Focus on “Java Back end technology stack ”
reply “000” Access to a lot of e-books
Class loader
Class loaders are bones that many people think are hard . It's not that terrible , Please listen to Lao Tian's words .
Loading (Load) Stage , Gets the binary byte stream defined by the fully qualified name of the class , It needs to be done with class loader , seeing the name of a thing one thinks of its function , It's for loading Class Of documents .
We can customize one above String Something went wrong. , The problem lies in JVM I don't know which class we want to use , therefore JVM It defines a norm .
Divide this kind of loader into several categories .
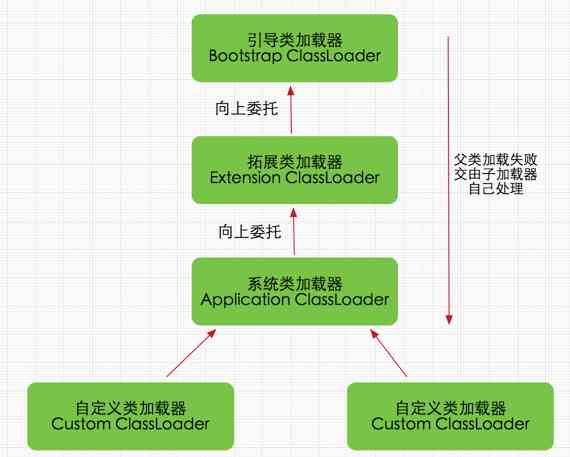
Bootstrap ClassLoader
Responsible for loading $JAVA_HOME in jre/lib/rt.jar All in class or Xbootclassoath Option specified jar package . from C++ Realization , No ClassLoader Subclass .
Extension ClassLoader
Responsible for loading Java Some of the extensions in the platform jar package , Include $JAVA_HOME in jre/lib/*.jar or -Djava.ext.dirs Specify... In the directory jar package .
App ClassLoader
Responsible for loading classpath Specified in the jar Package and Djava.class.path The classes in the specified directory and jar package .
Custom ClassLoader
adopt java.lang.ClassLoader Custom loading of subclasses class, It belongs to the application customized according to its own needs ClassLoader, Such as tomcat、jboss Will be based on j2ee Norms are self actualized ClassLoader.
Graphic class loading
Loading principles
Check if a class has been loaded : The order is bottom-up , from Custom ClassLoader To BootStrap ClassLoader Check layer by layer , Just one Classloader Loaded , Consider this class loaded , Guarantee that only ClassLoader To load a .
Order of loading : The order of loading is top-down , That is, the upper layer will try to load this class layer by layer .
ClassLoader Class analysis
java.lang.ClassLoader Three very important methods in :
loadClassMethod
findClassMethod
defineClassMethod
loadClass Method
1 public Class<?> loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
2 return loadClass(name, false);
3 }
4 protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve) throws ClassNotFoundException{
5 // Synchronous lock is used , Ensure that there is no repeated loading
6 synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
7 // First check whether you have loaded it
8 Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
9 // Did not find
10 if (c == null) {
11 long t0 = System.nanoTime();
12 try {
13 // There are fathers
14 if (parent != null) {
15 // Let the parent class load
16 c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
17 } else {
18 // If there is no parent class , Then delegate to the boot loader to load
19 c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
20 }
21 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
22 // ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
23 // from the non-null parent class loader
24 }
25
26 if (c == null) {
27 // If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
28 // to find the class.
29 long t1 = System.nanoTime();
30 // If none of them are found , It is implemented through customization findClass To find and load
31 c = findClass(name);
32
33 // this is the defining class loader; record the stats
34 sun.misc.PerfCounter.getParentDelegationTime().addTime(t1 - t0);
35 sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClassTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t1);
36 sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClasses().increment();
37 }
38 }
39 // Whether it needs to be resolved at load time
40 if (resolve) {
41 resolveClass(c);
42 }
43 return c;
44 }
45 } just as loadClass The method shows , When the class load request arrives , First look up the class object from the cache , If there is a direct return , If it does not exist, it will be sent to the parent loader loaded by the class to load , If there is no parent load, it will be sent to the top-level boot class loader to load , In the end, if we still can't find , Then use findClass() Method to load ( About findClass() I'll talk more about ).
from loadClass Implementation can also know , If you don't want to redefine the rules for loading classes , There's no complicated logic , Just want to load your own specified class at run time , So we can use it directly this.getClass().getClassLoder.loadClass("className"), So you can call it directly ClassLoader Of loadClass Method to get class object .
findClass Method
1 protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
2 throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
3 }
stay JDK1.2 Before , When the custom class loads , Always inherit ClassLoader Class and rewrite loadClass Method , So as to implement the custom class loading class , But in JDK1.2 After that, users are no longer recommended to overwrite loadClass() Method , Instead, it is recommended to write the custom class loading logic in findClass() In the method .
