当前位置:网站首页>Generics, generic defects and application scenarios that 90% of people don't understand
Generics, generic defects and application scenarios that 90% of people don't understand
2022-07-05 09:52:00 【hi-dhl】
Author's brief introduction : hi Hello everyone , I am a dhl, Is maintaining its own Personal website , Focus on sharing the latest technology and original articles , involve Kotlin、Jetpack、 Algorithm animation 、 data structure 、 System source code wait .
Reprint note : Not authorized , Prohibited reproduced .
The full text is divided into Video version and Text version ,
- Text version : Text focuses on detail and depth , Some knowledge , The video is not easy to express , The text description is more accurate
- Video version : The video will be more intuitive , Read the text version , Watching video , The knowledge points will be clearer
Video version bilibili Address :https://b23.tv/AdLtUGf
Generics are no stranger to every developer , I often see it in the project , But there are many friends , Every time I see wildcards ? extends 、 ? super 、 out 、 in I can't tell the difference between them , And under what circumstances .
Through this article, you will learn the following .
- Why generics
- Kotlin and Java The covariance of
- Kotlin and Java The inverse of
- wildcard
? extends、? super、out、inThe differences and application scenarios - Kotlin and Java The difference of array covariance
- The defect of array covariance
- Application scenarios of covariance and inversion
Why generics
stay Java and Kotlin We often use sets in ( List 、 Set 、 Map wait ) To store data , Various types of data may be stored in the collection , Now we have four data types Int 、 Float 、 Double 、 Number, Let's say there's no generics , We need to create four collection classes to store the corresponding data .
class IntList{ ...... }
class FloatList{ ...... }
class DoubleList{ ...... }
class NumberList{ ...... }
......
more
If there are more types , You need to create more collection classes to store the corresponding data , This shows that it is impossible , Generics are a “ Universal type matcher ”, At the same time, it can make the compiler ensure type safety .
Generics will be concrete types ( Int 、 Float 、 Double wait ) Use symbols instead of when declaring , When you use it , To specify a specific type .
// Use symbols instead of when declaring
class List<E>{
}
// stay Kotlin Use in , Specify the specific type
val data1: List<Int> = List()
val data2: List<Float> = List()
// stay Java Use in , Specify the specific type
List<Integer> data1 = new List();
List<Float> data2 = new List();
Generics help us solve the above problems , But new problems have arisen , We all know Int 、 Float 、 Double yes Number subtypes , Therefore, the following code can work normally .
// Kotlin
val number: Number = 1
// Java
Number number = 1;
Let's take three seconds to think , Whether the following code can be compiled normally .
List<Number> numbers = new ArrayList<Integer>();
The answer is no , As shown in the figure below , Compilation error .

