当前位置:网站首页>6_梯度下降法(Gradient Descent)
6_梯度下降法(Gradient Descent)
2022-07-26 22:37:00 【Acowardintheworld】
6_梯度下降法(Gradient Descent)
梯度下降法是在机器学习领域的一个重要的搜索策略。在这一章,我们将详细讲解梯度下降法的基本原理,一步一步改进梯度下降算法,让大家理解梯度下降法中各种参数,尤其是学习率的意义。
同时,我们还将引申出随机梯度下降法和小批量梯度下降法两个方法,让大家对梯度下降法家族有一个全方位的认识。…
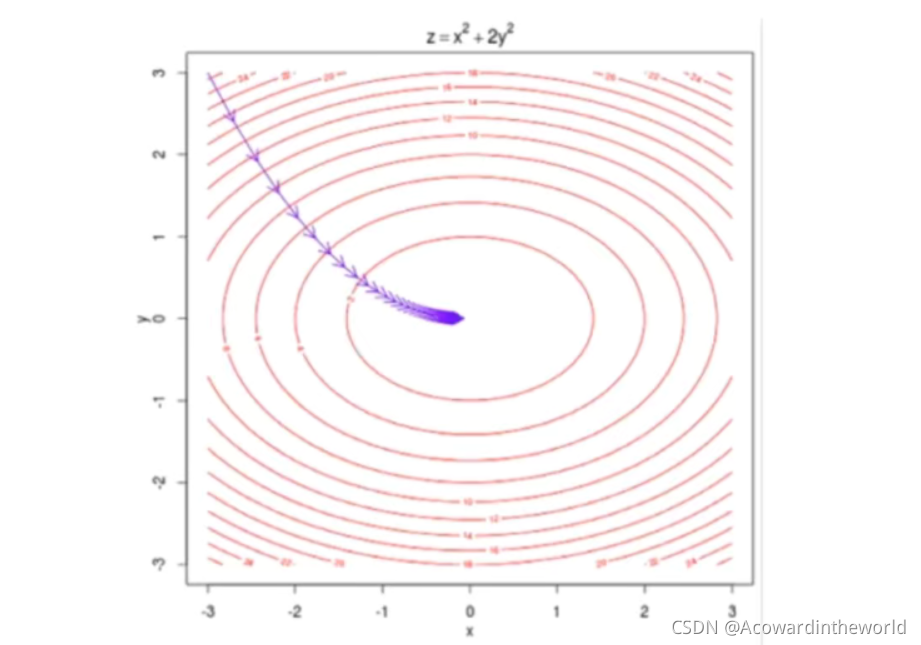
6-1 什么是梯度下降法



导数代表 theta单位变化时,J相应的变化
导数可以代表方向,对应J增大的方向





- 并不是所有函数都有唯一的极值点(多元多次函数)



