I/O Model
java Support 3 Network programming model I/O Pattern :BIO( Synchronize and block )、NIO( Synchronous nonblocking )、AIO( Asynchronous non-blocking )
Blocking refers to access IO Whether the thread of will block ( Or wait for ). Threads access resources , A way of handling whether the resource is ready .
Blocking and non blocking :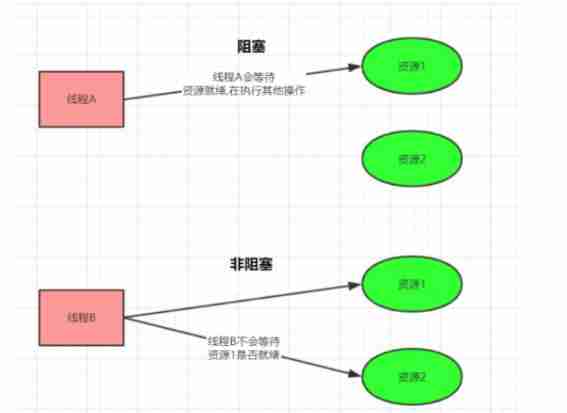
Synchronous and asynchronous :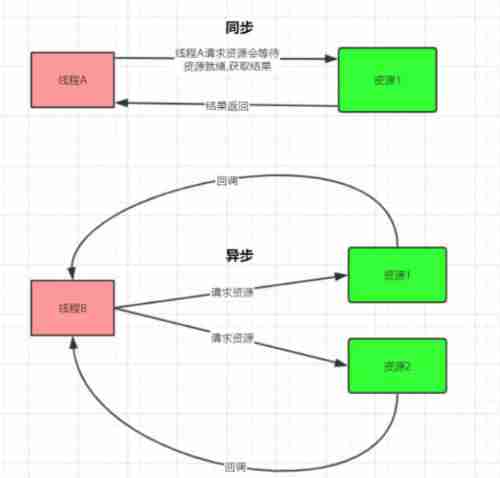
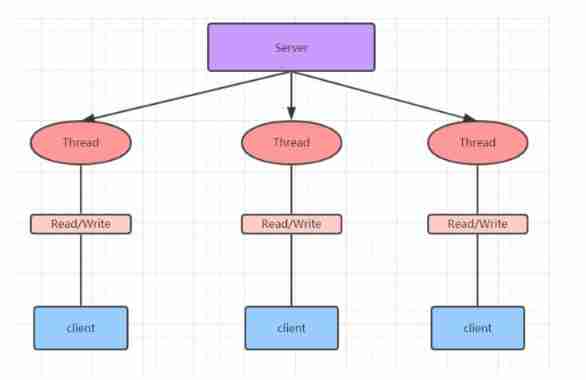
1.1 BIO
BIO: Synchronous blocking , The server implements a pattern of one thread per connection , That is, when the client has a connection request, the server needs to start a thread for processing , If this connection doesn't do anything, it will cause unnecessary thread overhead , It can be improved through the thread pool mechanism .
Code example :
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket=new ServerSocket(9999);
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
while (true){
Socket socket=serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println(" There is a client connection ");
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
int read = inputStream.read(b);
System.out.println(" Received client information :"+new String(b,0,read));
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write(" Hello, client ".getBytes(Charset.defaultCharset()));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
}
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",9999);
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write(" Hello, server ".getBytes(Charset.defaultCharset()));
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
inputStream.read(bytes);
System.out.println(" Received the server message :"+new String(bytes));
socket.close();
}
}
BIO Problem analysis :
- Each request needs to create a separate thread , Data with the corresponding client Read、 Business processing 、 data Write
- When the number of concurrent is large , A large number of threads need to be created to handle connections , The system resources take up a lot
- After the connection is established , If the current thread has no data to read temporarily , The thread is blocked in Read Operationally , Cause resource congestion .
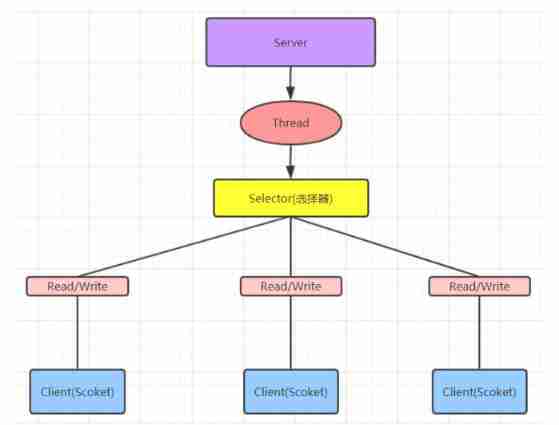
1.2 NIO
NIO: Synchronous nonblocking , The server implementation mode deals with multiple requests for one thread ( Connect ), That is, the connection requests sent by the client will be registered on the multiplexer , The multiplexer polls the connection to have I/O The request is processed .
Code example :
public class NioSelectorServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//1. Open the server channel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open();
//2. Binding port number
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999));
//3. Set the channel to non blocking
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//4. Create selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//5. Register the server channel to the selector , And specify the registered listening event as OP_ACCEPT
serverSocketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true){
//6. Check the selector release for events
// int select = selector.select(2000);
int select = selector.select();
if(select==0){
System.out.println(" There is no connection ");
continue;
}
//7. Get event collection
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
//8. Determine whether the event is a connection event
if(selectionKey.isAcceptable()){
//9. Get the client channel , And register the channel to the selector
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
System.out.println(" There is a client connection ");
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
//10. Determine whether it is a read ready event
else if(selectionKey.isReadable()){
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//11. Get the client channel , Read data to buffer
int read = 0;
read = channel.read(byteBuffer);
System.out.println(" Client message :"+new String(byteBuffer.array()));
System.out.println(" Simulating business processing ...");
Thread.sleep(5000);
if(read>0){
//12. Write back the data to the client
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(" Hello, client ".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
channel.close();
}
}
//13. Delete the corresponding event from the collection , Prevent secondary treatment
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
1.3 AIO
AIO The concept of asynchronous channel is introduced , Adopted Proactor Pattern , Simplified programming . Its characteristic is to inform the server program to start the thread to process after the operating system completes , It is generally applicable to applications with a large number of connections and a long connection time .
Proactor A pattern is a design pattern for asynchronous notification of messages ,Proactor Deployment readiness events notified , It's an operation completion event .
Applicable scenario :
- BIO It is applicable to the architecture with small and fixed number of connections , This approach is more demanding on server resources
- NIO It is suitable for architectures with a large number of connections and relatively short connections , For example, chat servers , Barrage system , Communication during service
- AIO It is suitable for architectures with many connections and long connections , Like the album server .
NIO Programming
2.1 NIO Introduce
Java NIO yes JDK What's new API.NIO There are three core parts :Channel,Buffer,Selector.NIO It's buffer oriented programming .JAVA NIO Non blocking mode of , A thread sends or reads data from a channel , Only the data currently available , If there is no data available , You will get nothing , Instead of blocking threads .
Easy to understand :NIO It can handle multiple operations with one thread . Suppose there is 1000 Please come here , According to the actual situation , Can allocate 50 or 100 Threads to handle . Unlike BIO like that , Obligatory distribution 1000 Threads .
NIO and BIO Compare
- BIO Is to process data in a stream , and NIO Is to process data in a buffer
- BIO It's blocked ,NIO It's non blocking
- BIO Operation based on byte stream and character stream , and NIO Is based on Channel and Buffer To operate .NIO be based on Selector Listen for events from multiple channels .