This means that generics are immutable ,IDE Think ArrayList<Integer> No List<Number> subtypes , This assignment is not allowed , So how to solve this problem , This requires covariance , Covariance allows the above assignment to be legal .
Kotlin and Java The covariance of
- stay Java Wildcards are used in
? extends TRepresents covariance ,extendsThe parent type is restrictedT, among?Indicates an unknown type , such as? extends Number, As long as the type passed in when declaring isNumberperhapsNumberAll subtypes of - stay Kotlin Key words in
out TRepresents covariance , Meaning and Java equally
Now let's modify the above code , Take three seconds to think , Whether the following code can be compiled normally .
// kotlin
val numbers: MutableList<out Number> = ArrayList<Int>()
// Java
List<? extends Number> numbers = new ArrayList<Integer>();
The answer is that you can compile normally , Covariant wildcards ? extends Number perhaps out Number Express acceptance Number perhaps Number The subtype is a collection of objects , Covariance relaxes constraints on data types , But relaxation comes at a price , We were thinking for three seconds , Whether the following code can be compiled normally .
// Koltin
val numbers: MutableList<out Number> = ArrayList<Int>()
numbers.add(1)
// Java
List<? extends Number> numbers = new ArrayList<Integer>();
numbers.add(1)
call add() Method will fail to compile , Although covariance relaxes the constraints on data types , Acceptable Number perhaps Number The subtype is a collection of objects , But at the cost of Unable to add element , You can only get elements , So covariance can only be a producer , Provide data to the outside .
Why can't I add elements
because ? Indicates an unknown type , So the compiler doesn't know what kind of data it will add to the collection , Therefore, it is simply not allowed to add elements to the collection .
But if you want the above code to compile and pass , Want to add elements to the collection , This requires inversion .
Kotlin and Java The inverse of
Inversion actually reverses the inheritance relationship , such as Integer yes Number Subtypes of , however Integer Add the inverse wildcard ,Number yes ? super Integer Subclasses of , As shown in the figure below .
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-8bRLR2Qd-1655947414076)(https://img.hi-dhl.com/16551339994410.jpg)]
- stay Java Wildcards are used in
? super TRepresent contravariant , among?Indicates an unknown type ,superMainly used to restrict subtypes of unknown typesT, such as? super Number, As long as the declaration is passed inNumberperhapsNumberThe parent type of the can - stay Kotlin Key words in
in TRepresent contravariant , Meaning and Java equally
Now let's simply modify the above code , Take three seconds to think about whether you can compile normally .
// Kotlin
val numbers: MutableList<in Number> = ArrayList<Number>()
numbers.add(100)
// Java
List<? super Number> numbers = new ArrayList<Number>();
numbers.add(100);
The answer can be compiled normally , Inverse wildcard ? super Number Or keywords in Reverse the inheritance relationship , Mainly used to restrict subtypes of unknown types , In the example above , The compiler knows that the subtype is Number, So as long as it's Number Subclasses of can be added .
Contravariant can add elements to the set , Can I get the elements ? Let's take three seconds to think about , Whether the following code can be compiled normally .
// Kotlin
val numbers: MutableList<in Number> = ArrayList<Number>()
numbers.add(100)
numbers.get(0)
// Java
List<? super Number> numbers = new ArrayList<Number>();
numbers.add(100);
numbers.get(0);
No matter call add() Method or call get() Method , Can be compiled normally , Now modify the above code , Think about whether you can compile normally .
// Kotlin
val numbers: MutableList<in Number> = ArrayList<Number>()
numbers.add(100)
val item: Int = numbers.get(0)
// Java
List<? super Number> numbers = new ArrayList<Number>();
numbers.add(100);
int item = numbers.get(0);
call get() Method will fail to compile , because numbers.get(0) The value obtained is Object The type of , So it cannot be assigned directly to int type , Contravariant is the same as covariant , Relaxed constraints on data types , But at the cost of Cannot read elements by generic type , That is, add... To the set int Data of type , call get() Method does not get int Data of type .
For the content of this section , Let's briefly summarize .
| keyword (Java/Kotlin) | add to | Read | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Covariance | ? extends / out | ||
| Inversion | ? super / in |
Kotlin and Java The difference of array covariance
Whether it's Kotlin still Java The meaning of covariance and contravariant is the same , But the wildcards are different , But they also have differences .
Java Support array covariance , The code is as follows :
Number[] numbers = new Integer[10];
however Java Array covariance in is defective , Change the above code , As shown below .
Number[] numbers = new Integer[10];
numbers[0] = 1.0;
Can compile normally , But it will crash when running .

