当前位置:网站首页>CUDA Programming
CUDA Programming
2022-07-07 04:03:00 【AphilGuo】
/* Program starts ->cpu function -> take cpu data copy To gpu->gpu function -> take gpu data copy To cpu->cpu function -> end */
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<cuda_runtime.h>
#include<device_launch_parameters.h>
// Defining macro , The main function is to detect cuda Error in function
#define CHECK(call) \ {
\ const cudaError_t err = call; \ if (err != cudaSuccess) \ {
\ fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s:%d, ", __FILE__, __LINE__); \ fprintf(stderr, "code: %d, reason: %s\n", err, \ cudaGetErrorString(err)); \ exit(1); \ } \ }
// Kernel functions
__global__ void helloFromGPU()
{
printf("======================\n");
}
// The main function
/* * <<<grid, block>>>: The three angle brackets are cuda specific , It is the execution configuration of kernel function , To call a kernel function, you must use * grid It's grid , This value represents how many block;block Is a thread block , Represents how many threads are called * cudaDeviceReset(): Explicitly release and empty the current process gpu resources */
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
printf("print from cpu\n");
helloFromGPU << <1, 10 >> > ();
CHECK(cudaDeviceReset());
return 0;
}
cuda The program contains both host Program , Contain, device Program , Respectively in cpu and gpu Up operation .host And device Communicate with each other , In this way, data can be copied .
1、 Distribute host Memory , And data initialization
2、 Distribute device Memory , And from host Copy data to device On
3、 call cuda The kernel function of device Complete the specified operation on
4、 take device Copy the result of the operation on to host On
5、 Release device and host Memory allocated on
stay cuda Every thread in the executes kernel functions , And each thread will be assigned a unique thread number threadid, This id The value can be passed through the built-in variable of the kernel function threadIdx To obtain a .
because gpu It's actually a heterogeneous model , So we need to distinguish host and device The code on , stay cuda Is distinguished by function type qualifiers host and device The function on , There are three main function type qualifiers :
global: stay device On the implementation , from host Call in , The return type must be void, Variable parameters are not supported , Cannot be a class member function ;__global__ Defined kernel It's asynchronous ,host Don't wait for kernel After execution, proceed to the next step .
device: stay device On the implementation , Only from device Call in , Not with __global__ Use at the same time .
host: stay host On the implementation , Only from host On the call , Omit not to write , It's impossible to get along with __global__ Simultaneous use , But it can be compared with __device__ Use it together , At this point, the function will be in device and host All compile .
kernel stay device When executing on, many threads are actually started , One kernel All threads started are called a grid (grid), Threads in the same grid share the same global memory space ,grid Is the first level of thread structure , And the grid can be divided into many thread blocks (block), A thread block contains many threads , This is the second level .
sm Its core components include cuda The core , Shared memory , Register, etc .sm Hundreds of threads can be executed concurrently , Concurrency depends on sm Number of resources owned . When one kernel When executed , its grid Thread blocks in are allocated to sm On , A thread block can only be in one sm Was dispatched to .
