当前位置:网站首页>Final review of Database Principles
Final review of Database Principles
2022-07-03 08:36:00 【Jiamei no error】
The first 1 Chapter
The introduction
database (DB): It is the aggregation of database data , And the data in this collection must be able to be managed by the computer and shared by multiple users
Database management system (DBMS): It is a large-scale software for manipulating and managing databases , It consists of a set of computer programs
Database system (DBS): By hardware and software 、 The database and users together constitute . Hardware is mainly used to store data in the database , Including computers 、 Storage devices, etc . The software part mainly includes the database management system 、 An operating system that supports the operation of a database management system , And support the access technology of multi language application development .
A complete database system generally consists of databases 、 Database management system 、 Application development tools 、 Application system 、 Database administrators and users .
The database system mainly includes the following 3 Components :
database : A place for storing data .
Database management system : Software for managing databases .
Database applications : In order to improve the processing capacity of the database system, the software used to manage the database is supplemented .
database (DataBase,DB) It provides a storage space to store all kinds of data , You can think of a database as a container for storing data . A database may contain many files , A database system usually contains many databases .
Database management system (Database Management System,DBMS) It's user creation 、 The software used to manage and maintain a database , Between the user and the operating system , Unified management of the database .DBMS Can define data storage structure , The operation mechanism of providing data , Maintain database security 、 Integrity and reliability .
Database applications (DataBase Application) The use of data management can meet the higher requirements of data management , It can also make the data management process more intuitive and friendly . The database application is responsible for working with DBMS communicate 、 Access and management DBMS Data stored in , Allow users to insert 、 modify 、 Delete data from database .
Characteristics of database system : Data structure 、 Low data redundancy 、 High sharing 、 Avoid data inconsistency 、 High data independence 、 from DBMS Unified management and control ( Security 、 integrity 、 concurrency control 、 Database recovery )
Data model :
Refers to the simulation and abstraction of real-world data and information , Used to describe data 、 Compose data and operate on data
classification : Conceptual data model 、 Logical data model 、 Physical data model
Components : data structure 、 Data manipulation 、 Data integrity constraints
Square box : Entity set
Diamond frame : contact
Elliptical box : attribute
Three level pattern structure : External mode 、 Conceptual model 、 Internal mode ( A database can have multiple external schemas 、 A database can only have one internal schema
Two level image : External mode image 、 Inside ~
The first 2 Chapter
relational database
Domain : Is a set of values with the same data type
code :
It consists of one or several attributes
Candidate code : In a relationship , Attribute or minimum attribute set that can uniquely identify tuples
Main code : There are multiple candidate codes in a relationship, choose one as the main code
Outer code
Relationship integrity constraints : Using integrity constraints is to use integrity rules to constrain the relationship
The values of the two main codes are unique in the table 、 affirmatory , All attributes of the specified relationship on the master code cannot be null , Instead, the main code as a whole cannot be null
Entity integrity : The primary code is unique and not empty
Referential integrity : The outer code is either empty , Or corresponding to other table main codes
User defined integrity : Write it completely
The cartesian product :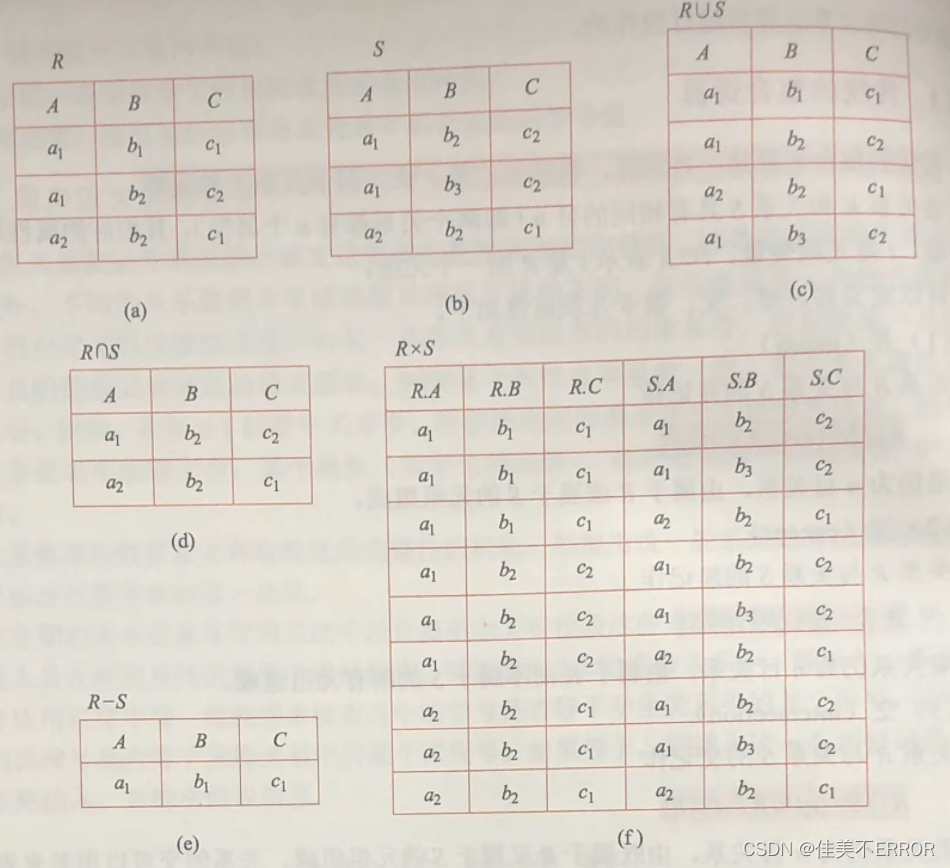 Inquire about :
Inquire about :

