当前位置:网站首页>Implementation of map and set
Implementation of map and set
2022-07-07 03:56:00 【Wuhu kaichong ~】
In front of us, we realized the red black tree ,https://blog.csdn.net/qq_55143256/article/details/125118713
Let's use it today map and set Encapsulate the red black tree
Catalog
Standard library map Related knowledge
Standard library set Relevant knowledge points of
map
KeyOfValue
If you take a closer look at the implementation code of red black tree , You will find something strange , Namely KeyOfValue, What is this for ? Is the packaging map It needs to be used when
It's in map Its function is to map The key value in it is right , Extract the key, Because we map When comparing , In fact, it is the key value pair of comparison key Of
[] heavy load
map Inside [] Symbols can not only take key Corresponding value, You can also insert , If there is no such key, It will key Insert in
 This is the official note , We just write according to the notes it gives
This is the official note , We just write according to the notes it gives
There is nothing else to pay attention to , because map It is the encapsulation of the original red black tree
Code
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.hpp" // The header file here is the header file composed of all the code in the red black tree blog
namespace cdd {
template<class K, class V>
class map {
typedef pair<K, V> ValueType;
struct KeyOfValue {
const K& operator()(const ValueType& value) {
return value.first;
}
};
typedef RBTree<ValueType, KeyOfValue> tree;
public:
typedef typename tree::iterator iterator;
public:
map()
:_t()
{}
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
size_t size()const
{
return _t.Size();
}
bool empty()const
{
return _t.Empty();
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
return (*(_t.Insert(make_pair(key, V())).first)).second;
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const ValueType& value)
{
return _t.Insert(value);
}
void swap(map<K, V>& m)
{
_t.Swap(m._t);
}
void clear()
{
_t.Clear();
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _t.Find(make_pair(key, V()));
}
private:
tree _t;
};
}Standard library map Related knowledge
The standard library is map The container is equipped with a bidirectional iterator (bidirectional iterator). It means ,map Container iterators can only ++p、p++、–p、p–、*p operation , And you can only use between iterators == perhaps != Operator to compare .
It is worth mentioning that , Compared with sequential containers ,map Containers provide more member methods ( As shown in the table 1 Shown ), By calling them , We can easily get iterators with specified meanings .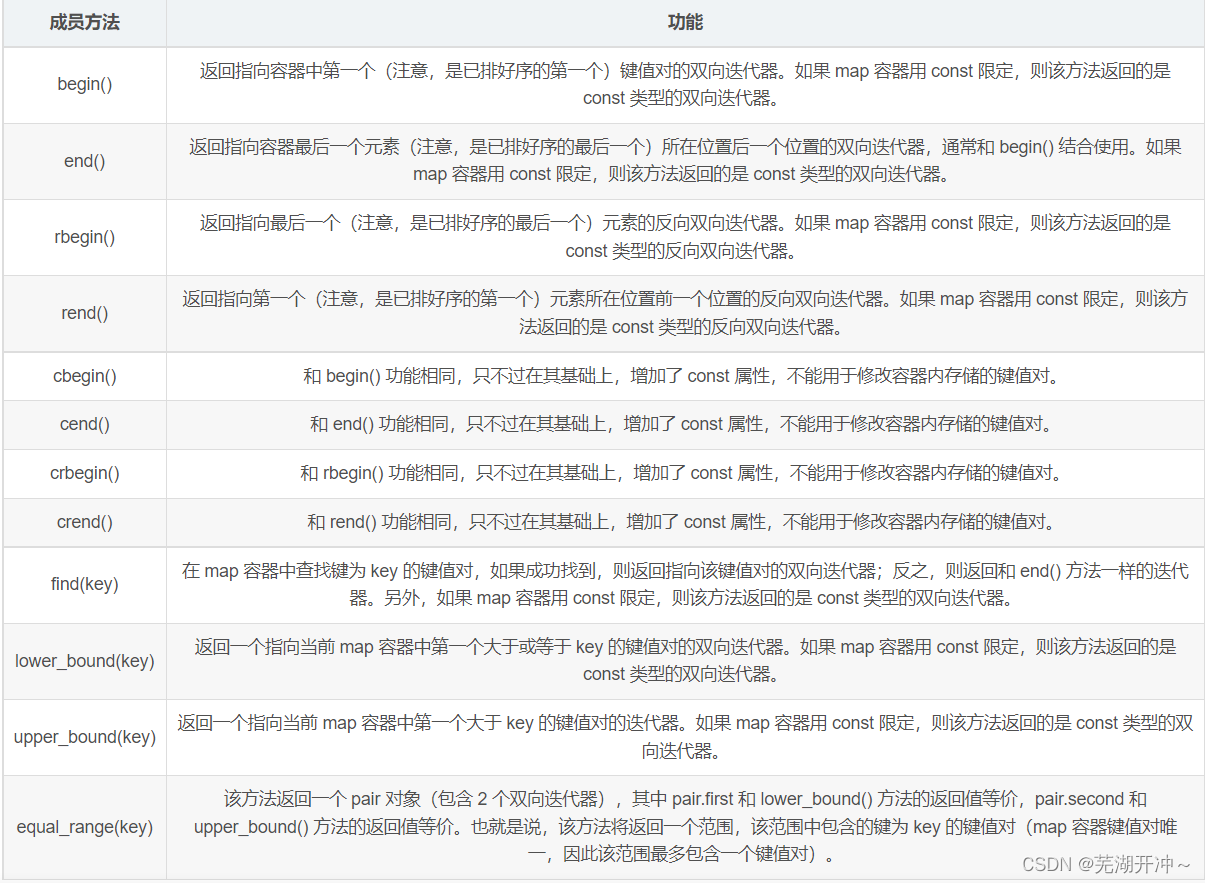
map The default collation for containers is : according to key Values are sorted from small to large , Of course , We can use the imitative function to sort
set
set There is nothing more difficult , It has no [] heavy load , Nor is it a key value pair , So there is really nothing wrong
Code
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.hpp"
namespace zds {
template<class K>
class set {
struct KeyOfValue {
const K& operator()(const K& value) {
return value;
}
};
typedef RBTree<K, KeyOfValue> tree;
public:
typedef typename tree::iterator iterator;
public:
set()
:_t()
{}
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
size_t size()const
{
return _t.Size();
}
bool empty()const
{