From the previous analysis, we can see ,findClass() The method is in loadClass() Called in method , When loadClass() Method after the parent loader fails to load , Will call your own findClass() Method to complete class loading , This ensures that the custom classloader also conforms to the parental delegation mode .
It should be noted that ,ClassLoader Class is not implemented findClass() Method , Instead, throw ClassNotFoundException abnormal . At the same time, we should know ,findClass The way is usually with defineClass Methods used together .
defineClass Method
1 protected final Class<?> defineClass(String name, byte[] b, int off, int len,
2 ProtectionDomain protectionDomain) throws ClassFormatError{
3 protectionDomain = preDefineClass(name, protectionDomain);
4 String source = defineClassSourceLocation(protectionDomain);
5 Class<?> c = defineClass1(name, b, off, len, protectionDomain, source);
6 postDefineClass(c, protectionDomain);
7 return c;
8 }
defineClass() The method is to use byte The byte stream resolves to JVM Recognizable Class object .
Through this method, we can not only pass through class File instantiation class object , It can also be instantiated in other ways class object , Such as receiving a class of bytecode through the network , And then convert to byte The byte stream creates the corresponding Class object .
How to customize class loader
User defined according to their needs . Need to inherit from ClassLoader, Rewriting methods findClass().
If you want to write your own class loader , It only takes two steps :
- Inherit
ClassLoaderclass - Cover
findClass(String className)Method
**ClassLoader** Superclass loadClass Method is used to delegate the loading operation of a class to its parent class loader , Only if the class has not been loaded and the parent class loader cannot load it , Only called findClass Method .
If you want to implement this method , We must do the following :
1. Load bytecode for a class from a local file system or other source .
2. call ClassLoader Superclass defineClass Method , Provide bytecode to the virtual machine .
On the model of parental delegation
This is also very frequent in the interview .
If a class loader receives a request to load a class , First find out if it has been loaded , If not loaded , It doesn't try to load the class itself first , Instead, the request task is delegated to the parent loader , Recursion in turn .
If the parent loader can complete the class loading task , You're back ; Only when the parent loader cannot complete this load task , Just load it yourself .
advantage
Java Class along with the class loader that loads it , With a hierarchy of priorities .
such as ,Java Medium Object class , It's stored in rt.jar In , No matter which class loader wants to load this class , Finally, it is delegated to the startup class loader at the top of the model for loading , therefore Object It's the same class in all kinds of class loading environments .
If you don't use the parental delegation model , So if each class loader takes the load by itself , So there are many different things in the system Object class .
Cases of breaking the parental delegation model
tomcat
tomcat adopt war Package for application release , In fact, it violates the principle of the two parent delegation mechanism . Take a brief look at tomcat Hierarchy of classloader .
For some non basic classes that need to be loaded , It's going to be called WebAppClassLoader The class loader of the . When it doesn't load , And then give it to the top ClassLoader Loading . This loader is used to isolate different applications .class file , Like your two apps , May rely on different versions of the same third party , They don't affect each other .
How to be in the same JVM in , Running two incompatible versions , Of course, it's something that needs custom loaders to do .
that tomcat How to break the parental delegation mechanism ?
Look at the picture WebAppClassLoader, It loads its own directory of .class file , It is not passed to the loader of the parent class . however , It can use SharedClassLoader The class loaded , The function of sharing and separation is realized .
But you write one yourself ArrayList, Put it in the app Directory ,tomcat Still doesn't load . It's just that the custom loader order is different , But for the top floor , It's still the same .
OSGi
OSGi It used to be very popular ,Eclipse Just use OSGi As the basis of plug-in system .
OSGi It's the specification of the service platform , Designed for use with long running times 、 Dynamic updates and systems with minimal disruption to the operating environment .
OSGi The specification defines a lot about the package lifecycle , And how the infrastructure interacts with the bundle . These rules , By using special Java Class loader to enforce , More domineering .
such as , In general Java In the application ,classpath All classes in are visible to all other classes , There is no doubt that . however ,OSGi Class loaders are based on OSGi Specification and the manifest.mf Options specified in the file , To limit the interaction of these classes , This makes the programming style very weird . But it's not hard to imagine , This is a load that goes against intuition , It must be implemented by a dedicated class loader .
With jigsaw The development of ( For the purpose of Java SE Platform design 、 Implement a standard modular system ), I personally think , current OSGi, It doesn't mean much anymore .
OSGi It's a huge topic , You just need to know , There's such a complex thing , Modularization is realized , Each module can be installed independently 、 start-up 、 stop it 、 uninstall , That's all right. .
SPI
Java There is one of them. SPI Mechanism , The full name is Service Provider Interface, yes Java A set of functions provided to be implemented or extended by a third party API, It can be used to enable framework extensions and replace components .
I will write an article on this later , I won't go into details here .
Recommended reading :
《 System architecture : Product design and development of complex systems 》.pdf
《 A practical guide for front-line architects 》.pdf
《 Step by step Linux ( The first 2 edition )》.pdf
Official account “Java Back end technology stack ”
Free access 500G The latest learning materials