Natural join :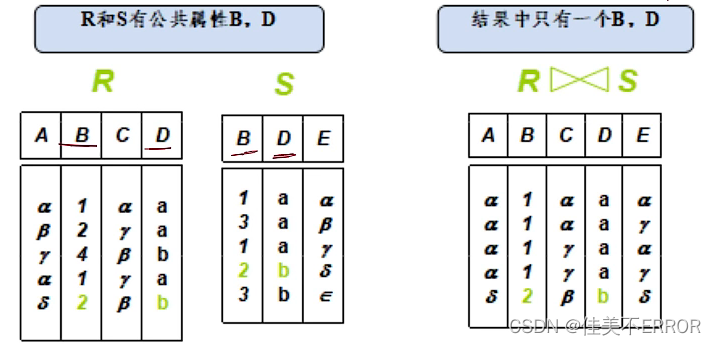
The discarded ones are called floating tuples
except :
The first 3 Chapter
Relational database standard language SQL
SQL characteristic : Highly unprocessed 、 Fully functional and integrated 、 Unified grammatical structure 、 The language is simple , Easy to learn and easy to use
SQL Define functions :
The definition of the table :
create table Table name ( Various attributes );
create table user(
name varchar(20),
age int
)
Delete
CASCADE For foreign key
drop table student CASCADE
Change
alter table student alter column sage int;
Inquire about
id,title Modifiable name
select *from student;
selsct *from user where id=9 and password=123;
The results were de duplicated
selsct distinct title Course name from edu_course;
Add conditions to the query results
selsct title Course name from edu_course where price between 10 and 999;
% Can represent multiple characters , Underline _ Representing one
group by grouping , Screen selection having
For equivalent connection where
select *from edu_course ec,edu_course_description ecd where ec.id=ecd.id;
Check the total number of students
select count(*) as The total number of
from Student ;
Check the average age of computer college students
select avg(year(now))- Year of birth ) as Average age
from Student
where college =' Computer '
Inquiry learning 180101 The highest score of students in course No
select max( achievement ) as The highest
from Study
where Course no. ='180101'
Check options 180102 Student ID and grade of course No , The results are ranked from high to low
select Student number , achievement
from Study
where Course no. ='180102'
order by achievement desc
Composite conditional join query
Check options 180101 And the grade is in 90 The student number of the above students , Name and grade
select Student . Student number , full name , achievement
from Student , Study
where Student . Student number = Study . Student number
and Study . Course no. ='180101'
and Study . achievement >90
nested queries
select full name
from Student
where Student number in
(select Student number
from Study
where Course no. ='180101');
Insert a single tuple
insert
into Student
values('111',' Xia Yu ',' male ',' Computer ');
Insert subquery results
insert
into dept_age(sdept,avg_age)
select college ,avg(year(now())- Year of birth )
from Student
group by college
Delete
delete
from Student
where Student number ='092010';
Change
update Student
set Place names =' jiangsu '
where Course no. ='1111'
Modification of subquery
update Study
set achievement =0
where Student number in
(select Student number
from Student
where college =' Computer ');
View :
create view cs_view
as select *
from Student
where college =' Computer ';
Delete view
drop view < View name >
Query view
select *
from cs_view
where year(now())- Year of birth <20;
Update the view
Insert 、 Delete 、 modify
The first 4 Chapter
Relationship normalization theory
Function dependency :
Functional dependence of code :
In relation mode R in , A set that uniquely determines the minimum attributes of a tuple
if X Sole determination Y, be XY There is a functional relationship between
set up K by R<U,F> Properties or property groups in , if K–f—>U, be K by R The candidate code for , There are more than one candidate codes. Choose one of them as the main code 