Because at first I will Number[] Covariant transformation Integer[], Then I added... To the array Double Data of type , So the operation will crash .
and Kotlin Our solution is very straightforward , Array covariance is not supported , There will be errors when compiling , For array inversion Koltin and Java Don't support .
Application scenarios of covariance and inversion
Covariant and inverse applications need to follow PECS(Producer-Extends, Consumer-Super) principle , namely ? extends perhaps out As a producer ,? super perhaps in As a consumer . The advantages of following this principle are , You can keep your code safe at compile time , Reduce the occurrence of unknown errors .
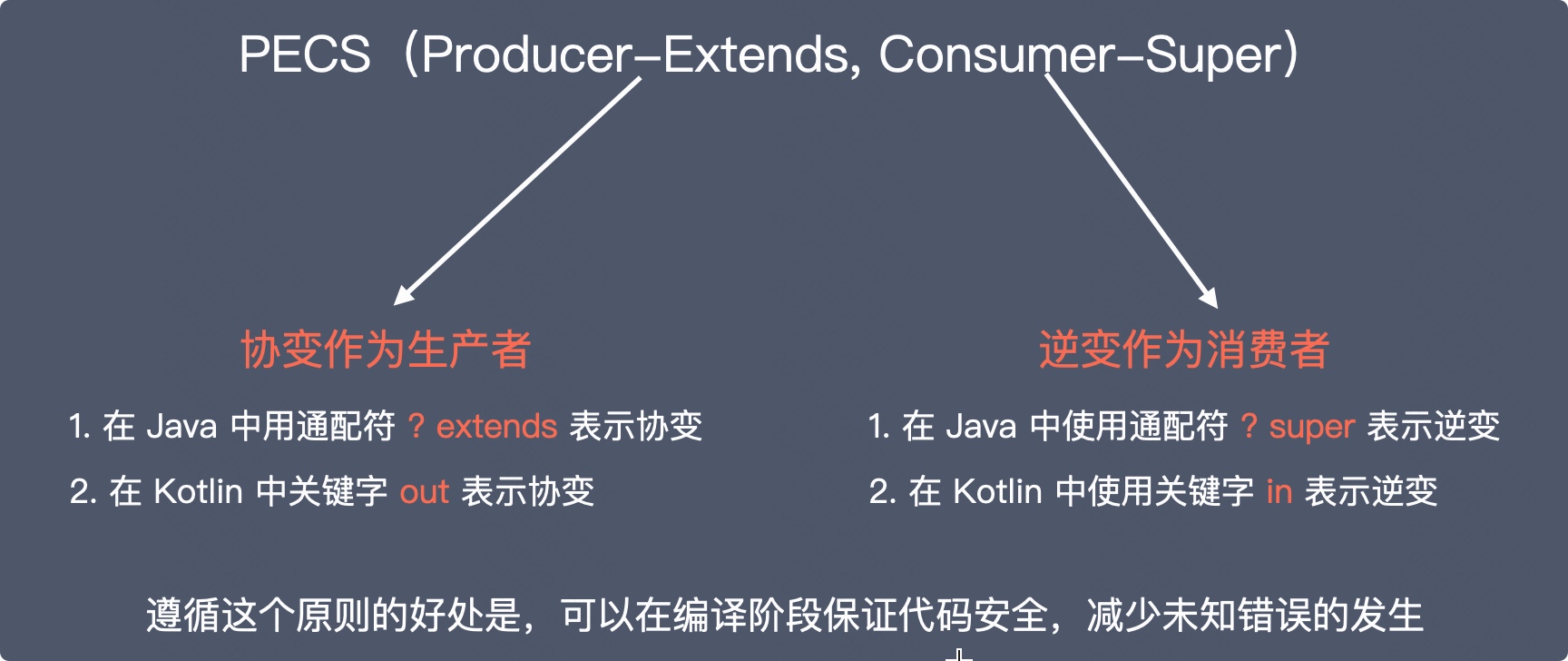
Covariant application
- stay Java Wildcards are used in
? extendsRepresents covariance - stay Kotlin Key words in
outRepresents covariance
Covariant can only read data , Can't add data , So I can only be a producer , Provide data to the outside , So it can only be used to output , It is not used to input .
stay Koltin A covariant class in , Add before parameter out After modification , This parameter is in the current class Can only be used as the return value of a function , Or modify the read-only attribute , The code is as follows .
// Normal compilation
interface ProduceExtends<out T> {
val num: T // For read-only properties
fun getItem(): T // Return value for function
}
// Compile failed
interface ProduceExtends<out T> {
var num : T // For variable attributes
fun addItem(t: T) // Parameters for function
}
When we determine that an object is only a producer , Provide data to the outside , Or as the return value of a method , We can use ? extends perhaps out.
- With Kotlin For example , for example
Iterator#next()Method , Keyword usedout, Returns each element in the collection

