1 ) s =c*(t_{2}-t_{1}) s=c∗(t2−t1)
5. Explanation of terms commonly used in chip field :DSP? DMA? SIMD? Noc? Traditional classics RISC Architecturally CPU Where is it? 5 It's a cascade of water ?
- DSP: Digital signal processing (Digital Signal Processing,DSP), Simply put, it is a chip that processes digital signals ;
- DMA:DMA(Direct Memory Access, Direct memory access ) Allow direct reading and writing of data between external devices and memory , No need to pass CPU intervention .
- SIMD: Full name Single Instruction Multiple Data, Single instruction multi data stream , Can copy multiple operands , And package them in a set of instructions in a large register . Simply put, one instruction can handle multiple operands , such as a = [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ] , b = [ 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 ] a=[1,2,3,4],b=[5,6,7,8] a=[1,2,3,4],b=[5,6,7,8], perform SIMD The instructions of can be completed directly c = a + b c=a+b c=a+b;
- Noc: Network on chip (NoC:Network-on-Chip) It is a kind of multi-core SoC Designed a new on-chip communication architecture , It is an electronic system based on network communication realized on a single chip , Its form is integrated circuit chip .
- Traditional classics RISC framework CPU Of 5 It's a cascade of water : Fingering , decoding , perform , Visiting and depositing , Write back ;
6. CPU in ,MMU Basic function ?WatchDog Basic function ? In terms of computer architecture, there are oneortwo factors that affect the depth of interrupt nesting ?CPU Which two timing problems should be paid attention to when resetting ?
- MMU Basic function :MMU yes Mermory Management Unit( Memory management unit ), When CPU When accessing a memory address ,MMU Responsible for CPU Want to access the virtual address of memory ( Or logical address ) Convert to physical address ;
- WatchDog The role of : watchdog , In a nutshell , Design a timer , The internal counter of the timer increases with time , When increasing to a certain value , System forced reset , And when the program runs normally , The timer will be reset at regular intervals , In this way, the system will not be reset , And when the program fails , When it cannot run normally , Naturally, it is difficult to clean the counter in time , This is a WatchDog( watchdog ) The system will be forcibly reset , So as to solve the problem of program flying .
- Factors that interrupt nesting depth : When an interrupt or higher interrupt comes , The system saves the location of the currently executing program to the stack , When the higher-level interrupt program is completed , Then successively take the program address from the stack , Continue to execute instructions that have not been completed before , therefore , The capacity of the stack affects the depth of interrupt nesting .
7. Please write down the commonly used low-power design ideas
- a. Power gating Power gating technology : It is to close temporarily unused modules , It's simpler and rougher ;
- b. Multi voltage power supply technology : Simply speaking , For different modules , Different voltages are distributed according to their characteristics , So as to achieve the effect of reducing the overall power consumption ;
- c. clock gating Gated clock technology : Only the clock signal of the currently running module is retained , For other modules, the clock signal is always 0, So as to reduce the invalid flip of the trigger of the system , Thus reducing the overall power consumption ;
- d. Register transfer level power reduction technology :(1) Resource sharing . If you implement more computational logic , Be sure to share the calculation results , Prevent double counting at different locations ;(2) Remove redundant conversions .
8. Please briefly explain what is MOS Dynamic power consumption of tubes , Static power consumption ;
Dynamic power consumption : Dynamic power consumption refers to the chip in operation , The power consumption caused by the transistor in the jump state .
Static power consumption : Static power consumption refers to leakage current power consumption , Is the power consumption when the circuit state is stable .
Simply speaking , That is, the power consumption generated by the conversion and reversal of each level signal in the system is the dynamic power consumption , When the level of each position in the system remains unchanged , The generated power consumption is static power consumption ;
9. Please briefly sram Related issues ,a. Single-port sram( Single port ) and dual-port sram( really - Dual port ) The difference between ;b.Two-port sram( Pseudo dual port sram) and dual-port sram The difference between ( Refers to dual ports that can support simultaneous reading and writing sram)
| RAM type | Official explanation | Number of data read / write interfaces | Number of address interfaces |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single port | Allow read and write access to storage through one port | 1 | 1 |
| Pseudo dual port | Two ports are provided A and B, Through the port A Write access , Through the port B Read access | 1 | 2 |
| Dual port | Provide two ports A and B, Both ports can read and write storage | 2 | 2 |
10. Please briefly describe the following two RTL The difference between sentences , Then compare their advantages and disadvantages .
(a)assign OUT1 = (SEL === 0) ? IN1 : IN2;
(b)always(*)
if(SEL === 0)
OUT1 = IN1;
else
OUT1 = IN2;
(b) in ,OUT1 by reg type ,always(*) Indicates that it is sensitive to all input signal levels , If SEL No change , So initial OUT1 Is unstable , and (a) Medium OUT1 by wire type ,OUT1 Initially, it will pass judgment SEL assignment ;
PS: The circuit actually synthesized , There is no difference between the two ways of writing , although b We need to put OUT1 Defined as reg type , But it is still wire
边栏推荐
- Hydra common commands
- Structure summary of SystemVerilog integrable model
- LeetCode 78:子集
- word删除括号里内容
- Oracle column to row -- a field is converted to multiple rows according to the specified separator
- leetcode841. Keys and rooms (medium)
- 树莓派串口登录与SSH登录方法
- Oracle database 11gr2 uses TDE transparent data encryption to report an error ora28353. If you run to close the wallet, you will report an error ora28365. If you run to open the wallet, you will repor
- Wechat brain competition answer applet_ Support the flow main belt with the latest question bank file
- OpenJudge NOI 2.1 1661:Bomb Game
猜你喜欢
Path analysis model

Leetcode 78: subset
杰理之AD 系列 MIDI 功能说明【篇】
学go之路(一)go的基本介绍到第一个helloworld

The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
MVVM of WPF
Thought map of data warehouse construction
NiO programming introduction
Leetcode59. spiral matrix II (medium)
Idea console color log
随机推荐
Upgraded wechat tool applet source code for mobile phone detection - supports a variety of main traffic modes
Excel的相关操作
Raspberry pie 3B update VIM
[JDBC] quick start tutorial
Oracle column to row -- a field is converted to multiple rows according to the specified separator
Oracle database 11gr2 uses TDE transparent data encryption to report an error ora28353. If you run to close the wallet, you will report an error ora28365. If you run to open the wallet, you will repor
TypeScript 接口属性
supervisor 使用文档
微信脑力比拼答题小程序_支持流量主带最新题库文件
杰理之如若需要大包发送,需要手机端修改 MTU【篇】
剪映的相关介绍
word设置目录
qt颜色与字符串、uint相互转换
Multithreading and concurrent programming (2)
Configure raspberry pie access network
杰理之BLE【篇】
Uni app practical project
Cookie技术&Session技术&ServletContext对象
The best way to learn SEO: search engine
作者已死?AI正用艺术征服人类