6-3 线性回归中的梯度下降法



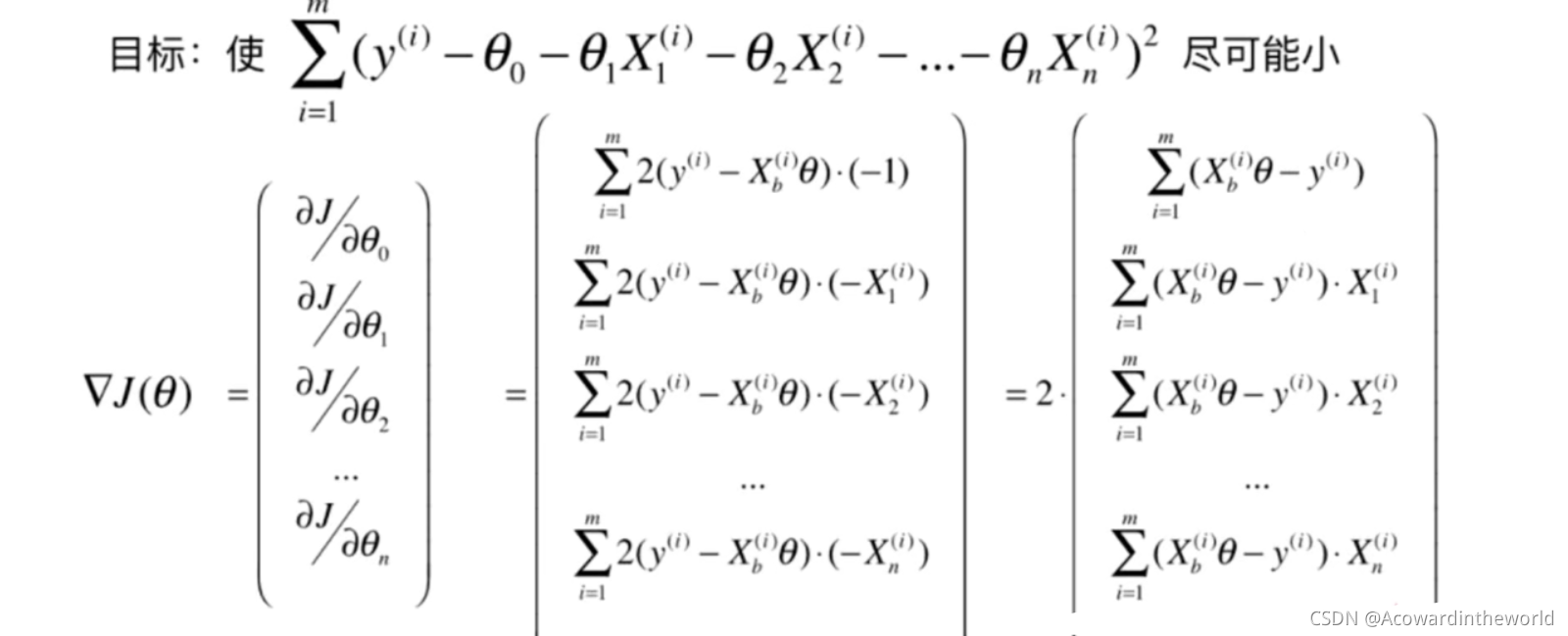
由于梯度的大小受样本数m影响,显然不合理,故除以样本数m,使其不受样本数量的影响。
6-4 实现线性回归中的梯度下降法
6-5 梯度下降法的向量化和数据标准化