Normal form to BC normal form :

Closure :

Code value theory :
Armstrong axiom 

rely on :
Minimum dependence :
The first 6 Chapter
Database protection
Business :
It is to package a group of database operations to form a logically independent work unit , This unit of work is indivisible , The database operations included in it either all occur , Or none of it will happen
characteristic : Atomicity 、 Uniformity 、 Isolation, 、 persistence
Database recovery :
Fault type : Transaction internal failure 、 System failure 、 Media failure 、 Computer virus
implementation technique : Establish redundancy through data dump 、 Establish redundancy through log files 、 Fault recovery
边栏推荐
- Unity Editor Extension - Outline
- Golang's range
- matlab神经网络所有传递函数(激活函数)公式详解
- Campus lost and found platform based on SSM, source code, database script, project import and operation video tutorial, Thesis Writing Tutorial
- 图像处理8-CNN图像分类
- [concurrent programming] thread foundation and sharing between threads
- OpenGL learning notes
- Visual Studio (VS) shortcut keys
- Development experience and experience
- Sequence of map implementation classes
猜你喜欢
Unity4.3.1 engine source code compilation process
GIS实战应用案例100篇(七十八)-多规合一数据库设计及数据入库

KunlunBase MeetUP 等您来!
了解小程序的笔记 2022/7/3

UE4 source code reading_ Bone model and animation system_ Animation node

Chocolate installation
![[cloud native] introduction and use of feign of microservices](/img/39/05cf7673155954c90e75a8a2eecd96.jpg)
[cloud native] introduction and use of feign of microservices

二进制转十进制,十进制转二进制
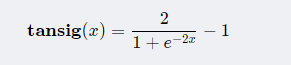
Detailed explanation of all transfer function (activation function) formulas of MATLAB neural network

单调栈-42. 接雨水
随机推荐
LinkedList set
Unity notes 1
Introduction to hexadecimal coding
十六进制编码简介
Dotween plug-in
Pit & ADB wireless debugging of vivo real machine debugging
Unity Editor Extension - drag and drop
796 · unlock
Creation and content of mapnode -- osgearth rendering engine series (2)
Conversion between string and int types in golang
Development material set
Osgearth starry background
Base64编码简介
Find the intersection of line segments
swagger文档配置
【Rust笔记】06-包和模块
[K & R] Chinese Second Edition personal questions Chapter1
C course design employee information management system
Mxone Pro adaptive 2.0 film and television template watermelon video theme apple cmsv10 template
redis集群系列四