- One . About ext4 file system
- Two .linux The composition of the file system (inode,block)
- 3、 ... and . problem : Why delete is faster than copy ?
- Four . problem : When we delete files by mistake , The first thing to do ?
- 5、 ... and . Preparing the test environment
- 6、 ... and . install extundelet
- 7、 ... and . Recovery of deleted files by mistake
One . About ext4 file system
EXT4 It's the fourth generation extended file system ( English :Fourth extended filesystem, Abbreviation for ext4) yes Linux Log file system under the system , yes ext3 File system
Subsequent versions .Ext4 By Ext3 The maintainer of Theodore Tso Leading the development team to achieve . Compared with ext3 file system ,ext4 File systems support larger file systems and more
Big papers , More subdirectories , More blocks and i- The number of nodes and so on .
about ext4 Delete files on the file system by mistake , have access to extundelete recovery , about ext3 file system , Then use ext3grep Recover files deleted by mistake . stay windows On
To recover the files deleted by mistake, you can use final data v2.0 Chinese version and easyrecovery.
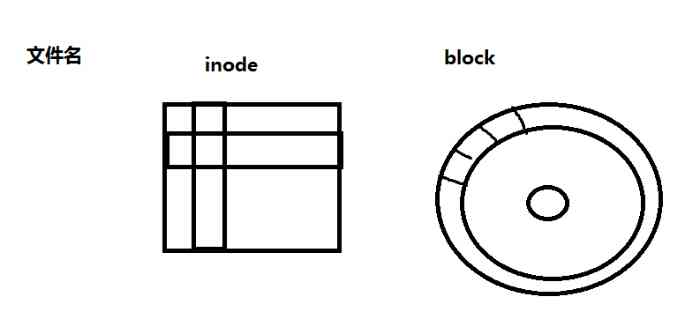
Two .linux The composition of the file system (inode,block)
Linux The file system consists of three parts : file name ,inode,block.inode Store file metadata information ,block It's the real place to store data .windows It also consists of three parts .
Each file has a inode Number , have access to ls -i and stat see .
[root@node5 ~]# ls -i test.txt
34566868 test.txt
[root@node5 ~]# stat test.txt
File: ‘test.txt’
Size: 12 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file
Device: fd00h/64768d Inode: 34566868 Links: 1
Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root)
Access: 2020-10-10 17:30:12.532654117 +0800
Modify: 2020-10-10 17:30:12.532654117 +0800
Change: 2020-10-10 17:30:12.533654118 +0800
Birth: -
3、 ... and . problem : Why delete is faster than copy ?
Because it's just a logical deletion . Deleting is not really deleting the entire data , It just sets the file list to be writable , When there is new data to write , straight
Then overlay the original data . You can use the figure below to show :
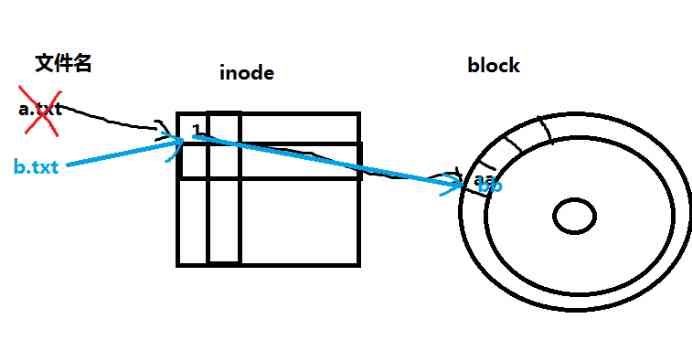
Four . problem : When we delete files by mistake , The first thing to do ?
Because in linux in , Deletion is just a logical deletion , At this time, we should avoid the contents of the file deleted by mistake to be covered by the newly written file . You can unmount the partition that needs to recover files or just
Mount by reading .
If you delete a file under the root , Want to recover data , What to do ?
Method 1: Power off immediately , Then read the disk as read-only , Mount to another computer for recovery .
Method 2: hold extundelete On a virtual machine ( The virtual machine system should be the same as the server version ), Install it in advance and then copy it to U Plate , hold U Disk insert server , recovery
when , The recovered files should be saved to U Plate ,( Don't let recovered data write / Next , That will overwrite the previously deleted file ).