return _t.Empty();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& value)
{
return _t.Insert(value);
}
void swap(set<K>& s)
{
_t.Swap(s._t);
}
void clear()
{
_t.Clear();
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _t.Find(key);
}
private:
tree _t;
};
}Standard library set Relevant knowledge points of
set The method inside
begin() , return set The first element of the container
end() , return set The last element of the container
clear() , Delete set All the elements in the container
empty() , Judge set Whether the container is empty
max_size() , return set The maximum number of elements a container can contain
size() , Returns the current set The number of elements in the container
rbegin , The return value and end() identical
rend() , The return value and rbegin() identical
count() , Used to find set The number of times a key value appears in the . This function is in the set It's not very practical , Because a key value is in set It's only possible 0 or 1 Time , In this way, it becomes to judge whether a key value is set There have been
erase(iterator) , Delete locator iterator The value of the point
erase(first,second), Delete locator first and second Between the value of the
erase(key_value), Delete key value key_value Value
find() , Returns the value of the given value , If not, return end().
These are some commonly used , Actually set The biggest function is to sort and de duplicate a group of elements , Um. , That is to say, its nature is the greatest function
Last , If you have any questions, please leave a message in the comments section
边栏推荐
- 使用 Dumpling 备份 TiDB 集群数据到 GCS
- tflite模型转换和量化
- NoSQL之Redis配置与优化
- 23. (ArcGIS API for JS) ArcGIS API for JS ellipse collection (sketchviewmodel)
- 【mysql】mysql中行排序
- Construction of Hisilicon universal platform: color space conversion YUV2RGB
- Ggplot facet detail adjustment summary
- CMB's written test - quantitative relationship
- Set WiFi automatic connection for raspberry pie
- 代码质量管理
猜你喜欢
【DPDK】dpdk样例源码解析之三:dpdk-l3fwd_001

QT 使用QToolTip 鼠标放上去显示文字时会把按钮的图片也显示了、修改提示文字样式
Class常量池与运行时常量池
Force buckle ----- path sum III
PHP lightweight Movie Video Search Player source code
【knife-4j 快速搭建swagger】
![[dpdk] dpdk sample source code analysis III: dpdk-l3fwd_ 001](/img/f6/dced69ea36fc95ef84bb546c56dd91.png)
[dpdk] dpdk sample source code analysis III: dpdk-l3fwd_ 001
My brave way to line -- elaborate on what happens when the browser enters the URL
机器学习笔记 - 使用机器学习进行鸟类物种分类

20. (ArcGIS API for JS) ArcGIS API for JS surface collection (sketchviewmodel)
随机推荐
Optimization cases of complex factor calculation: deep imbalance, buying and selling pressure index, volatility calculation
C task expansion method
Flutter3.0, the applet is not only run across mobile applications
Can the applet run in its own app and realize live broadcast and connection?
[leetcode] 700 and 701 (search and insert of binary search tree)
Free PHP online decryption tool source code v1.2
再AD 的 界面顶部(菜单栏)创建常用的快捷图标
Enumeration general interface & enumeration usage specification
VHDL implementation of arbitrary size matrix multiplication
运算放大器应用汇总1
【开发软件】 tilipa开发者软件
22.(arcgis api for js篇)arcgis api for js圆采集(SketchViewModel)
数据的存储
大白话高并发(二)
20. (ArcGIS API for JS) ArcGIS API for JS surface collection (sketchviewmodel)
未来发展路线确认!数字经济、数字化转型、数据...这次会议很重要
MySQL storage engine
Clock in during winter vacation
红米k40s root玩机笔记
接口数据安全保证的10种方式