#include<cuda_runtime.h>
#include<device_launch_parameters.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define CHECK(call) \ {
\ const cudaError_t err = call; \ if (err != cudaSuccess) \ {
\ fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s:%d, ", __FILE__, __LINE__); \ fprintf(stderr, "code: %d, reason: %s\n", err, \ cudaGetErrorString(err)); \ exit(1); \ } \ }
int main()
{
int dev = 0;
cudaDeviceProp devProp;
CHECK(cudaGetDeviceProperties(&devProp, dev));
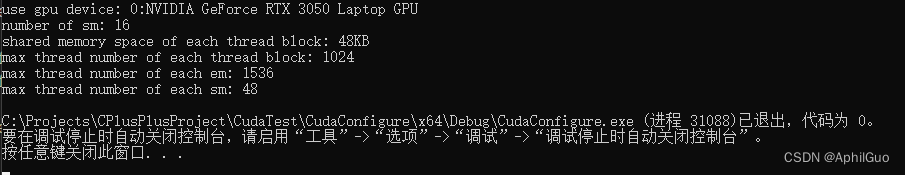
std::cout << "use gpu device: " << dev << ":" << devProp.name << std::endl;
std::cout << "number of sm: " << devProp.multiProcessorCount << std::endl;
std::cout << "shared memory space of each thread block: " << devProp.sharedMemPerBlock / 1024.0 << "KB" << std::endl;
std::cout << "max thread number of each thread block: " << devProp.maxThreadsPerBlock << std::endl;
std::cout << "max thread number of each em: " << devProp.maxThreadsPerMultiProcessor << std::endl;
std::cout << "max thread number of each sm: " << devProp.maxThreadsPerMultiProcessor / 32 << std::endl;
}
cuda Programming api:
cudaMalloc function :cudaError_t cudaMalloc(void** devPtr, size_t size);
stay device Apply for a certain byte size of video memory , among devPtr Is a pointer to the allocated memory . At the same time, free up the allocated memory usage cudaFree function , Another important function is responsible for host and device Data communication between cudaMemcpy function :
cudaError_t cudaMemcpy(void* dst, const void* src,size_t count, cudaMemcpyKind king)
src: Point to the data source ,dst It's the target area , const Is the number of bytes copied ,kind Controls the direction of replication :
cudaMemcpyHostToHost, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost as well as cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice.
#include<cuda_runtime.h>
#include<device_launch_parameters.h>
#include<iostream>
/*#define CHECK(call) \ { \ const cudaError_t err = call; \ if (err != cudaSuccess) \ { \ fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s:%d, ", __FILE__, __LINE__); \ fprintf(stderr, "code: %d, reason: %s\n", err, \ cudaGetErrorString(err)); \ exit(1); \ } \ } */
// Kernel functions
__global__ void add(float* x, float* y, float* z, int n)
{
// Get global index 1-dim
int index = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
// step
int stride = blockDim.x * gridDim.x;
for (int i = index; i < n; i += stride)
{
z[i] = x[i] + y[i];
}
}
int main()
{
int N = 1 << 20; // take 1 Move left 20 position
int nBytes = N * sizeof(float);
// apply host Space
float* x, * y, * z;
x = (float*)malloc(nBytes);
y = (float*)malloc(nBytes);
z = (float*)malloc(nBytes);
// Initialization data
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
x[i] = 10.0;
y[i] = 20.0;
}
// apply device Memory
float* d_x, * d_y, * d_z;
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_x, nBytes);
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_y, nBytes);
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_z, nBytes);
// take host Copy the data to device
cudaMemcpy((void*)d_x, (void*)x, nBytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy((void*)d_y, (void*)y, nBytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
// Definition kernel Implementation configuration of
dim3 blockSize(256);
dim3 gridSize((N + blockSize.x - 1) / blockSize.x);
// perform kernel
add << <gridSize, blockSize >> > (d_x, d_y, d_z, N);
// take device Copy the results to host
cudaMemcpy((void*)z, (void*)d_z, nBytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// Check the execution results
float maxError = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
maxError = fmax(maxError, fabs(z[i] - 30.0));
}
std::cout << "max error: " << maxError << std::endl;
// Release device Memory
cudaFree(d_x);
cudaFree(d_y);
cudaFree(d_z);
// Release host Memory
free(x);
free(y);
free(z);
return 0;
}
Unified memory management , It needs to be alone host and device Memory allocation on the , And make a copy of the data , It's easy to make a mistake .cuda6.0 Introduce unified memory to avoid this trouble . It is to use managed memory one by one to jointly manage host and device Memory in , And automatically in host and device Data transmission in .cuda Use in cudaMallocManaged Function to allocate managed memory :
cudaError_t cudaMallocManaged(void** devPtr, size_t size, unsigned int flag=0);
边栏推荐
- 三重半圆环进度条,直接拿去就能用
- Top 50 hit industry in the first half of 2022
- NoSQL之Redis配置与优化
- First understand the principle of network
- UltraEdit-32 温馨提示:右协会,取消 bak文件[通俗易懂]
- Binary, octal, hexadecimal
- The JSON format of the international area code of the mobile phone number is obtained with PHP
- Mobile measurement and depth link platform - Branch
- The true face of function pointer in single chip microcomputer and the operation of callback function
- 【knife-4j 快速搭建swagger】
猜你喜欢
What is Ba? How about Ba? What is the relationship between Ba and Bi?