5、 ... and . Preparing the test environment
1. First go https://sourceforge.net/projects/extundelete/ This website downloads extundelete-0.2.4.tar.bz2 Software . It is worth mentioning that http://sourceforge.net/ It's an open source software distribution center , A lot of software can be downloaded here .
2. You can add a hard disk , Or partition the existing hard disk . The general steps of disk partition are fdisk partition , Create mount point , Format as ext4 file system , most
Post Mount . For specific disk partitions, please refer to the partition tools section .
3. Prepare test files , Delete test file , Uninstall partition
# because /dev/sdb5 yes ext4 file system , So in /sdb5 Create test file in directory
[root@node5 ~]# df -hT
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/centos-root xfs 17G 11G 6.2G 64% /
devtmpfs devtmpfs 3.9G 0 3.9G 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 3.9G 8.0K 3.9G 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs tmpfs 3.9G 8.8M 3.9G 1% /run
tmpfs tmpfs 3.9G 0 3.9G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 xfs 1014M 125M 890M 13% /boot
/dev/sdb1 xfs 47M 2.7M 45M 6% /sdb1
/dev/sdb5 ext4 190M 1.6M 175M 1% /sdb5
/dev/sdb6 xfs 295M 16M 280M 6% /sdb6
tmpfs tmpfs 785M 0 785M 0% /run/user/0
[root@node5 ~]# cd /sdb5
[root@node5 sdb5]# pwd
/sdb5
[root@node5 sdb5]# ls
lost+found
# Copy some files as test files
[root@node5 sdb5]# cp /etc/passwd ./
[root@node5 sdb5]# cp /etc/hosts ./
[root@node5 sdb5]# cp -r /boot/grub2 ./
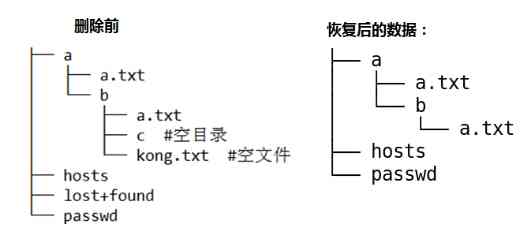
[root@node5 sdb5]# mkdir -p a/b/c/d
[root@node5 sdb5]# touch a/b/test.txt
[root@node5 sdb5]# tree ./ -L 2
./
├── a
│ └── b
├── grub2
│ ├── device.map
│ ├── fonts
│ ├── grub.cfg
│ ├── grubenv
│ ├── i386-pc
│ └── locale
├── hosts
├── lost+found
└── passwd
7 directories, 5 files
[root@node5 sdb5]# ls
a grub2 hosts lost+found passwd
# Delete test file
[root@node5 sdb5]# rm -rf a grub2 hosts passwd
[root@node5 sdb5]# ls
lost+found
# Uninstall partition , Avoid writing new data over the original data
[root@node5 sdb5]# cd
[root@node5 ~]# umount /sdb5
6、 ... and . install extundelet
1. because extundelete-0.2.4.tar.bz2 It's the source package , So install extundelete Use the source code installation method .
2. Source code compilation and installation extundelete
[root@node5 ~]# ls extundelete*
extundelete-0.2.4.tar.bz2
# Unzip the installation package
[root@node5 ~]# tar jxvf extundelete-0.2.4.tar.bz2
[root@node5 ~]# ls
201810240430234009.pcm apache-tomcat-8.0.51.tar.gz extundelete-0.2.4 idea Shortcut key .txt linux-4.19.77.tar qemu-4.1.0 test2.txt
a busybox-1.24.2 extundelete-0.2.4.tar.bz2 iu.jpg linux Script .sh qemu-4.1.0.tar test.txt
aaa.txt busybox-1.24.2.tar.bz2 glibc-aarch64-linux-gnu-2.24-2.sdl7.2.noarch.rpm jdk-8u172-linux-x64.tar.gz nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz rootfs Test garbled files .txt
anaconda-ks.cfg ceshi.txt glibc-aarch64-linux-gnu-devel-2.24-2.sdl7.2.noarch.rpm linux-4.19.77 qemu-2.11.0.tar.xz telnet-0.17-64.el7.x86_64.rpm
[root@node5 ~]# cd extundelete-0.2.4
[root@node5 extundelete-0.2.4]# pwd
/root/extundelete-0.2.4
[root@node5 extundelete-0.2.4]# ls
acinclude.m4 aclocal.m4 autogen.sh config.h.in configure configure.ac depcomp install-sh LICENSE Makefile.am Makefile.in missing README src
# Install dependency packages
[root@node5 extundelete-0.2.4]# yum -y install e2fsprogs-devel
# Check the system installation environment
[root@node5 extundelete-0.2.4]# ./configure
Configuring extundelete 0.2.4
Writing generated files to disk
#$? Returns the return value of the previous command , return 0 It's right
[root@node5 extundelete-0.2.4]# echo $?