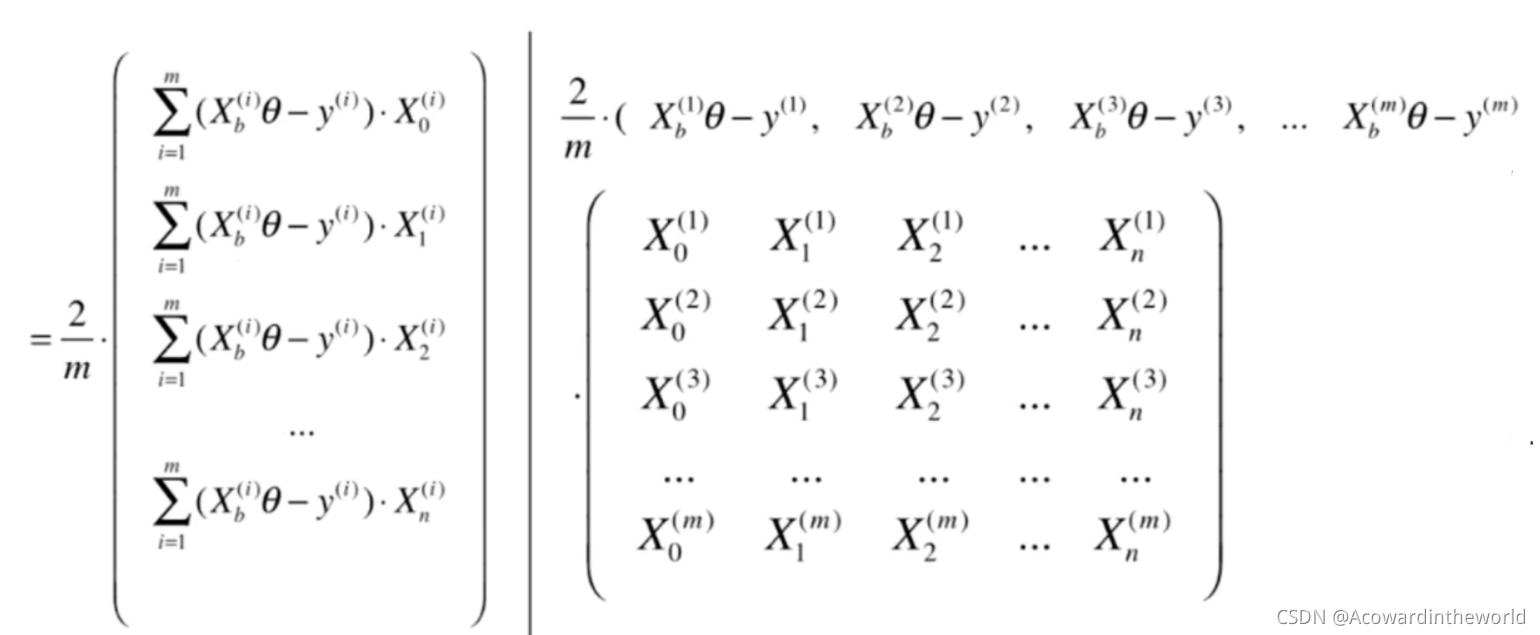


6-6 随机梯度下降法

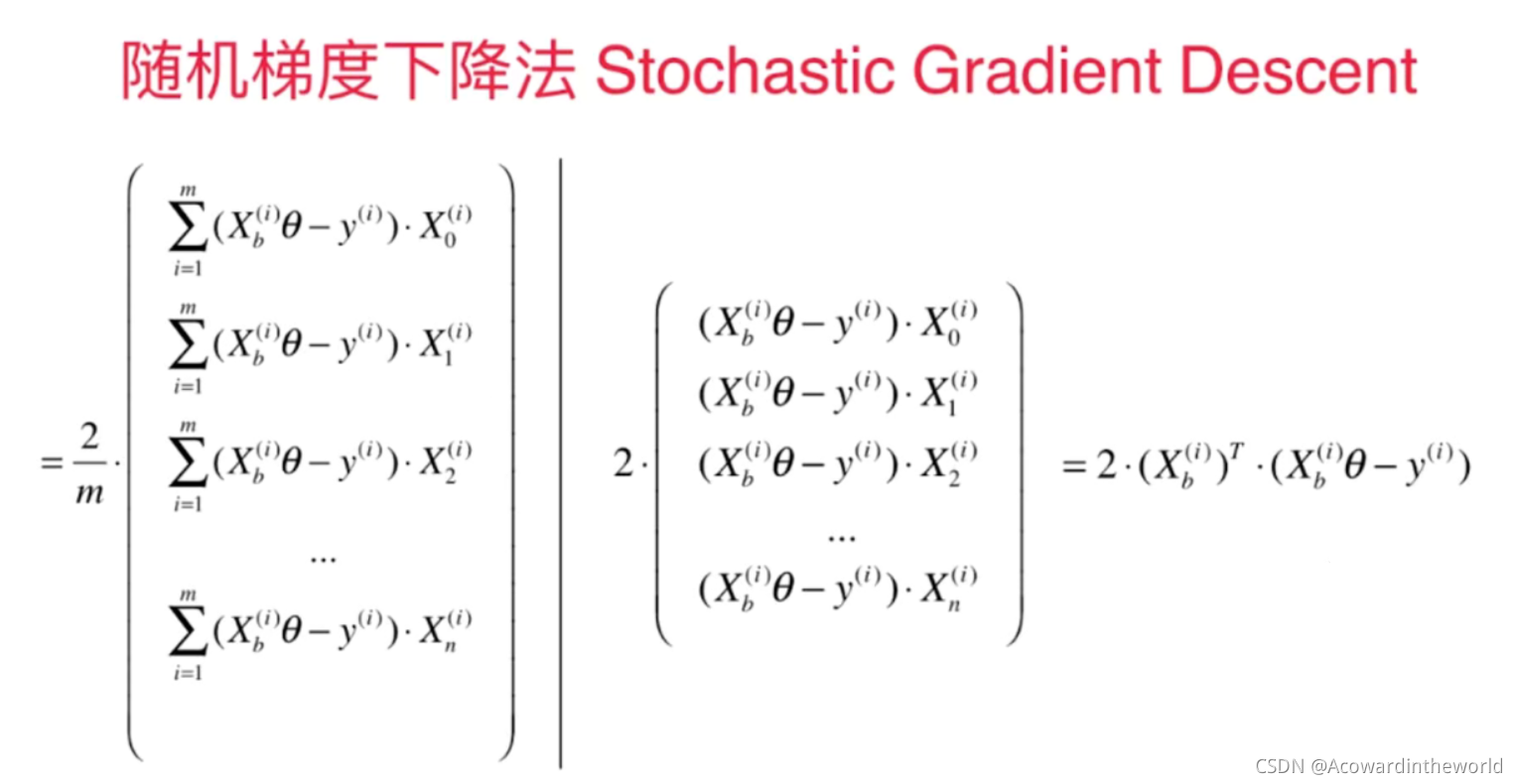
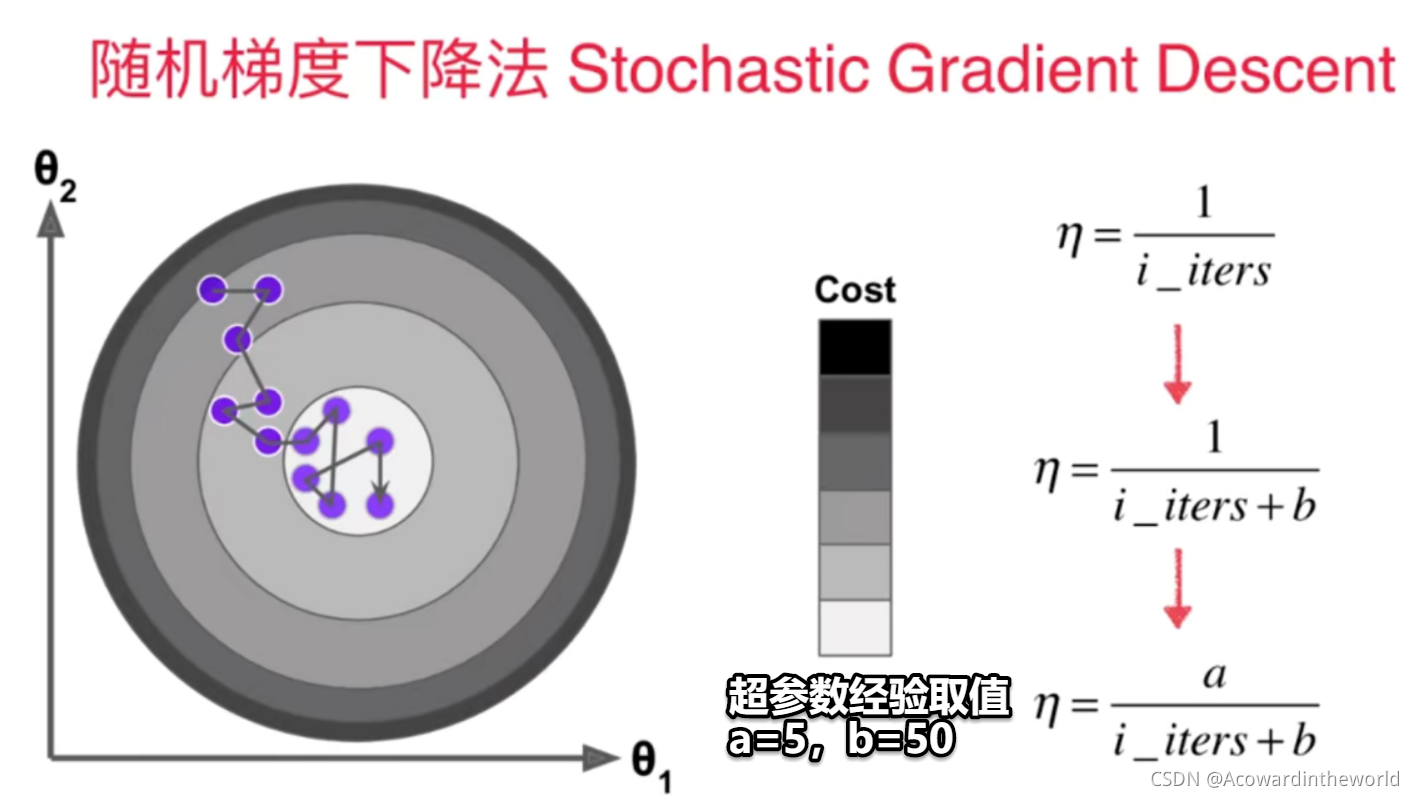
- 模拟退火算法思想:模仿自然界退火现象而得,利用了物理中固体物质的退火过程与一般优化问题的相似性。
从某一初始温度开始,伴随温度的不断下降,结合概率突跳特性在解空间中随机寻找全局最优解
6-8 如何确定梯度计算的准确性?调试梯度下降法