Docker部署Mysql8的实现步骤

What is the experience of maintaining Wanxing open source vector database
机械臂速成小指南(十):可达工作空间
Create commonly used shortcut icons at the top of the ad interface (menu bar)

2022夏每日一题(一)
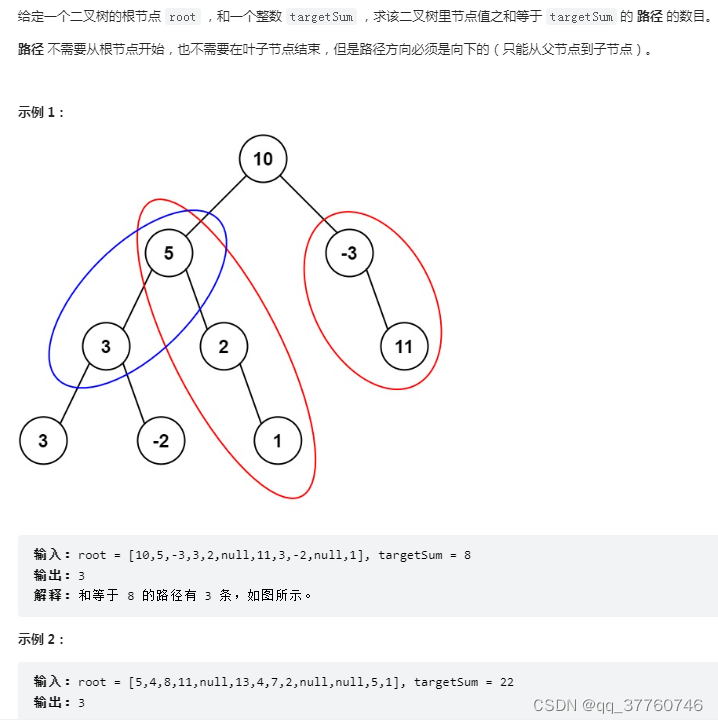
力扣------路径总和 III
【刷题记录】2. 两数相加

API data interface of A-share index component data
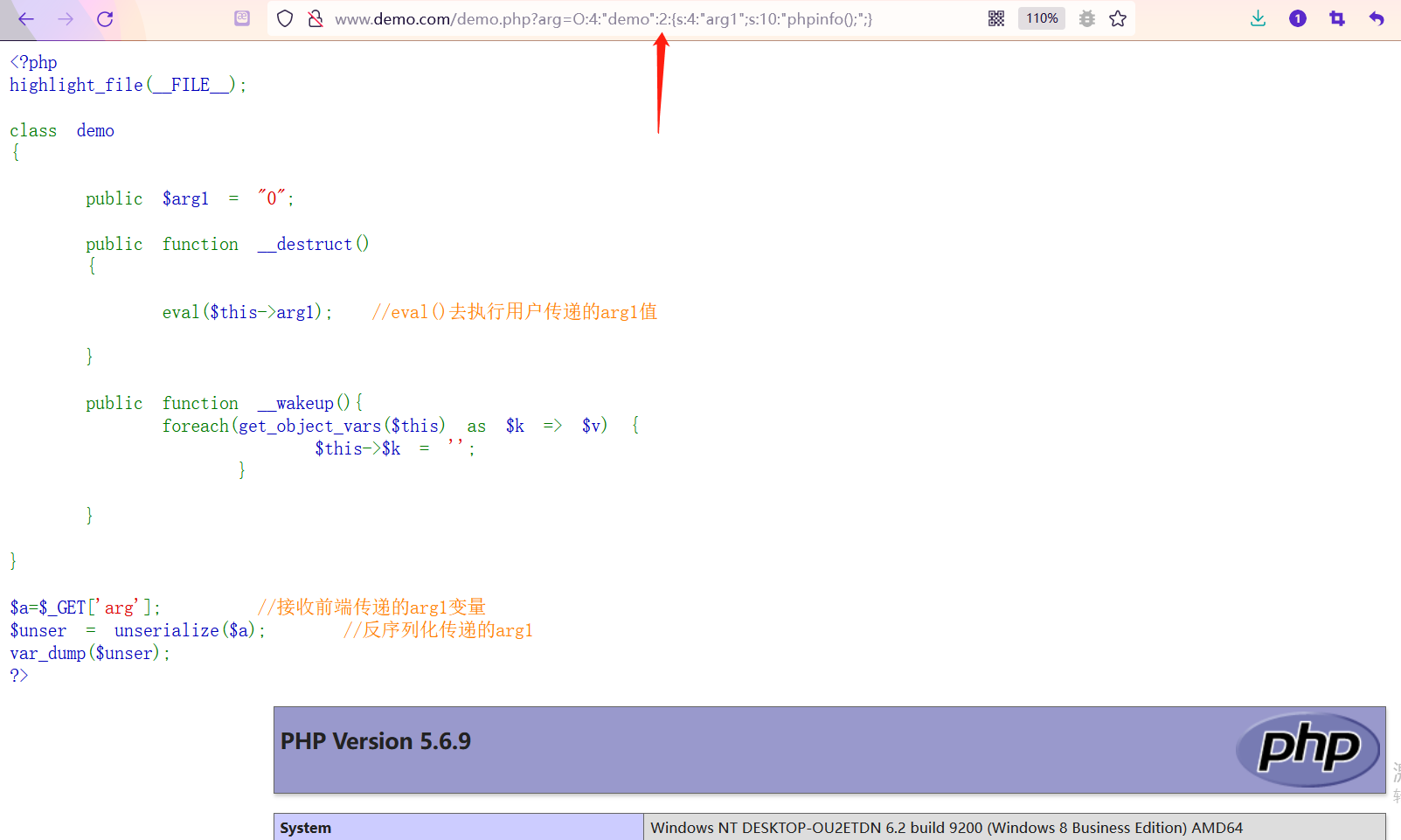
【安全攻防】序列化與反序列,你了解多少?
随机推荐
POJ培训计划2253_Frogger(最短/floyd)
Triple half circle progress bar, you can use it directly
ABAP dynamic inner table grouping cycle
Hongmi K40S root gameplay notes
接口数据安全保证的10种方式
QT item table new column name setting requirement exercise (find the number and maximum value of the array disappear)
什么是 BA ?BA怎么样?BA和BI是什么关系?
Create commonly used shortcut icons at the top of the ad interface (menu bar)
ggplot 分面的细节调整汇总
Enter the rough outline of the URL question (continuously updated)
Collection of idea gradle Lombok errors
Codeworks 5 questions per day (1700 average) - day 7
ERROR: Could not build wheels for pycocotools which use PEP 517 and cannot be installed directly
Quick completion guide of manipulator (10): accessible workspace
When QT uses qtooltip mouse to display text, the picture of the button will also be displayed and the prompt text style will be modified
AVL树插入操作与验证操作的简单实现
学习使用js把两个对象合并成一个对象的方法Object.assign()
API data interface of A-share index component data
What is Ba? How about Ba? What is the relationship between Ba and Bi?
Implementation of binary search tree