0
# compile , Compile the source code into executable binaries .-j 4 Said the use of 4 Processes compile at the same time , Speed up compilation or use 4 nucleus CPU Compile at the same time
[root@node5 extundelete-0.2.4]# make -j 4
make -s all-recursive
Making all in src
extundelete.cc: In function ‘ext2_ino_t find_inode(ext2_filsys, ext2_filsys, ext2_inode*, std::string, int)’:
extundelete.cc:1272:29: warning: narrowing conversion of ‘search_flags’ from ‘int’ to ‘ext2_ino_t {aka unsigned int}’ inside { } [-Wnarrowing]
buf, match_name2, priv, 0};
^
[root@node5 extundelete-0.2.4]# echo $?
0
# Compilation and installation
[root@node5 extundelete-0.2.4]# make install
Making install in src
/usr/bin/install -c extundelete '/usr/local/bin'
[root@node5 extundelete-0.2.4]# echo $?
0
# You can see that there is already extundelete This executable file
[root@node5 extundelete-0.2.4]# which extundelete
/usr/local/bin/extundelete
# Expand install and cp What's the difference? ?
#install You can specify permissions when copying , however cp Can not be
# for example
[root@node5 ~]# install -m 777 /bin/find /opt/a.sh
[root@node5 ~]# ll /opt/
7、 ... and . Recovery of deleted files by mistake
1. There are four ways to recover a file that was accidentally deleted :
- adopt inode No. 1 restores data
- Recover data by file name
- Restore the specified directory
- Recover all files
2. Create a folder for storing recovery data , adopt inode Node to view the deleted file name .
[root@node5 ~]# pwd
/root
[root@node5 ~]# mkdir reback
[root@node5 ~]# cd reback/
[root@node5 reback]# pwd
/root/reback
# adopt inode Node to view the deleted file name
# Expand :ext4 Of the partition root of the file system inode The value is 2,xfs Partition root inode The value is 64
[root@node5 reback]# extundelete /dev/sdb5 --inode 2
NOTICE: Extended attributes are not restored.
Loading filesystem metadata ... 25 groups loaded.
Group: 0
Contents of inode 2:
0000 | ed 41 00 00 00 04 00 00 78 fe 83 5f 76 fe 83 5f | .A......x.._v.._
0010 | 76 fe 83 5f 00 00 00 00 00 00 03 00 02 00 00 00 | v.._............
0020 | 00 00 08 00 08 00 00 00 0a f3 01 00 04 00 00 00 | ................
0030 | 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 01 00 00 00 24 11 00 00 | ............$...
0040 | 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 | ................
0050 | 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 | ................
0060 | 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 | ................
0070 | 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 | ................
Inode is Allocated
File mode: 16877
Low 16 bits of Owner Uid: 0
Size in bytes: 1024
Access time: 1602485880
eation time: 1602485878
▽odification time: 1602485878
Deletion Time: 0
Low 16 bits of Group Id: 0
Links count: 3
Blocks count: 2
File flags: 524288
File version (for NFS): 0
File ACL: 0
Directory ACL: 0
Fragment address: 0
Direct blocks: 127754, 4, 0, 0, 1, 4388, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
Indirect block: 0
Double indirect block: 0
Triple indirect block: 0
File name | Inode number | Deleted status
. 2
.. 2
lost+found 11
passwd 12 Deleted
hosts 13 Deleted
grub2 14 Deleted
a 324 Deleted
3. adopt inode Restore the specified data
[root@node5 reback]# extundelete /dev/sdb5 --restore-inode 12
4. Recover the specified data by the file name
[root@node5 reback]# extundelete /dev/sdb5 --restore-file hosts
5. Restore all files in the specified directory
[root@node5 reback]# extundelete /dev/sdb5 --restore-directory a
6. Restore all files
[root@node5 reback]# extundelete /dev/sdb5 --restore-all
7. Be careful :extundelete When recovering files, you can't automatically create empty files and empty directories . for example