# ipynb上的代码,没有print()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(666)
X = np.random.random(size = (1000,10))
true_theta = np.arange(1,12,dtype = float)
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X),1)),X] )
y = X_b.dot(true_theta) + np.random.normal(size = 1000)
print(X.shape)
print(y.shape)
print(true_theta)
def J(theta,X_b,y): #定义损失函数
try:
return np.sum((y-X_b.dot(theta))**2 ) / len(X_b)
except:
return float("inf")
def dJ_math(theta,X_b,y): # 定义梯度 数学公式计算
return X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta) - y)*2. / len(y)
def dJ_debug(theta,X_b,y,epsilon=.01): # 定义梯度 debug计算
res = np.empty(len(theta))
for i in range(len(theta)):
theta_1 = theta.copy()
theta_1[i] += epsilon
theta_2 = theta.copy()
theta_2[i] -= epsilon
res[i] = (J(theta_1,X_b,y) - J(theta_2,X_b,y))/(2*epsilon)
return res
def gradient_descent(dJ,X_b,y,initial_theta,eta=1e-2,epsilon=1e-8,n_iters=1e4):
theta = initial_theta
i_iters = 0
while i_iters < n_iters:
gradient = dJ(theta,X_b,y)
last_theta = theta
theta = theta - eta * gradient
if (abs(J(theta,X_b,y)-J(last_theta,X_b,y)))< epsilon:
break
i_iters += 1
return theta
X_b = np.hstack( ( np.ones((len(X),1)),X) )
initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])
eta = 0.01
%time theta = gradient_descent(dJ_debug,X_b,y,initial_theta,eta)
theta
%time theta = gradient_descent(dJ_math,X_b,y,initial_theta,eta)
theta
tip
dJ_debug用于验证调试梯度,速度较慢,可以取少量样本用dJ_debug得到正确的结果,再用公式推出数学解,对比结果。
dJ_debug不受当前损失函数J的影响,求梯度具有普适性。
6-9 有关梯度下降法的更多深入讨论

BGD:每次都需要遍历整个样本,每次向梯度下降最快的方向一定,稳定但是慢。
SGD:每次只看一个样本,梯度下降的方向不确定,甚至可能向反方向移动, 快但是不稳定。
MBGD:两种极端方法折中,每次却k个样本,k也成了一个超参数。



总结:有些相关的代码只能在VSC运行,Jupyter就跑不了,特别是hstack()函数。
边栏推荐
- Convolutional neural network -- lenet (pytorch Implementation)
- Configure deeplobcut 1 with your head covered
- Halloween treatments (drawer principle)
- [PCB open source sharing] stc8a8k64d4 development board
- RecBole使用1
- Chapter 7 course summary
- 滑动窗口问题总结
- MySQL数据库复杂操作:数据库约束,查询/连接表操作
- Relationship between Unicode and UTF-8
- 蒙着头配置deeplabcut 1
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
滑动窗口问题总结
The crawler parses the object of the web page. Element name method
RecBole使用1
类与对象笔记一
About no module named'django.db.backends.mysql'
Midge paper reading notes
12_决策树(Decision tree)
Deployment of yolov5 on Jetson nano deepstream
Sliding window problem summary
Design of electronic scale based on 51 single chip microcomputer
Iptables prevent nmap scanning and binlog
Signal and system impulse response and step response
Complex SQL_ 01
Configure deeplobcut 1 with your head covered
Alexnet (pytoch Implementation)
Geek challenge 2019 (review the loopholes)
Error generating yolov5.wts file
MySQL transaction, phantom reading, current reading, snapshot reading related notes
傅里叶分析(基础介绍)
Shang school software testing (1) software testing curriculum system, advantages, learning suggestions, understanding software, software testing and defects, software testing process, debugging and te









