当前位置:网站首页>Part 1 - Chapter 2 pointer operation
Part 1 - Chapter 2 pointer operation
2020-11-08 19:28:00 【Li Lihao】
stay C In language , For any type T, Can be in T A corresponding variable containing the address of the object is generated at the memory address where it is located . This variable , It's actually a variable that points to an object , therefore , These variables are called The pointer .
Pointers are precise and efficient tools for building data structures and manipulating memory .
Chapter structure
- Pointer basis
- Storage allocation
- Arithmetic operations on data sets and pointers
- As a pointer to a function parameter
- The pointer to the pointer
- Generic pointers and type conversions
- A function pointer
Pointer basis
A pointer stores the address of the data in memory, not the data itself .
The best way to understand pointers : Charting .
- The pointer is usually linked by position with arrows , Instead of drawing the actual address in the icon .
- When the pointer complements any data ,, That is, the pointer is set to NULL when , Use two vertical lines to show .
- Dangling pointer : Pointer to an invalid address .
Some examples of errors that may result in dangling pointers : Cast any integer variable into a pointer variable ; Manipulating pointers that exceed the bounds of the array ; Release one or more pointers that are still referenced .
Storage allocation
The size of pointer variables is usually related to the compiler settings and some specific C Implementation of the Type qualifiers of .
- You must remember : When you declare a pointer , It just allocates space for the pointer itself , There is no space allocated for the data referenced by the pointer .
by Data allocation space Two methods of :
- (1) Declare a variable directly
- (2) Dynamically allocate storage space at runtime ( for example : Use malloc or realloc).
When you declare a variable , What happened?
When you declare a variable , The compiler will reserve enough memory space according to the type of variable .
The storage space of variables is automatically allocated by the system , But this storage space does not exist permanently throughout the life cycle of the program .
The automatic variable is A variable whose storage space can be automatically allocated and released when entering or leaving a module or function
stay C In language , When you want to dynamically allocate storage space , You get a pointer to a heap storage space ( The first 3 Chapter ), This storage space is managed by us , And it will always be there , Unless we explicitly release it .
As a pointer to a function parameter
stay C The function in the call language plays an important role . most important of all , Pointers support passing parameters as references to functions ( Call by reference ).
When passing parameters by reference , When the function changes this parameter , The value of the changed parameter will always exist , Even after the function exits . When a pass function is called by value , At this point, the value change can only last until the function returns .
It is an efficient way to pass large and complex function parameters with pointers : Because it's just passing a pointer instead of a full copy of the data into the function , This can greatly save memory space
Call the pass function by reference
版权声明
本文为[Li Lihao]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- net.sf.json.JSONObject对时间戳的格式化处理
- CountDownLatch 瞬间炸裂!同基于 AQS,凭什么 CyclicBarrier 可以这么秀?
- Solution to cross domain problem of front end separation
- Learn volatile, you change your mind, I see
- Chapter 2 programming exercises
- awk实现类sql的join操作
- Express framework
- Talk about go code coverage technology and best practices
- 存储过程动态查询处理方法
- PHP generates unique strings
猜你喜欢
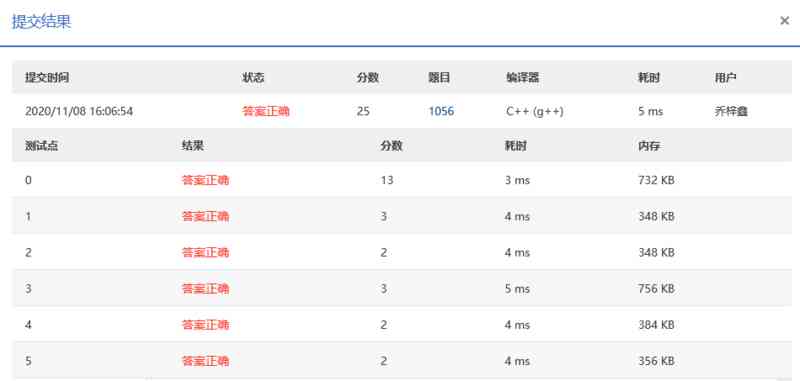
PAT_甲级_1056 Mice and Rice
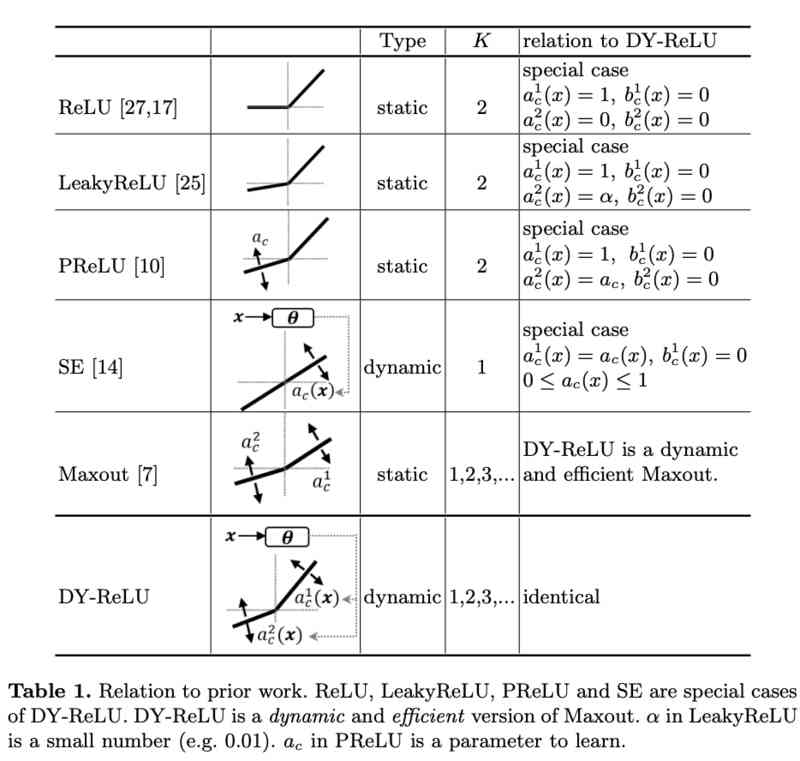
Dynamic ReLU:微软推出提点神器,可能是最好的ReLU改进 | ECCV 2020