- With Java For example , for example
ArrayList#addAll()Method , Wildcards are used? extends

Pass in the parameter Collection<? extends E> c As a producer to ArrayList Provide data .
Inverter applications
- stay Java Use wildcards in
? superRepresent contravariant - stay Kotlin Use keywords in
inRepresent contravariant
Inversion can only add data , Cannot read data by generics , So only as a consumer , Therefore, it can only be used to input , Cannot be used to output .
stay Koltin An inverse class in , Add before parameter in After modification , This parameter is in the current class Can only be used as an argument to a function , Or modify variable attributes .
// Normal compilation , Parameters for function
interface ConsumerSupper<in T> {
fun addItem(t: T)
}
// Compile failed , Return value for function
interface ConsumerSupper<in T> {
fun getItem(): T
}
When we determine that an object is only a consumer , When passed in as a parameter , Only for adding data , We use wildcards ? super Or keywords in,
- With Kotlin For example , For example, extension methods
Iterable#filterTo(), Keyword usedin, Internally, it is only used to add data

- With Java For example , for example
ArrayList#forEach()Method , Wildcards are used? super

I don't know if my friends have noticed , In the source code above , Different generic tags are used separately T and E, Actually, let's pay a little attention , There are several high-frequency generic tags in the source code T 、 E 、 K 、 V wait , They are applied to different scenarios .
| Marker | Application scenarios |
|---|---|
| T(Type) | class |
| E(Element) | aggregate |
| K(Key) | key |
| V(Value) | value |
This is the end of the article , Thanks for reading , It's not easy to stick to originality , Welcome to 、 give the thumbs-up 、 Share it with your friends , I will continue to share original dry goods !!!
边栏推荐
- Lepton 无损压缩原理及性能分析
- [listening for an attribute in the array]
- Solve the problem of no all pattern found during Navicat activation and registration
- Thermometer based on STM32 single chip microcomputer (with face detection)
- 植物大战僵尸Scratch
- Apache DolphinScheduler 入门(一篇就够了)
- The most comprehensive promotion strategy: online and offline promotion methods of E-commerce mall
- Resolve the horizontal (vertical) sliding conflict between viewpager and WebView
- 基于模板配置的数据可视化平台
- LeetCode 31. Next spread
猜你喜欢
A keepalived high availability accident made me learn it again
![[sourcetree configure SSH and use]](/img/9a/1cd4ca29e5b7a3016ed6d5dc1abbef.png)
[sourcetree configure SSH and use]
Officially launched! Tdengine plug-in enters the official website of grafana
移动端异构运算技术-GPU OpenCL编程(进阶篇)
剪掉ImageNet 20%数据量,模型性能不下降!Meta斯坦福等提出新方法,用知识蒸馏给数据集瘦身...
写入速度提升数十倍,TDengine 在拓斯达智能工厂解决方案上的应用
Tongweb set gzip

E-commerce apps are becoming more and more popular. What are the advantages of being an app?

MySQL installation configuration and creation of databases and tables

Deep understanding of C language pointer
随机推荐
Thermometer based on STM32 single chip microcomputer (with face detection)
[two objects merged into one object]
Design and exploration of Baidu comment Center
Online chain offline integrated chain store e-commerce solution
写入速度提升数十倍,TDengine 在拓斯达智能工厂解决方案上的应用
MySQL installation configuration and creation of databases and tables
[sourcetree configure SSH and use]
分布式数据库下子查询和 Join 等复杂 SQL 如何实现?
[how to disable El table]
百度APP 基于Pipeline as Code的持续集成实践
7 月 2 日邀你来TD Hero 线上发布会
Vs code problem: the length of long lines can be configured through "editor.maxtokenizationlinelength"
What about wechat mall? 5 tips to clear your mind
Are databases more popular as they get older?
Community group buying has triggered heated discussion. How does this model work?
Node-RED系列(二九):使用slider与chart节点来实现双折线时间序列图
H. 265 introduction to coding principles
Baidu app's continuous integration practice based on pipeline as code
Cross process communication Aidl
SQL learning alter add new field