C/C++学习日记:原码、反码和补码
VirtualBox install centos7

单例模式的五种设计方案

Your random IO hard disk

C / C + + knowledge sharing: function pointer and pointer function, can you understand after reading this article?
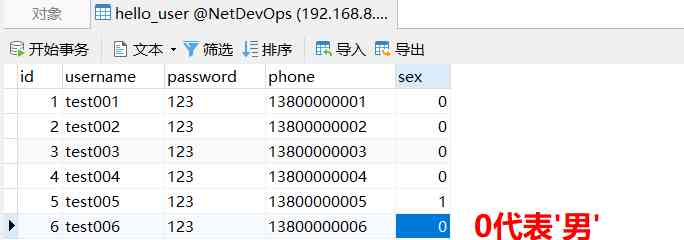
Django之简易用户系统(3)
接口测试用例思路总结

experiment
随机推荐
Part I - Chapter 1 Overview
Python 列表的11个重要操作
opencv 解决ippicv下载失败问题ippicv_2019_lnx_intel64_general_20180723.tgz离线下载
If the programming language as martial arts unique! C++ is Jiu Yin Jing. What about programmers?
[elastic search technology sharing] - ten pictures to show you the principle of ES! Understand why to say: ES is quasi real time!
Iptables from introduction to mastery
Using fastai to develop and deploy image classifier application
都说程序员钱多空少,程序员真的忙到没时间回信息了吗?
机械硬盘随机IO慢的超乎你的想象
Dynamic ReLU:微软推出提点神器,可能是最好的ReLU改进 | ECCV 2020
Tencent: Although Ali's Taichung is good, it is not omnipotent!
Not a programmer, code can't be too ugly! The official writing standard of Python: pep8 everyone should know
线程池运用不当的一次线上事故
IT industry salary has been far ahead! Ten years later, is the programmer still a high paying profession?
Suffix expression to infix expression
微信小程序相关
Proficient in high concurrency and multithreading, but can't use ThreadLocal?
单例模式的五种设计方案
C + + opencv4.3 sift matching
实验